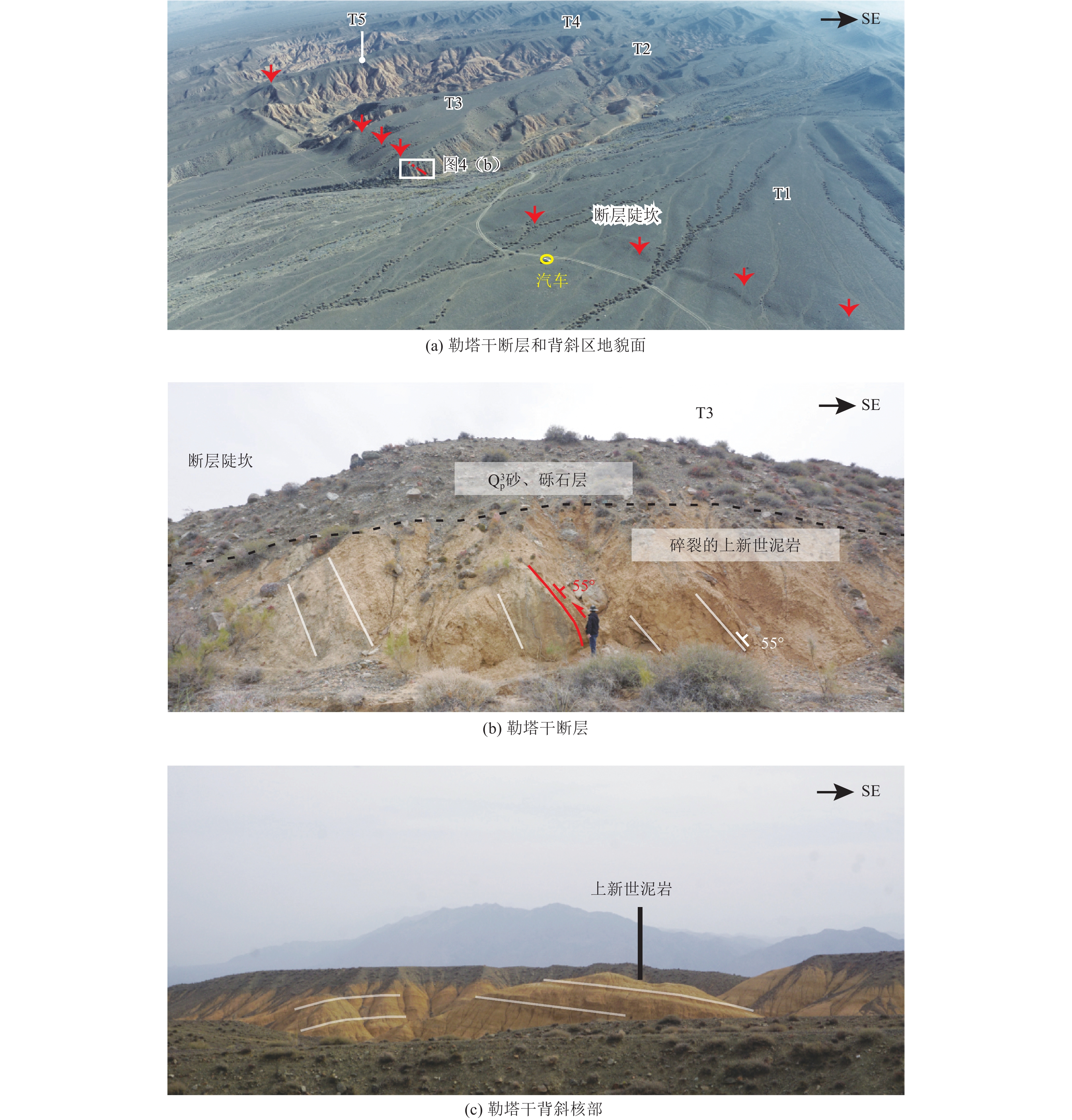
| [1] |
陈建波, 沈军, 李军, 等, 2007. 北天山西段库松木楔克山山前断层新活动特征初探. 西北地震学报, 29(4): 335—340Chen J. B. , Shen J. , Li J. , et al. , 2007. Preliminary study on new active characteristics of Kusongmuxieke Mountain front fault in the West Segment of North Tianshan. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 29(4): 335—340. (in Chinese)
|
| [2] |
邓起东, 冯先岳, 张培震等, 2000. 天山活动构造. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
| [3] |
沈军, 吴传勇, 陈建波, 2008. 新疆主要逆断层-褶皱构造区基本地震构造特征与潜在震源划分问题. 震灾防御技术, 3(2): 101—110 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2008.02.001Shen J. , Wu C. Y. , Chen J. B. , 2008. Basic features of the Major thrust Fault-Fold tectonics and determination of potential earthquake source in Xinjiang. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 3(2): 101—110 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2008.02.001
|
| [4] |
杨晓平, 冉洪流, 2010. 活动推覆构造区潜在震源的边界和震级上限——以1902年阿图什8¼级地震构造区为例. 震灾防御技术, 5(2): 145—156 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2010.02.001Yang X. P. , Ran H. L. , 2010. The boundary and upper limit magnitude of potential seismic source zone in active nappe structure region——an example from M8¼ Atushi seismic structure region. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 5(2): 145—156 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2010.02.001
|
| [5] |
张培震, 邓起东, 杨晓平等, 1996. 天山的晚新生代构造变形及其地球动力学问题. 中国地震, 12(2): 127—140Zhang P. Z. , Deng Q. D. , Yang X. P. , et al. , 1996. Late Cenozoic tectonic deformation and mechanism along the Tianshan mountain, northwestern China. Earthquake Research in China, 12(2): 127—140 (in Chinese).
|
| [6] |
Abdrakhmatov K. Y. , Aldazhanov S. A. , Hager, B. H. , et al. , 1996. Relatively recent construction of the Tien Shan inferred from GPS measurements of present-day crustal deformation rates. Nature, 384(6608): 450—453. doi: 10.1038/384450a0
|
| [7] |
Allen M. B. , Vincent S. J. , Wheeler P. J. , 1999. Late Cenozoic tectonics of the Kepingtage thrust zone: interactions of the Tien Shan and Tarim Basin, northwest China. Tectonics, 18(4): 639—654. doi: 10.1029/1999TC900019
|
| [8] |
Avouac J. P. , Tapponnier P. , 1993. Kinematic model of active deformation in central Asia. Geophysical Research Letters, 20(10): 895—898. doi: 10.1029/93GL00128
|
| [9] |
Burchfiel B. C. , Brown E. T. , Deng Q. D. , et al. , 1999. Crustal shortening on the margins of the Tien Shan, Xinjiang, China. International Geology Review, 41(8): 665—700. doi: 10.1080/00206819909465164
|
| [10] |
Campbell G. E. , Walker R. T. , Abdrakhmatov K. , et al. , 2013. The Dzhungarian fault: late quaternary tectonics and slip rate of a major right-lateral strike-slip fault in the northern Tien Shan region. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 118(10): 5681—5698. doi: 10.1002/jgrb.50367
|
| [11] |
Charreau J. , Avouac J. P. , Chen Y. , et al. , 2008. Miocene to present kinematics of fault-bend folding across the Huerguosi anticline, northern Tianshan (China), derived from structural, seismic, and magnetostratigraphic data. Geology, 36(11): 871—874. doi: 10.1130/G25073A.1
|
| [12] |
Charreau J. , Saint-Carlier D. , Dominguez S. , et al. , 2017. Denudation outpaced by crustal thickening in the eastern Tianshan. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 479: 179—191. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2017.09.025
|
| [13] |
Charreau J. , Sartégou A. , Saint-Carlier D. , et al. , 2020. Late Miocene to quaternary slip history across the Qiulitag anticline in the southern Tianshan piedmont. Terra Nova, 32(1): 89—96. doi: 10.1111/ter.12439
|
| [14] |
Ghose S. , Hamburger M. W. , Ammon C. J. , 1998. Source parameters of moderate-sized earthquakes in the Tien Shan, central Asia from regional moment tensor inversion. Geophysical Research Letters, 25(16): 3181—3184. doi: 10.1029/98GL02362
|
| [15] |
Gong W. Y. , Zhang Y. F. , Li T. , et al. , 2019. Multi-sensor geodetic observations and modeling of the 2017 MW 6.3 Jinghe earthquake. Remote Sensing, 11(18): 2157. doi: 10.3390/rs11182157
|
| [16] |
Grützner C. , Walker R. T. , Abdrakhmatov K. E. , et al. , 2017. Active tectonics around Almaty and along the Zailisky Alatau rangefront. Tectonics, 36(10): 2192—2226. doi: 10.1002/2017TC004657
|
| [17] |
Hendrix M. S. , Dumitru T. A. , Graham S. A. , 1994. Late Oligocene-early Miocene unroofing in the Chinese Tian Shan: an early effect of the India-Asia collision. Geology, 22(6): 487—490. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1994)022<0487:LOEMUI>2.3.CO;2
|
| [18] |
Hu X. F. , Pan B. T. , Kirby E. , et al. , 2015. Rates and kinematics of active shortening along the eastern Qilian Shan, China, inferred from deformed fluvial terraces. Tectonics, 34(12): 2478—2493. doi: 10.1002/2015TC003978
|
| [19] |
Hu Z. K. , Yang X. P. , Yang H. B. , et al. , 2021. Slip rate and Paleoseismology of the Bolokenu-Aqikekuduk (Dzhungarian) right-lateral strike-slip fault in the Northern Tian Shan, NW China. Tectonics, 40(8): e2020TC006604.
|
| [20] |
Huang W. L. , Yang X. P. , Li A. , et al. , 2015. Late Pleistocene shortening rate on the northern margin of the Yanqi Basin, southeastern Tian Shan, NW China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 112: 11—24. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.08.024
|
| [21] |
Huang W. L. , Yang X. P. , Jobe J. A. T. , et al. , 2019. Alluvial plains formation in response to 100-ka glacial–interglacial cycles since the Middle Pleistocene in the southern Tian Shan, NW China. Geomorphology, 341: 86—101. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.05.013
|
| [22] |
Hubert-Ferrari A. , Suppe J. , Gonzalez-Mieres R. , et al. , 2007. Mechanisms of active folding of the landscape (southern Tian Shan, China). Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 112(B3): B03S09.
|
| [23] |
Lavé J. , Avouac J. P. , 2000. Active folding of fluvial terraces across the Siwaliks Hills, Himalayas of central Nepal. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 105(B3): 5735—5770. doi: 10.1029/1999JB900292
|
| [24] |
Makarov V. I. , Alekseev D. V. , Batalev V. Y. , et al. , 2010. Underthrusting of Tarim beneath the Tien Shan and deep structure of their junction zone: main results of seismic experiment along MANAS Profile Kashgar-Song-Köl. Geotectonics, 44(2): 102—126. doi: 10.1134/S0016852110020020
|
| [25] |
Molnar P. , Tapponnier P. , 1975. Cenozoic tectonics of Asia: effects of a continental collision: features of recent continental tectonics in Asia can be interpreted as results of the India-Eurasia collision. Science, 189(4201): 419—426. doi: 10.1126/science.189.4201.419
|
| [26] |
Molnar P. , Deng Q. D. , 1984. Faulting associated with large earthquakes and the average rate of deformation in central and eastern Asia. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 89(B7): 6203—6227. doi: 10.1029/JB089iB07p06203
|
| [27] |
Ren G. X. , Li C. Y. , Wu C. Y. , et al. , 2021. Late Quaternary slip rate and kinematics of the Baoertu fault, constrained by 10Be exposure ages of displaced surfaces within eastern Tian Shan. Lithosphere, 2021(1): 7866920. doi: 10.2113/2021/7866920
|
| [28] |
Rizza M. , Abdrakhmatov K. , Walker R. , et al. , 2019. Rate of slip from multiple Quaternary dating methods and paleoseismic investigations along the Talas-Fergana Fault: tectonic implications for the Tien Shan Range. Tectonics, 38(7): 2477—2505. doi: 10.1029/2018TC005188
|
| [29] |
Saint-Carlier D. , Charreau J. , Lavé J. , et al. , 2016. Major temporal variations in shortening rate absorbed along a large active fold of the southeastern Tianshan piedmont (China). Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 434: 333—348. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2015.11.041
|
| [30] |
Stockmeyer J. M., Shaw J. H., Guan S. W., 2014. Seismic hazards of multisegment thrust-fault ruptures: insights from the 1906 MW 7.4-8.2 Manas, China, earthquake. Seismological Research Letters, 85(4): 801—808. Stockmeyer J. M., Shaw J. H., Brown N. D., et al., 2017. Active thrust sheet deformation over multiple rupture cycles: a quantitative basis for relating terrace folds to fault slip rates. GSA Bulletin, 129(9—10): 1337—1356.
|
| [31] |
Sun J. M. , Zhu R. X. , Bowler J. , 2004. Timing of the Tianshan Mountains uplift constrained by magnetostratigraphic analysis of molasse deposits. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 219(3—4): 239—253. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00008-1
|
| [32] |
Sun J. M. , Zhang Z. Q. , 2009. Syntectonic growth strata and implications for late Cenozoic tectonic uplift in the northern Tian Shan, China. Tectonophysics, 463(1—4): 60—68. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2008.09.008
|
| [33] |
Tapponnier P. , Molnar P. , 1979. Active faulting and Cenozoic tectonics of the Tien Shan, Mongolia, and Baykal regions. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 84(B7): 3425—3459. doi: 10.1029/JB084iB07p03425
|
| [34] |
Thompson S. C. , Weldon R. J. , Rubin C. M. , et al. , 2002. Late Quaternary slip rates across the central Tien Shan, Kyrgyzstan, central Asia. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 107(B9): 2203.
|
| [35] |
Wang M. , Shen Z. K. , 2020a. Present-day crustal deformation of continental China derived from GPS and its tectonic implications. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 125(2): e2019JB018774.
|
| [36] |
Wang S. Y. , Jiao R. H. , Ren Z. K. , et al. , 2020b. Active thrusting in an intermontane basin: the Kumysh Fault, eastern Tian Shan. Tectonics, 39(8): e2019TC006029.
|
| [37] |
Wu C. Y. , Ren G. X. , Yu J. X. , et al. , 2020. Oblique right-lateral faulting along the Northern Margin of the Ili Basin in the Northern Tian Shan, Northwest China. Tectonics, 39(10): e2020TC006061.
|
| [38] |
Yang S. M. , Li J. , Wang Q. , 2008. The deformation pattern and fault rate in the Tianshan Mountains inferred from GPS observations. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 51(8): 1064—1080. doi: 10.1007/s11430-008-0090-8
|
| [39] |
Yin A. , Nie S. , Craig P. , et al. , 1998. Late Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the southern Chinese Tian Shan. Tectonics, 17(1): 1—27. doi: 10.1029/97TC03140
|
| [40] |
Zhang Z. L. , Sun J. M. , Lü L. X. , et al. , 2018. Neogene paleomagnetic study of the western Baicheng Depression: implications for the intensified deformation of Tian Shan since the latest Miocene. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 123(12): 10349—10369.
|
| [41] |
Zhong Y. Z. , Xiong J. G. , Li Y. L. , et al. , 2020. Constraining Late Quaternary crustal shortening in the eastern Qilian Shan from deformed river terraces. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 125(9): e2020JB020631.
|
| [42] |
Zubovich A. V. , Wang X. Q. , Scherba Y. G. , et al. , 2010. GPS velocity field for the Tien Shan and surrounding regions. Tectonics, 29(6): TC6014.
|




 下载:
下载: