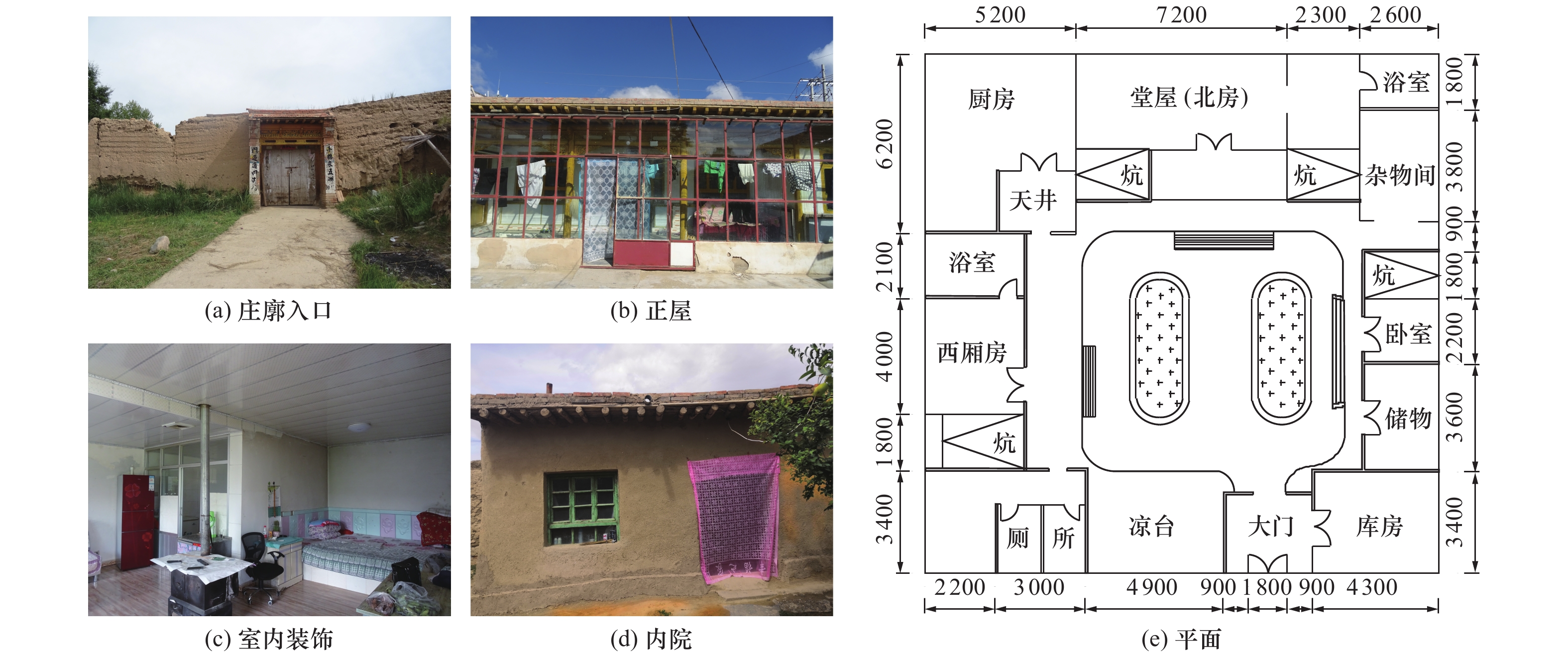
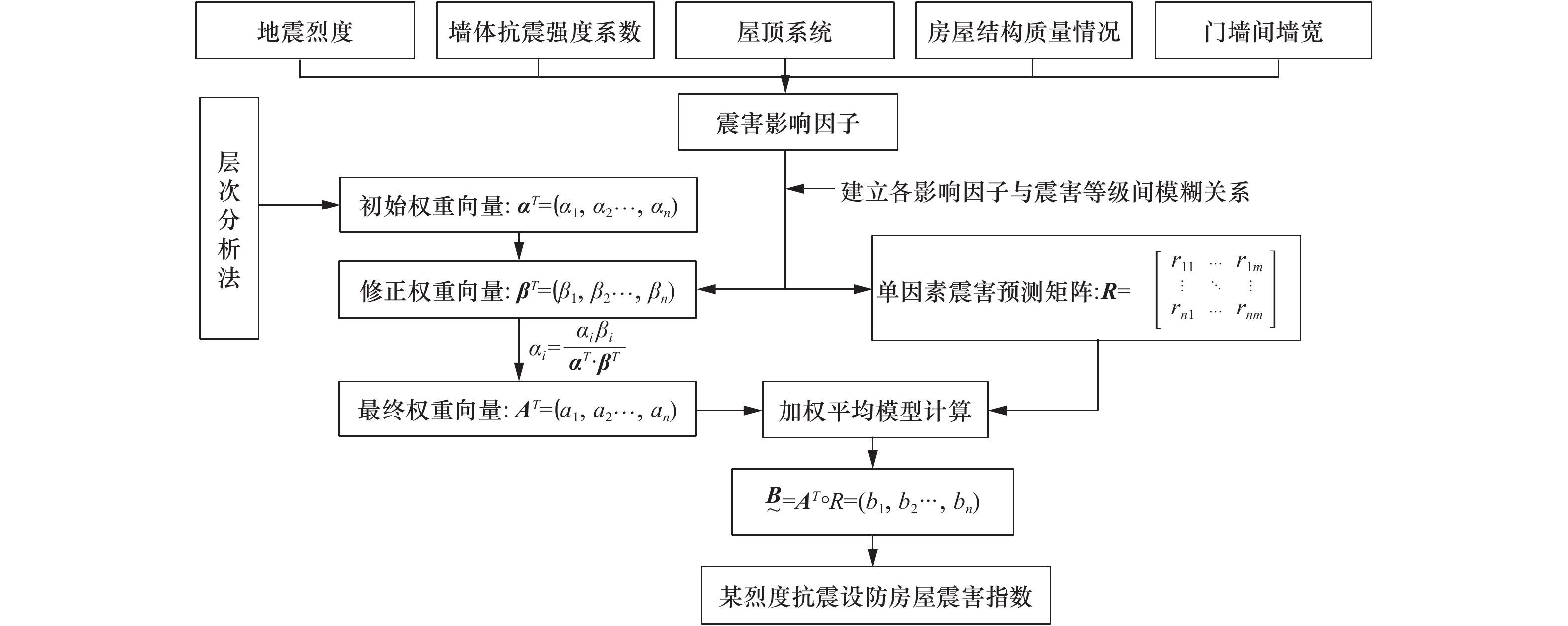
Analysis of Structural Characteristics and Seismic Performance of Rural Residential Buildings in Gonghe County, Qinghai Province
-
摘要: 青海省共和地区位于柴达木—阿尔金地震带内,具备发生中强地震的构造背景,近年来该地区地震活动频繁,农村地区受经济和技术等条件的限制,造成了巨大的人员伤亡和经济损失。为深入了解共和地区农村民居结构特征与抗震性能现状,开展实地调查,基于历史震害资料,总结区域内典型农村民居震害特点,并进行震害预测,得到不同地震烈度下农村民居不同的破坏结果。结果表明:青海省共和地区农村民居中的砖混结构和砖木结构房屋数量约占48%、47%,其中约68%砖混结构房屋未设置构造柱和圈梁等抗震设防措施;该地区主要农村民居基本达到Ⅶ度抗震设防要求,仅部分建造年代久的土木结构房屋破坏严重;地震烈度为Ⅷ度时,大部分房屋以中等破坏和严重破坏为主;地震烈度为Ⅸ、Ⅹ度时,农村民居将发生大范围严重破坏,甚至毁坏。Abstract: The Gonghe County of Qinghai Province is located in the Qaidam-Altun seismic zone, and has the tectonic background of moderate to strong earthquakes. In recent years, there have been frequent earthquake activities in Qinghai, and rural areas are restricted by economic and technological conditions, causing huge casualties and economic losses. In order to investigate the structural characteristics and seismic performance of rural residential buildings in Gonghe region, a field survey of rural houses of Qinghai Province was conducted. In addition, based on historical seismic damage data, the seismic damage characteristics of typical rural residential buildings in Qinghai Province are summarized. Finally, the seismic damage prediction analysis of buildings in the rural region that our team investigated by using the theory of seismic damage prediction was conducted, and the different damage results of the rural buildings in the different earthquake intensity ranges in Gonghe region were obtained. The results show that: The number of brick masonry buildings and brick-wood structural buildings of rural residential buildings in Gonghe region of Qinghai accounts for 48% and 47% of the total number of houses. Nearly 70% of the brick masonry buildings are not provided with seismic fortification measures such as structural columns and ring beams. The prediction results show that the main rural residential buildings basically meets the requirements of 7-degree seismic intensity protection, and only part of the soil-wood structural building built in disrepair will have severe damage; For 8-degree areas, most buildings will have medium-severe damage; For 9-or 10-degree areas, there will be extensive severe damage or even be destroyed of rural residential buildings in Gonghe County. The above research results can provide a basis for the earthquake prevention and disaster reduction work of rural residential buildings in Qinghai.
-
表 1 农村民居房屋结构类型现状
Table 1. Types and proportion of rural buildings in different villages in Gonghe region of Qinghai province
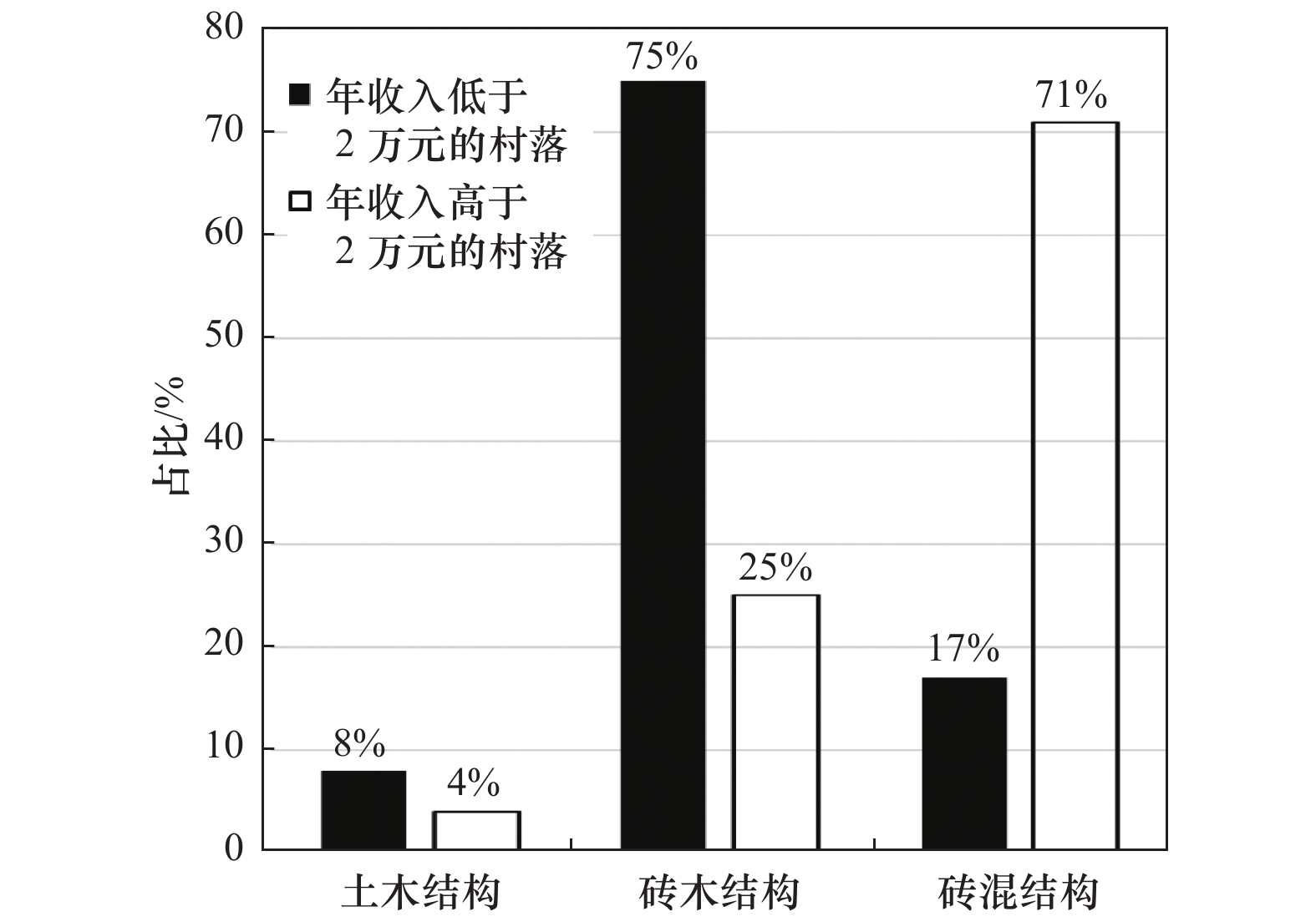
村镇 户籍人口/人 年收入/万元 房屋数/栋 砖混结构占比/% 砖木结构占比/% 土木结构占比/% 龙羊新村 700 2~3 230 80 15 5 西台村 1 376 4~5 360 60 35 5 东巴村 1 000 1~2 300 1 94 5 西香卡村 1 200 4~5 200 50 45 5 次汗素村 714 2~3 217 40 30 30 阿乙亥村 1 041 3~4 286 70 30 0 沙有村 398 1~2 104 15 85 0 上合乐寺村 908 1~2 273 8 90 2 克才村 713 1~2 213 30 60 10 次汉土亥村 1 400 2~3 340 90 5 5 下塔迈村 1 021 4~6 247 90 5 5 上塔迈村 1 610 3~4 428 60 40 0 尕当村 1 104 2~3 237 10 90 0 表 2 1990年以来青海省中强地震统计结果
Table 2. Statistics of middle-strong earthquakes of Qinghai since 1990
发震时间/
年-月-日发震地点 震级 极震区烈度 主要房屋震害情况 地震损失/
万元1990-04-26 塘格木 7.0 Ⅸ 砖柱土坯结构平房大量倒塌,砖混结构房屋屋顶局部塌落,墙身多数开裂,极震区土坯房几乎全部倒塌 7 792.46 1997-10-13 玛多县 4.2 Ⅵ 地基下陷,墙体发生倾斜和裂缝,少数房屋出现倒塌 194.54 1997-12-06 玛多县 4.4 Ⅵ 1999-09-27 河南蒙古族自治县 5.1 Ⅵ 房屋出现裂缝,墙体严重倾斜并与木架屋体分离,室内墙体有
贯穿的水平走向横断裂缝114.14 1999-11-26 玛沁县 5.0 Ⅵ 多数房屋墙体开裂、墙砖松动,极个别房屋出现附属房倒塌 1 233 2000-04-15 玉树州杂多 5.3 Ⅶ 大多数房屋墙体出现细小裂缝,木屋顶有梭瓦现象 324.1 2000-09-12 兴海县 6.6 Ⅷ 土坯房遭受严重破坏,其余建筑以墙体开裂、木架屋顶梭瓦为主 541.93 2003-04-17 德令哈 6.6 Ⅷ 大量墙体出现弯曲水平裂缝与剪切斜裂缝,墙体与砖柱脱离;屋架下弦檐口处墙体出现竖向裂缝 7 324.34 2004-05-11 德令哈 5.9 Ⅶ 旧房墙体出现严重开裂,部分房屋倒塌 5 911.8 2006-07-18 玉树州日玛村 5.0 Ⅶ 房屋承重墙与房梁、墙角及门窗连接处墙体开裂严重,部分墙体倒塌,出现墙倒房倒、柱倒房塌的震害现象 4 253.89 2006-07-19 玉树州日玛村 5.6、5.4 Ⅶ 2008-11-10 海西州大柴旦 6.3 Ⅶ 大量土木结构房屋出现墙体开裂,局部倒塌现象 26 611.32 2009-08-28 海西 6.4 Ⅶ 极震区房屋破损严重,墙面出现斜裂缝、水平裂缝,木屋架塌落 23 368.05 2010-04-14 玉树 7.1 Ⅸ 30多万间民居出现不同程度损伤,20多万间民居倒塌 7 551 000 2011-06-26 囊谦县 5.2 Ⅵ 老旧房屋毁坏情况严重,多数房屋出现墙体倒塌 6 502.81 2016-01-21 门源县 6.4 Ⅷ 墙体开裂,有竖向裂缝、横向裂缝和斜向裂缝,围墙倒塌 122 251.09 2016-10-17 玉树州杂多县 6.2 Ⅶ 大多数房屋墙体出现贯穿裂缝,少数房屋开裂 28 466 2018-05-06 玉树州称多县 5.3 Ⅵ 房屋主体结构局部开裂,多数墙体出现长裂缝,木屋顶梭瓦现象明显 11 754.5 表 3 土木结构、砖木结构房屋震害矩阵(%)
Table 3. Earthquake damage matrix of civil and brick-wood structures (Unit:%)
地震烈度 结构类型 破坏等级 基本完好 轻微破坏 中等破坏 严重破坏 毁坏 Ⅵ 砖木结构 67.5 22.0 8.9 1.4 0.2 土木结构 48.8 30.0 17.1 3.5 0.6 Ⅶ 砖木结构 32.1 32.9 25.1 8.1 1.8 土木结构 10.2 33.6 31.5 19.5 5.2 Ⅷ 砖木结构 8.8 21.7 30.2 29.5 9.8 土木结构 3.3 6.0 25.0 36.7 29.0 Ⅸ 砖木结构 0.7 7.3 19.6 40.1 32.3 土木结构 1.3 3.4 14.3 23.5 57.5 Ⅹ 砖木结构 0.4 1.4 9.7 26.3 62.2 土木结构 0.0 0.4 1.0 8.3 90.3 表 4 修正系数取值
Table 4. Correction factor value
修正因素 修正系数Ci 满足规范要求 不满足规范要求 横墙最大间距 0 0.10 楼、屋盖刚性 0 0.15 平、立面规整性 0 0.10~0.20 结构施工质量 0 0.20 符合《建筑抗震设计规范》(GB 50011—2001) −0.35 0 符合《建筑抗震设计规范》(GBJ 11—89)要求,但不符合《建筑抗震设计规范》(GB 50011—2001)要求 −0.20 0 表 5 建筑物震害等级与其相应的震害指数
Table 5. Earthquake damage grade of building and corresponding earthquake damage index
震害等级 项目 基本完好 轻微破坏 中等破坏 严重破坏 毁坏 震害指数 0 0.2 0.4 0.7 1.0 指数范围 D≤0.1 0.1<D≤0.3 0.3<D≤0.55 0.55<D≤0.85 D>0.85 表 6 农村民居基本参数
Table 6. Parameters of rural residential buildings
基本参数 砖混结构(设防) 砖混结构(未设防) 砖木结构 土木结构 结构1 结构2 结构3 结构4 结构5 结构6 建筑年份 2014 2004 2000 2000 1990 1990 房屋层数 2 1 2 1 1 1 建筑层高/m 3~4 3~4 3~4 3~4 2~3 2~3 墙体砌筑 实心 实心 实心 实心 实心 土坯 外墙厚度/cm 24 24 24 24 24 38 内墙厚度/cm 24 24 24 24 18 12 墙体抗剪强度/MPa 0.11 0.08 0.06 0.06 0.06 无 楼面(屋顶)材料 钢筋混凝土 钢筋混凝土 预制楼板 预制楼板 轻质瓦屋顶 轻质瓦屋顶 配筋间距/cm 15 15 — — — — 柱尺寸/cm 35×35 35×35 — — — — 门洞尺寸/m 2.5×3.5 2.5×3.0 2.5×3.0 2.5×3.0 1.5×2.1 1.2×2.1 窗口尺寸/m 2.1×2.5 1.8×2.1 1.5×1.8 1.5×1.8 1.2×1.5 0.8×1.2 基础 地梁 砖砌 毛石 毛石 毛石 毛石 圈梁 钢筋混凝土 钢筋混凝土 无 无 无 无 单层面积/m2 185 142 128 92 92 80 表 7 砖混结构房屋震害预测结果
Table 7. Earthquake damage prediction results of rural masonry buildings
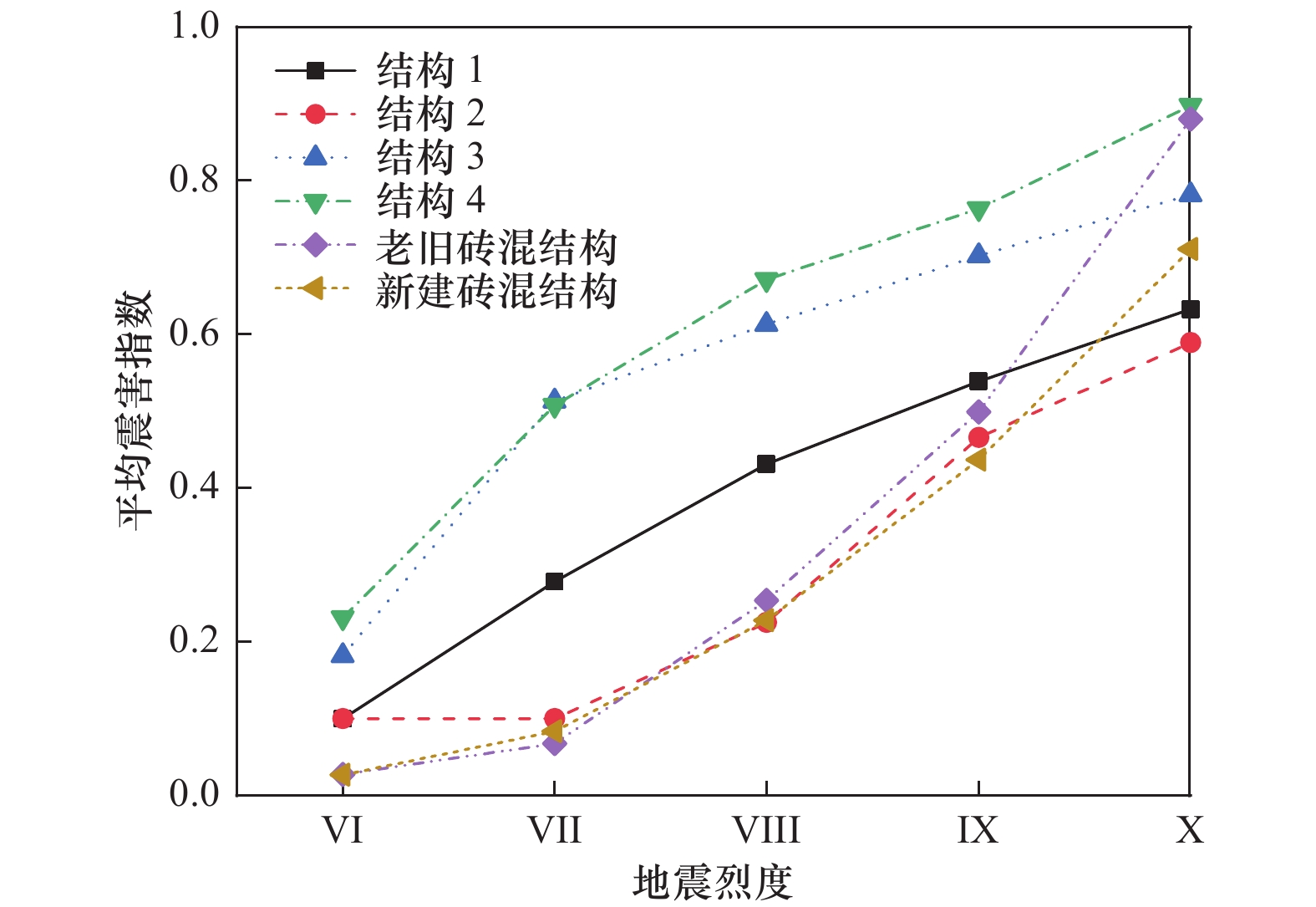
建筑物类型 项目 地震烈度 Ⅵ Ⅶ Ⅷ Ⅸ Ⅹ 结构1 震害指数 <0.100 0 0.278 6 0.431 5 0.538 9 0.632 5 震害等级 基本完好 轻微破坏 中等破坏 中等破坏 严重破坏 结构2 震害指数 <0.100 0 <0.100 0 0.225 0 0.466 0 0.589 4 震害等级 基本完好 基本完好 轻微破坏 中等破坏 严重破坏 结构3 震害指数 0.182 5 0.513 4 0.612 7 0.702 4 0.781 6 震害等级 轻微破坏 中等破坏 严重破坏 严重破坏 严重破坏 结构4 震害指数 0.231 4 0.507 4 0.671 2 0.763 2 0.897 5 震害等级 轻微破坏 中等破坏 严重破坏 严重破坏 毁坏 表 8 砖木结构房屋震害预测结果
Table 8. Earthquake damage prediction results of rural brick structural buildings
建筑物类型 项目 地震烈度 Ⅶ Ⅷ Ⅸ 结构5 震害指数 0.4 0.6 0.8 震害等级 中等破坏 严重破坏 倒塌 表 9 土木结构房屋震害预测结果
Table 9. Earthquake damage prediction results of rural civil structural buildings
建筑物类型 项目 地震烈度 Ⅶ Ⅷ Ⅸ 结构6 震害指数 0.6 0.8 0.9 震害等级 严重破坏 倒塌 倒塌 -
[1] 白国良, 薛冯, 徐亚洲, 2011. 青海玉树地震村镇建筑震害分析及减灾措施. 西安建筑科技大学学报(自然科学版), 43(3): 309—315.Bai G. L., Xue F., Xu Y. Z., 2011. Seismic damage analysis and reduction measures of buildings in village and town in the Yushu Earthquake. Journal of Xi'an University of Architecture & Technology (Natural Science Edition), 43(3): 309—315. (in Chinese) [2] 崔文河, 2015. 青海多民族地区乡土民居更新适宜性设计模式研究. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学.Cui W. H., 2015. Appropriate design pattern of the vernacular dwellings renewal of multi-ethnic areas in Qinghai. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology. (in Chinese) [3] 杜晓霞, 2016. 村镇砖砌体房屋平面外抗震能力研究. 北京: 北京工业大学.Du X. X., 2016. Research on out-of-plane seismic capacity of brick masonry buildings in rural areas. Beijing: Beijing University of Technology. (in Chinese) [4] 郭宁, 2012. 南北地震带具有区域特殊性的典型房屋建筑抗震性能分析. 哈尔滨: 中国地震局工程力学研究所.Guo N., 2012. The seismic capability anlaysis of typical building with regional and characteristics in North-South seismic belt. Harbin: Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese) [5] 郭小东, 王志涛, 段春辉, 2011. 村镇木构建筑震害预测方法. 建筑科学, 27(S2): 64—67.Guo X. D., Wang Z. T., Duan C. H., 2011. Earthquake damage assessment method for rural timber buildings. Building Science, 27(S2): 64—67. (in Chinese) [6] 刘志刚, 张守谊, 宋西战等, 1990. 青海省共和-兴海地震震害调查报告. 工程抗震, (3): 45—49. [7] 朴永军, 2013. 云南省青海省房屋地震易损性研究. 哈尔滨: 中国地震局工程力学研究所.Piao Y. J., 2013. Study on housing seismic vulnerability of Yunnan and Qinghai province. Harbin: Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese) [8] 秦松涛, 李智敏, 谭明等, 2010. 青海玉树7.1级地震震害特点分析及启示. 灾害学, 25(3): 65—70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2010.03.014Qin S. T., Li Z. M., Tan M., et al., 2010. Analysis of damage characteristics of the M 7.1 Yushu earthquake of Qinghai and the enlightenments. Journal of Catastrophology, 25(3): 65—70. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2010.03.014 [9] 邱舒睿, 高惠瑛, 2015. 青海省农居地震灾害易损性研究. 震灾防御技术, 10(4): 969—978. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20150415Qiu S. R., Gao H. Y., 2015. The research of rural dwelling's seismic vulnerability in Qinghai. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 10(4): 969—978. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20150415 [10] 邵峰, 2017. 江西地震重点监视防御区内村镇房屋抗震能力调查与分析. 南昌: 南昌大学.Shao F., 2017. Investigation and analysis of rural houses in Jiangxi earthquake monitoring area. Nanchang: Nanchang University. (in Chinese) [11] 苏延芬, 王铭勇, 2013. 青海农村民居抗震性能调查与分析. 建筑科学, 29(9): 13—16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8528.2013.09.003Su Y. F, Wang M. Y, 2013. Investigation and analysis on seismic performance of rural houses in Qinghai. Building Science, 29(9): 13—16. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8528.2013.09.003 [12] 唐月, 李玉荣, 蔡康锋, 2012. 关于砖混结构震害预测方法的探讨. 混凝土与水泥制品, (2): 57—60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4637.2012.02.015Tang Y., Li Y. R., Cai K. F., 2012. Discussion on methods for seismic damage prediction in brick-and-concrete composite construction. China Concrete and Cement Products, (2): 57—60. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4637.2012.02.015 [13] 王强, 2009. 砖木结构房屋抗震性能评价方法研究. 兰州: 中国地震局兰州地震研究所.Wang Q., 2009. The methodological analysis on the assessment of the anti-seismic performance of the brick-wood building. Lanzhou: China Earthquake Administration Lanzhou Institute of Seismology. (in Chinese) [14] 王强, 王兰民, 袁中夏等, 2011. 基于模糊数学的农村砖木民房震害预测研究. 西北地震学报, 33(3): 279—283.Wang Q., Wang L. M., Yuan Z. X., et al., 2011. Study on earthquake damage prediction of the rural brick-wood building based on fuzzy mathematics. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 33(3): 279—283. (in Chinese) [15] 杨娜, 王龙, 刘爱文等, 2018. 青海东南部农村民居结构特点及抗震能力分析. 震灾防御技术, 13(1): 206—214. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20180119Yang N., Wang L., Liu A. W., et al., 2018. Structural characteristics and seismic capacity analysis of rural buildings in the southeast of Qinghai province. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 13(1): 206—214. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20180119 [16] 尹之潜, 李树桢, 杨淑文等, 1990. 震害与地震损失的估计方法. 地震工程与工程振动, 10(1): 99—108.Yin Z. Q., Li S. Z., Yang S. W., et al., 1990. Estimating method of seismic damage and seismic loss. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 10(1): 99—108. (in Chinese) [17] 尹之潜, 1996. 结构易损性分类和未来地震灾害估计. 中国地震, 12(1): 49—55.Yin Z. Q, 1996. Classification of structure vulnerability and evaluating earthquake damage from future earthquake. Earthquake Research in China, 12(1): 49—55. (in Chinese) [18] 中国地震局监测预报司, 1996. 中国大陆地震灾害损失评估汇编: 1990—1995. 北京: 地震出版社. [19] 中国地震局监测预报司, 2001. 中国大陆地震灾害损失评估汇编: 1996—2000. 北京: 地震出版社. [20] 中国地震局监测预报司, 2010. 2001—2005年中国大陆地震灾害损失评估报告汇编. 北京: 地震出版社. [21] 中国地震局震灾应急救援司, 2015. 2006—2010年中国大陆地震灾害损失评估汇编. 北京: 地震出版社. [22] 钟秀梅, 袁中夏, 常想德等, 2019. 西北地区农村房屋结构细化分类及抗震性能分析. 地震研究, 42(2): 151—157. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2019.02.001Zhong X. M., Yuan Z. X., Chang X. D., et al., 2019. Structure refinement and seismic performance analysis of rural houses in northwest China. Journal of Seismological Research, 42(2): 151—157. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2019.02.001 [23] 左丹, 2015. 青海乡村传统民居院落景观的设计研究. 西宁: 青海大学.Zuo D., 2015. The study of the courtyard landscape design of Qinghai rural tradtion residence. Xining: Qinghai University. (in Chinese) -



 下载:
下载: