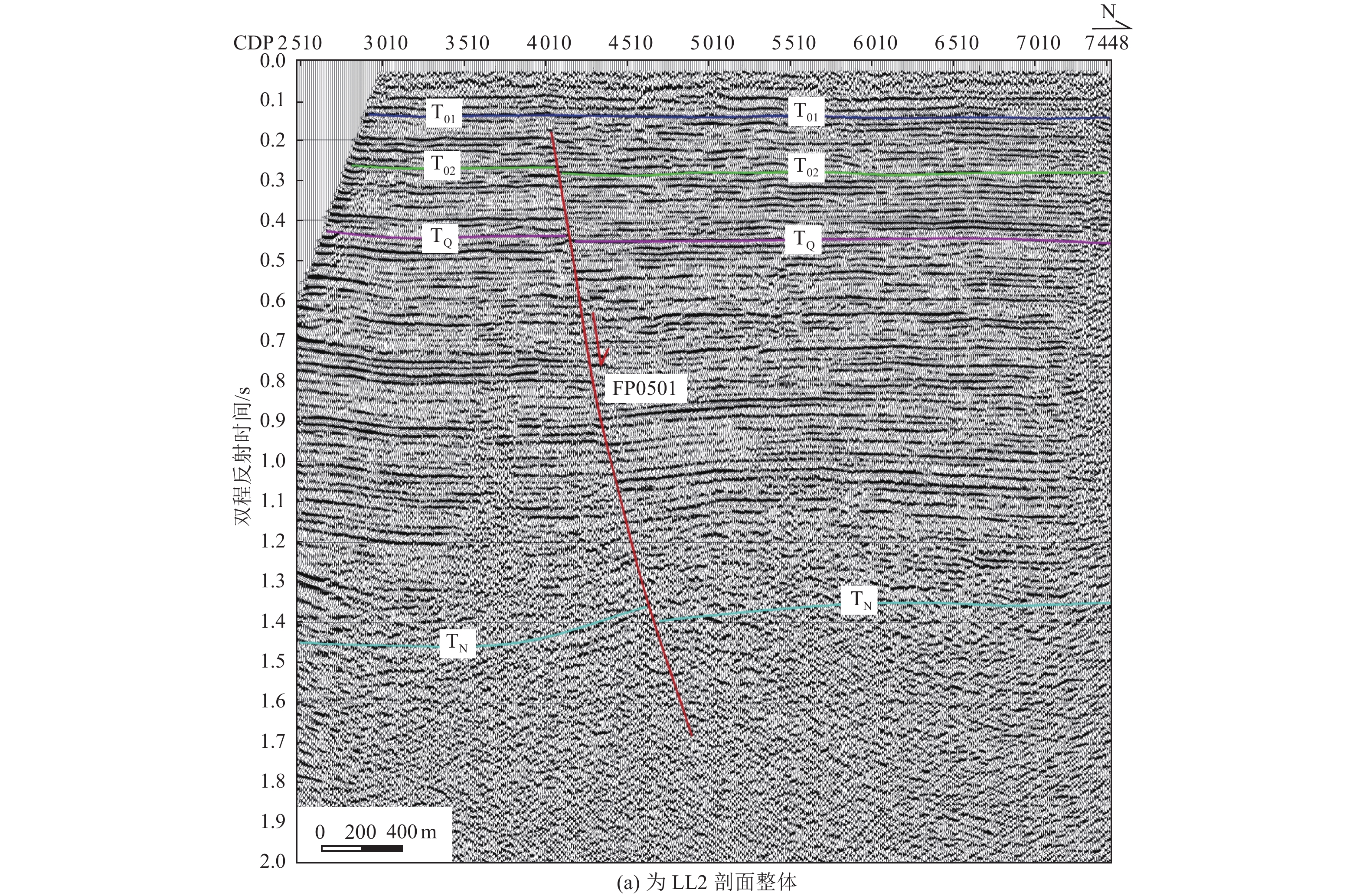
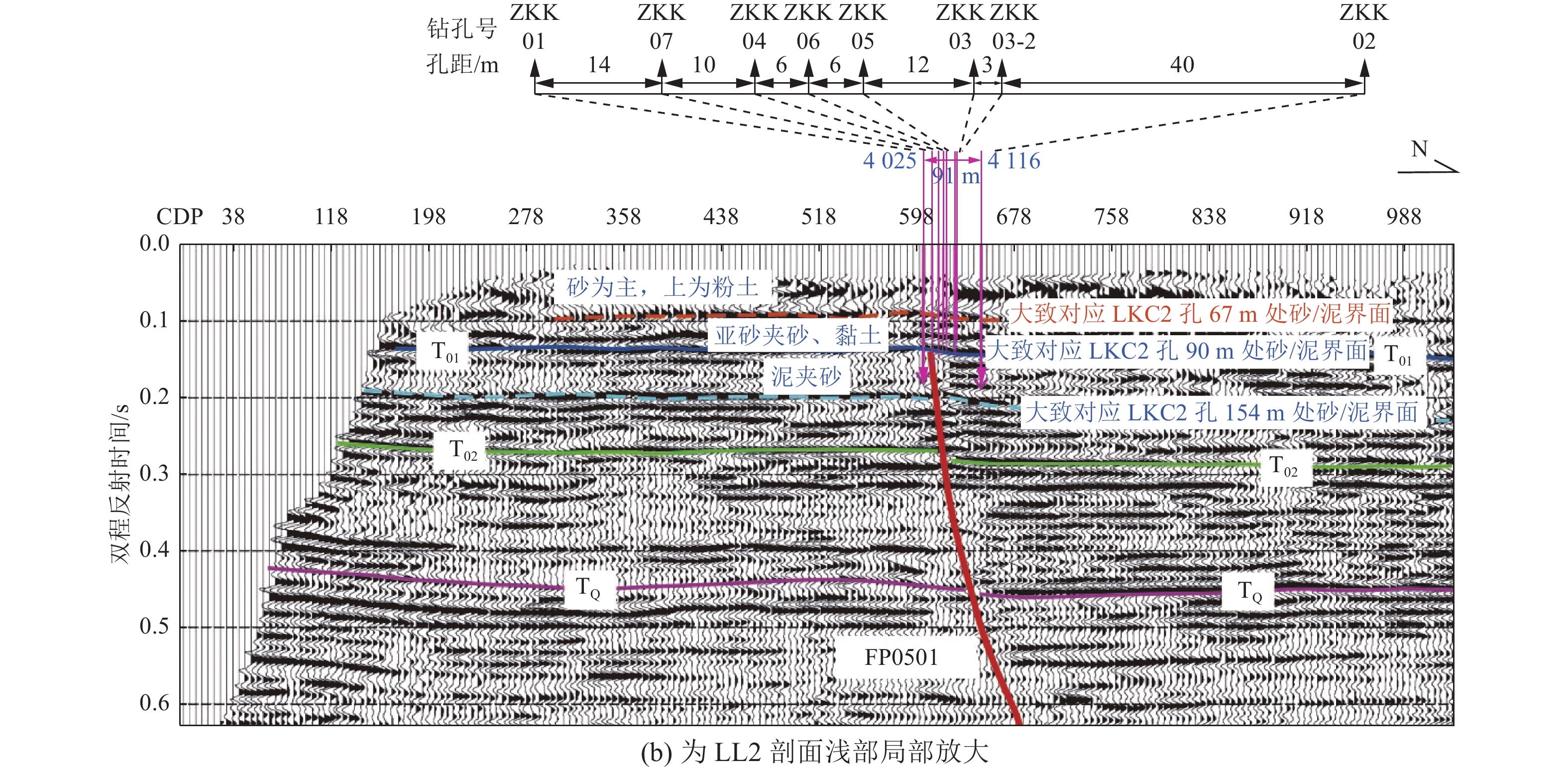
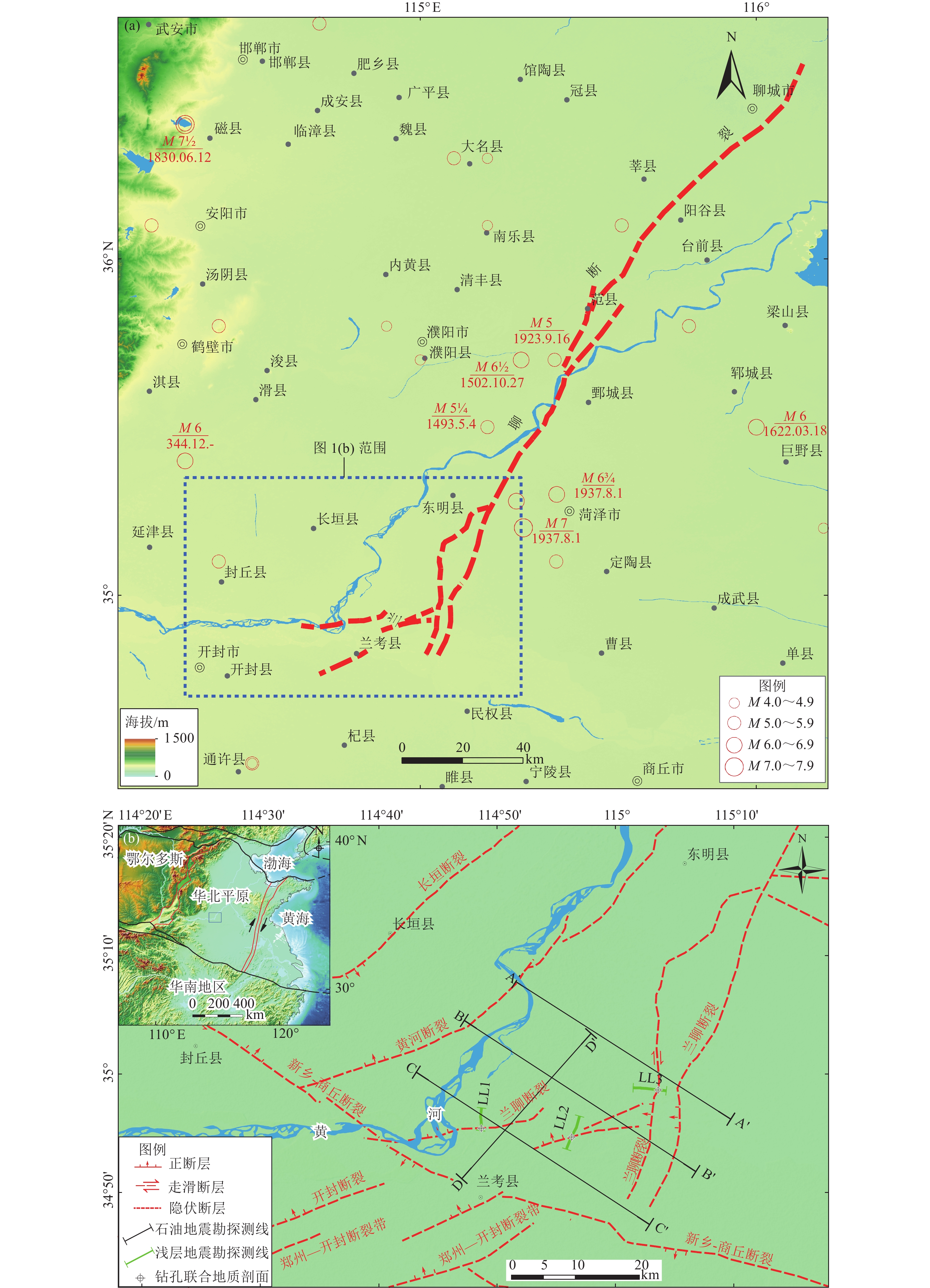
Structural Style and Latest Activity Analysis of the Southern Segment of the Lanliao Fault
-
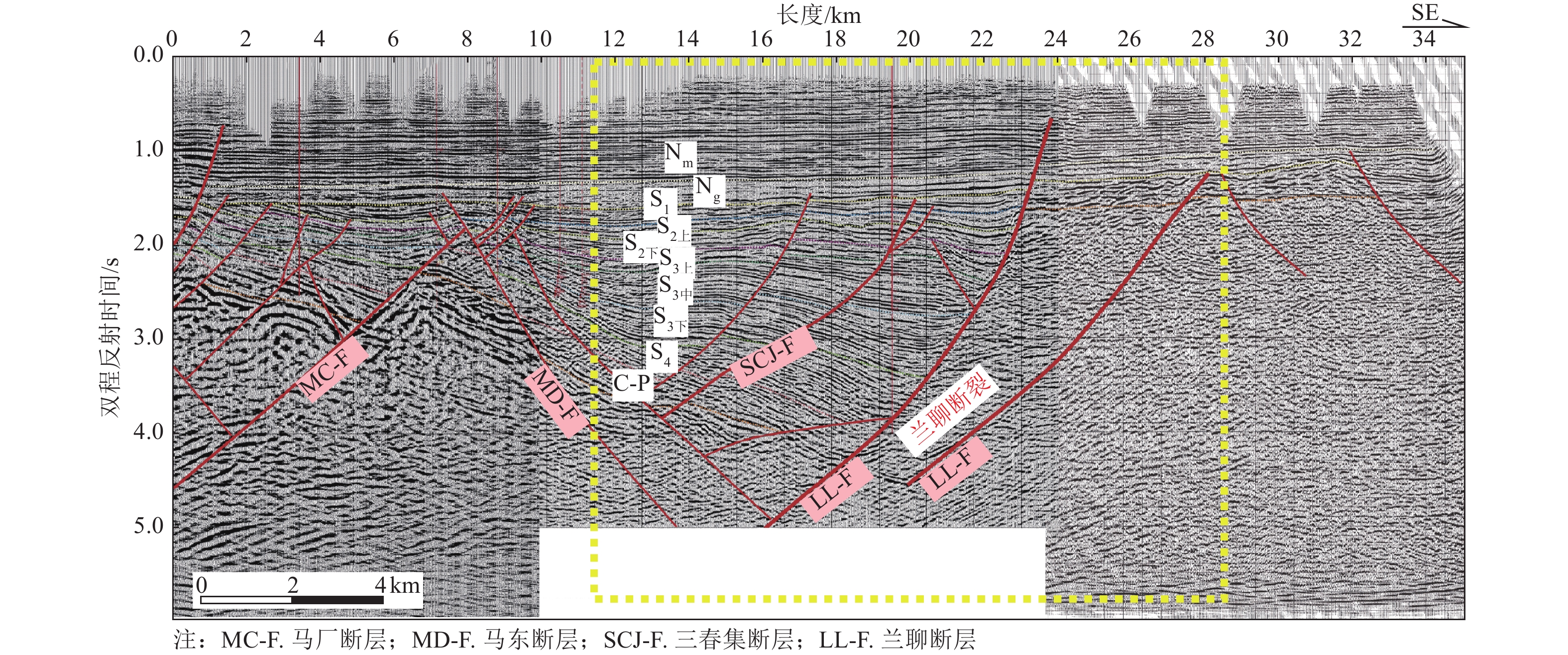
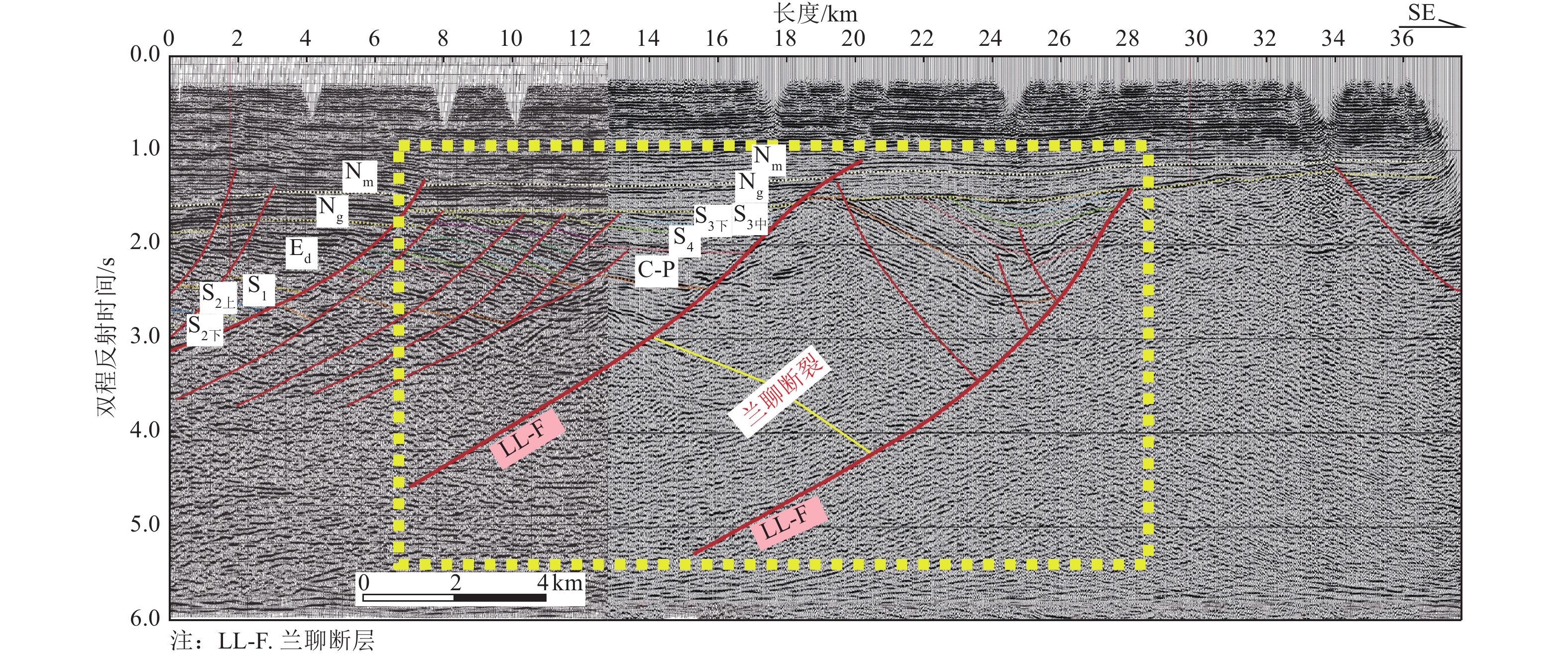
摘要: 兰聊断裂南段构造样式复杂,分段活动特征明显。已有学者针对兰聊断裂的研究,主要集中在范县—东明县一带,而兰聊断裂南段的构造样式与最新活动性研究匮乏。为此采用地震反射剖面与钻孔联合剖面探测方法,对兰聊断裂南段进行较系统地分析,认为兰聊断裂南段构造样式为伸展走滑断裂尾端“马尾扇”结构,其最新活动时代为中更新世中晚期,晚更新世以来未活动,中更新世最大滑动速率为0.061 mm/a,据此判断兰聊断裂南段为中更新世断裂。Abstract: The southern segment of the Lanliao Fault has a complex structural style and obvious features of segmental activity. Previous researches on the Lanliao Fault mainly focused on the Fanxian-Dongming county area, while the structural style and latest activity of the southern segment of the Lanliao Fault were lacking. In this study, the artificial seismic reflection profile and the composite drilling geological sections are used to systematically analyze the southern segment of the Lanliao Fault. It is considered that the structural style of the southern segment of the Lanliao Fault is an extensional imbricate fans (horsetail splay). Its latest active era is the middle and late Middle Pleistocene, and it is inactive since the Late Pleistocene. The maximum slip rate of the Middle Pleistocene is 0.061 mm/a. Based on this, it can be concluded that the southern segment of the Lanliao Fault is a Middle Pleistocene fault.
-
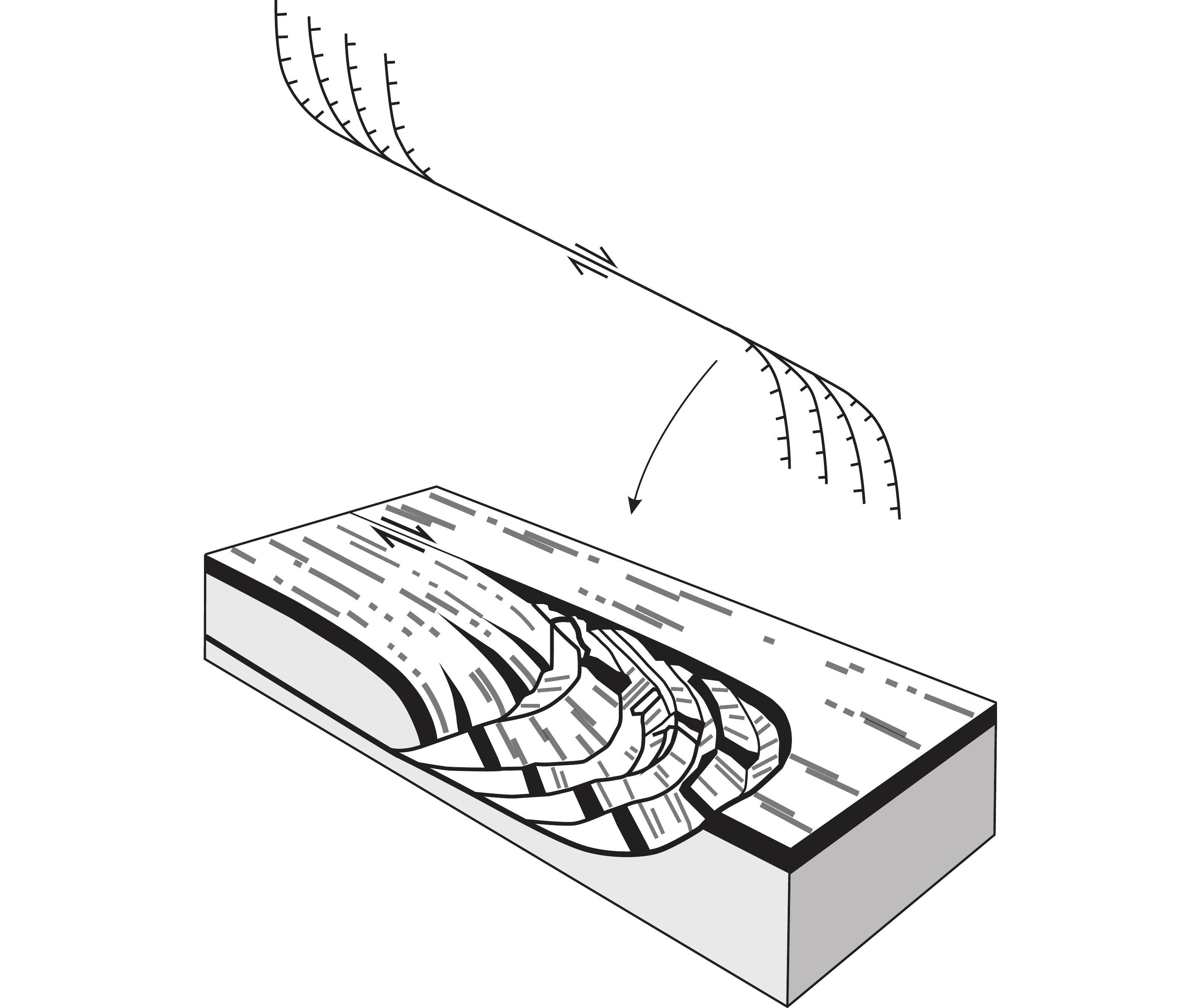
图 12 伸展叠瓦扇(马尾扇)结构示意(Cabrera等,1988)
Figure 12. Schematic diagram of extensional imbricate fans (Cabrera et al., 1988)
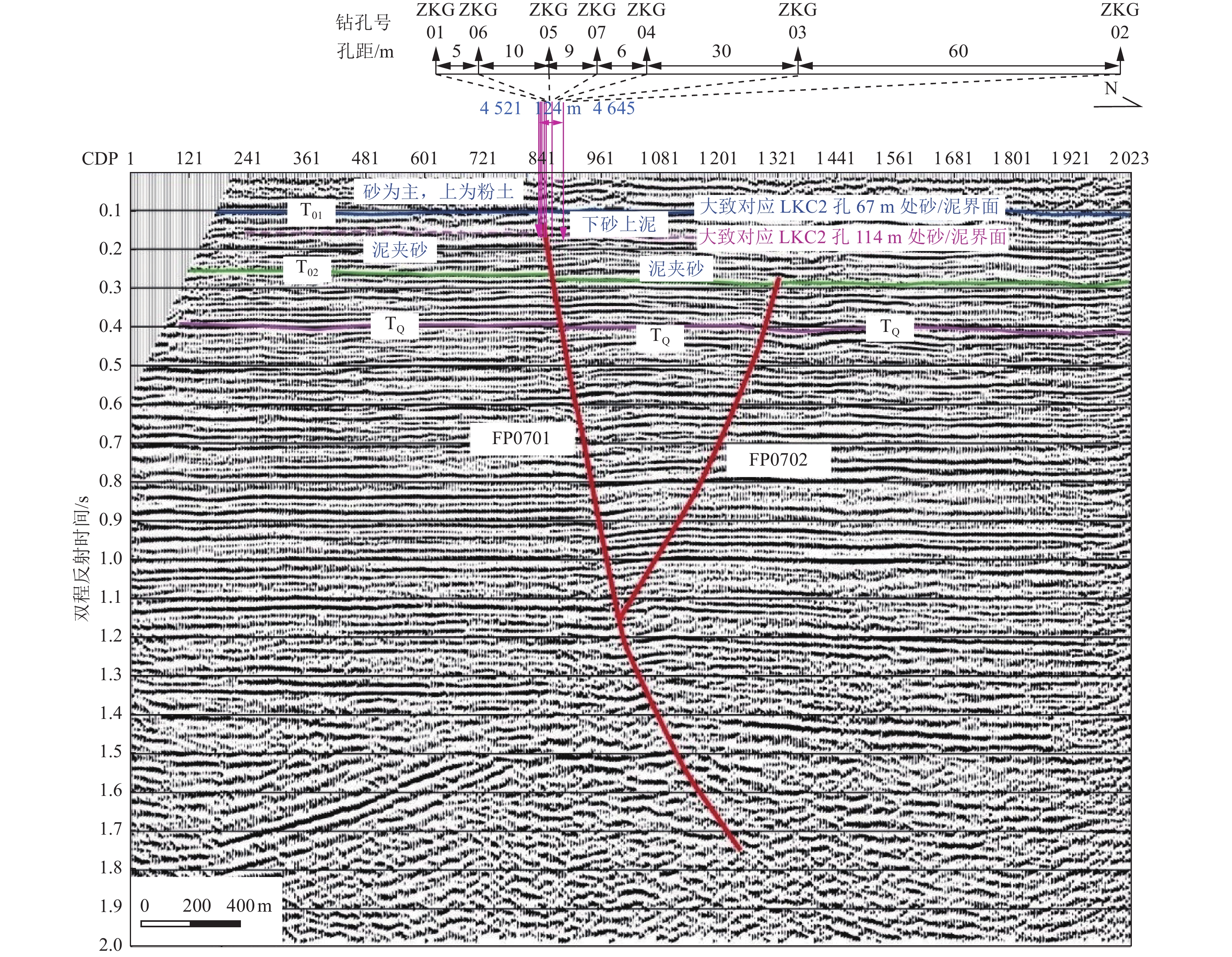
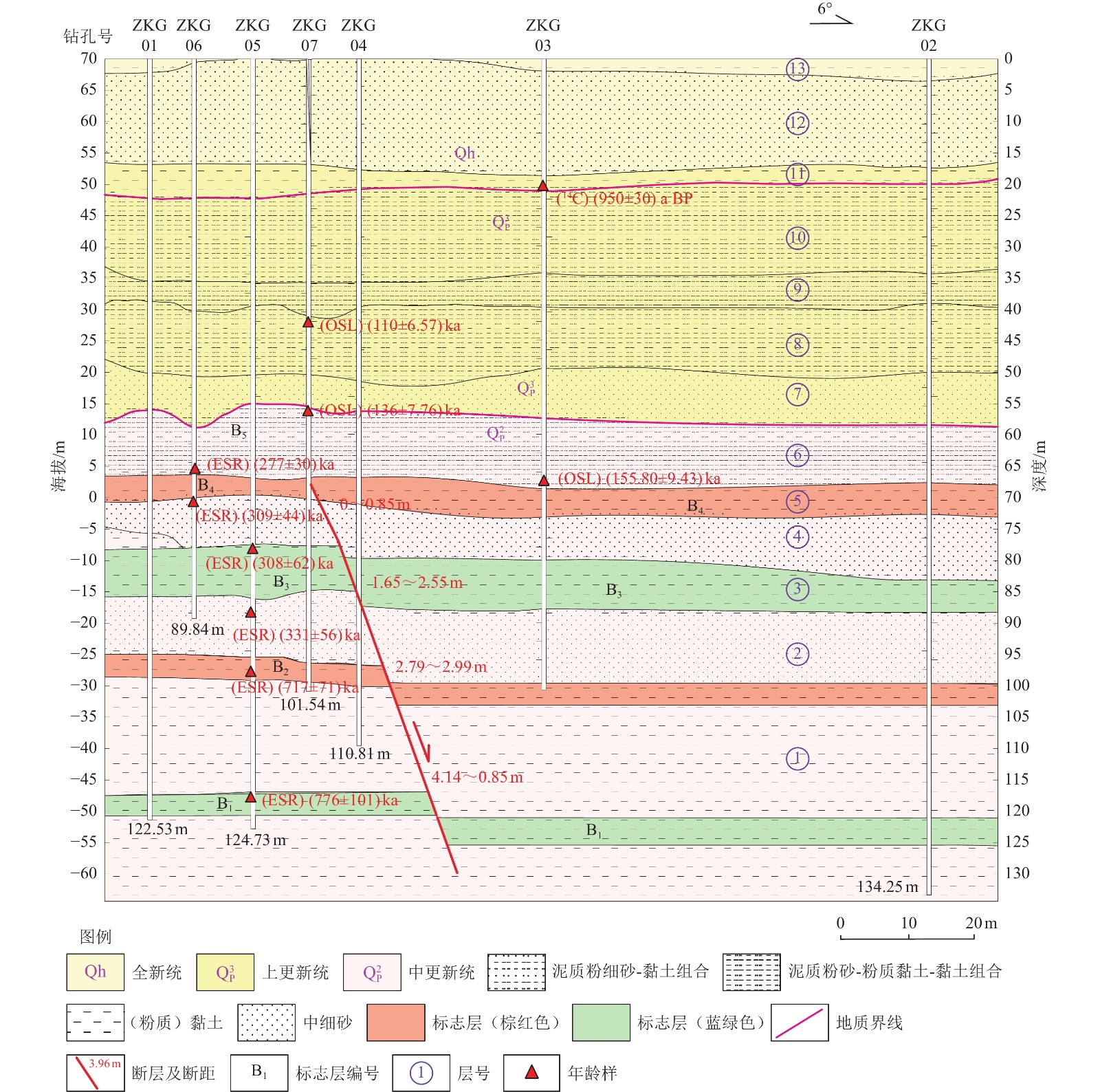
表 1 官庄钻孔联合剖面年龄样品测试结果
Table 1. Test results of age samples of the Guanzhuang composite drilling geological section
钻孔编号 样品埋深/m 地层/标志层 所处构造位置 测试类型 距今年龄/ka ZKG0314C01 20.13 层⑪(暗棕红色黏土) 上覆地层 14C 0.95±0.03 ZKG07OSL02 40.47 层⑨(棕黄色泥质粉细砂) 上覆地层 OSL 110.80±6.57 ZKG07OSL03 57.38 层⑥(棕黄色泥质粉砂) 上覆地层 OSL 136.48±7.76 ZKG06ESR01 65.79 层⑥/B5(棕黄色泥质粉砂) 上覆地层 ESR 277±30 ZKG03OSL04 69.98 层⑤/B4(棕黄色泥质粉细砂) 上覆地层 OSL 155.80±9.43 ZKG06ESR02 71.00 层④(棕黄色泥质粉细砂) 断层下盘 ESR 309±44 ZKG05ESR01 79.03 层③ (棕黄色泥质粉砂) 断层下盘 ESR 308±62 ZKG05ESR03 88.10 层②(棕色粉细砂) 断层下盘 ESR 331±56 ZKG05ESR05 98.70 层①/B2(棕黄色泥质粉砂) 断层下盘 ESR 717±71 ZKG05ESR10 119.14 层①/B1 (蓝灰色泥质粉砂) 断层下盘 ESR 776±101 表 2 官庄钻孔联合剖面主要标志层断距与沉积年龄
Table 2. Fault throw and sedimentary age table of marker layers in the Guanzhuang composite drilling geological section
编号 地层岩性 上盘(下降盘) 下盘(上升盘) 断距/m 距今年龄/ka 埋深/m 厚度/m 埋深/m 厚度/m B5 灰黄-棕黄色具锈黄染泥质粉砂与棕灰色淤泥韵律互层 顶界 65.49 1.74 顶界 65.16 2.35 未错断 266.50 底界 67.23 底界 67.51 未错断 281.00 B4 血红色黏土,中部夹1层棕黄色含中量锈黄染泥质粉砂 顶界 67.23 3.94 顶界 67.51 2.81 未错断 281.00 底界 71.17 底界 70.32 0.85 287.53 B3 下部为蓝灰色黏土、上部为棕红-棕色黏土 顶界 80.69 7.19 顶界 79.04 6.29 1.65 308.03 底界 87.88 底界 85.33 2.55 324.15 B2 下部为蓝灰色黏土,中、上部为棕红色黏土夹棕黄色蓝灰染泥质粉砂 顶界 100.18 3.52 顶界 97.39 3.32 2.79 640.67 底界 103.7 底界 100.71 2.99 722.74 B1 蓝灰色黏土、棕色具蓝灰染黏土夹蓝灰色泥质粉砂 顶界 121.61 4.38 顶界 117.47 3.78 4.14 770.63 底界 125.99 底界 121.25 4.74 782.03 表 3 官庄钻孔联合剖面第四纪不同时期断层垂直位移与平均滑动速率
Table 3. Vertical displacement and average slip rate of faults in different periods in Guanzhuang section
层段 沉积年龄/ka BP 时段长/ka 各时段垂直位移/m 平均滑动速率/
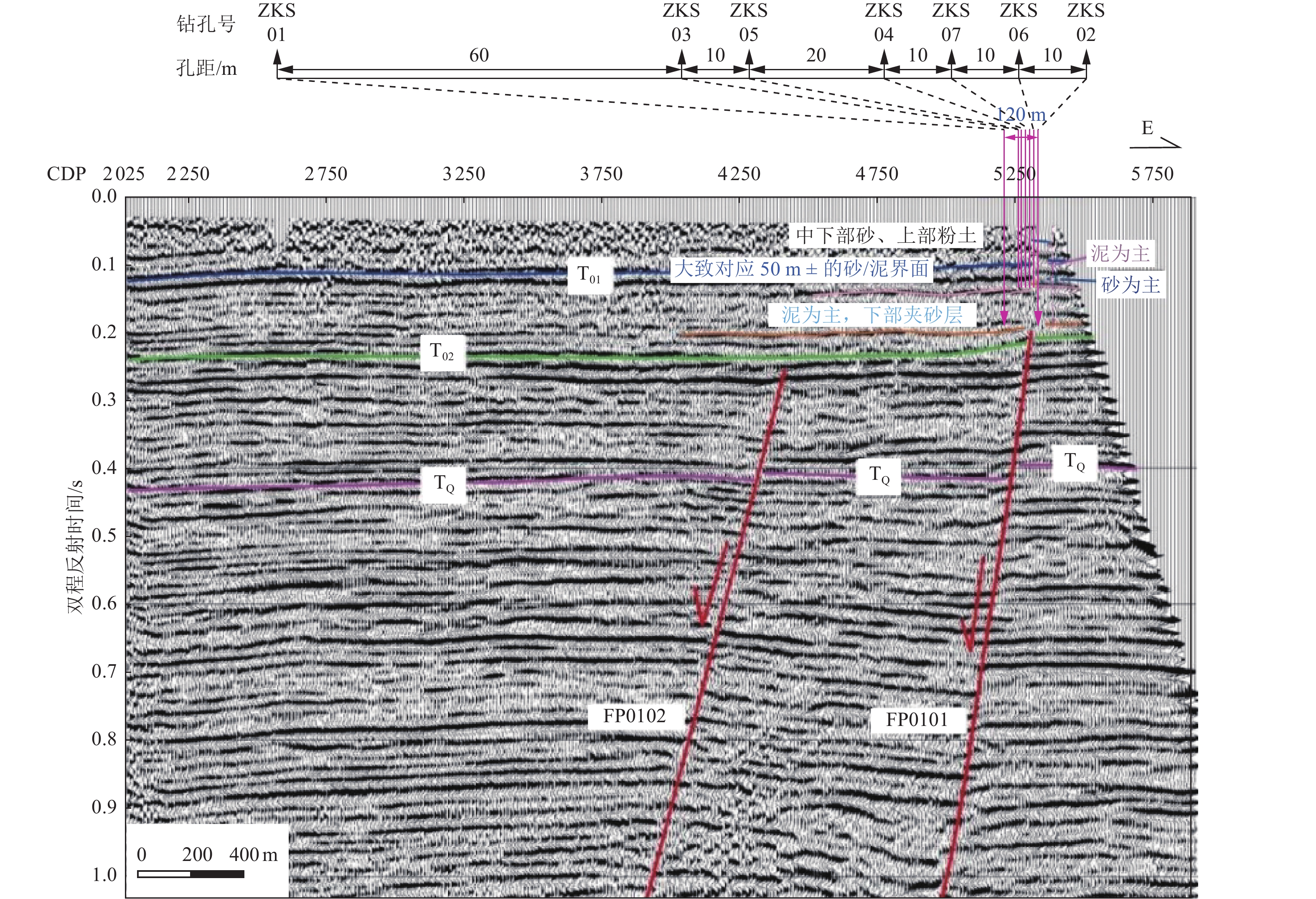
mm·a−1地质年代 B4顶界之上 281.00 281.00 0 0 中更新世末期以来 B4顶界至B3顶界 281.00~308.03 27.03 1.65 0.061 中更新世晚期 B3顶界至B2顶界 308.03~640.67 332.64 1.14 0.003 中更新世中期 B2顶界至B1底界 640.67~782.03 141.36 1.95 0.014 中更新世早期 表 4 孔庄钻孔联合剖面年龄样品测试结果
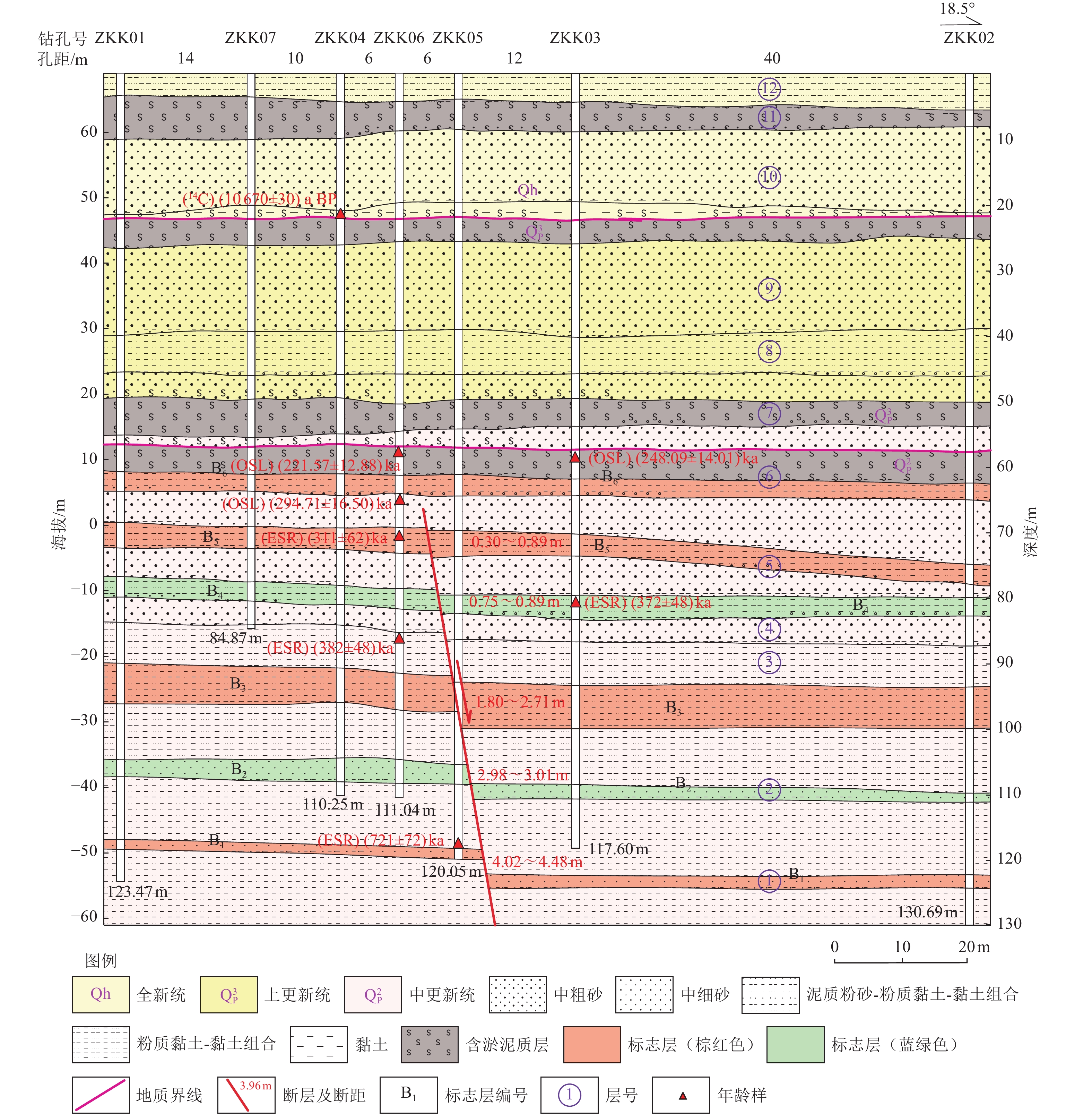
Table 4. Test results of age samples of the Kongzhuang composite drilling geological section
钻孔编号 样品埋深/m 地层/标志层 所处构造位置 测试类型 距今年龄/ka ZKK03OSL06 58.47 层⑥ 上覆地层 OSL 248.09±14.01 ZKK03ESR01 79.59 层⑤ 断层上盘 ESR 372±48 ZKK0414C01 22.11 层⑨ 上覆地层 14C 10.67±0.03 ZKK05ESR02 117.45 层① 断层下盘 ESR 721±72 ZKK06OSL03 57.78 层⑥ 上覆地层 OSL 221.57±12.88 ZKK06OSL05 66.53 层⑥ 上覆地层 OSL 294.71±16.50 ZKK06 ESR-1 70.53 层⑤ 断层下盘 ESR 311±62 ZKK06ESR03 86.95 层③ 断层下盘 ESR 382±48 表 5 孔庄钻孔联合剖面主要标志层断距及沉积年龄
Table 5. Fault throw and sedimentary age table of marker layers in the Kongzhuang composite drilling geological section
编号 地层岩性 上盘(下降盘) 下盘(上升盘) 断距/m 距今年龄/ka 埋深/m 厚度/m 埋深/m 厚度/m B6 棕红色黏土-浅绿黄色粉质黏土 顶界 62.08 1.67 顶界 62.08 1.67 0 257.4 底界 63.75 底界 63.75 0 271.3 B5 棕红色含钙核黏土-棕黄色泥质粉细砂-棕红色黏土 顶界 69.71 4.25 顶界 69.41 4.06 0.30 312.7 底界 73.96 底界 73.47 0.49 338.1 B4 棕红色含钙核粉质黏土-黄棕色泥质粉细砂 顶界 79.75 2.90 顶界 78.86 3.04 0.89 373.5 底界 82.65 底界 81.90 0.75 401.1 B3 棕黄、灰黄色细砂、泥质粉细砂-棕红、棕黄色含蓝灰染(粉质)黏土 顶界 93.49 6.49 顶界 91.69 5.58 1.80 490.1 底界 99.98 底界 97.27 2.71 540.8 B2 棕红色含蓝灰染含铁锰核黏土与棕黄色含锈黄蓝灰染泥质粉细砂互层 顶界 109.14 2.51 顶界 106.13 2.54 3.01 621.4 底界 111.65 底界 108.67 2.98 644.5 B1 棕色含蓝灰染黏土与黄棕色含蓝灰锈黄染含泥质粉细砂互层 顶界 122.47 2.06 顶界 118.45 1.60 4.02 727.3 底界 124.53 底界 120.05 4.48 737.3 表 6 孔庄钻孔联合剖面第四纪不同时期断层垂直位移及平均滑动速率
Table 6. Vertical displacement and average slip rate of faults in different periods in Kongzhuang section
层段 沉积年龄/ka BP 时段长/ka 各时段垂直位移/m 平均滑动速率/
mm·a−1地质年代 B6底界之上 271.3 271.3 0 0 中更新世晚期以来 B6底界至B5顶界 271.3~312.7 41.4 0.30 0.007 中更新世晚期 B5顶界至B1底界 312.7~737.3 424.6 4.18 0.010 中更新世早、中期 表 7 北宋庄钻孔联合剖面年龄样品测试结果
Table 7. Test results of age samples of the Beisongzhuang composite drilling geological section
钻孔编号 样品埋深/m 地层/标志层 所处构造位置 测试类型 距今年龄/ka ZKS05-OSL01 21.03 层⑯(泥质细砂) 上覆地层 OSL 23.24±1.67 ZKS06-OSL01 50.48 层⑪(黄棕色细砂) 上覆地层 OSL 122.08±9.96 ZKS06-ESR01 60.14 层⑩(黄棕色泥质粉砂) 上覆地层 ESR 328±32 ZKS02-ESR03 91.24 层⑥/B5(棕黄色泥质粉细砂) 上覆地层 ESR 451±46 ZKS07-ESR04 93.73 层⑥/B5 (黄棕色泥质粉砂) 上覆地层 ESR 588±58 ZKS07-ESR05 103.89 层④(棕黄色泥质粉砂) 断层上盘 ESR 642±64 ZKS07-ESR07 118.31 层③/B3(黄棕色泥质粉砂) 断层下盘 ESR 799±160 ZKS02-ESR05 131.81 层①(黄棕色泥质粉砂) 断层下盘 ESR 848±170 表 8 北宋庄钻孔联合剖面主要标志层断距与沉积年龄
Table 8. Fault throw and sedimentary age table of marker layers in the Beisongzhuang composite drilling geological section
编号 地层岩性 上盘(下降盘) 下盘(上升盘) 断距/m 距今年龄/ka 埋深/m 厚度/m 埋深/m 厚度/m B5 棕色细中粒砂-黄棕色泥质粉砂与棕红色黏土互层 顶界 92.55 10.03 顶界 91.88 未错断 577.31 底界 102.58 底界 102.63 未错断 634.58 B4 棕黄色泥质粉砂(或棕色中细砂)-较厚的浅棕红色黏土 顶界 104.34 2.76 顶界 103.27 2.45 1.07 646.09 底界 107.1 底界 105.72 1.38 671.18 B3 棕红色具蓝灰染黏土与黄棕色泥质粉砂互层,顶部为蓝灰色黏土 顶界 118.23 4.47 顶界 116.27 3.85 1.96 772.36 底界 122.7 底界 120.12 2.58 805.46 B2 黄棕色泥质粉砂-蓝灰色黏土 顶界 124.05 1.92 顶界 121.90 2.49 2.15 811.82 底界 125.97 底界 124.39 1.58 820.71 B1 蓝灰色泥质粉砂-棕红色黏土 顶界 130.33 1.30 顶界 127.43 1.89 2.90 832.36 底界 131.63 底界 129.32 2.31 839.11 表 9 北宋庄钻孔联合剖面第四纪不同时期断层垂直位移与平均滑动速率
Table 9. Vertical displacement and average slip rate of faults in different periods in Beisongzhuang section
层段 沉积年龄/ka BP 时段长/ka 各时段垂直位移/m 平均滑动速率/
mm·a−1地质年代 B5底界之上 634.58 634.58 0 0 中更新世中期以来 B5底界至B4底界 634.58~671.18 36.60 1.38 0.038 中更新世早中期 B4底界至B3顶界 671.18~772.36 101.18 0.58 0.006 中更新世早期 B3顶界至B1底界 772.36~839.11 66.75 0.35 0.005 早更新世晚期 -
[1] 郭秀岩, 张建伟, 袁西龙等, 2011. 聊考断裂活动性综合分析研究. 山东国土资源, 27(7): 10—13 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2011.07.007Guo X. Y. , Zhang J. W. , Yuan X. L. , et al. , 2011. Comprehensive study on activities in Liaokao fault zone. Shandong Land and Resources, 27(7): 10—13. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2011.07.007 [2] 河南省地质矿产局, 1989. 河南省区域地质志. 北京: 地质出版社, 258—312. [3] 刘凯, 海长洪, 陈燕娥等, 2014. 聊考断裂带地震活动特征研究. 防灾减灾学报, 30(1): 29—32 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8565.2014.01.006Liu K. , Hai C. H. , Chen Y. E. , et al. , 2014. Study of the characteristics of seismic activities on Liaokao Fault zone. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Reduction, 30(1): 29—32. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8565.2014.01.006 [4] 漆家福, 王德仁, 陈书平等, 2006. 兰聊断层的几何学、运动学特征对东濮凹陷构造样式的影响. 石油与天然气地质, 27(4): 451—459 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2006.04.003Qi J. F. , Wang D. R. , Chen S. P. , et al. , 2006. Impact of geometry and kinematics of Lanliao fault on structural styles in Dongpu sag. Oil & Gas Geology, 27(4): 451—459. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2006.04.003 [5] 孙小龙, 夏修军, 李源, 2018. 濮城油田注水驱油引起的地震活动特征分析. 地球物理学进展, 33(1): 104—111 doi: 10.6038/pg2018BB0075Sun X. L. , Xia X. J. , Li Y. , 2018. Characteristics of the seismic activity associated with fluid injection in Pucheng oilfield. Progress in Geophysics, 33(1): 104—111. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6038/pg2018BB0075 [6] 万天丰, 2011. 中国大地构造学. 北京: 地质出版社, 226—247. [7] 王明健, 何登发, 李文涛等, 2011. 渤海湾盆地临清坳陷东部边界断裂——兰聊断层几何学、形成演化与成因机制. 地质科学, 46(3): 775—786 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2011.03.013Wang M. J. , He D. F. , Li W. T. , et al. , 2011. Geometry, formation evolution and mechanism of Lanliao fault: The boundary of eastern Linqing depression, Bohaiwan Gulf. Chinese Journal of Geology, 46(3): 775—786. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2011.03.013 [8] 王志铄, 2017. 河南省地震构造特征. 北京: 地震出版社, 96—105. [9] 吴智平, 薛雁, 颜世永等, 2013. 渤海海域渤东地区断裂体系与盆地结构. 高校地质学报, 19(3): 463—471 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2013.03.008Wu Z. P. , Xue Y. , Yan S. Y. , et al. , 2013. The development characteristics of the fault system and basin structures of the Bodong Sag, East China. Geological Journal of China Universities, 19(3): 463—471. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2013.03.008 [10] 吴智平, 张婧, 任健等, 2016. 辽东湾坳陷东部地区走滑双重构造的发育特征及其石油地质意义. 地质学报, 90(5): 848—856 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.05.002Wu Z. P. , Zhang J. , Ren J. , et al. , 2016. Development characteristic of strike-slip duplex in the eastern part of Liaodong bay depression and its petroleum geological significance. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(5): 848—856. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.05.002 [11] 向宏发, 王学潮, 虢顺民等, 2000. 聊城-兰考隐伏断裂第四纪活动性的综合探测研究. 地震地质, 22(4): 351—359 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2000.04.003Xiang H. F. , Wang X. C. , Guo S. M. , et al. , 2000. Integrated survey and investigation on the Quaternary activity of the Liaocheng-Lankao buried fault. Seismology and Geology, 22(4): 351—359. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2000.04.003 [12] 杨源源, 姚大全, 郑海刚等, 2019. 郯庐断裂带明光—定远池河镇段的新活动性. 震灾防御技术, 14(1): 152—163 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20190115Yang Y. Y. , Yao D. Q. , Zheng H. G. , et al. , 2019. New activity of the Mingguang-Chihe segmented of the Tanlu Fault zone in Anhui province. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 14(1): 152—163. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20190115 [13] 于平, 杨冬, 杨宝俊, 2003. 华北地台聊城—兰考断裂地球物理场基本特征及其构造意义. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 33(1): 106—110Yu P. , Yang D. , Yang B. J. , 2003. The basic character of geophysical field and the tectonic significance of Liaocheng-Lankao Fault in northern China platform. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 33(1): 106—110. (in Chinese) [14] 张成科, 任青芳, 赵金仁等, 1992. 菏泽地震区地壳深部结构. 见: 1992年中国地球物理学会第八届学术年会论文集. 昆明: 中国地球物理学会, 60. [15] 张扬, 王志铄, 周栋梁等, 2018. 南华北盆地沈丘凹陷新构造时期断裂活动特征. 地震地磁观测与研究, 39(5): 30—38.Zhang Y., Wang Z. S., Zhou D. L., et al., 2018. Shenqiu depression faults movement characteristics in southern North China basin during the neotectonic period. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research, 39(5): 30—38. (in Chinese) [16] 郑建常, 吕子强, 许萍等, 2013. 濮阳小震集中区发震机理分析与讨论. 中国地震, 29(1): 11—25 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2013.01.002Zheng J. C. , Lv Z. Q. , Xu P. , et al. , 2013. Analyses and discussion on mechanism of clustered microearthquakes in Puyang, Henan Province. Earthquake Research in China, 29(1): 11—25. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2013.01.002 [17] 朱日祥, 徐义刚, 朱光等, 2012. 华北克拉通破坏. 中国科学: 地球科学, 42(8): 1135—1159Zhu R. X. , Xu Y. G. , Zhu G. , et al. , 2012. Destruction of the North China craton. Science China Earth Sciences, 42 (8): 1135—1159. (in Chinese) [18] Cabrera L. , Roca E. , Santanach P. , 1988. Basin formation at the end of a strike-slip fault: the Cerdanya Basin (eastern Pyrenees). Journal of the Geological Society, 145(2): 261—268. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.145.2.0261 [19] Jiang L. , Liu L. B. , Xu Z. P. , et al. , 2019. Crustal density structure of the southern segment of the Liaocheng-Lankao fault, China. Geodesy and Geodynamics, 10(5): 347—355. doi: 10.1016/j.geog.2019.07.001 [20] Li T. , Zhang Y. , Lu R. Q. , et al. , 2021. 3D geometry of the Lanliao Fault revealed by seismic reflection profiles: implications for earthquake clustering in the Dongpu Sag, North China. Tectonophysics, 806: 228798. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2021.228798 [21] Liu J. R. , Ren Z. K. , Zhang H. P. , et al. , 2022. Slip rates along the Laohushan fault and spatial variation in slip rate along the Haiyuan fault zone. Tectonics, 41(2): e2021TC006992. [22] Woodcock N. H. , Fischer M. , 1986. Strike-slip duplexes. Journal of Structural Geology, 8(7): 725—735. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(86)90021-0 -



 下载:
下载: