An Approach and Experiments for Human Respiratory Signal Recognition based on UWB Radar and Support Vector Machine
-
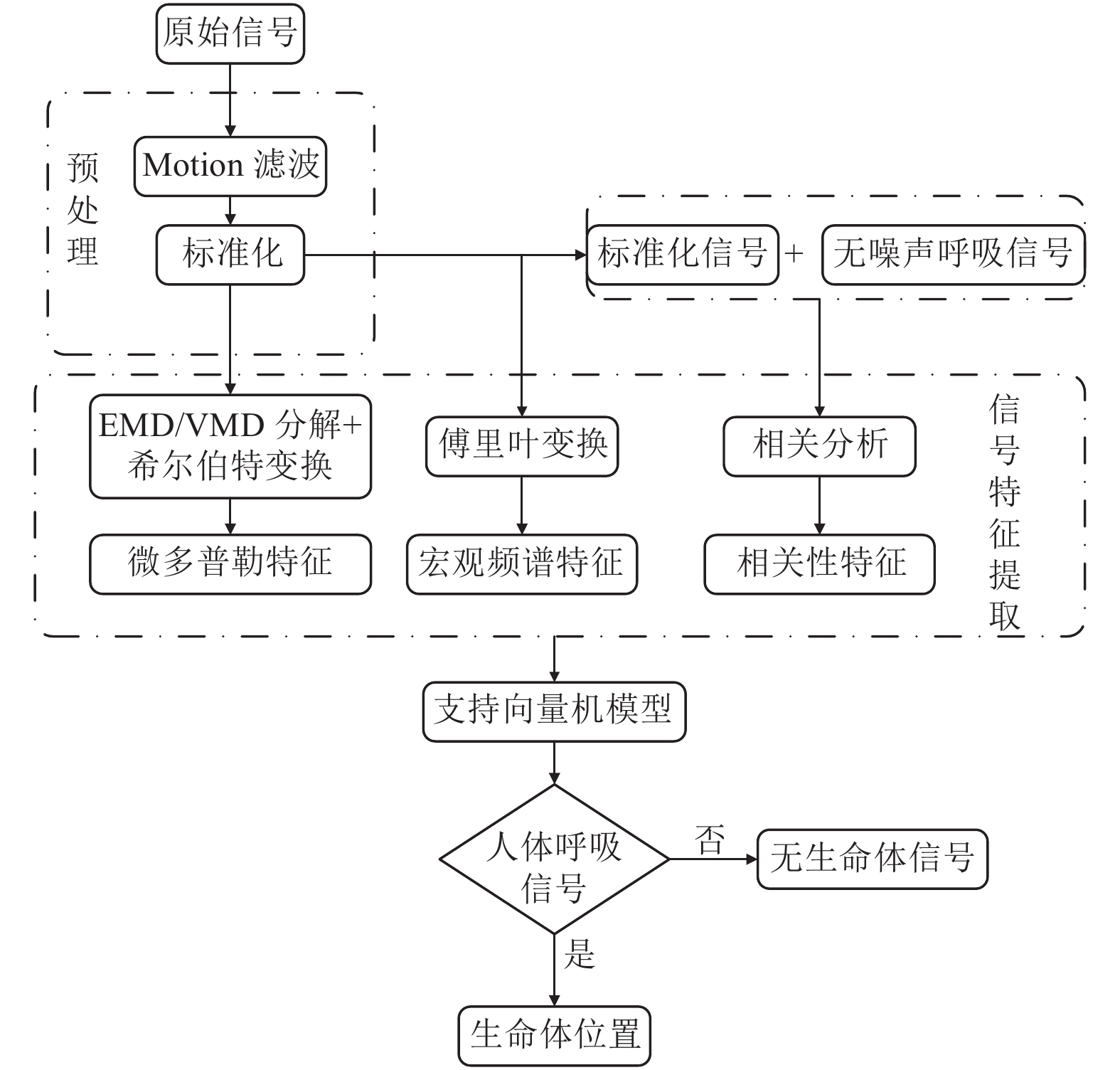
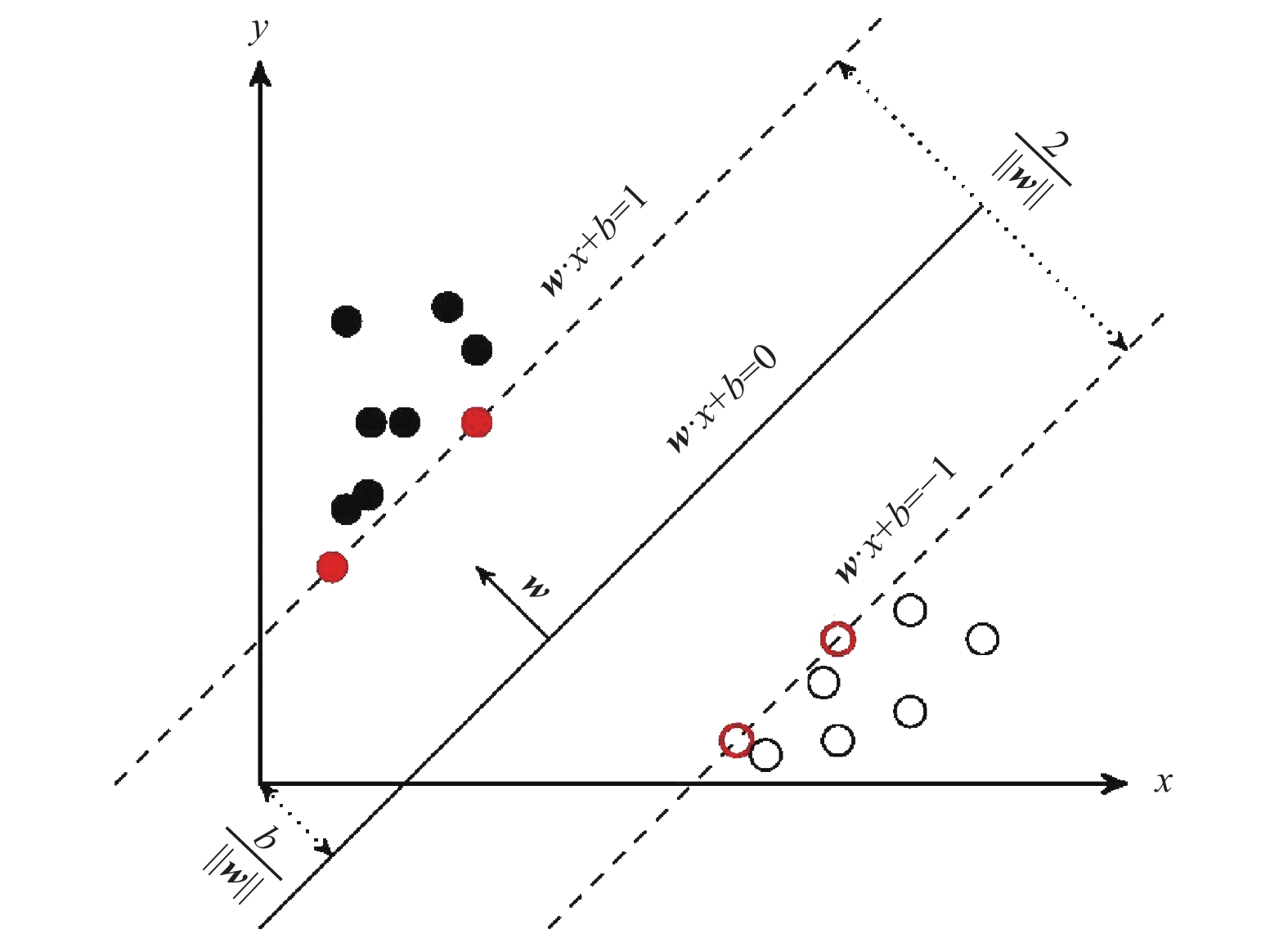
摘要: 与常规雷达相比,超宽带雷达具有距离分辨力高、近距离盲区小、穿透性强、目标识别率高等特点,已被广泛应用于灾后搜寻、救援工作中,以对受困生命体征目标进行生命探测。为实现使用超宽带雷达对受困生命体征目标的识别定位,本研究提出基于信号多特征提取技术及支持向量机模型的人体呼吸信号识别方法。首先,使用经验模态分解、变分模态分解及希尔伯特变换提取雷达探测信号的微多普勒特征,使用傅里叶变换提取宏观频谱特征,使用相关分析获取相关性特征;然后,以提取的信号特征为输入,使用支持向量机模型对信号进行分类,进而对人体呼吸信号进行识别,对人体位置进行定位。不同障碍物场景下的试验结果表明,本方法可有效识别砖墙、建筑楼板等遮挡物下的受困生命体征目标,并提供其位置信息。Abstract: Compared with conventional radar, the ultra-wideband (UWB) radar has the advantages of high distance resolution, small blind spot at close range, strong penetration, and high target recognition rate. Therefore, it has been widely used in post-disaster Radar-based Life Detecting System. In order to identify and locate the trapped person using UWB radar, a method based on signal multi-feature extraction and support vector machine model for human respiratory signal recognition is proposed in this paper. Firstly, we use empirical mode decomposition, variational mode decomposition, and Hilbert transformation to extract the micro-Doppler characteristics of echo signals use Fourier transformation to extract the spectrum characteristics and use correlation analysis to obtain the correlation characteristics. Then, the signals are classified by a support vector machine model based on these signal features. As a result, the respiratory signal can be identified and the position of the human body can be located. The experimental results obtained from different scenes show that the proposed method can effectively identify the human body which is shielded by brick walls and floor slabs, and the location of the human body can be determined at the same time.
-
Key words:
- Ultra-broadband radar /
- Life detection /
- Signal processing /
- Support vector machine
-
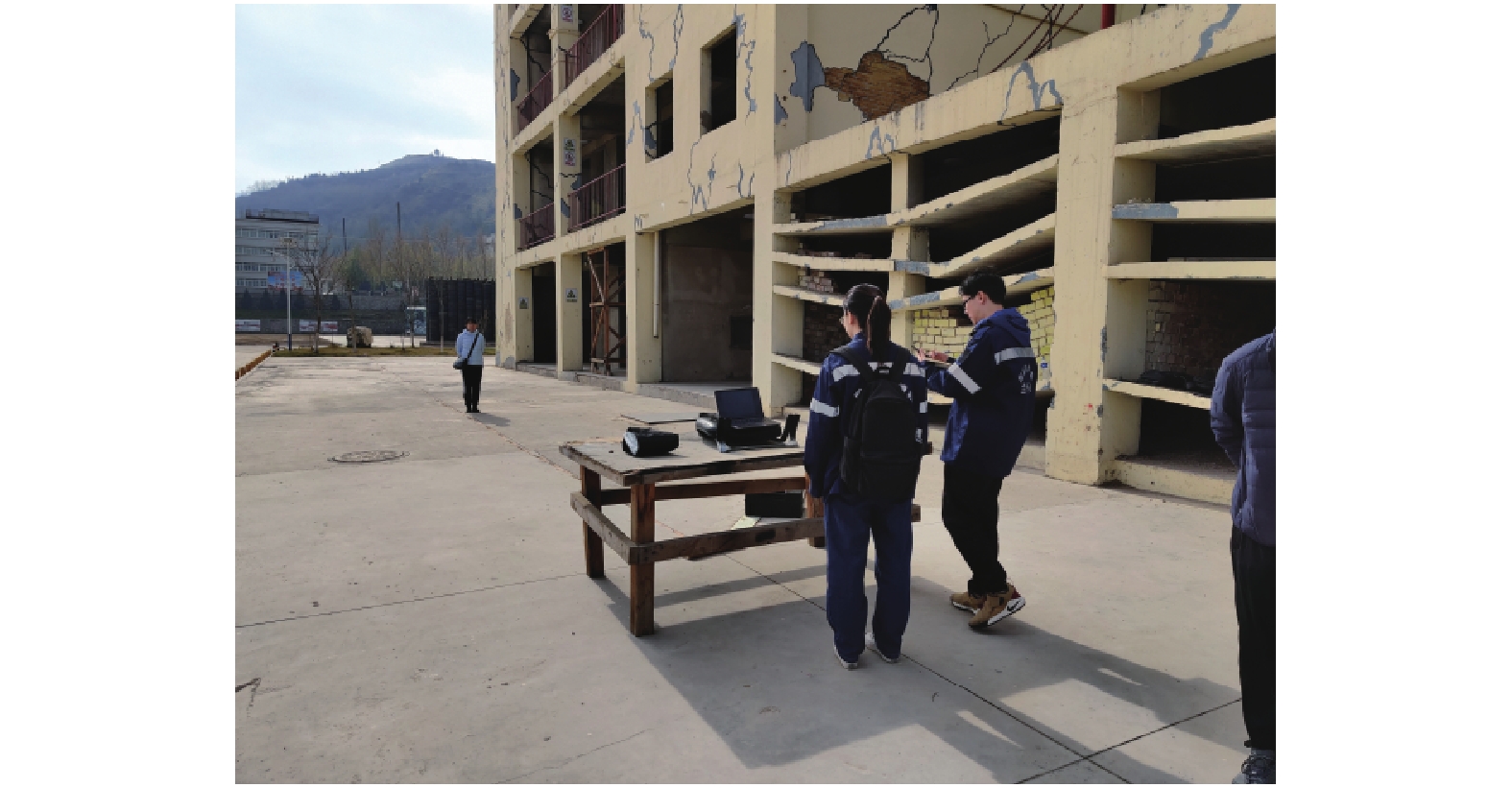
表 1 训练样本探测环境
Table 1. Scenarios for human detection
障碍物类别 障碍物厚度/cm 探测距离/m 无障碍 — 1、2、3、5、10、15、20 泡沫板 3 1、2、3、5、10、15、20 玻璃 1 1、2、3、5、10、15、20 木门 5 1、2、3、5、10、15、20 砖墙 28 1、2、3、5、10、15、20 表 2 平板天线主要技术参数
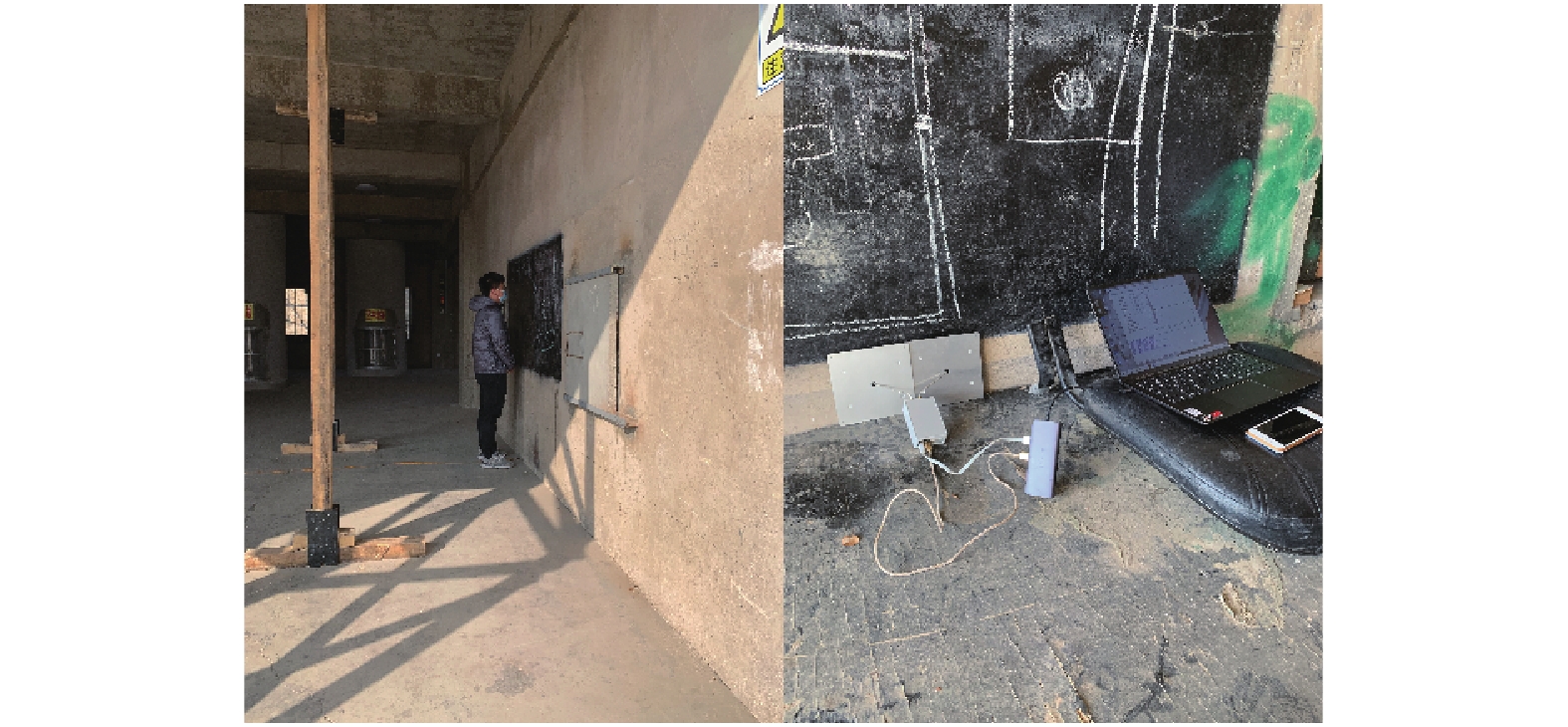
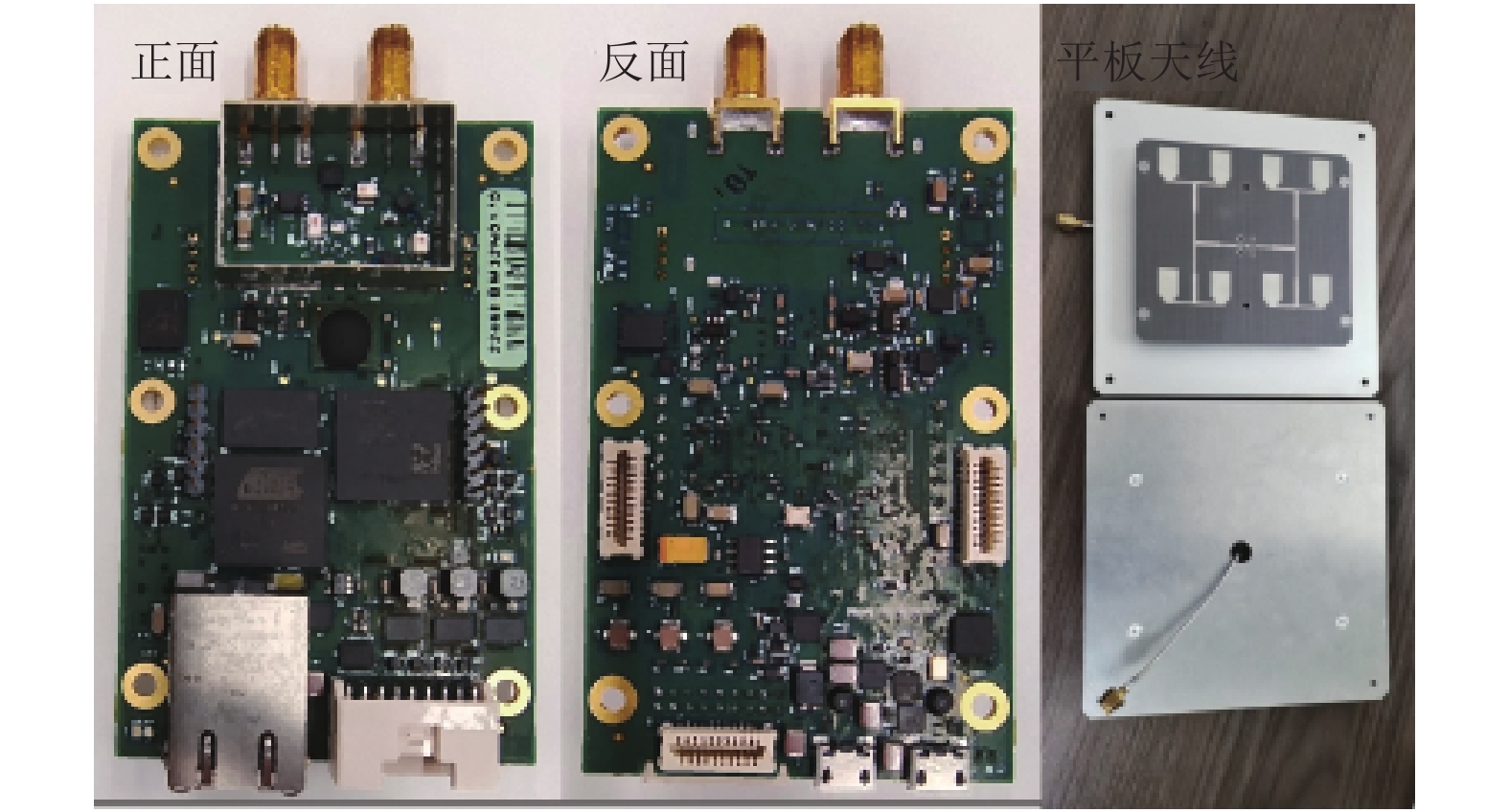
Table 2. Technical parameters of panel antenna
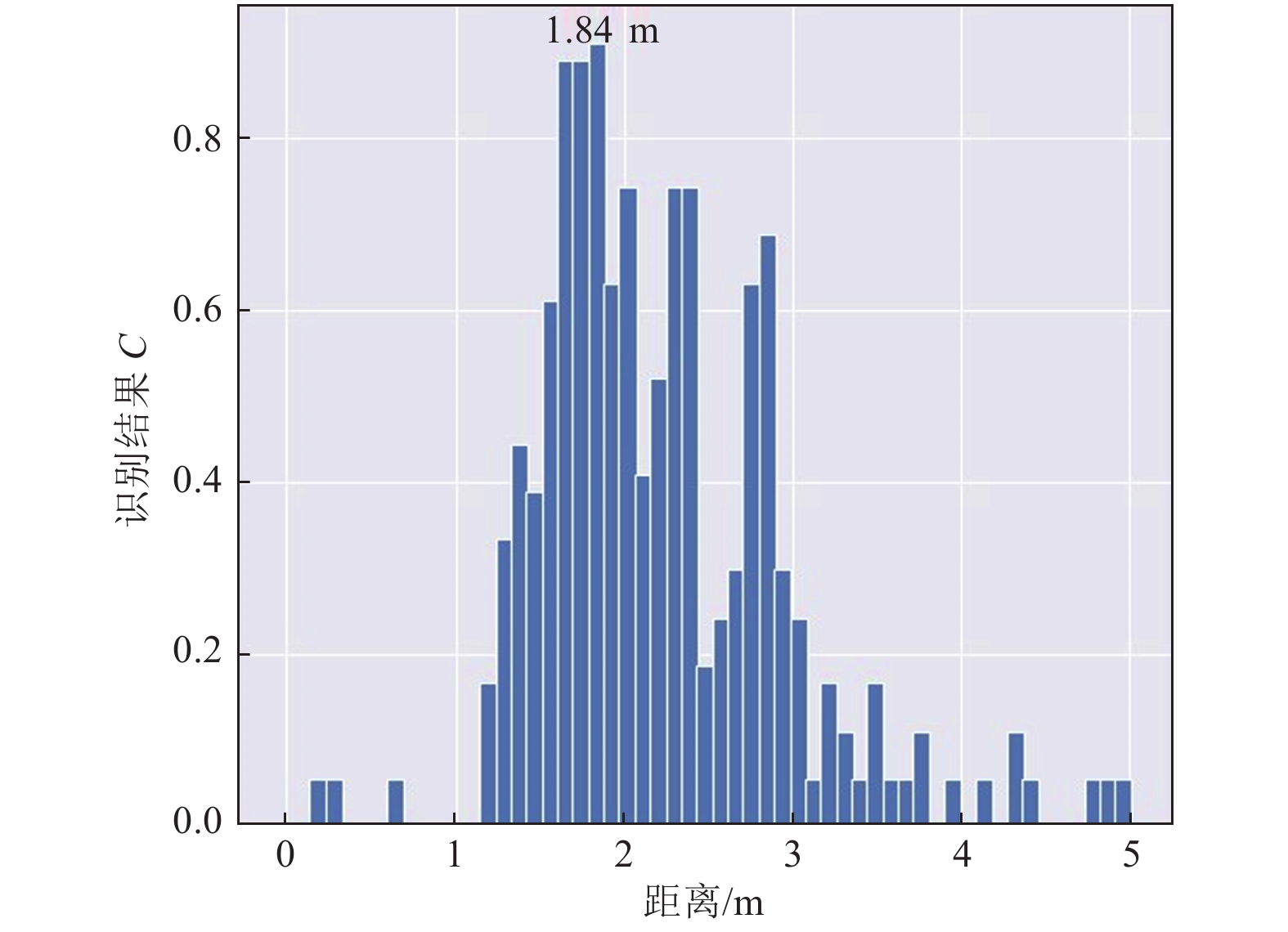
参数名称 参数值 尺寸/mm 150×150×18 覆盖频段/GHz 3.25~3.75 3 dB角 30° 增益/dB 15 表 3 无障碍物场景下分类准确度
Table 3. Accuracy of classification in experiments without obstacle
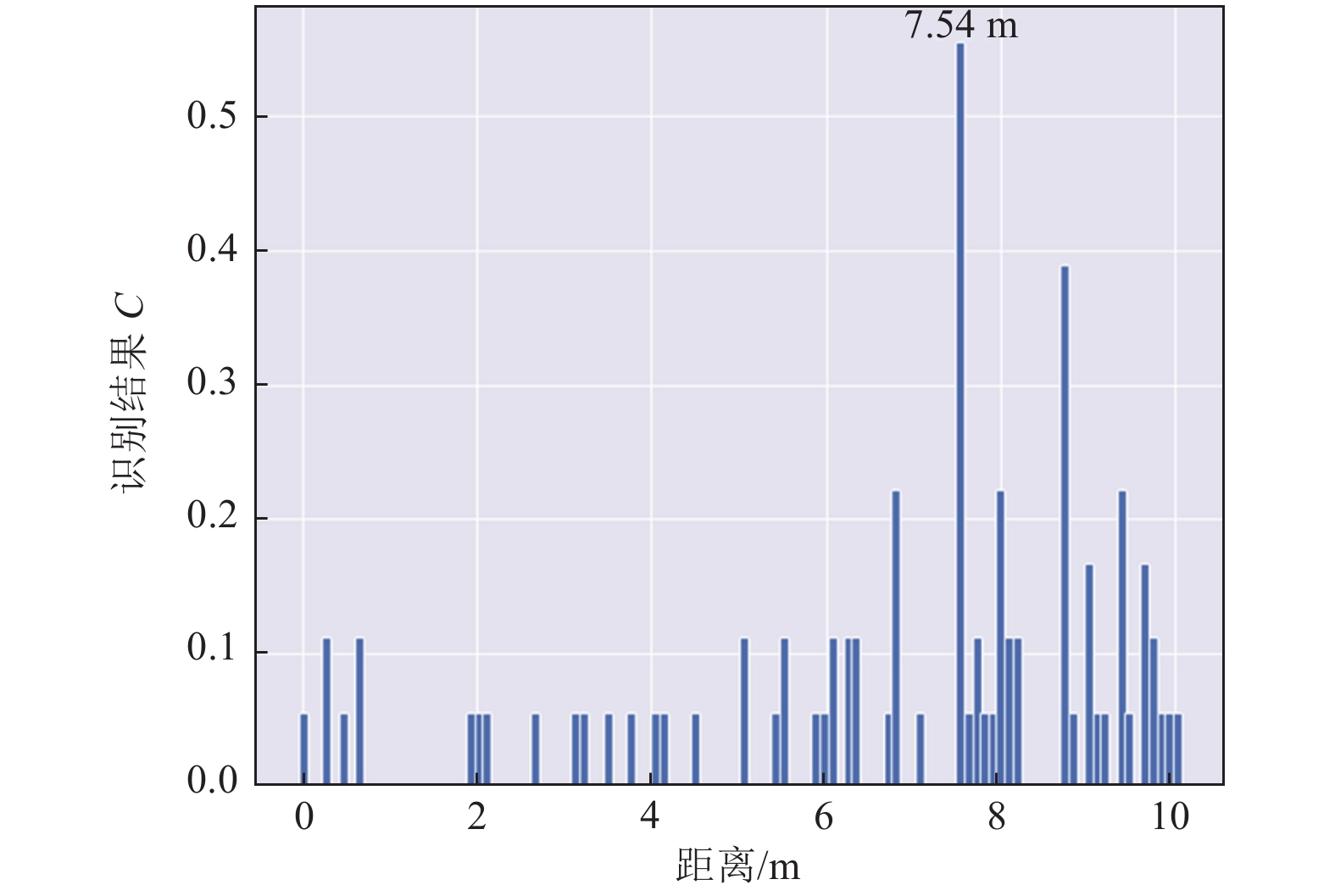
探测距离/m 准确度/% ±10 cm误差 ±30 cm误差 10 87 88 15 82 83 20 89 91 25 97 98 30 95 96 表 4 砖墙隔挡场景下分类准确度
Table 4. Accuracy of classification in the experiments with the block of brick wall
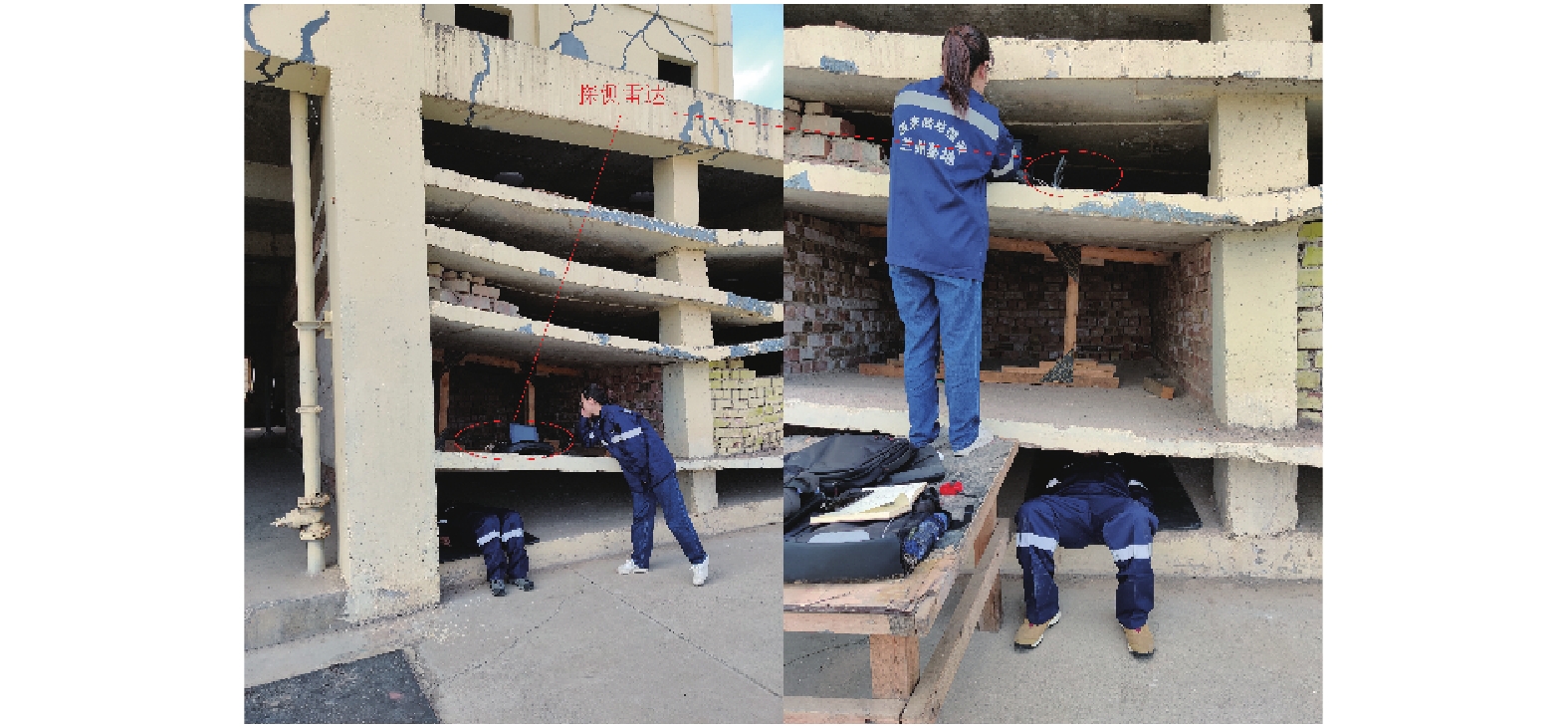
探测距离/m 障碍物厚度/cm 准确度/% ±10 cm误差 ±30 cm误差 0.24 24 72 72 1.24 24 81 81 3.24 24 72 73 5.24 24 85 86 7.24 24 83 81 表 5 楼板隔挡场景下探测工况
Table 5. Scenarios for human detection with the block of floorslabs
障碍物
层数障碍物
总厚度/m探测
距离/m探测
时长/min被探测
人员1 0.1 0.50 3 男性1 2 0.2 1.53 3 男性1 1 0.1 0.50 5 男性1 1 0.1 0.50 5 男性2 1 0.1 0.50 5 男性3 2 0.2 1.53 5 男性1 2 0.2 1.53 5 男性2 2 0.2 1.53 5 男性3 2 0.2 1.53 5 男性1 表 6 楼板隔挡场景下分类准确度
Table 6. Accuracy of classification in the experiments with the block of floorslabs
楼板层数 障碍物厚度/m 探测距离/m 准确度/% ±10 cm误差 ±30 cm误差 1 0.1 0.50 75 78 2 0.2 1.53 73 77 -
[1] 崔学荣, 杨雷, 李娟等, 2021. 复杂场景下基于UWB雷达的呼吸特征检测算法. 电子测量技术, 44(4): 70—74Cui X. R. , Yang L. , Li J. , et al. , 2021. Respiratory feature detection algorithm based on UWB radar in complex scene. Electronic Measurement Technology, 44(4): 70—74. (in Chinese) [2] 蒋留兵, 魏光萌, 车俐, 2019. 基于卷积神经网络的雷达人体动作识别方法. 计算机应用与软件, 36(11): 168—174, 234 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2019.11.028Jiang L. B. , Wei G. M. , Che L. , 2019. Human motion recognition method by radar based on CNN. Computer Applications and Software, 36(11): 168—174, 234. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2019.11.028 [3] 孙公德, 郭勇, 沈建等, 2017. 分布式超宽带雷达地震被困人员协同探测技术. 震灾防御技术, 12(4): 966—977 doi: 10.11899/zzfy20170424Sun G. D. , Guo Y. , Shen J. , et al. , 2017. Collaborative detection technology for detecting trapped personnel by distributed UWB radar earthquake. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 12(4): 966—977. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20170424 [4] 王亚夫, 梁步阁, 杨德贵等, 2021. 基于CNN的超宽带穿墙雷达静目标数量识别技术. 传感器与微系统, 40(4): 19—22Wang Y. F. , Liang B. G. , Yang D. G. et al. , 2021. Quantity identifying technology for static target of ultra-wideband through-wall radar based on CNN. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 40(4): 19—22. (in Chinese) [5] Cortes C. , Vapnik V. , 1995. Support-vector networks. Machine Learning, 20(3): 273—297. [6] Cristianini N. , Shawe-Taylor J. , 2000. An introduction to support vector machines and other kernel-based learning methods. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [7] Dragomiretskiy K. , Zosso D. , 2014. Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 62(3): 531—544. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2288675 [8] Gibbs J. E. , 1970. Transmission of information by orthogonal functions. Electronics & Power, 16(4): 138. [9] Harmuth H. , 1969a-09-30. System for the transmission of information by carrier waves over a single conductor: US, 3470324DA. [10] Harmuth H. F. , 1969b. Applications of Walsh functions in communications. IEEE Spectrum, 6(11): 82—91. doi: 10.1109/MSPEC.1969.5214175 [11] Huang N. E. , Shen Z. , Long S. R. , et al. , 1998. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 454(1998): 903—995. [12] Li C. Z. , Cummings J. , Lam J. , et al. , 2009. Radar remote monitoring of vital signs. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 10(1): 47—56. doi: 10.1109/MMM.2008.930675 [13] Li J. , Liu L. B. , Zeng Z. F. , et al. , 2014. Advanced signal processing for vital sign extraction with applications in UWB radar detection of trapped victims in complex environments. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 7(3): 783—791. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2013.2259801 [14] Luz E. J. D. S. , Schwartz W. R. , Cámara-Chávez G. , et al. , 2016. ECG-based heartbeat classification for arrhythmia detection: a survey. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 127: 144—164. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2015.12.008 [15] Ma Y. Y. , Wang P. F. , Huang W. Z. , et al. , 2021. A robust multi-feature based method for distinguishing between humans and pets to ensure signal source in vital signs monitoring using UWB radar. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2021(1): 27. doi: 10.1186/s13634-021-00738-2 [16] Ossberger G. , Buchegger T. , Schimback E. , et al. , 2004. Non-invasive respiratory movement detection and monitoring of hidden humans using ultra wideband pulse radar. In: 2004 International Workshop on Ultra Wideband Systems Joint with Conference on Ultra Wideband Systems and Technologies. Kyoto: IEEE, 395—399. [17] Platt J. C. , 1999. Fast training of support vector machines using sequential minimal optimization. In: Schölkopf B. , Burges C. J. C. , Smola A. J. , eds. , Advances in Kernel Methods: Support Vector Learning. Cambridge: MIT Press, 185—208. [18] Ren L. Y. , Wang H. F. , Naishadham K. , et al. , 2016. Phase-based methods for heart rate detection using UWB impulse Doppler radar. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 64(10): 3319—3331. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2016.2597824 [19] Scalise L. , Primiani V. M. , Russo P. , et al. , 2013. Wireless sensing for the respiratory activity of human beings: measurements and wide-band numerical analysis. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2013: 396459. [20] Tariq A. , Ghafouri-Shiraz H. , 2011. Vital signs detection using Doppler radar and continuous wavelet Transform. In: Proceedings of the 5th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation. Rome: IEEE, 285—288. [21] Withington P. , Fluhler H. , Nag S. , 2003. Enhancing homeland security with advanced UWB sensors. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 4(3): 51—58. doi: 10.1109/MMW.2003.1237477 [22] Wu S. Y. , Tan K. , Xia Z. H. , et al. , 2016. Improved human respiration detection method via ultra-wideband radar in through-wall or other similar conditions. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 10(3): 468—476. [23] Yarovoy A. G. , Ligthart L. P. , Matuzas J. , et al. , 2006. UWB radar for human being detection. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 21(11): 22—26. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2006.284354 -



 下载:
下载: