Identification of Pulse-like Strong Ground Motions Based on Convolution Neural Network
-
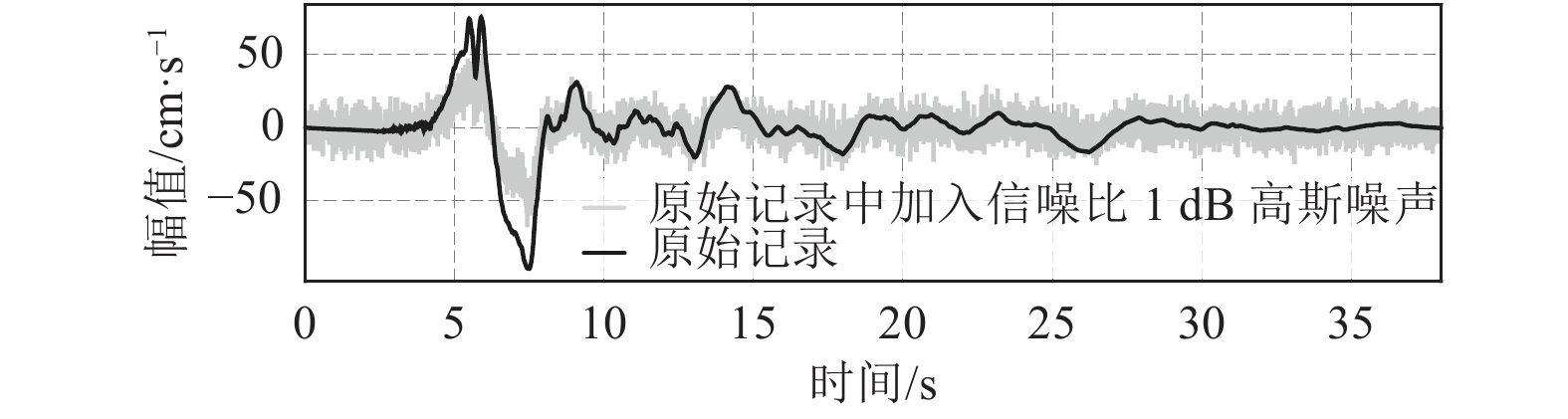
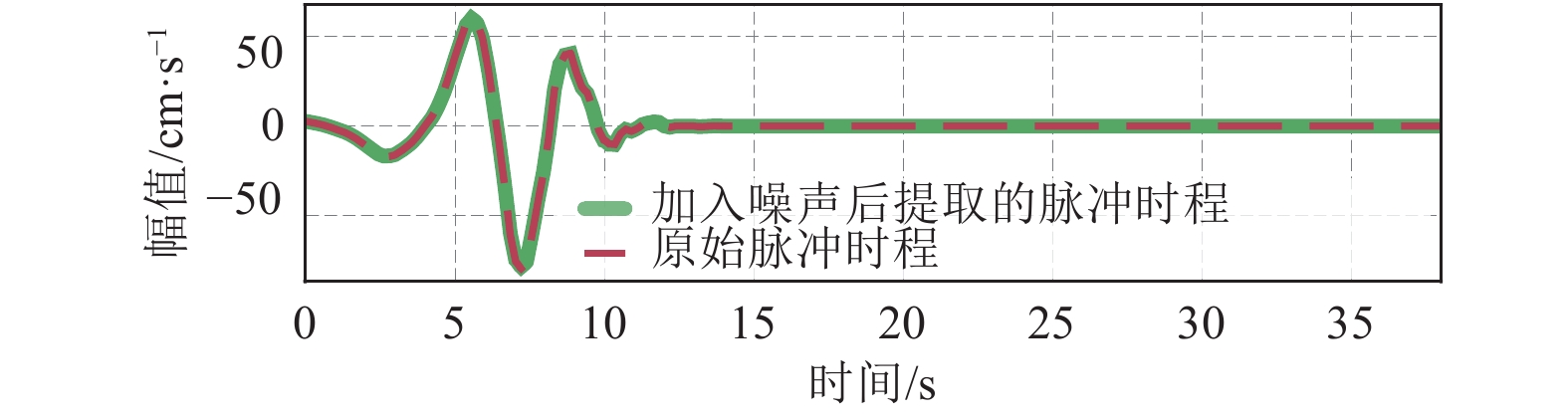
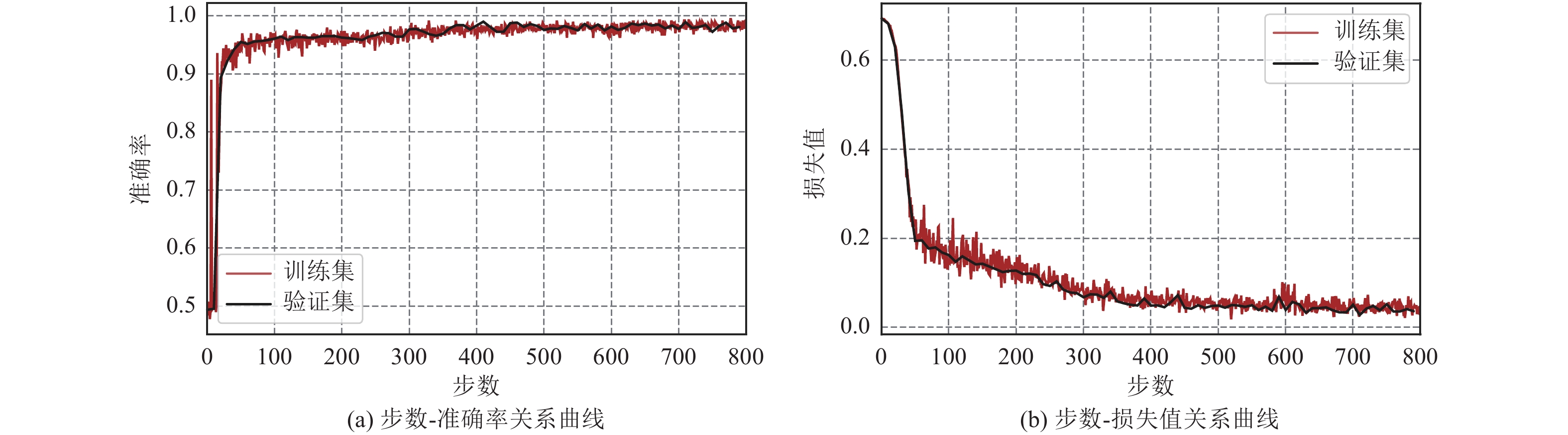
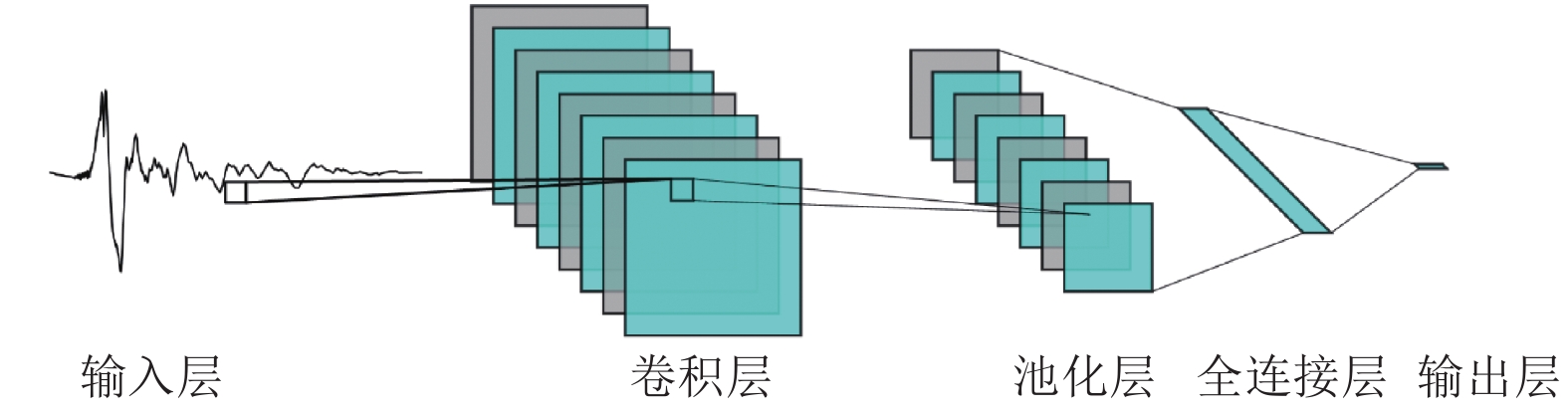
摘要: 含速度大脉冲的强地震动具有复杂的特性,人工提取速度大脉冲特征的方法较繁琐,故利用卷积神经网络(CNN)在图像特征自动提取方面的优势,提出基于卷积神经网络图像识别的速度大脉冲识别方法。基于美国太平洋地震工程研究中心NGA-West1数据库提供的强地震动记录,筛选出6 000条非脉冲记录和91条含有速度大脉冲的强地震动记录。采用在原始记录中加入高斯噪声和过采样的方法,使2类记录样本数量达到均衡。利用本文建立的卷积神经网络模型对2类记录速度时程图进行特征自动提取和分类识别,结果显示测试集准确率为99%,表明本文卷积神经网络模型能够自动提取速度大脉冲特征,进而复现已有结果。将本文方法与传统方法进行了对比,结果表明,对含有多个速度脉冲的强地震动记录的识别,本文方法优于传统方法,具有较高的可靠性、鲁棒性、灵活性。
-
关键词:
- 强地震动 /
- 速度脉冲 /
- 卷积神经网络(CNN) /
- 图像识别
Abstract: Aiming at the tedious problem of strong ground motion containing big velocity pulse, which has complex characteristics and requires manual feature extraction. Taking advantage of the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) in the automatic extraction of image features, we propose a big velocity pulse recognition method based on CNN image recognition. Firstly, based on the strong motion records provided by the NGA-West1 database of the Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center of the United States, 6000 non-pulse records and 91 strong ground motion records containing big velocity pulse were screened out. Secondly, using the method of adding Gaussian noise and oversampling to the original record, the number of samples of the two types is balanced, and the number of samples of each type is 6000. Then, the CNN model established in this paper is used to automatically extract features and classify and recognize the two types of recording speed time history graphs, the results show that the accuracy of the test set is 99%. Finally, the method in this paper is compared with the traditional method, and it is better than the traditional method in identifying multiple velocity pulses. It shows that the method in this paper can automatically extract high-speed pulse information for identification, and has high effectiveness, robustness and flexibility.-
Key words:
- Strong ground motion /
- Velocity pulse /
- Convolution neural network /
- Image recognition
-
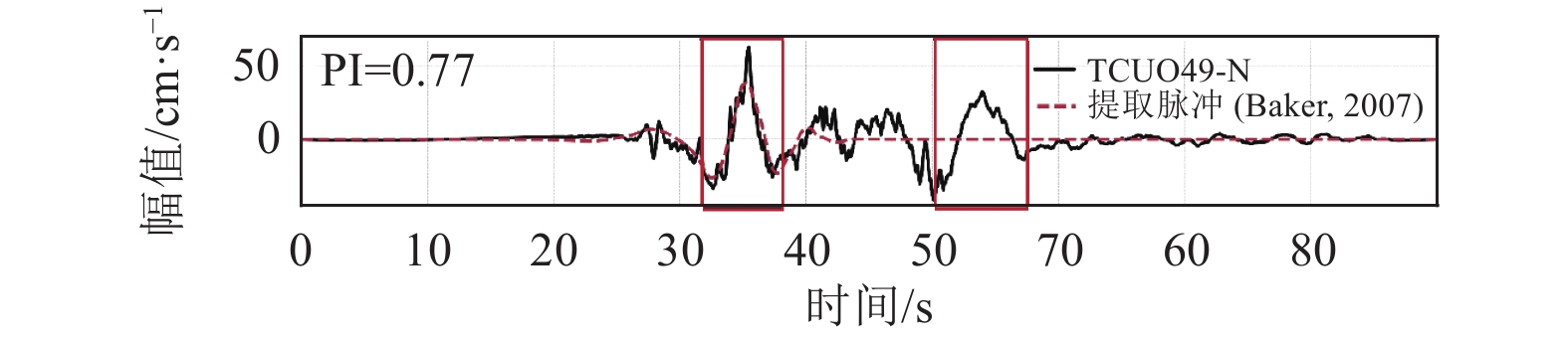
表 1 地震动记录信息及识别结果
Table 1. Ground motion record information and identification results
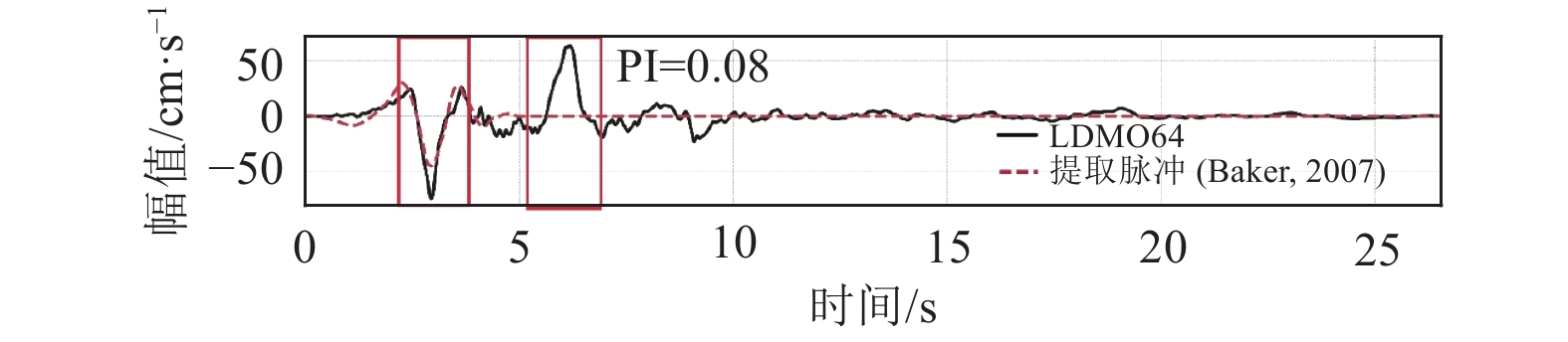
地震动编号 地震名称 PI(Baker,2007) CNN识别结果 RSN180 Imperial Valley-06 0.23 速度脉冲 RSN292 Irpinia, Italy-01 0.13 速度脉冲 RSN1013 Northridge-01 0.08 速度脉冲 RSN1489 Chi-Chi 0.77 速度脉冲 RSN2628 Chi-Chi 0.04 速度脉冲 RSN3317 Chi-Chi 0.28 速度脉冲 -
[1] 段友祥,李根田,孙歧峰,2016.卷积神经网络在储层预测中的应用研究.通信学报,37(S1):1—9.Duan Y. X., Li G. T., Sun Q. F., 2016. Research on convolutional neural network for reservoir parameter prediction. Journal on Communications, 37(S1): 1—9. (in Chinese) [2] 罗全波,陈学良,高孟潭等,2018.近断层速度脉冲与震源机制的关系浅析.震灾防御技术,13(3):646—661.Luo Q. B., Chen X. L., Gao M. T., et al., 2018. Relationship between near-fault velocity pulse and focal mechanism. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 13(3): 646—661. (in Chinese) [3] 曲哲,师骁,2016.汶川地震和鲁甸地震的脉冲型地震动比较研究.工程力学,33(8):150—157. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2015.01.0039Qu Z., Shi X., 2016. Comparative study on the pulse-like ground motions in the Wenchuan and the Ludian earthquakes. Engineering Mechanics, 33(8): 150—157. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2015.01.0039 [4] 谢俊举,温增平,高孟潭等,2011.2008年汶川地震近断层地震动的非平稳特征.地球物理学报,54(3):728—736. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.03.012Xie J. J., Wen Z. P., Gao M. T., et al., 2011. Non-stationary characteristics of near-fault strong motions during the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(3): 728—736. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.03.012 [5] 杨成,唐泽楠,常志旺等,2017.基于经验模态分解的速度脉冲型地震动量化识别.工程力学,34(4):206—212.Yang C., Tang Z. N., Chang Z. W., et al., 2017. EMD-based quantitative categorization for velocity pulse-like ground motions. Engineering Mechanics, 34(4): 206—212. (in Chinese) [6] 杨福剑, 王国新. 2019. 一种改进的近断层脉冲型地震动模拟方法. 震灾防御技术, 14(3): 489—500. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20190303Yang F. J., Wang G. X., 2019. An improved approach for near-fault pulse-like ground motion simulation. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 14(3): 489—500. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20190303 [7] 赵明,陈石,Yuen D.,2019.基于深度学习卷积神经网络的地震波形自动分类与识别.地球物理学报,62(1):374—382. doi: 10.6038/cjg2019M0151Zhao M., Chen S., Yuen D., 2019. Waveform classification and seismic recognition by convolution neural network. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 62(1): 374—382. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6038/cjg2019M0151 [8] 朱继梅,1996.小波变换及其工程应用(连载) 第二讲 小波系数的性质及变换算法.振动与冲击,15(3):94—101. [9] Baker J. W., 2007. Quantitative classification of near-fault ground motions using wavelet analysis. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 97(5): 1486—1501. doi: 10.1785/0120060255 [10] Krizhevsky A., Sutskever I., Hinton G. E., 2012. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, Nevada: Curran Associates Inc., 1097—1105. [11] Mavroeidis G. P., Papageorgiou A. S., 2003. A mathematical representation of near-fault ground motions. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 93(3): 1099—1131. doi: 10.1785/0120020100 [12] Perol T., Gharbi M., Denolle M., 2018. Convolutional neural network for earthquake detection and location. Science Advances, 4(2): e1700578. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1700578 [13] Ross Z. E., Meier M. A., Hauksson E., et al., 2018. Generalized seismic phase detection with deep learning. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 108(5A): 2894—2901. doi: 10.1785/0120180080 [14] Somerville P. G., 2003. Magnitude scaling of the near fault rupture directivity pulse. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 137(1—4): 201—212. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9201(03)00015-3 [15] Zhai C. H., Chang Z. W., Li S., et al., 2013. Quantitative identification of near-fault pulse-like ground motions based on energy. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 103(5): 2591—2603. doi: 10.1785/0120120320 [16] Zhao G. C., Xu L. J., Xie L. L., 2016. A simple and quantitative algorithm for identifying pulse-like ground motions based on zero velocity point method. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 106(3): 1011—1023. doi: 10.1785/0120150226 [17] Zhu W. Q., Beroza G. C., 2019. PhaseNet: a deep-neural-network-based seismic arrival-time picking method. Geophysical Journal International, 216(1): 261—273. -



 下载:
下载: