Analysis of Toppling Failure of Anti Toppling Rock Slope Based on Numerical Manifold Method
-
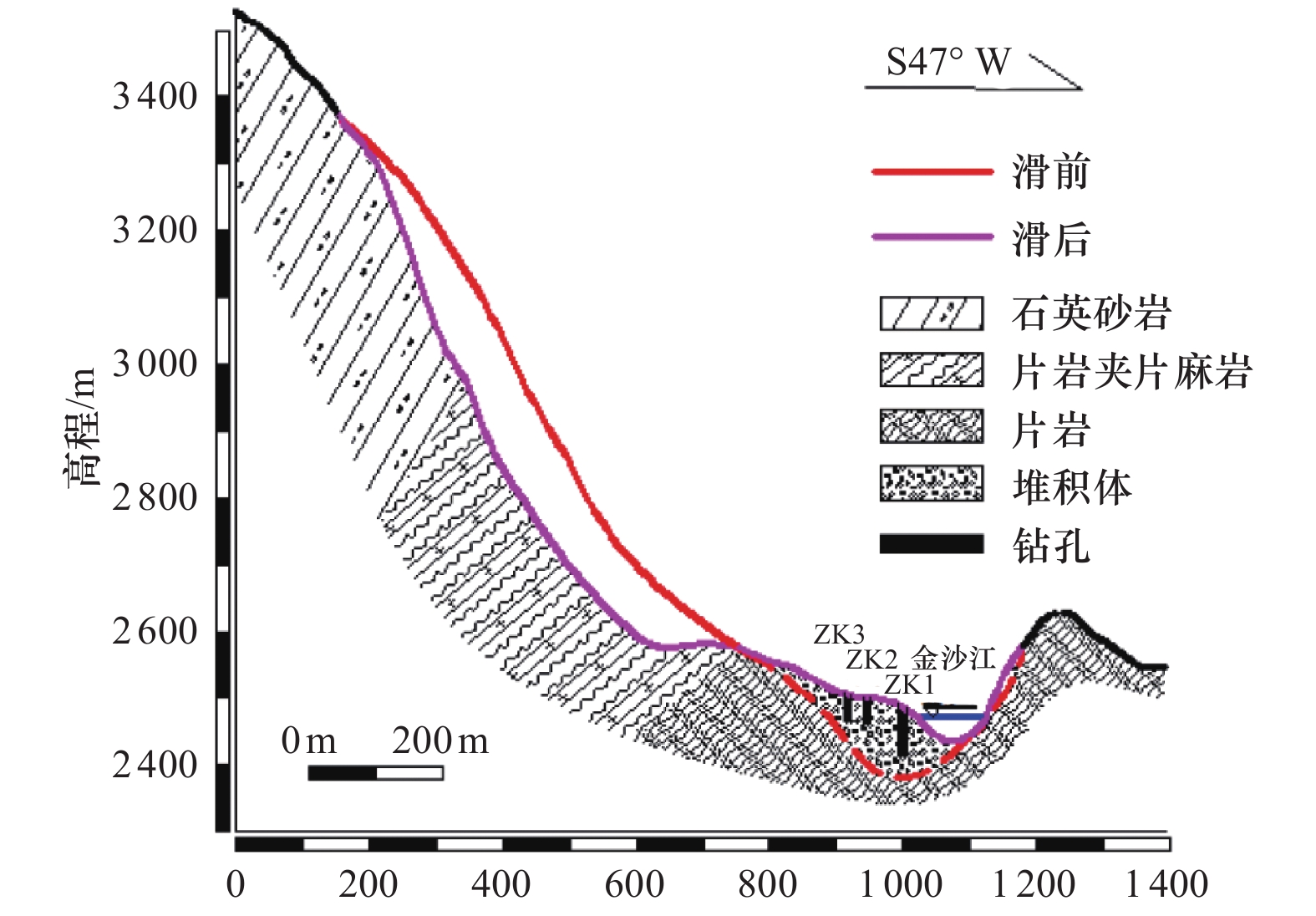
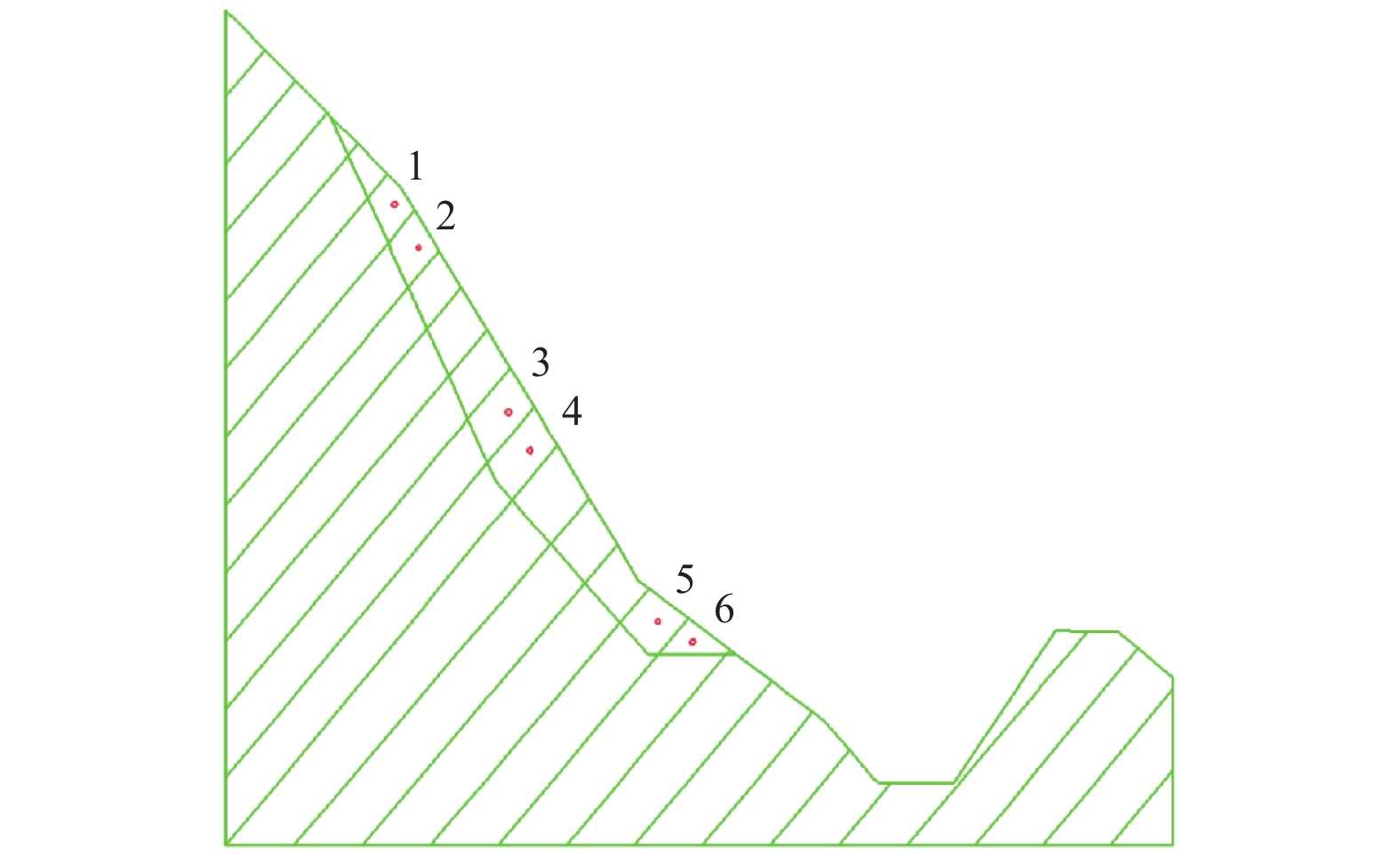
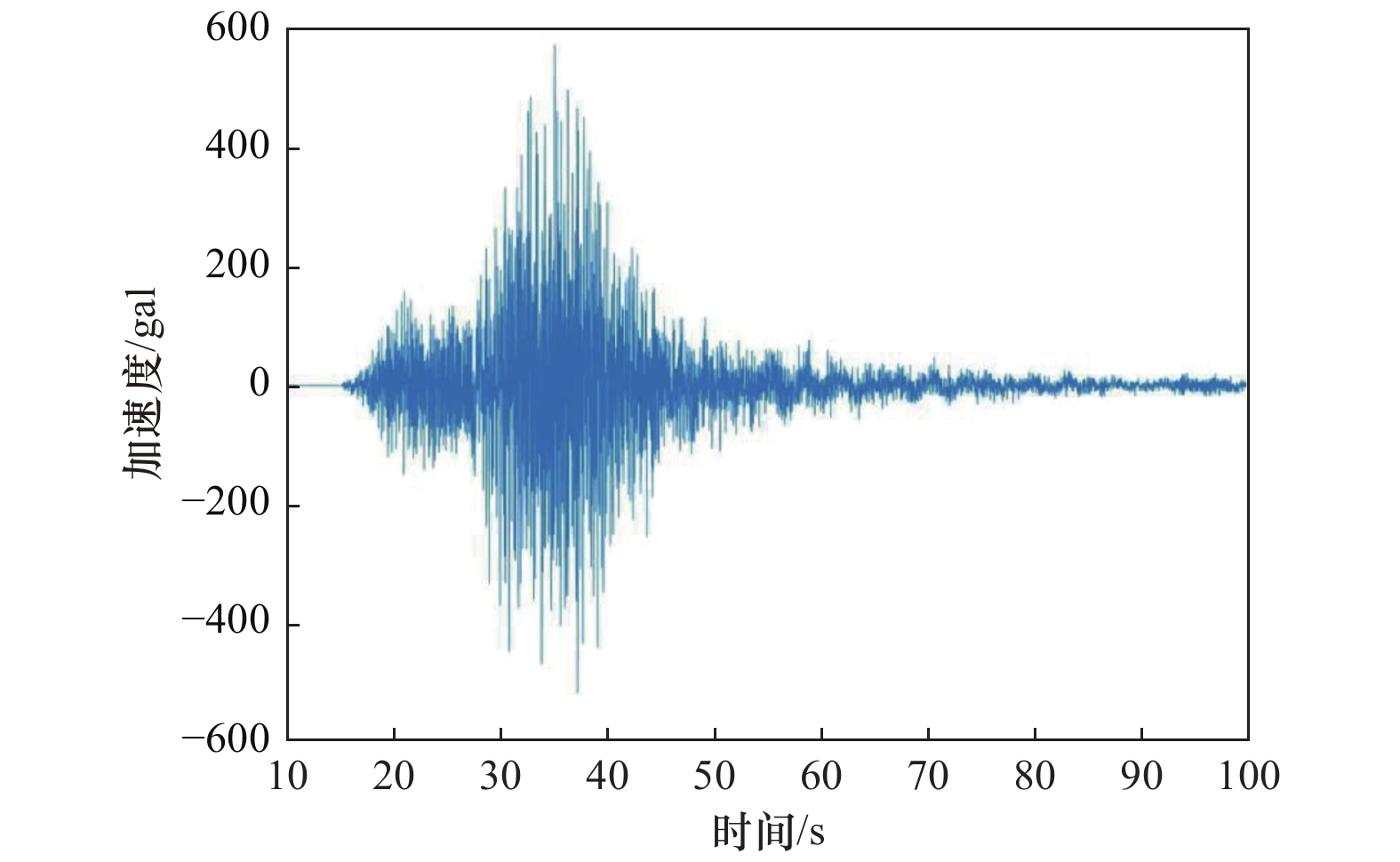
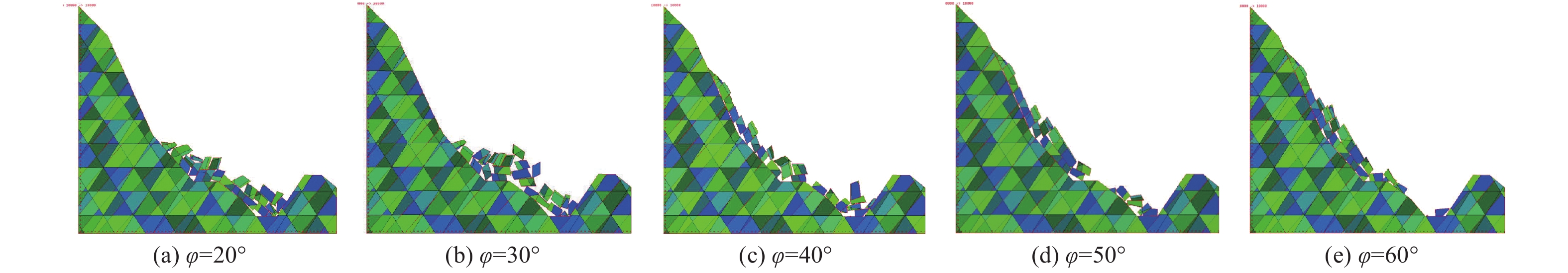
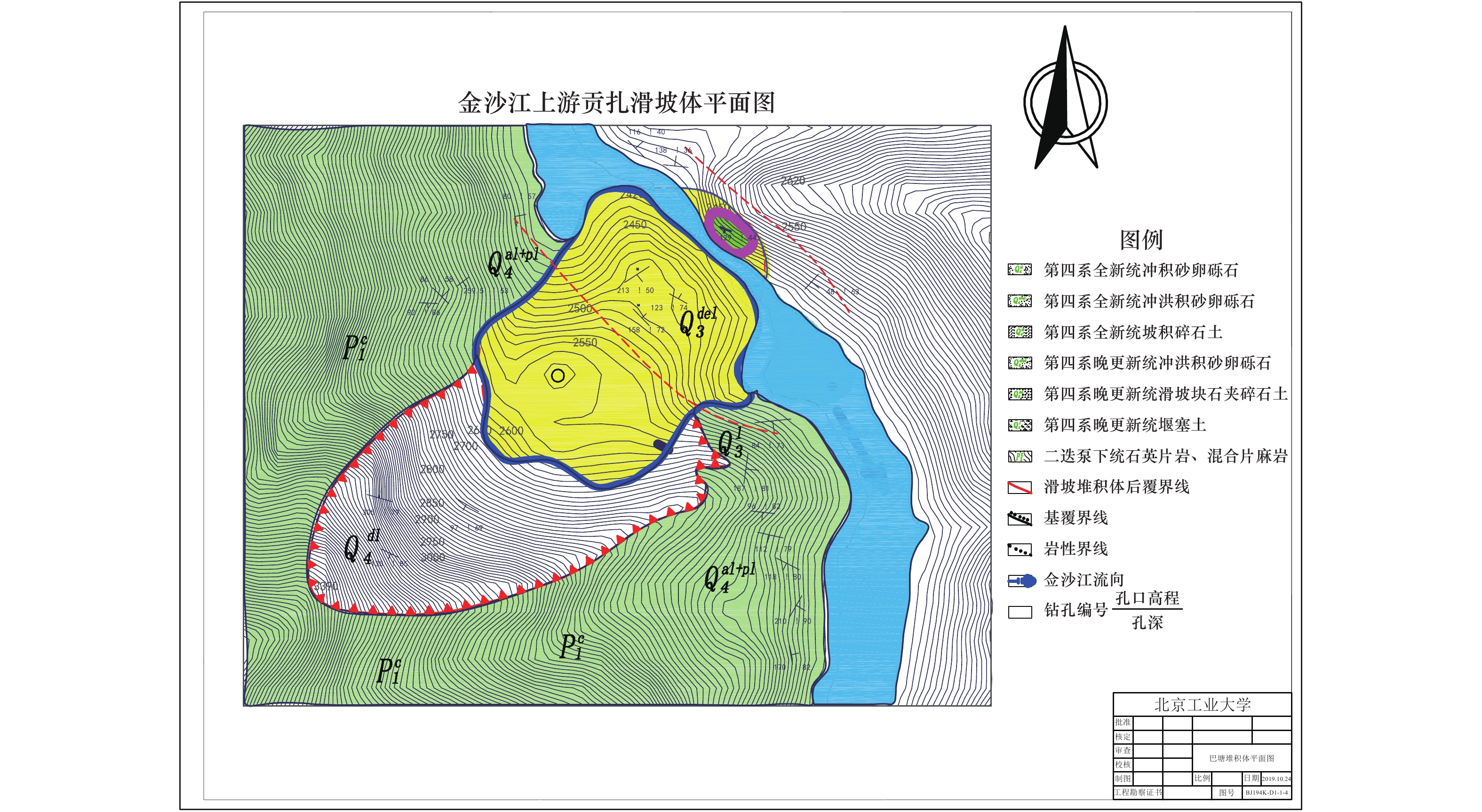
摘要: 边坡破坏是累积性过程,从变形到破坏的过程中会产生永久位移,如果永久位移过大,极有可能产生滑坡。因此根据不同工况下采集到的位移数据,分析地震作用下反倾层状岩质边坡在不同内摩擦角下的破坏特征。利用二维数值流形法(NMM),以青藏高原金沙江流域西藏昌都地区芒康县索多西乡贡扎倾倒滑坡为研究对象,依据实地考察数据及室内力学试验得到的物理力学参数,建立数值计算模型,模拟地震作用下反倾层状岩质边坡倾倒破坏过程,并在边坡上布置3组监测点获取位移数据。模拟结果表明:随着内摩擦角的增大,边坡坡体从开始破坏到新的平衡状态和达到最大位移所需的时间越短,同时,滑动块体最大水平位移逐渐减小;内摩擦角<40°时,坡体在前15 s呈整体移动趋势,大部分岩块产生整体滑移,靠近坡顶处的岩块发生轻微转动,推动前面的岩块加速滑动,呈倾倒-滑移模式;内摩擦角>40°时,靠近坡顶的岩块首先产生滑动,并转动驱使前面的岩块,推动坡脚处岩块产生滑动,最终上部岩块达到新的平衡,呈渐进式倾倒破坏,产生整体性破坏的可能性较小。Abstract: Slope failure is a cumulative process, and permanent displacement will be produced from deformation to failure process, if the value of permanent displacement is too large, it is very likely to produce landslide. Therefore, the displacement data generated by different friction angles under seismic load are used to analyze the failure characteristics of anti dip layered rock slope under different friction angles. Based on the two-dimensional numerical manifold method (NMM) proposed by Dr. Shi Genhua, the gongzha landslide in suoduoxi Township, Mangkang County, Changdu Prefecture, Tibet, is studied. According to the field investigation data and the required physical and mechanical parameters obtained from the indoor mechanical test, a numerical calculation model is established to simulate the toppling failure process of the anti inclined rock slope under the action of earthquake. In the process of simulation, three groups of monitoring points were arranged on the slope to obtain displacement data. The simulation results show that: with the increase of friction angle, the process of slope from failure to new equilibrium state and the time to reach the maximum displacement value are shorter. At the same time, the maximum horizontal displacement of the sliding block decreases gradually. When the friction angle is less than 40 degrees, the slope will move as a whole in the first 15 seconds, most of the rock blocks will slide as a whole, and the rock blocks near the top of the slope will rotate slightly to accelerate the sliding of the rock blocks in front, showing a toppling sliding mode; when the friction angle is more than 40 degrees, the rock blocks near the top of the slope will first slide and rotate to drive the rock blocks in front, and push the rock blocks at the foot of the slope to slide Finally, the upper rock mass reaches a new balance and presents progressive collapse failure, so the possibility of overall failure is small.
-
表 1 岩石力学参数取值
Table 1. Rock mechanical parameters
岩层 密度/ g·m−3 体积模量/MPa 抗拉强度/MPa 剪切模量/MPa 黏聚力/MPa 内摩擦角/° 石英片岩 2.86 1677 9.44 2500 17.23 47.39 片麻岩 1.78 1225 1.11 1 838 2.02 41.57 -
[1] 代仲海, 胡再强, 尹小涛等, 2018. 工程荷载作用下缓倾角反倾似层状岩质边坡变形稳定性分析. 岩土力学, 39(S1): 412—418.Dai Z. H., Hu Z. Q., Yin X. T., et al., 2018. Deformation stability analysis of gentle reverse inclined layer-like rock slope under engineering load. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 39(S1): 412—418. (in Chinese) [2] 韩贝传, 王思敬, 1999. 边坡倾倒变形的形成机制与影响因素分析. 工程地质学报, 7(3): 213—217. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.1999.03.004Han B. C., Wang S. J., 1999. Mechanism for toppling deformation of slope and analysis of influencing factors on it. Journal of Engineering Geology, 7(3): 213—217. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.1999.03.004 [3] 黄润秋, 2007. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制. 岩石力学与工程学报, 26(3): 433—454. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.03.001Huang R. Q., 2007. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in China since the 20th century. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 26(3): 433—454. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.03.001 [4] 李明霞, 董联杰, 2015. 层状反倾边坡变形特征及影响因素分析. 计算力学学报, 32(6): 831—837. doi: 10.7511/jslx201506019Li M. X., Dong L. J., 2015. Analysis on influential factors and deformation characteristics of toppling slope. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 32(6): 831—837. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7511/jslx201506019 [5] 刘云鹏, 邓辉, 黄润秋等, 2012. 反倾软硬互层岩体边坡地震响应的数值模拟研究. 水文地质工程地质, 39(3): 30—37.Liu Y. P., Deng H., Huang R. Q., et al., 2012. Numerical simulation of seismic response of anti-dumping rock slope interbedded by hard and soft layers. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 39(3): 30—37. (in Chinese) [6] 裴觉民, 1997. 数值流形方法与非连续变形分析. 岩石力学与工程学报, 16(3): 80—93.Pei J. M., 1997. Numerical manifold method and discontinuous deformation analysis. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 16(3): 80—93. (in Chinese) [7] 陶志刚, 张海江, 尹利洁等, 2017. 基于FDEM的戒台寺古滑体开裂破坏过程数值模拟. 水文地质工程地质, 44(3): 105—112.Tao Z. G., Zhang H. J., Yin L. J., et al., 2017. Numerical modeling of cracking for the Jietai temple ancient landslide with the combined finite-discrete element method. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 44(3): 105—112. (in Chinese) [8] 王霄, 陈志坚, 徐进鹏等, 2018. 似层状岩质边坡倾倒变形破坏过程数值模拟. 水文地质工程地质, 45(1): 137—143.Wang X., Chen Z. J., Xu J. P., et al., 2018. Numerical simulation of deformation and failure process of a toppling-sliding rock slope with a quasi-lamellar structure. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 45(1): 137—143. (in Chinese) [9] 王宇, 李晓, 王梦瑶等, 2013. 反倾岩质边坡变形破坏的节理有限元模拟计算. 岩石力学与工程学报, 32(S2): 3945—3953.Wang Y., Li X., Wang M. Y., et al., 2013. Failure mechanism of topping rock slope using jointed finite element simulation method. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 32(S2): 3945—3953. (in Chinese) [10] 王章琼, 晏鄂川, 尹晓萌等, 2014. 层状反倾岩质边坡崩塌机理研究: 以湖北鹤峰红莲池铁矿边坡为例. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 45(7): 2295—2302.Wang Z. Q., Yan E. C., Yin X. M., et al., 2014. Study on collapse mechanism of anti inclined rock slope: A case study of Honglianchi Iron Mine slope in Hefeng, Hubei province. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 45(7): 2295—2302. (in Chinese) [11] Goodman R. E., Bray J. W., 1976. Toppling of rock slopes. In: Proceedings of the Specialty Conference on Rock Engineering for Foundations and Slopes. Boulder: American Society of Civil Engineering, 201-234. -



 下载:
下载: