Application of Energy Dissipation Technology in Reconstruction and Reinforcement of A Public Building
-
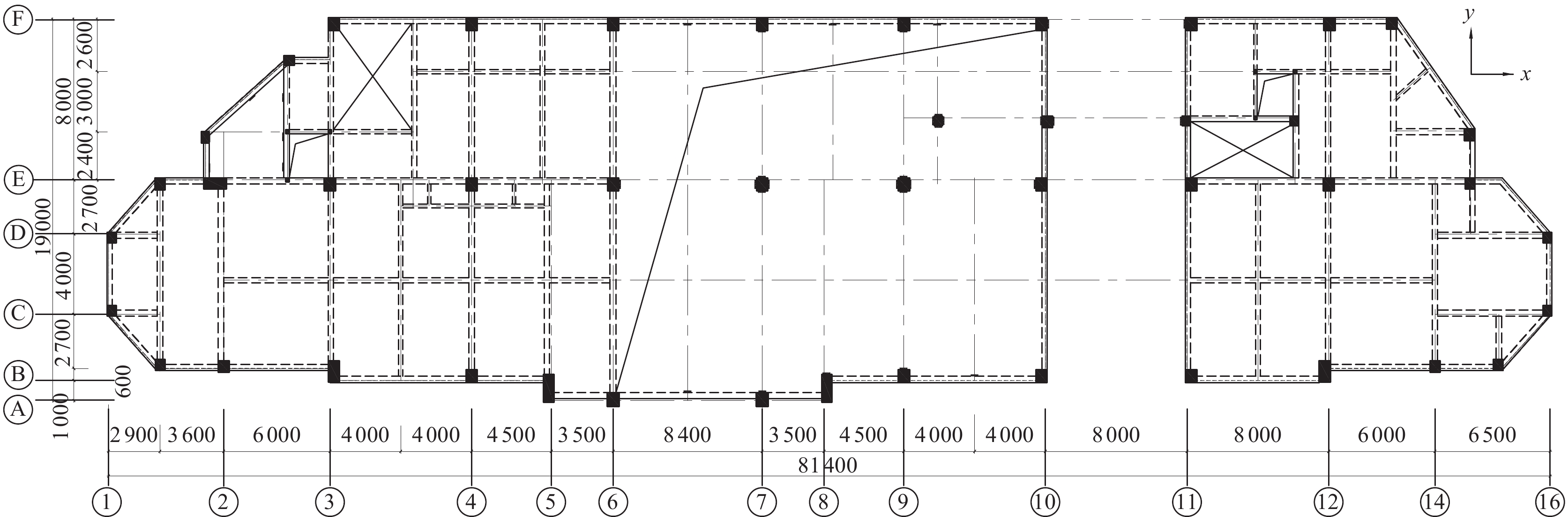
摘要: 本文以某公共建筑改造工程为背景,针对改造过程中存在的大量梁、柱承载力不足,且主控参数超限等问题,提出了在框架结构中适当位置增设黏滞阻尼器的加固方案,使改造后的结构形成消能减震体系,减小地震作用。采用有限元软件分析了加固方案下结构在多遇和罕遇地震作用下的时程反应,研究了消能减震效果。结果表明,经加固改造后,各主控参数均可满足现行规范要求,大幅度提高了罕遇地震作用下结构抗震性能;通过合理设置黏滞阻尼器,减小了地震作用,大幅度缩小了梁、柱加固范围。Abstract: In the process of implementing a public building renovation project, many problems are found: a large number of beam and column with insufficient bearing capacity the main control parameters exceed the limit and other problems. Therefore, a reinforcement scheme is proposed to add a viscosity damper in the appropriate position in the modified frame structure, so that the modified structure can form an energy dissipation and shock absorption system and reduce the seismic effect. In this paper, the finite element software is used to analyze the time-course response of the structure under the reinforcement scheme under the action of frequent and rare earthquakes, and the effect of energy dissipation and shock absorption is studied. The research results show that after reinforcement and transformation, each main control parameter can meet the requirements of the current specification, and greatly improve the seismic performance of the structure under the action of rare earthquakes, and through the reasonable setting of viscous dampers, the seismic effect can be reduced effectively, and the reinforcement range of beams and columns can be reduced greatly.
-
Key words:
- Energy dissipation /
- Public buildings /
- Reconstruction /
- Reinforcement /
- Viscous damper
-
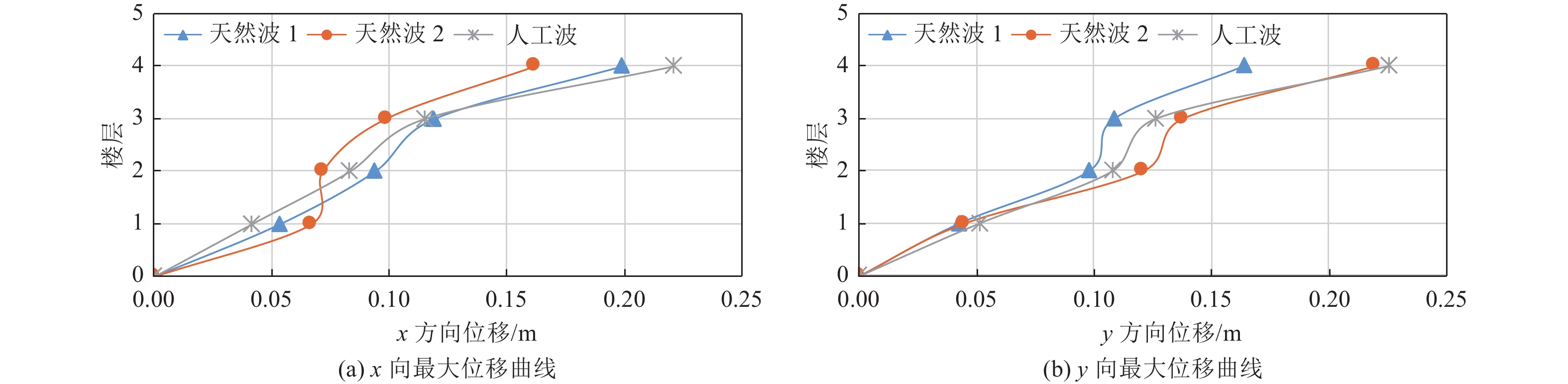
表 1 基底剪力
Table 1. Time history analysis of base shear
项目 x向基底剪力/kN y向基底剪力/kN 天然波1 4 596 4 677 天然波2 4 581 5 032 人工波 4 900 5 116 时程平均 4 693 4 942 反应谱 5 413 5 055 表 2 小震时程结构附加阻尼比
Table 2. Structure additional damping ratio of small earthquake time-history
地震方向 地震波 初始阻尼比/% 附加阻尼比/% x向 天然波1 5 8.2 天然波2 5 8.8 人工波 5 9.4 y向 天然波1 5 8.9 天然波2 5 9.7 人工波 5 9.8 表 3 传统加固方案与消能隔震方案加固构件数量表
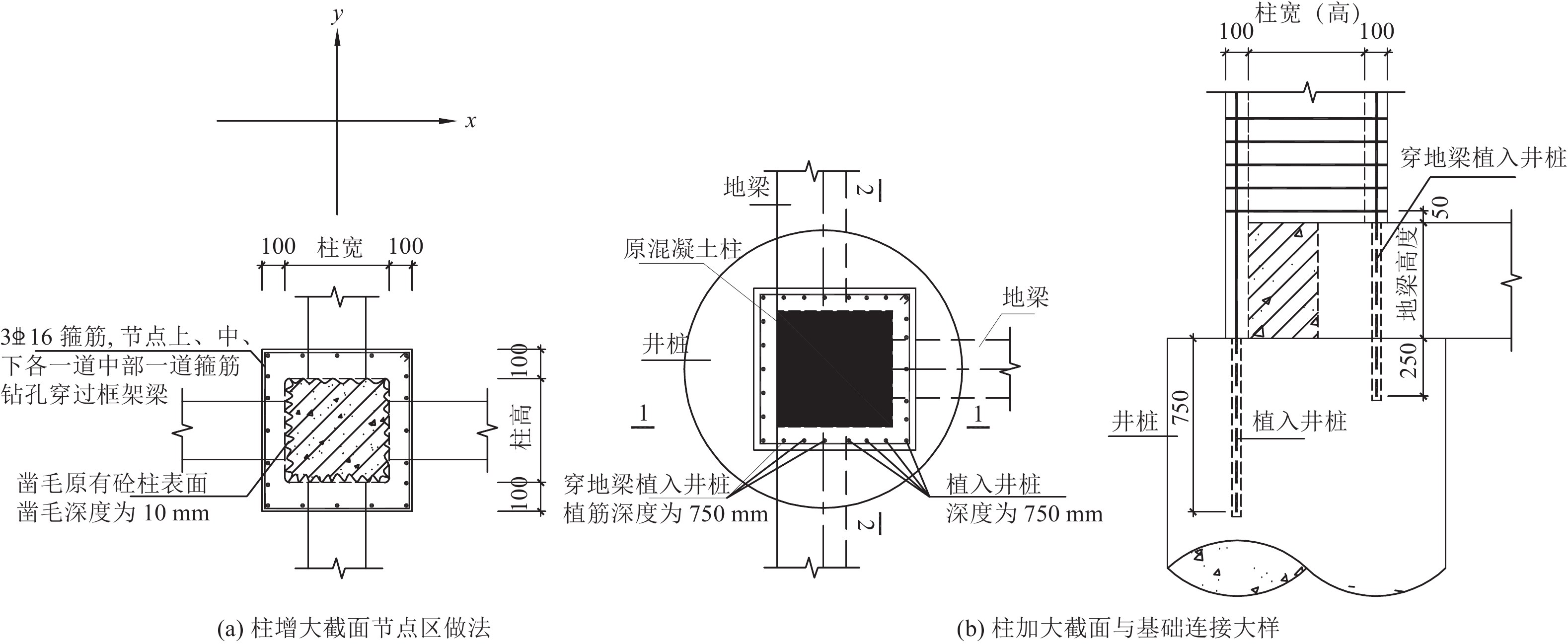
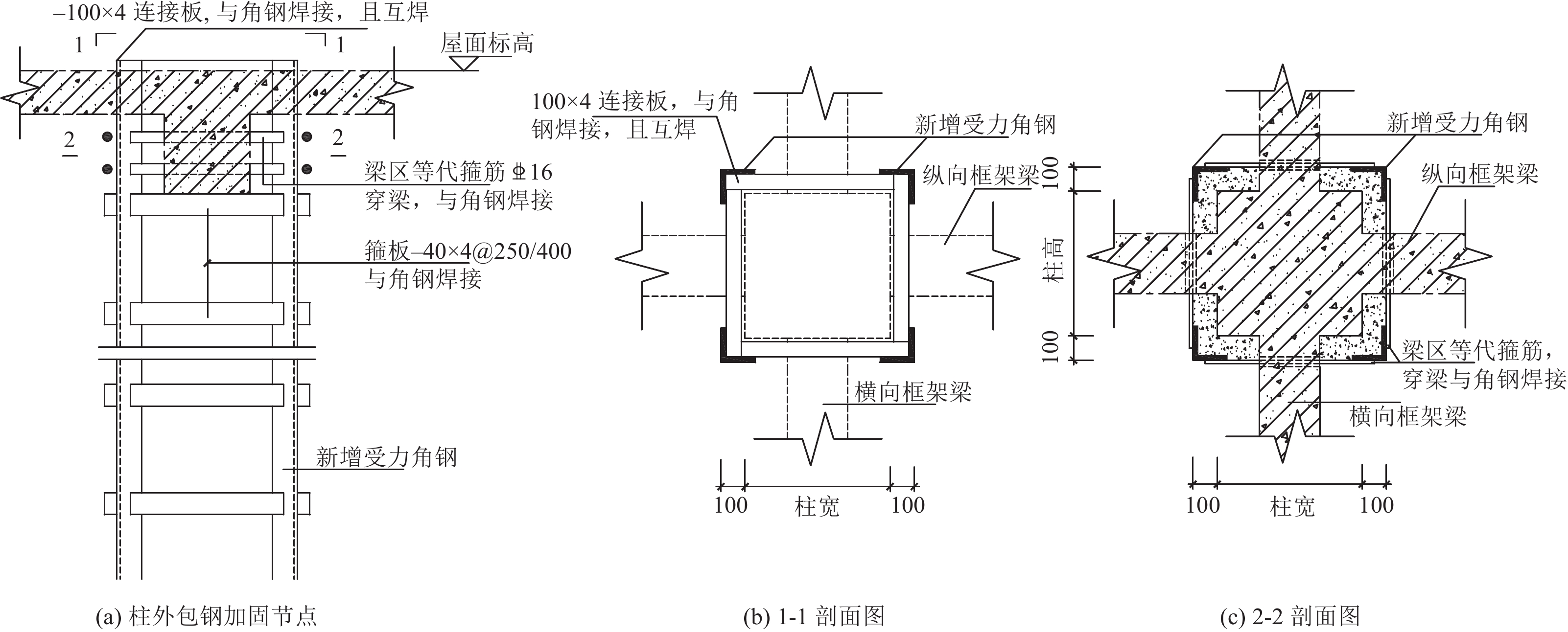
Table 3. The components quantity of traditional reinforced and energy dissipation reinforcement scheme
构件名称 加固方案 构件数量/根(占比/%,标高/m) 框架柱 消能减震 11(24.4,−0.050~16.800 ) 传统加固 33(73.3,−0.050~16.800 ) 框架梁 消能减震 9(7.2,−0.050 ) 9(11.0,5.950 ) 15(12.7,11.350 ) 29(27.4,16.800 ) 传统加固 44(35.2,−0.050 ) 34(41.5,5.950 ) 30(25.4,11.350 ) 47(44.3,16.800) 表 4 抗震性能目标
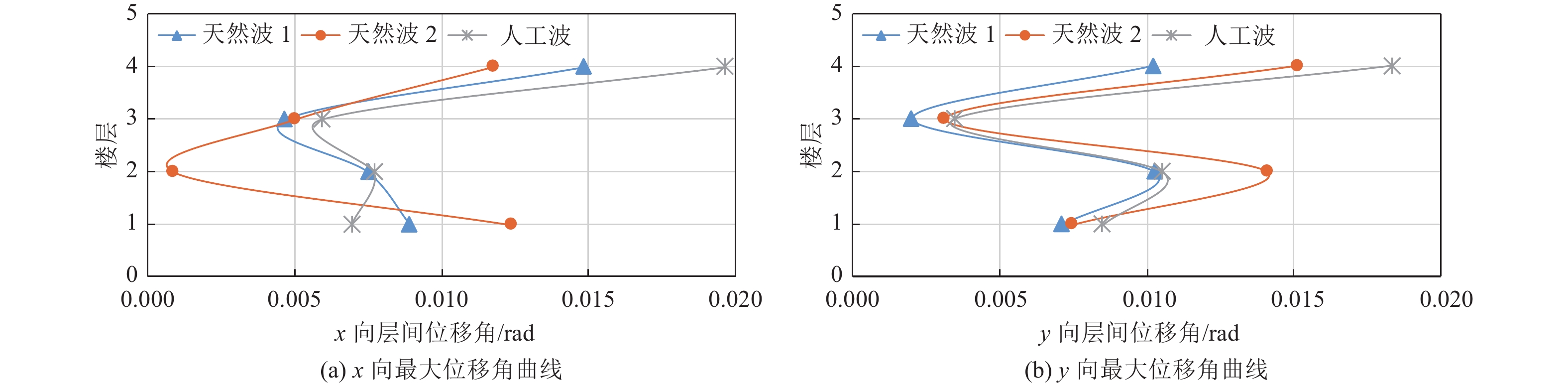
Table 4. Anti-seismic performance objectives
项目 地震动水准 小震 大震 层间位移角 1/550 1/50 总体性能 无损坏 较严重损坏 框架梁 无损坏,OP:θ=0.0% 较严重损坏,CP:θ≤2.0% 框架柱 无损坏,OP:θ=0.0% 中度损坏,LS:θ≤1.0%;部分较严重损坏,LS:θ≤1.5% 表 5 结构模型质量、周期对比
Table 5. Comparison of structural model quality and natural periods
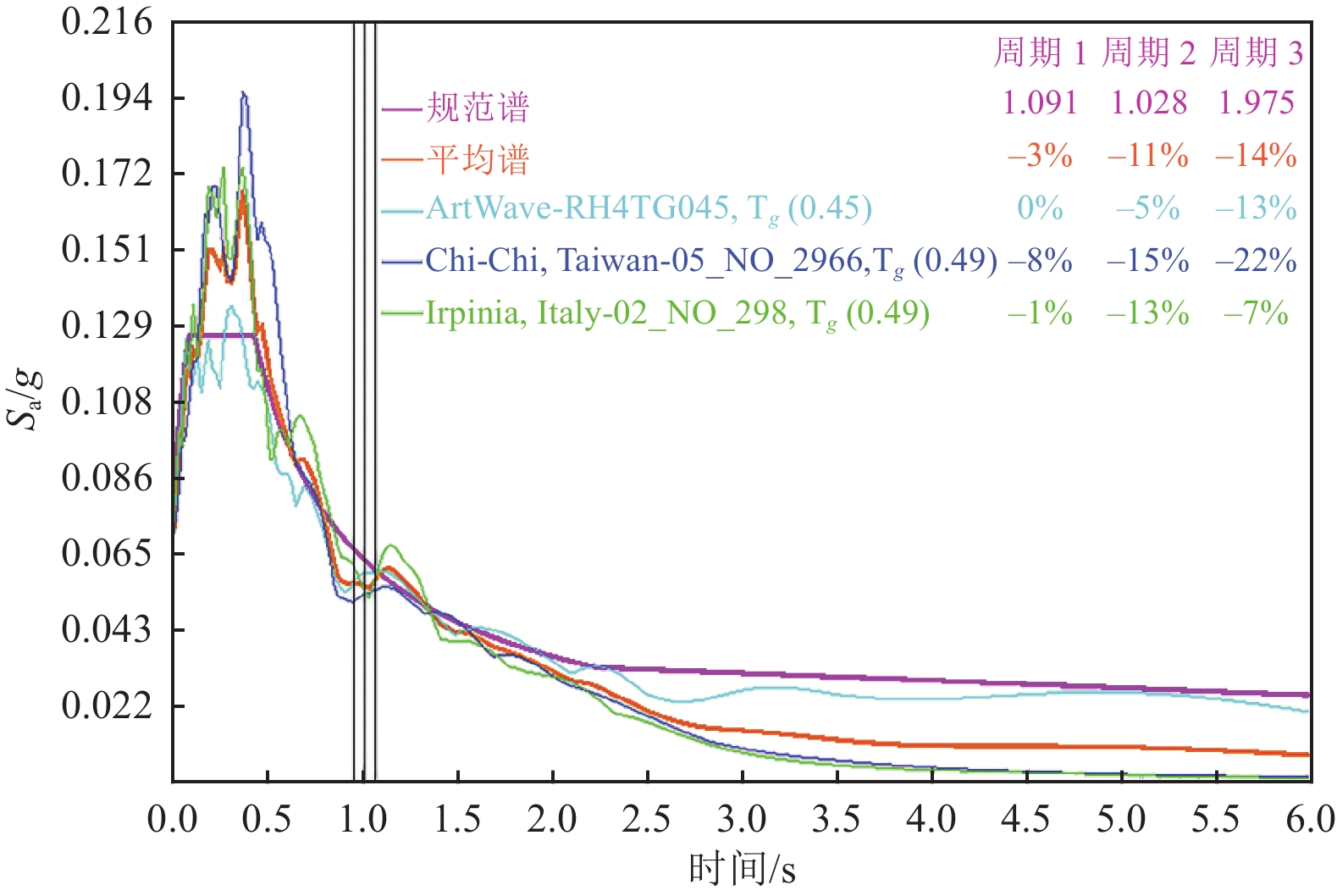
项目 YJK PERFORM-3D 差值/% 质量/t 10 522 10 370 –1.44 第1周期/s 1.092 4 1.100 0 0.70 第2周期/s 1.027 2 1.044 0 1.64 第3周期/s 0.972 1 0.989 1 1.75 -
[1] 陈越, 刘雪冰, 何相宇, 2020. 北京某既有公共建筑的消能减震设计. 建筑结构, 50(S1): 391—395Chen Y. , Liu X. B. , He X. Y. , 2020. Seismic energy dissipation design of an existing public building in Beijing. Building Structure, 50(S1): 391—395. (in Chinese) [2] 傅友东, 2020. 组合减震技术在钢筋混凝土框架结构加固工程中的应用与研究. 水利与建筑工程学报, 18(3): 202—208 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1144.2020.03.035Fu Y. D. , 2020. Research and application of combination damping technology in reinforcement project. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering, 18(3): 202—208. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1144.2020.03.035 [3] 贺峰, 卓军, 陶洪明等, 2015. 消能减震技术在结构抗震加固工程中的应用. 工程抗震与加固改造, 37(4): 96—101He F. , Zhuo J. , Tao H. M. , et al, 2015. Application of energy dissipation technology in the structural seismic strengthening engineering. Earthquake Resistant Engineering and Retrofitting, 37(4): 96—101. (in Chinese) [4] 刘小萌, 张长会, 卢志强等, 2015. 黏滞阻尼器在煤矿井塔结构抗震加固中的应用. 震灾防御技术, 10(1): 126—134 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20150113Liu X. M. , Zhang C. H. , Lu Z. Q. , et al, 2015. The application of fluid viscous damper on the anti-earthquake strengthening of mine well tower. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 10(1): 126—134. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20150113 [5] 张波, 2016. 钢筋混凝土框架节点抗震加固的研究进展. 震灾防御技术, 11(2): 306—313 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20160213Zhang B. , 2016. Review of research progress in seismic strengthening of reinforced concrete frame nodes. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 11(2): 306—313. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20160213 [6] 张雅杰, 2018. 某公共建筑利用消能减震的加固方法分析. 福建建筑, (10): 50—54Zhang Y. J. , 2018. Analysis of a public building using retrofit methods of energy dissipation. Fujian Architecture & Construction, (10): 50—54. (in Chinese) [7] 中国工程建设标准化协会, 2004. CECS 160—2004 建筑工程抗震性态设计通则. 北京: 中国计划出版社.China Association for Engineering Construction Standardization, 2004. CECS 160—2004 General rule for performance-based seismic design of buildings. Beijing: China Planning Press. (in Chinese) [8] 中国工程建设标准化协会, 2015. CECS 392-2014 建筑结构抗倒塌设计规范. 北京: 中国计划出版社.China Association for Engineering Construction Standardization, 2015. CECS 392-2014 Code for anti-collapse design of building structures. Beijing: China Planning Press. (in Chinese) [9] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2010. GB 50011—2010 建筑抗震设计规范. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, 2010. GB 50011-2010 Code for seismic design of buildings. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press. (in Chinese) -



 下载:
下载: