Quaternary Activity Characteristic of the Kaifeng Fault
-
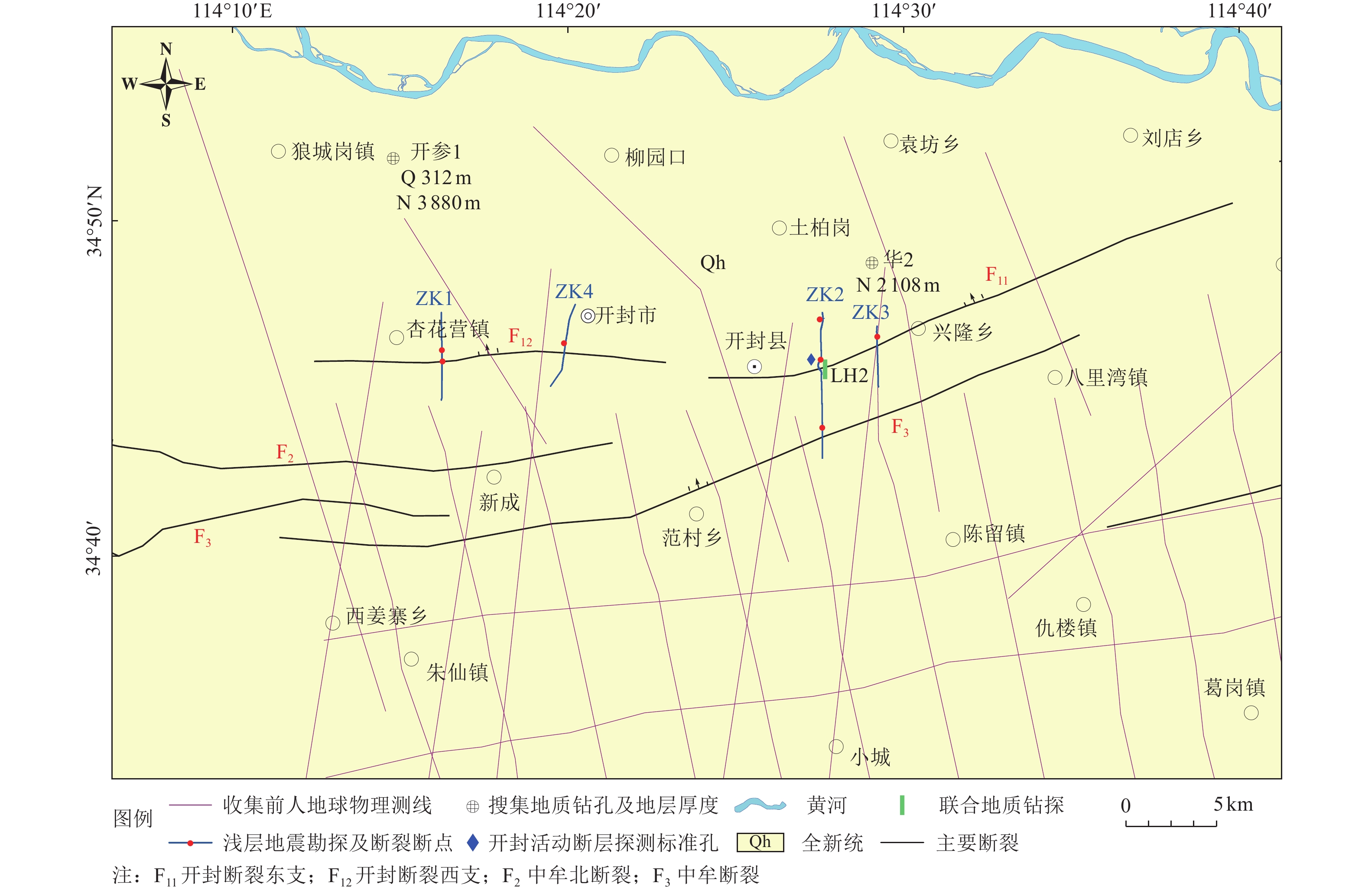
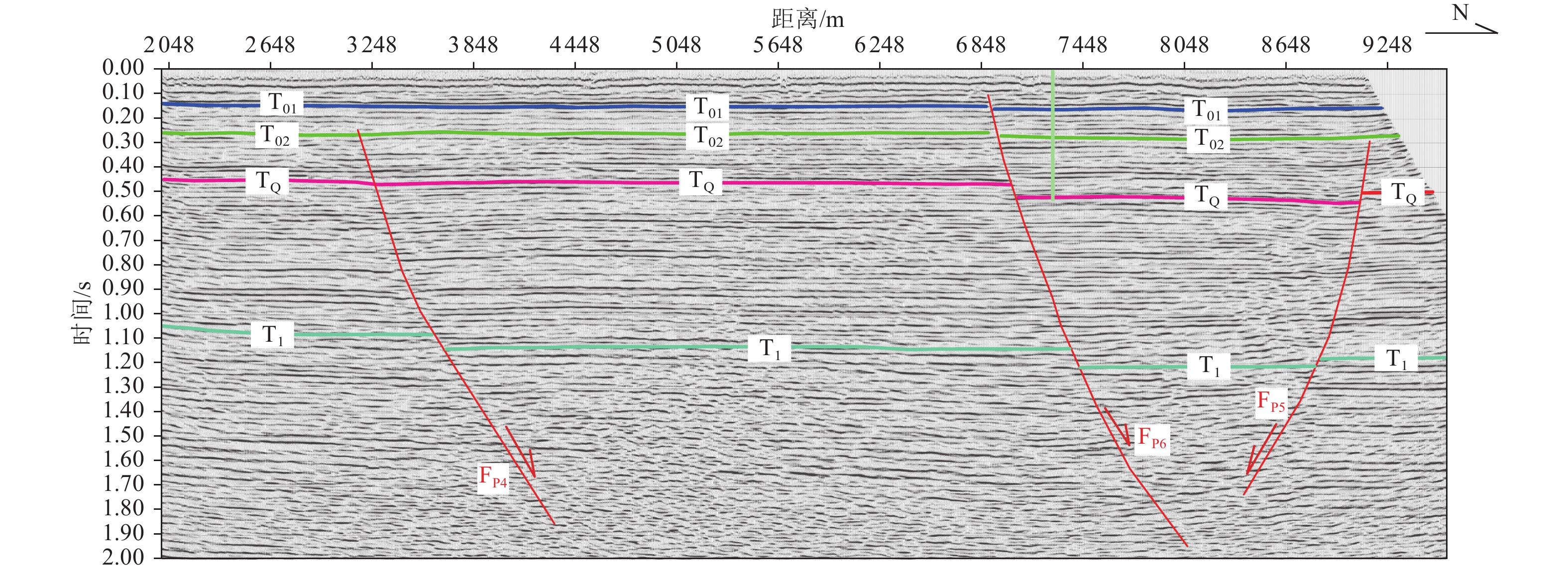
摘要: 开封断裂是郑州-开封断裂带的重要组成部分,也是黄河中下游平原的一条重要控制性断裂。利用浅层地震勘探发现,开封断裂为总体走向EW,倾向N的正断层;断裂分为东、西2支,断裂活动性具有明显的分段特征,东支活动性较西支强。钻孔联合剖面揭示开封断裂东支断裂上断点埋深27~35 m,根据地层年代学结果,其最新活动时间为晚更新世。研究成果为开封市城乡规划、重大工程选址和地震区划工作提供了重要的基础数据。Abstract: Kaifeng fault is an important segment of Zhengzhou-Kaifeng fault zone,and it is also an important controlling fault in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River Plain. It is found that Kaifeng fault is a normal fault with overall strike EW and dip N by using shallow seismic exploration. The fault can be divided into East and West branches, and has obvious differentiated segmented characteristics. The activity of the East branch is stronger than that of the West Branch. The borehole joint geological profile reveals that the buried depth of the breakpoint on the fault is between 27 m and 35 m. Combining with the chronological results, the latest age of activity is the late Pleistocene. The results can provide important basic data for Kaifeng urban and rural planning, major project site selection and seismic zoning.1) 2河南省平原第四纪地质图及地质图说明书(1/50万). 郑州:河南省地质局. 开封市活动断层探测与地震危险性评价. 郑州:河南省地震局.
-
表 1 观测系统参数表
Table 1. Parameter table of the observation system
线号 道距/m 炮距/m 偏移距/m 接收道数 覆盖次数 采样间隔/ms 前放增益/db 记录时间/s 震源吨位/t ZK1 5 20 0 240 30 0.5 12 3 26 ZK2 5 20 0 260 32 0.5 12 3 26 ZK3 4 16 0 320 40 0.5 12 2 9 ZK4 5 20 0 260 32 0.5 12 3 26 表 2 勘察断点参数表
Table 2. Parameter table of the upper offset point of fault
资料来源 探测断裂 上断点埋深 断距特征 断裂活动性判断 收集石油测线 开封断裂 浅层数据被切除,
可识别最大埋深300 m新近系底部断距150 m PreQ 古近系底界 2 000 m ZK1 开封断裂西支 95 m 3~5 m $ {\mathrm{Q}}_{\mathrm{P}}^{2} $ ZK4 开封断裂西支 139 m 5~8 m $ {\mathrm{Q}}_{\mathrm{P}}^{2} $ ZK2 开封断裂东支 50 m 2~3 m $ {\mathrm{Q}}_{\mathrm{P}}^{3} $ ZK3 开封断裂东支 45~50 m 1~3 m $ {\mathrm{Q}}_{\mathrm{P}}^{3} $ 表 3 钻孔联合剖面主要地层层断距
Table 3. Respective displacement of the mark layer in composite geological profile
主要标志层 地层岩性 下盘埋深/m 上盘埋深/m 断距/m 地层①泥炭层 灰黑色泥碳层 Z2:15.29~15.95
Z4:15.45~15.74
Z8:15.81~16.21
Z9:15.67~16.42Z1:15.37~16.55
Z7:15.49~15.81
Z5:15.97~16.04
Z10:15.47~15.81— 地层②底界面 上部为棕灰、棕黄色细砂,
下部棕灰、棕黄色黏土-粉土,
界线明显Z1:35.29
Z6:35.53
Z8:35.84
Z9:35.74
Z11:35.23
Z12:35.84Z1:36.36
Z3:36.78
Z5:36.55
Z7:37.42
Z10:36.990.75 地层③泥炭夹层 黑色泥炭层 Z2:40.84~41.47
Z4:40.20~40.77
Z6:39.92~40.37
Z8:40.93~42.35
Z9:40.14~42.51
Z11:40.19~40.34Z5:42.23~42.38
Z7:42.03~42.24
Z10:42.96~43.261 地层③底界面 上部为黄棕色、灰棕色粉砂,下部为深棕色、黄棕色粉质黏土,界线清晰 Z2:50.20
Z3:50.81
Z4:50.26
Z11:50.74Z7:52.24
Z5:51.80
Z10:51.971.7 地层④底界面 上部深棕色粉砂,下部为深棕色黏土分界面,界线清晰 Z2:60.37
Z4:60.51
Z9:62.48Z5:65.58
Z7:65.61
Z1:66.443.1 地层⑤底界面 上部为棕黄色、浅棕色粉砂
下部深棕色黏土层,界线清晰Z2:77.48
Z3:79.20
Z4:78.27Z1:88.64
Z5:86.987.1 -
[1] 柴炽章, 孟广魁, 杜鹏等, 2006. 隐伏活动断层的多层次综合探测——以银川隐伏活动断层为例. 地震地质, 28(4): 536—546 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2006.04.002Chai C. Z. , Meng G. K. , Du P. , et al. , 2006. Comprehensive multi-level exploration of buried active fault: an example of Yinchuan buried active fault. Seismology and Geology, 28(4): 536—546. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2006.04.002 [2] 邓起东, 徐锡伟, 张先康等, 2003. 城市活动断裂探测的方法和技术. 地学前缘, 10(1): 93—104 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.01.012Deng Q. D. , Xu X. W. , Zhang X. K. , et al. , 2003. Methods and techniques for surveying and prospecting active faults in urban areas. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(1): 93—104. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.01.012 [3] 侯江飞, 邢磊, 张扬等, 2021. 新乡—商丘断裂延津段浅部地层结构特征研究. 工程地球物理学报, 18(4): 486—494 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2021.04.0011Hou J. F. , Xing L. , Zhang Y. , et al. , 2021. The shallow structural characteristics of the Yanjin section of Xinxiang-Shangqiu fault. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 18(4): 486—494. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2021.04.0011 [4] 雷启云, 柴炽章, 郑文俊等, 2014. 钻探揭示的黄河断裂北段活动性和滑动速率. 地震地质, 36(2): 464—477 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.02.015Lei Q. Y. , Chai C. Z. , Zheng W. J. , et al. , 2014. Activity and slip rate of the northern section of Yellow River fault revealed by drilling. Seismology and Geology, 36(2): 464—477. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.02.015 [5] 李峰, 环文林, 2021. 粤东滨海断裂带第四纪活动特征研究. 震灾防御技术, 16(1): 19—28 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20210103Li F. , Huan W. L. , 2021. Quaternary activity characteristics of the coastal fault zone in eastern Guangdong. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 16(1): 19—28. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20210103 [6] 刘保金, 柴炽章, 酆少英等, 2008. 第四纪沉积区断层及其上断点探测的地震方法技术——以银川隐伏活动断层为例. 地球物理学报, 51(5): 1475—1483 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2008.05.021Liu B. J. , Chai C. Z. , Feng S. Y. , et al. , 2008. Seismic exploration method for buried fault and its up-breakpoint in Quaternary sediment area-An example of Yinchuan buried active fault. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 51(5): 1475—1483. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2008.05.021 [7] 宋佳佳, 田晓峰, 王帅军等, 2021. 南华北块体及邻区地质结构构造研究进展. 地球物理学进展, 36(3): 940—952 doi: 10.6038/pg2021EE0286Song J. J. , Tian X. F. , Wang S. J. , et al. , 2021. Research progress of geological structure in the South North China and adjacent areas. Progress in Geophysics, 36(3): 940—952. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6038/pg2021EE0286 [8] 王定一, 汤锡元, 陈乃明, 1994. 开封坳陷构造特征、形成演化与油气远景. 石油学报, 15(2): 39—47 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.1994.02.005Wang D. Y. , Tang X. Y. , Chen N. M. , 1994. Structural features, evolution and oil and gas prospects of Kaifeng depression. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 15(2): 39—47. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.1994.02.005 [9] 王晶, 李德文, 马保起等, 2021. 黄河郑州—济南段河型变化特征及其与隐伏断层活动的关系. 地质论评, 67(6): 1605—1618Wang J. , Li D. W. , Ma B. Q. , et al. , 2021. River pattern anomalies of Zhengzhou—Jinan segment of Yellow River, North of China, and its relationship with activity of subtle faults. Geological Review, 67(6): 1605—1618. (in Chinese) [10] 王学潮, 向宏发, 2001. 聊城—兰考断裂综合研究及黄河下游河道稳定性分析. 郑州: 黄河水利出版社, 1—163. [11] 王志铄, 马兴全, 2018. 郑州-开封断裂新生代活动特征. 地震地质, 40(3): 511—522 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2018.03.001Wang Z. S. , Ma X. Q. , 2018. The activity characteristics of Zhengzhou-Kaifeng fault during kainozoic. Seismology and Geology, 40(3): 511—522. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2018.03.001 [12] 闫震鹏, 2009. 地质构造对黄河下游悬河稳定性的控制作用. 人民黄河, 31(7): 16—17, 19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2009.07.007Yan Z. P. , 2009. Control function of Geologic structure to the stability of elevated section of the Lower Yellow River. Yellow River, 31(7): 16—17, 19. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2009.07.007 [13] Liang K. , Sun C. B. , Ma B. Q. , et al. , 2018. Investigation of the Yellow River buried fault in the Wuhai basin, northwestern ordos block, China, using deep/shallow seismic reflection and drilling techniques. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 163: 54—69. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.05.025 [14] Yu Z. Y. , Pan H. , Xi H. , et al. , 2019. Late Quaternary paleoseismicity of the Xiadian fault in the North China Plain with implications for earthquake potential. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 184: 103997. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.103997 -




 下载:
下载: