Influence of Bi-directional Horizontal Ground Motion on the Vulnerability of a Reinforced Concrete Continuous Beam Bridge
-
摘要: 以双向水平地震动作为输入,对钢筋混凝土连续箱梁高架桥开展非线性动力时程分析。建立基于双向水平地震动强度参数的桥梁结构易损性曲面,比较单向及双向水平地震动输入下桥梁结构易损性差异,分析双向水平地震动输入下横桥向地震动强度对桥梁整体易损性的影响规律。研究结果表明,双向水平地震动输入下的桥梁结构易损性明显高于单向地震动输入的情况,且随着横桥向输入地震动强度的增加,结构各破坏状态的超越概率明显增大。Abstract: The nonlinear dynamic time history analysis of reinforced concrete continuous box girder bridge is carried out with bidirectional horizontal ground motion as input. The vulnerability surface of bridge structure is established based on bidirectional horizontal ground motion intensity parameters. The difference of vulnerability of bridge structure under unidirectional and bidirectional horizontal ground motion input is compared, and the influence law of transverse seismic intensity on overall vulnerability of bridge under bidirectional horizontal ground motion input is analyzed. The results show that: the vulnerability of bridge structure under bidirectional horizontal ground motion input is significantly higher than that under unidirectional ground motion input, and with the increase of transverse ground motion input intensity, the exceeding probability of each failure state of the structure also increases significantly.
-
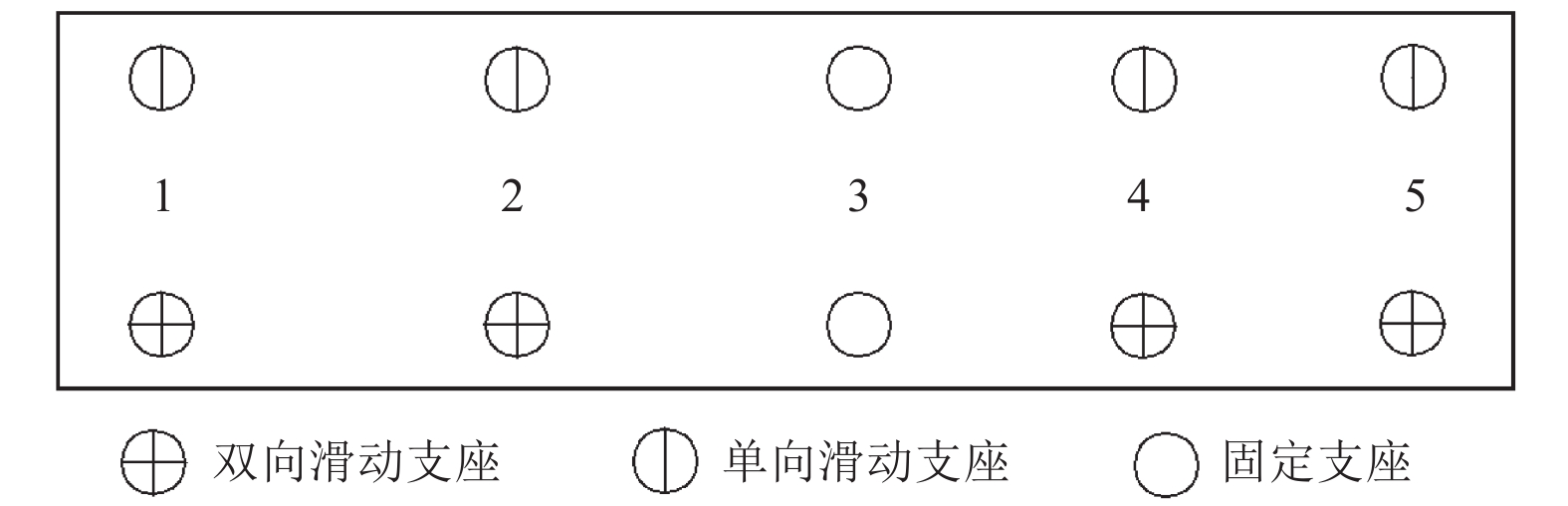
表 1 支座参数
Table 1. Parameter of bearings
支座类型 支座型号 支座位置 盆式固定支座 GPZ4000GX 3 盆式单向滑动支座 GPZ4000DX 1、2、4、5(上) 盆式双向滑动支座 GPZ4000SX 1、2、4、5(下) 表 2 损伤破坏准则
Table 2. Damage failure criterion
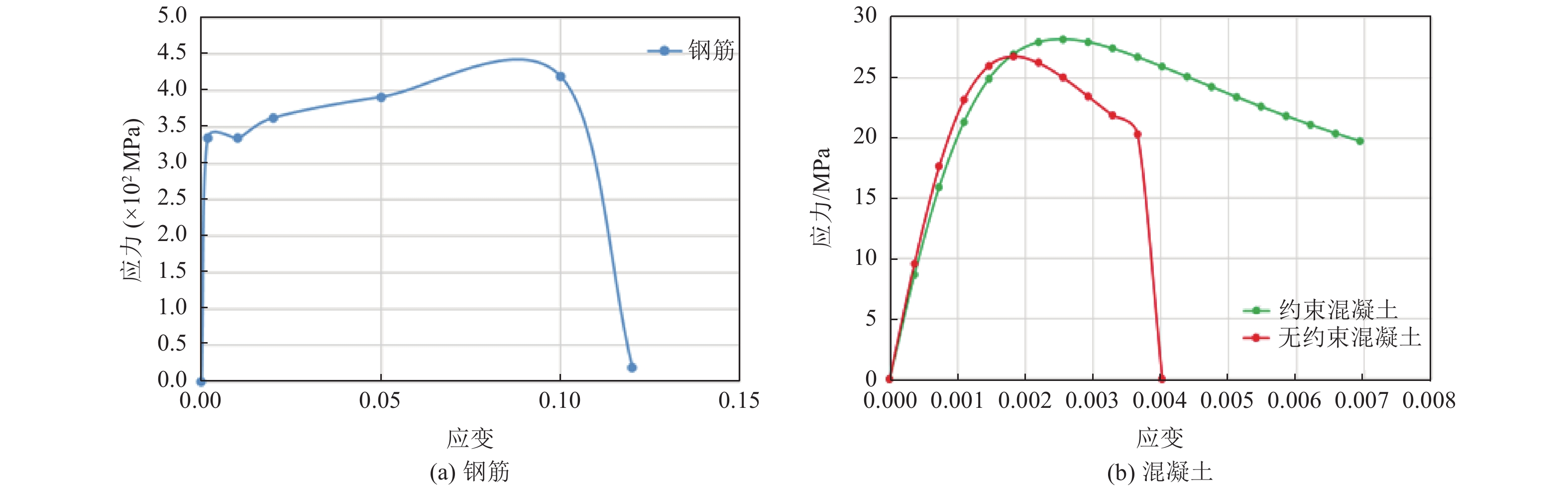
损伤状态 基本完好 轻微破坏 中等破坏 严重破坏 完全破坏 破坏准则 0<μ≤μcy1 μcy1<μ≤μcy μcy<μ≤μc4 μc4<μ≤μcmax μcmax≤μ 表 3 桥墩截面弯矩-曲率关系(单位:rad·m−1)
Table 3. Moment- curvature relationship of pier section(Unit: rad·m−1)
分析参数 фy1 фy фc4 фu 桥墩截面曲率 2.353 3.045 18.390 50.630 表 4 损伤指标与损伤等级关系
Table 4. Relationship between damage index and damage grade
损伤状态 基本完好 轻微破坏 中等破坏 严重破坏 完全破坏 破坏准则 0<μ≤1.00 1.00<μ≤1.29 1.29<μ≤3.34 3.34<μ≤6.34 6.34<μ 表 5 不同地震动强度参数的相关系数
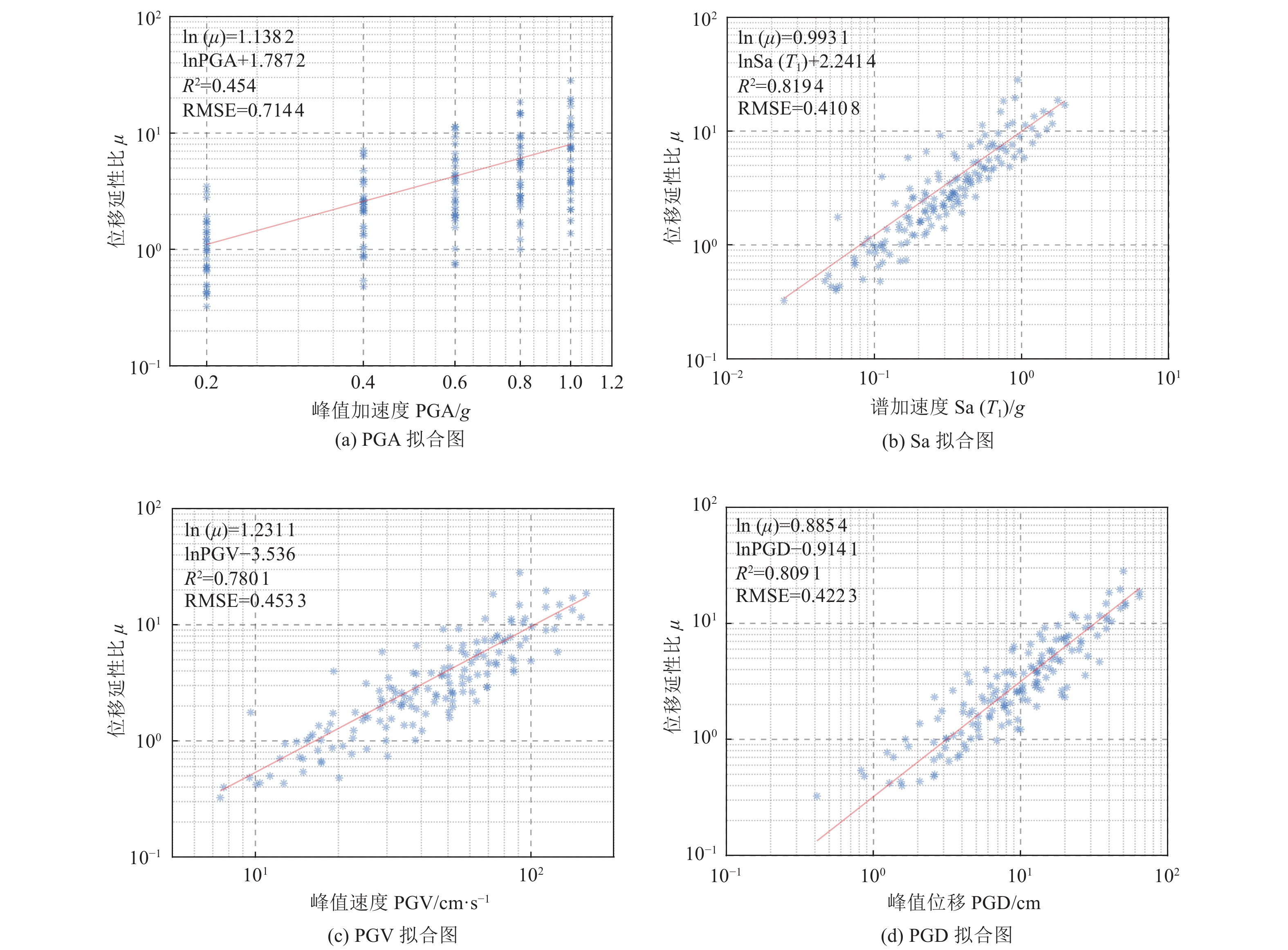
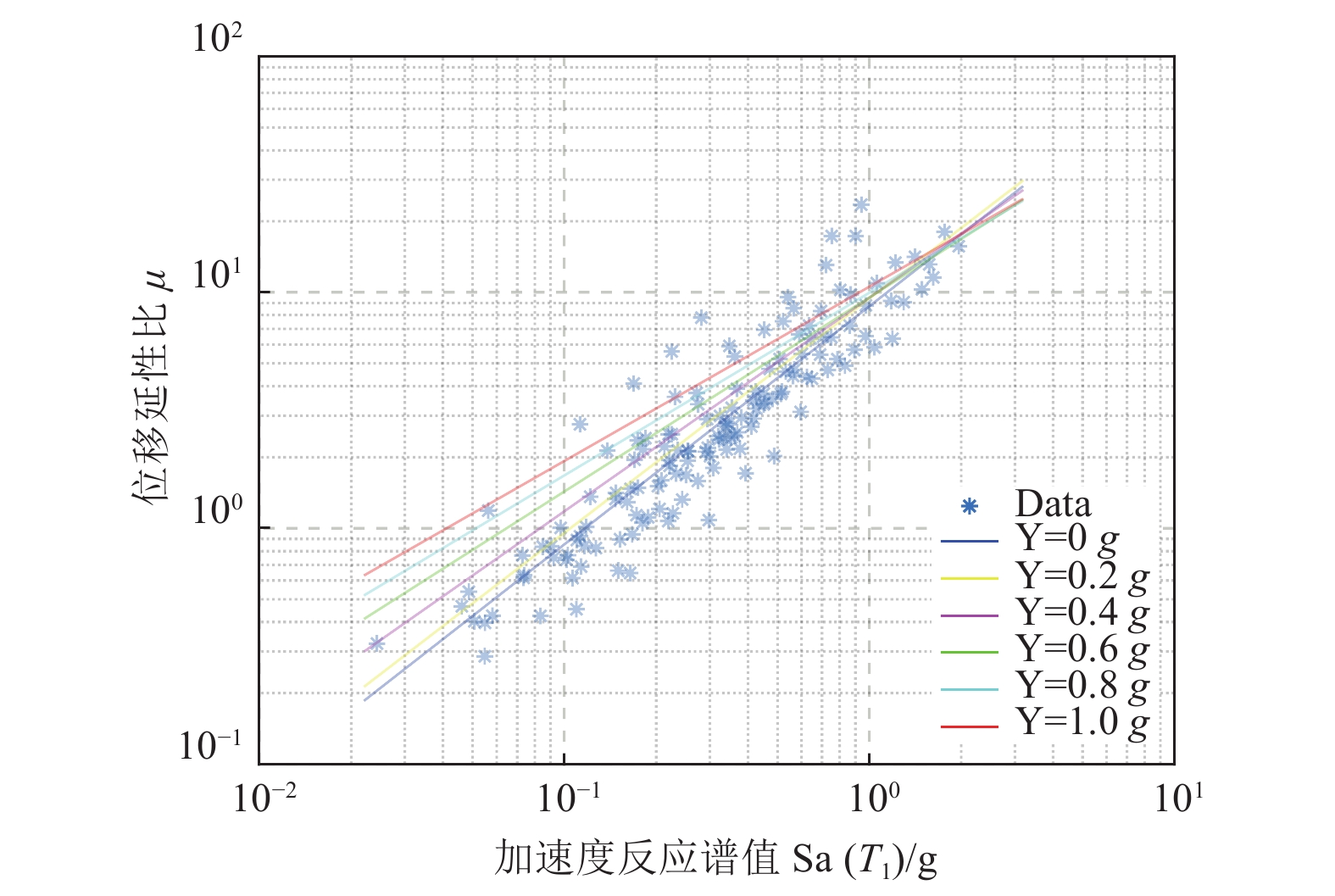
Table 5. Determination coefficients of different ground motion intensity parameters
强度参数 Y=0 g Y=0.2 g Y=0.4 g Y=0.6 g Y=0.8 g Y=1.0 g Sa(T1) 0.837 5 0.819 4 0.763 8 0.716 5 0.683 1 0.657 5 PGA 0.485 7 0.454 0 0.419 8 0.373 6 0.336 9 0.301 7 PGV 0.813 5 0.780 1 0.714 6 0.659 5 0.611 8 0.572 2 PGD 0.813 7 0.809 1 0.769 8 0.739 1 0.714 0 0.693 9 表 6 不同地震动强度参数的均方根误差
Table 6. Root mean square error of different ground motion intensity parameters
强度参数 Y=0 g Y=0.2 g Y=0.4 g Y=0.6 g Y=0.8 g Y=1.0 g Sa(T1) 0.391 8 0.410 8 0.443 7 0.455 9 0.464 7 0.469 9 PGA 0.697 0 0.714 4 0.695 3 0.677 7 0.672 3 0.670 9 PGV 0.419 7 0.453 3 0.487 7 0.499 7 0.514 4 0.525 1 PGD 0.419 5 0.423 3 0.438 0 0.437 4 0.441 4 0.444 2 -
[1] 陈力波, 郑凯锋, 庄卫林等, 2012. 汶川地震桥梁易损性分析. 西南交通大学学报, 47(4): 558—566 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2012.04.004Chen L. B. , Zheng K. F. , Zhuang W. L. , et al. , 2012. Analytical investigation of bridge seismic vulnerability in wenchuan earthquake. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 47(4): 558—566. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2012.04.004 [2] 谷音, 李晓芳, 2019. 考虑氯离子侵蚀的近海桥梁结构地震易损性分析. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 27(5): 1019—1032Gu Y. , Li X. F. , 2019. Seismic fragility analysis of offshore bridge structure considering chloride erosion. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 27(5): 1019—1032. (in Chinese) [3] Hwang H, 刘晶波, 2004. 地震作用下钢筋混凝土桥梁结构易损性分析. 土木工程学报, 37(6): 47—51 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2004.06.009Hwang H, 刘晶波, 2004. 地震作用下钢筋混凝土桥梁结构易损性分析. 土木工程学报, 37(6): 47—51. Hwang H. , Liu J. B. , 2004. Seismic fragility analysis of reinfo钢筋混凝土ed concrete bridges. China Civil Engineering Journal, 37(6): 47—51. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2004.06.009 [4] 姬淑艳, 李英民, 刘立平等, 2006. 考虑双向水平地震作用的结构设计问题研究. 地震工程与工程振动, 26(5): 68—72 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1301.2006.05.011Ji S. Y. , Li Y. M. , Liu L. P. , et al. , 2006. Study on bi-directional seismic action in structural seismic design. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 26(5): 68—72. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1301.2006.05.011 [5] 李立峰, 吴文朋, 胡思聪等, 2016. 考虑氯离子侵蚀的高墩桥梁时变地震易损性分析. 工程力学, 33(1): 163—170 doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2014.06.0530Li L. F. , Wu W. P. , Hu S. C. , et al. , 2016. Time-dependent seismic fragility analysis of high pier bridge based on chloride ion induced corrosion. Engineering Mechanics, 33(1): 163—170. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2014.06.0530 [6] 李勇, 闫维明, 刘晶波等, 2018. 近断层高架连续梁桥地震易损性与振动台试验研究. 工程力学, 35(4): 52—60, 86 doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2017.03.0236Li Y. , Yan W. M. , Liu J. B. , et al. , 2018. Seismic vulnerability analysis and a shaking table test of a near-fault continuous viaduct. Engineering Mechanics, 35(4): 52—60, 86. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2017.03.0236 [7] 林庆利, 林均岐, 刘金龙, 2017. 汶川地震公路桥梁易损性研究. 振动与冲击, 36(4): 110—118, 126Lin Q. L. , Lin J. Q. , Liu J. L. , 2017. A study on the fragility of highway bridges in the Wenchuan earthquake. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 36(4): 110—118, 126. (in Chinese) [8] 刘洋, 吕大刚, 于晓辉, 2016. 近场地震作用下型钢-混凝土组合结构桥易损性分析. 土木工程学报, 49(S1): 56—60, 77Liu Y. , Lv D. G. , Yu X. H. , 2016. Seismic fragility analysis of steel-concrete composite bridges excited by near-fault ground motions. China Civil Engineering Journal, 49(S1): 56—60, 77. (in Chinese) [9] 宋帅, 王帅, 吴刚等, 2020. 中小跨径梁桥地震易损性研究. 振动与冲击, 39(9): 118—125Song S. , Wang S. , Wu G. , et al. , 2020. Seismic vulnerability analysis of small and medium span girder bridges. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 39(9): 118—125. (in Chinese) [10] 徐超, 温增平, 2017. 不同设防标准钢筋混凝土框架结构基于易损性分析的抗震性能评估. 震灾防御技术, 12(4): 845—857 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20170413Xu C. , Wen Z. P. , 2017. Seismic performance evaluation of 钢筋混凝土 frames with different seismic precautionary intensity based on vulnerability analysis. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 12(4): 845—857. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20170413 [11] 易方民, 高小旺, 张维嶽等, 2003. 高层建筑钢结构在多维地震动输入作用下的反应. 建筑结构学报, 24(3): 33—43 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6869.2003.03.005Yi F. M. , Gao X. W. , Zhang W. Y. , et al. , 2003. Response of tall building steel structure to multi dimensional seismic action. Journal of Building Structures, 24(3): 33—43. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6869.2003.03.005 [12] 张菊辉, 2006. 基于数值模拟的规则梁桥墩柱的地震易损性分析. 上海: 同济大学.Zhang J. H., 2006. Study on seismic vulnerability analysis of normal beam bridge piers based on numerical simulation. Shanghai: Tongji University. (in Chinese) [13] 中华人民共和国交通运输部, 2015. JTG D60-2015 公路桥涵设计通用规范. 北京: 人民交通出版社.Ministry of Transport of the People's Republic of China, 2015. JTG D60-2015 General specifications for design of highway bridges and culverts. Beijing: China Communications Press. (in Chinese) [14] 中华人民共和国交通运输部, 2019. JT/T 391—2019 公路桥梁盆式支座. 北京: 人民交通出版社.Ministry of Transport of the People's Republic of China, 2019. JT/T 391—2019 Pot bearing for highway bridge. Beijing: China Communications Press. (in Chinese) [15] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2010. GB 50011—2010 建筑抗震设计规范. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, 2010. GB 50011—2010 Code for seismic design of buildings. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press. (in Chinese) [16] 周长东, 田苗旺, 张许等, 2017. 考虑多维地震作用的高耸钢筋混凝土烟囱结构易损性分析. 土木工程学报, 50(3): 54—64Zhou C. D. , Tian M. W. , Zhang X. , et al. , 2017. Seismic fragility analysis for high-rise 钢筋混凝土 chimney considering multi-dimensional seismic actions. China Civil Engineering Journal, 50(3): 54—64. (in Chinese) [17] Cornell C. A. , Jalayer F. , Hamburger R. O. , 2002. Probabilistic basis for 2000 SAC federal emergency management agency steel moment frame guidelines. Journal of Structural Engineering, 128(4): 526—533. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2002)128:4(526) [18] Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), 2001. HAZUS 99 Estimated annualized earthquake losses for the United States. Washington: FEMA. [19] Shinozuka M. , Feng M. Q. , Lee J. , et al. , 2000. Statistical analysis of fragility curves. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 126(12): 1224—1231. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(2000)126:12(1224) [20] Shome N., 1999. Probabilistic seismic demand analysis of nonlinear structures. Stanford: Stanford University. [21] Yamazaki F., Motomura H., Hamada T., 2000. Damage assessment of expressway networks in Japan based on seismic monitoring. In: Proceeding of the 12th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Upper Hutt, New Zealand: WCEE, 0551. -




 下载:
下载: