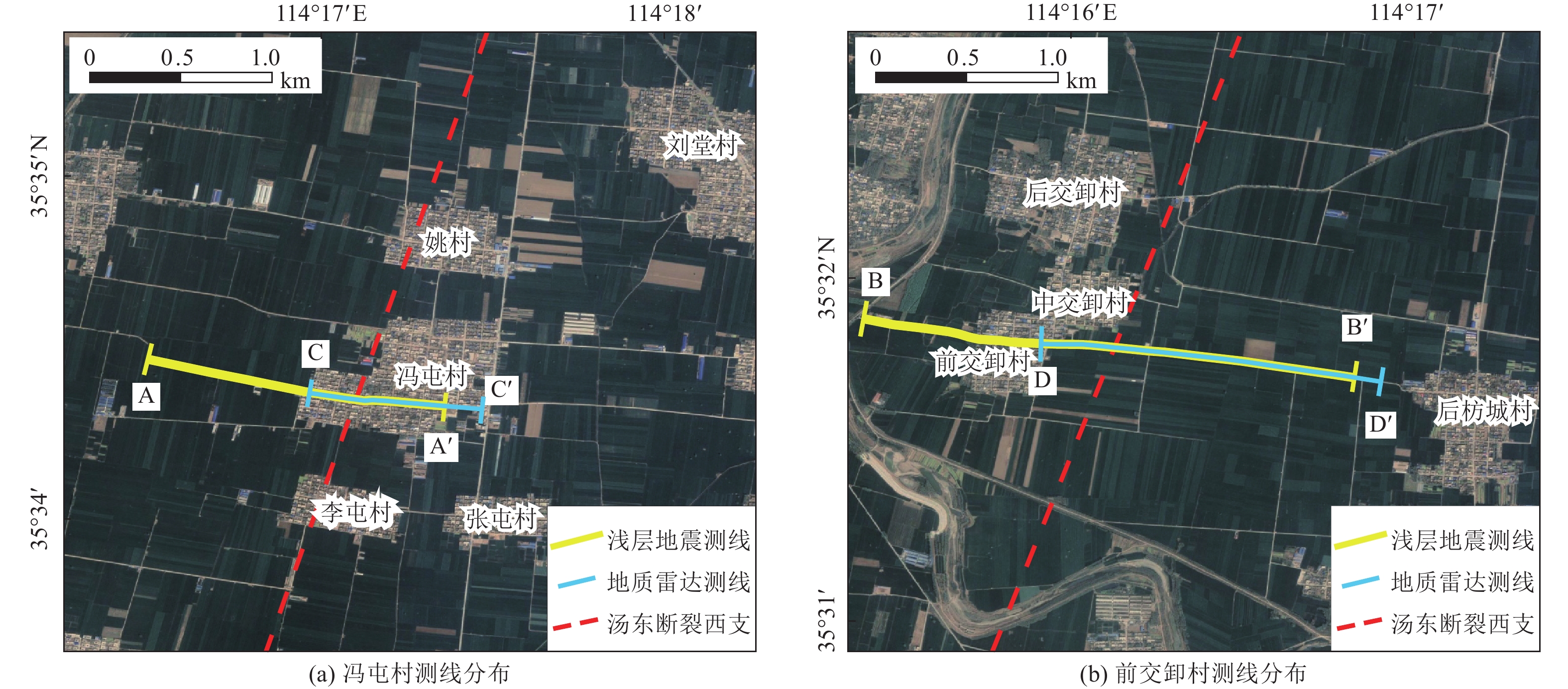
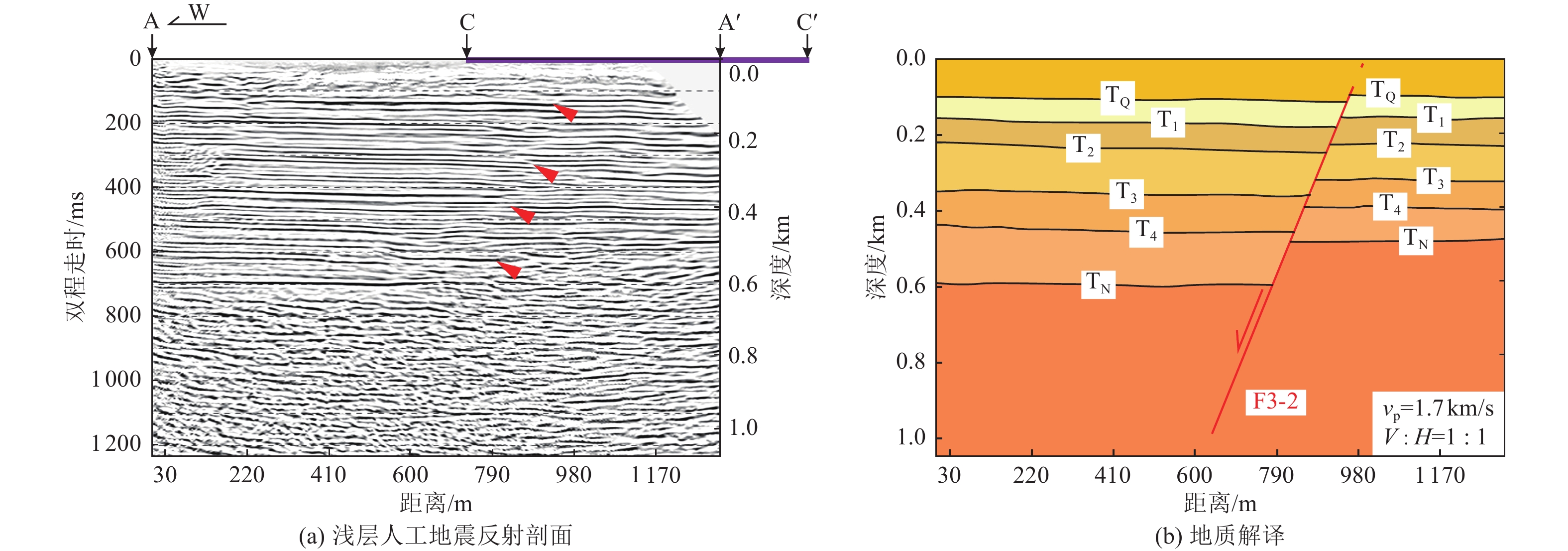
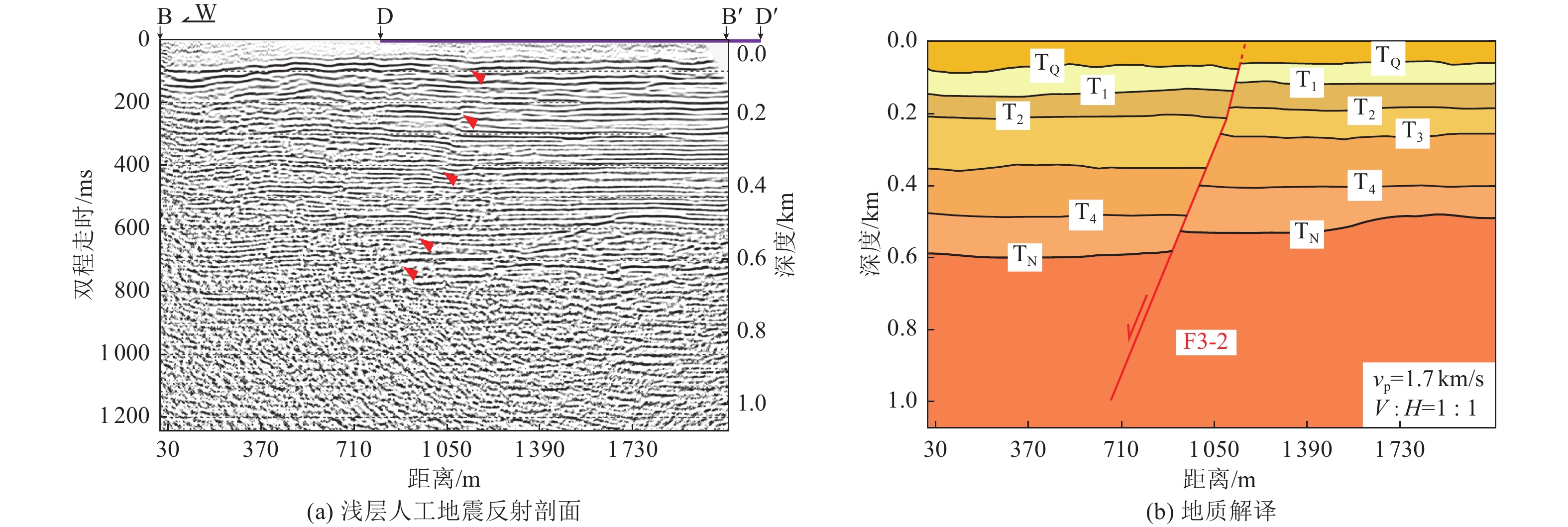
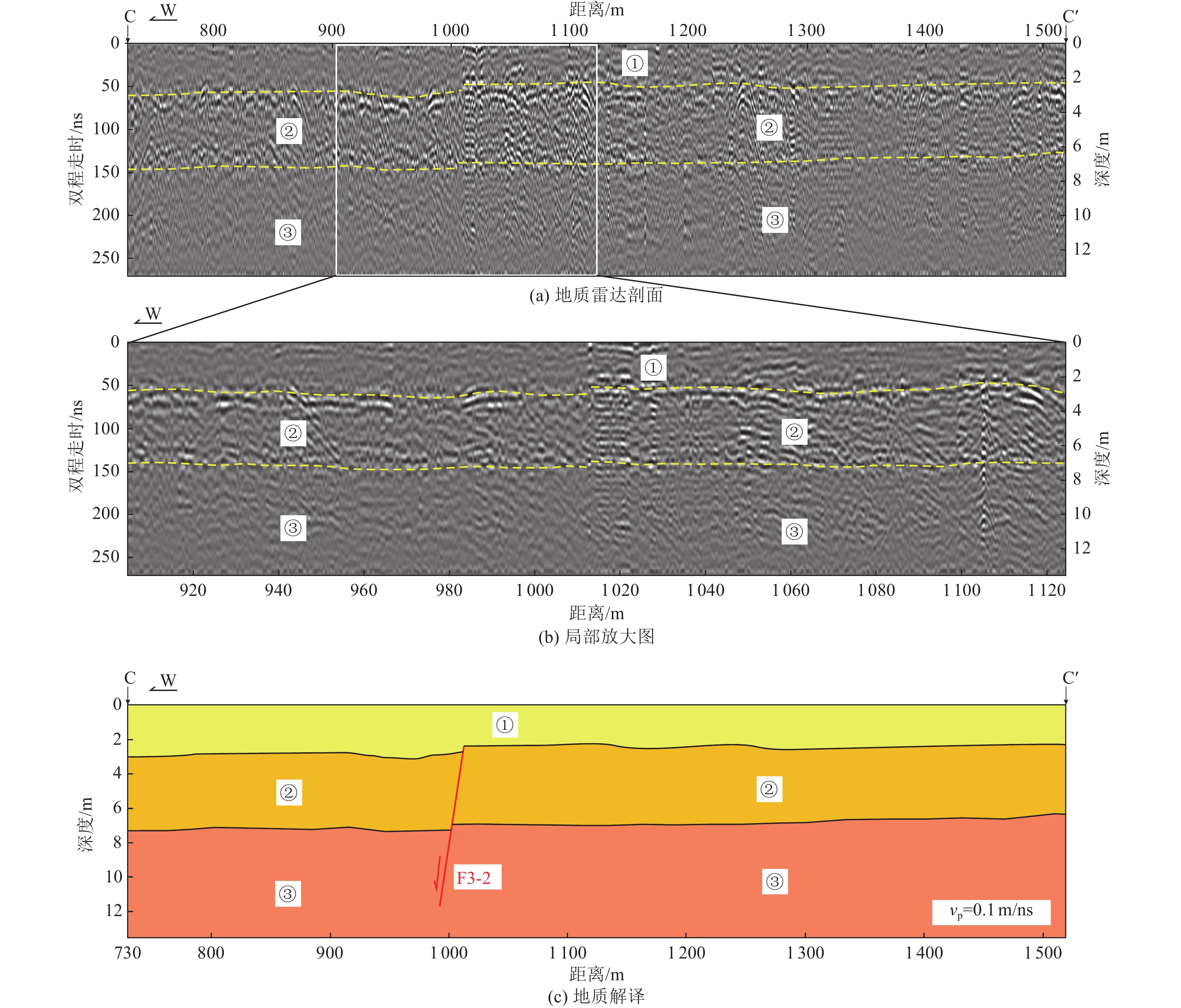
| [1] |
柴炽章, 孟广魁, 杜鹏等, 2006. 隐伏活动断层的多层次综合探测−以银川隐伏活动断层为例. 地震地质, 28(4): 536—546 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2006.04.002Chai C. Z. , Meng G. K. , Du P. , et al. , 2006. Comprehensive multi-level exploration of buried active fault: an example of Yinchuan buried active fault. Seismology and Geology, 28(4): 536—546. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2006.04.002
|
| [2] |
邓起东, 卢造勋, 杨主恩, 2007. 城市活动断层探测和断层活动性评价问题. 地震地质, 29(2): 189—200 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2007.02.001Deng Q. D. , Lu Z. X. , Yang Z. E. , 2007. Remarks on urban active faults exploration and associated activity assessment. Seismology and Geology, 29(2): 189—200. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2007.02.001
|
| [3] |
方盛明, 张先康, 刘保金等, 2002. 探测大城市活断层的地球物理方法. 地震地质, 24(4): 606—613 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.016Fang S. M. , Zhang X. K. , Liu B. J. , et al. , 2002. Geophysical methods for the exporation of urban active faults. Seismology and Geology, 24(4): 606—613. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.016
|
| [4] |
顾勤平, 康清清, 许汉刚等, 2013. 薄覆盖层地区隐伏断层及其上断点探测的地震方法技术−以废黄河断层为例. 地球物理学报, 56(5): 1609—1618 doi: 10.6038/cjg20130518Gu Q. P. , Kang Q. Q. , Xu H. G. , et al. , 2013. Seismic exploration methods for buried faults and its up-breakpoint in thin sediment areas−an example of the Feihuanghe fault. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(5): 1609—1618. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6038/cjg20130518
|
| [5] |
顾勤平, 许汉刚, 赵启光, 2015. 厚覆盖层地区隐伏活断层探测的地震方法技术——以桥北镇—宿迁断层为例. 物探与化探, 39(2): 408—415Gu Q. P. , Xu H. G. , Zhao Q. G. , 2015. The seismic exploration method for buried active faults in thick sediment area: a case study of Qiaobei-Suqian fault. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 39(2): 408—415. (in Chinese)
|
| [6] |
韩慕康, 赵景珍, 1980. 河南汤阴地堑的地震地质特征与地震危险性. 地震地质, 2(4): 47—58Han M. K. , Zhao J. Z. , 1980. Seismotectonic characteristics of Tangyin graben, Henan Province, and its earthquake risk. Seismology and Geology, 2(4): 47—58. (in Chinese)
|
| [7] |
何正勤, 叶太兰, 丁志峰等, 2001. 城市活断层探测中的浅层地震勘探方法. 国际地震动态, (3): 1—6 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4975.2001.03.001He Z. Q. , Ye T. L. , Ding Z. F. , et al. , 2001. The application of shallow seismic prospecting methods to active fault dectection in cities. Recent Developments in World Seismology, (3): 1—6. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4975.2001.03.001
|
| [8] |
李建军, 张军龙, 2015. 探地雷达在探测隐伏活动断层中的应用. 地震, 35(4): 83—89 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2015.04.009Li J. J. , Zhang J. L. , 2015. Application of GPR in surveying underlied active faults. Earthquake, 35(4): 83—89. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2015.04.009
|
| [9] |
李自红, 刘保金, 袁洪克等, 2014. 临汾盆地地壳精细结构和构造−地震反射剖面结果. 地球物理学报, 57(5): 1487—1497 doi: 10.6038/cjg20140513Li Z. H. , Liu B. J. , Yuan H. K. , et al. , 2014. Fine crustal structure and tectonics of Linfen Basin−from the results of seismic reflection profile. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(5): 1487—1497. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6038/cjg20140513
|
| [10] |
刘保金, 张先康, 方盛明等, 2002. 城市活断层探测的高分辨率浅层地震数据采集技术. 地震地质, 24(4): 524—532 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.006Liu B. J. , Zhang X. K. , Fang S. M. , et al. , 2002. Acquisition technique of high-resolution shallow seismic data for surveying of urban active faults. Seismology and Geology, 24(4): 524—532. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.006
|
| [11] |
刘保金, 柴炽章, 酆少英等, 2008. 第四纪沉积区断层及其上断点探测的地震方法技术−以银川隐伏活动断层为例. 地球物理学报, 51(5): 1475—1483 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2008.05.021Liu B. J. , Chai C. Z. , Feng S. Y. , et al. , 2008. Seismic exploration method for buried fault and its up-breakpoint in Quaternary sediment area−an example of Yinchuan buried active fault. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 51(5): 1475—1483. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2008.05.021
|
| [12] |
刘保金, 何宏林, 石金虎等, 2012. 太行山东缘汤阴地堑地壳结构和活动断裂探测. 地球物理学报, 55(10): 3266—3276 doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.10.009Liu B. J. , He H. L. , Shi J. H. , et al. , 2012. Crustal structure and active faults of the Tangyin graben in the eastern margin of Taihang Mountain. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 55(10): 3266—3276. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.10.009
|
| [13] |
茹瑞典, 张金才, 戚筱俊, 1996. 地质雷达探测技术的应用研究. 工程地质学报, 4(2): 51—56Ru R. D. , Zhang J. C. , Qi X. J. , 1996. Study on application of ground penetrating radar survey technique. Journal of Engineering Geology, 4(2): 51—56. (in Chinese)
|
| [14] |
苏鹏, 田勤俭, 李文巧等, 2015. 地质雷达在活动断裂研究中的应用. 震灾防御技术, 10(2): 281—290 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20150208Su P. , Tian Q. J. , Li W. Q. , et al. , 2015. Application of ground penetrating radar in the study of active faults. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 10(2): 281—290. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20150208
|
| [15] |
苏鹏, 鲁人齐, 徐芳等, 2021. 地质雷达在城市活动断层探测中的应用−以鹤壁市汤东断裂为例. 地质论评, 67(S1): 40—42Su P. , Lu R. Q. , Xu F. , et al. , 2021. Application of ground penetration radar in active fault detection in the urban area−taking Tangdong fault in Hebi as an example. Geological Review, 67(S1): 40—42. (in Chinese)
|
| [16] |
许汉刚, 范小平, 冉勇康等, 2016. 郯庐断裂带宿迁段F5断裂浅层地震勘探新证据. 地震地质, 38(1): 31—43 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.01.003Xu H. G. , Fan X. P. , Ran Y. K. , et al. , 2016. New evidences of the Holocene fault in Suqian segment of the Tanlu fault zone discovered by shallow seismic exploration method. Seismology and Geology, 38(1): 31—43. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.01.003
|
| [17] |
徐杰, 计凤桔, 2015. 渤海湾盆地构造及其演化. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
| [18] |
张迪, 李家存, 吴中海等, 2016. 地质雷达在活动断裂探测中的应用与进展. 地质力学学报, 22(3): 733—746 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.03.027Zhang D. , Li J. C. , Wu Z. H. , et al. , 2016. Application and progress of ground penetrating radar in active fault detection. Journal of Geomechanics, 22(3): 733—746. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.03.027
|
| [19] |
周绪文, 1989. 反射波地震勘探方法. 北京: 石油工业出版社.
|
| [20] |
朱日祥, 徐义刚, 朱光等, 2012. 华北克拉通破坏. 中国科学: 地球科学, 42(8): 1135—1159. Zhu R. X. , Xu Y. G. , Zhu G. , et al. , 2012. Destruction of the North China craton. Science China Earth Sciences, 55(10): 1565—1587.
|
| [21] |
Fan L. G. , Meng Q. R. , Wu G. L. , et al. , 2019. Paleogene crustal extension in the eastern segment of the NE Tibetan Plateau. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 514: 62—74. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2019.02.036
|
| [22] |
Lei X. Q. , Ren J. J, Xu X. W. , et al. , 2022. Application of high-power ground-penetrating radar antennas with different frequencies to quickly locate the upper breakpoint of active buried faults in an urban area in the Datong basin (northern China). Journal of Applied Geophysics, 196: 104515. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2021.104515
|
| [23] |
Neal A. , 2004. Ground-penetrating radar and its use in sedimentology: principles, problems and progress. Earth-Science Reviews, 66(3—4): 261—330. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2004.01.004
|
| [24] |
Su P. , He H. L. , Tan X. B. , et al. , 2021. Initiation and evolution of the Shanxi rift system in North China: evidence from low-temperature thermochronology in a plate reconstruction framework. Tectonics, 40(3): e2020TC006298.
|
| [25] |
Wang W. T. , Kirby E. , Zhang P. Z. , et al. , 2013. Tertiary basin evolution along the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau: Evidence for basin formation during Oligocene transtension. GSA Bulletin, 125(3—4): 377—400. doi: 10.1130/B30611.1
|
| [26] |
Xu X. W. , Ma X. Y. , 1992. Geodynamics of the Shanxi rift system, China. Tectonophysics, 208(1—3): 325—340. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(92)90353-8
|
| [27] |
Zhang Y. G. , Zheng W. J. , Wang Y. J. , et al. , 2018. Contemporary deformation of the north china plain from global positioning system data. Geophysical Research Letters, 45(4): 1851—1859. doi: 10.1002/2017GL076599
|
| [28] |
Zhang Y. Q. , Mercier J. L. , Vergély P. , 1998. Extension in the graben systems around the Ordos (China), and its contribution to the extrusion tectonics of South China with respect to Gobi-Mongolia. Tectonophysics, 285(1—2): 41—75. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(97)00170-4
|




 下载:
下载: