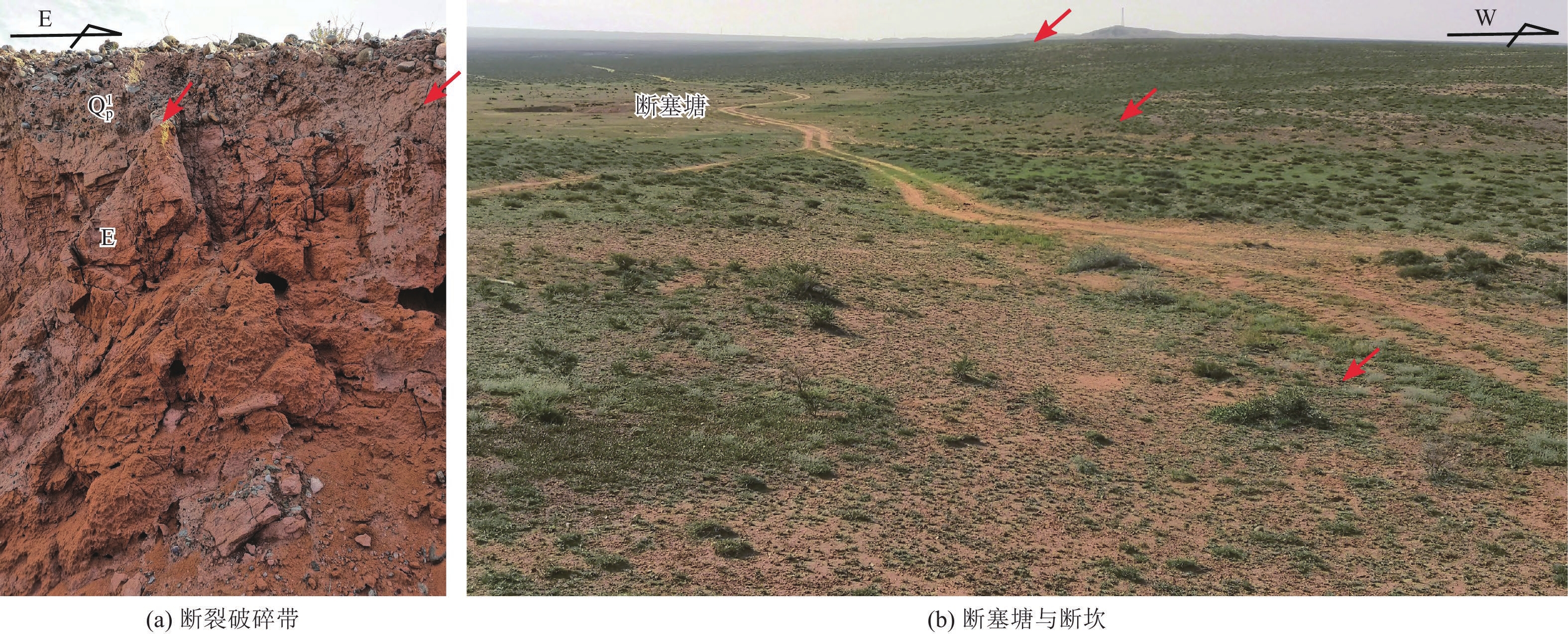
| [1] |
蔡利飘, 周娟, 2018. 银川盆地断裂体系发育特征及其对盆地的控制作用. 油气地球物理, 16(2): 53—59Cai L. P. , Zhou J. , 2018. Development characteristics of the fault system in Yinchuan Basin and its control action on the Basin. Petroleum Geophysics, 16(2): 53—59. (in Chinese)
|
| [2] |
邓起东, 程绍平, 闵伟等, 1999. 鄂尔多斯块体新生代构造活动和动力学的讨论. 地质力学学报, 5(3): 13—21 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.1999.03.003Deng Q. D. , Cheng S. P. , Min W. , et al. , 1999. Discussion on Cenozoic tectonics and dynamics of Ordos block. Journal of Geomechanics, 5(3): 13—21. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.1999.03.003
|
| [3] |
方盛明, 赵成彬, 柴炽章等, 2009. 银川断陷盆地地壳结构与构造的地震学证据. 地球物理学报, 52(7): 1768—1775 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.07.010Fang S. M. , Zhao C. B. , Chai C. Z. , et al. , 2009. Seismic evidence of crustal structures in the Yinchuan faulted basin. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(7): 1768—1775. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.07.010
|
| [4] |
郭宝震, 塔拉, 周海涛等, 2017. 基于精密水准的鄂尔多斯西北缘现今垂直运动分析. 震灾防御技术, 12(3): 523—528Guo B. Z. , Ta L. , Zhou H. T. , et al. , 2007. Current vertical motion analysis of northwestern margin of Ordos Based on precise leveling. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 12(3): 523—528. (in Chinese)
|
| [5] |
国家地震局“鄂尔多斯活动断裂系”课题组. 1988. 鄂尔多斯周缘活动断裂系. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
| [6] |
郭祥云, 蒋长胜, 王晓山等, 2017. 鄂尔多斯块体周缘中小地震震源机制及应力场特征. 大地测量与地球动力学, 37(7): 675—685Guo X. Y. , Jiang C. S. , Wang X. S. , et al. , 2017. Characteristics of small to moderate focal mechanism solutions stress field of the Circum-Ordos block. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 37(7): 675—685. (in Chinese)
|
| [7] |
黄雄南, 张家声, 李天斌等, 2012. 南北地震带北段与蒙古中部活动断裂构造特征. 地震地质, 34(4): 637—658 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2012.04.009Huang X. N. , Zhang J. S. , Li T. B. , et al. , 2012. Characteristics of active faults between the north segment of the North—South seismic belt and the central Mongolia. Seismology and Geology, 34(4): 637—658. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2012.04.009
|
| [8] |
荆振杰, 谢富仁, 张世民等, 2019. 巴彦浩特断裂1: 50000活动断层填图数据库及说明书. (2019-01-01) [2021-01-01]. https://www.activefault-datacenter.cn/data_share.
|
| [9] |
雷启云, 2016. 青藏高原东北缘弧形构造带的扩展与华北西缘银川盆地的演化. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所.Lei Q. Y. , 2016. The extension of the arc tectonic belt in the northeastern margin of the Tibet plateau and the evolution of the Yinchuan Basin in the western margin of the North China. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administrator. (in Chinese)
|
| [10] |
雷启云, 张培震, 郑文俊等, 2017. 贺兰山西麓断裂右旋走滑的地质地貌证据及其构造意义. 地震地质, 39(6): 1297—1315 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.06.014Lei Q. Y. , Zhang P. Z. , Zheng W. J. , et al. , 2017. Geological and geomorphic evidence for dextral strike slip of the Helan Shan west-piedmont fault and its tectonic implications. Seismology and Geology, 39(6): 1297—1315. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.06.014
|
| [11] |
刘保金, 酆少英, 姬计法等, 2017. 贺兰山和银川盆地的岩石圈结构和断裂特征—深地震反射剖面结果. 中国科学: 地球科学, 47(2): 179—190.Liu B. J., Feng S. Y., Ji J. F., et al., 2017. Lithospheric structure and faulting characteristics of the Helan Mountains and Yinchuan Basin: Results of deep seismic reflection profiling. Science China Earth Sciences, 60(3): 589—601. (in Chinese)
|
| [12] |
刘建辉, 张培震, 郑德文等, 2010. 贺兰山晚新生代隆升的剥露特征及其隆升模式. 中国科学: 地球科学, 40(1): 50—60.Liu J. H., Zhang P. Z., Zheng D. W., et al., 2010. Pattern and timing of late Cenozoic rapid exhumation and uplift of the Helan Mountain, China. Science China Earth Science, 53(3): 345—355. (in Chinese)
|
| [13] |
刘绍平, 刘学锋, 2002. 巴彦浩特盆地的构造类型. 西南石油学院学报, 24(3): 24—27Liu S. P. , Liu X. F. , 2002. Structural types and its relation with oil and gas of Bayanhot Basin. Journal of Southwest Petroleum Institute, 24(3): 24—27. (in Chinese)
|
| [14] |
马静辉, 何登发, 2019. 贺兰山构造带及邻区中—新生代构造事件: 来自不整合面和裂变径迹的约束. 岩石学报, 35(4): 1121—1142 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.04.10Ma J. H. , He D. F. , 2019. Meso-Cenozoic tectonic events in the Helanshan tectonic belt and its adjacent areas: constraints from unconformity and fission track data. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(4): 1121—1142. (in Chinese) doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.04.10
|
| [15] |
盛书中, 万永革, 黄骥超等, 2015. 应用综合震源机制解法推断鄂尔多斯块体周缘现今地壳应力场的初步结果. 地球物理学报, 58(2): 436—452 doi: 10.6038/cjg20150208Sheng S. Z. , Wan Y. G. , Huang J. C. , et al. , 2015. Present tectonic stress field in the Circum-Ordos region deduced from composite focal mechanism method. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(2): 436—452. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6038/cjg20150208
|
| [16] |
王晓山, 吕坚, 谢祖军等, 2015. 南北地震带震源机制解与构造应力场特征. 地球物理学报, 58(11): 4149—4162Wang X. S. , Lü J. , Xie Z. J. , et al. , 2015. Focal mechanisms and tectonic stress field in the North-South Seismic Belt of China. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(11): 4149—4162. (in Chinese)
|
| [17] |
王银, 杜鹏, 雷启云, 2007. 银川市活断层探测进展概述. 震灾防御技术, 2(2): 166—175 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2007.02.007Wang Y. , Du P. , Lei Q. Y. , 2007. Summary on recent progress of active fault exploration project in Yinchuan City. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 2(2): 166—175. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2007.02.007
|
| [18] |
杨勇, 杨文明, 2018. 基于电性特征的银川盆地第四系分布特征研究. 宁夏工程技术, 17(1): 15—19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7244.2018.01.004Yang Y. , Yang W. M. , 2018. Quaternary distribution characteristics of Yinchuan basin based on electrical characteristics. Ningxia Engineering Technology, 17(1): 15—19. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7244.2018.01.004
|
| [19] |
Bi H. Y. , Zheng W. J. , Lei Q. Y. , et al. , 2020. Surface slip distribution along the West Helanshan Fault, Northern China, and its implications for fault behavior. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 125(7): e2020JB019983.
|
| [20] |
Liang S. M. , Gan W. J. , Shen C. Z. , et al. , 2013. Three-dimensional velocity field of present-day crustal motion of the Tibetan Plateau derived from GPS measurements. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 118(10): 5722—5732. doi: 10.1002/2013JB010503
|
| [21] |
Middleton T. A. , Walker R. T. , Rood D. H. , et al. , 2016. The tectonics of the western Ordos Plateau, Ningxia, China: slip rates on the Luoshan and East Helanshan Faults. Tectonics, 35(11): 2754—2777. doi: 10.1002/2016TC004230
|
| [22] |
Tapponnier P. , Xu Z. Q. , Roger F. , et al. , 2001. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau. Science, 294(5547): 1671—1677. doi: 10.1126/science.105978
|
| [23] |
Yang X. Y. , Dong Y. P. , 2018. Mesozoic and Cenozoic multiple deformations in the Helanshan tectonic belt, northern China. Gondwana Research, 60: 34—53. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2018.03.020
|
| [24] |
Zhang J. , Cunningham D. , Yun L. , et al. , 2021. Kinematic variability of late Cenozoic fault systems and contrasting mountain building processes in the Alxa block, western China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 205: 104597. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2020.104597
|



 下载:
下载: