Experimental Study on Seismic Performance of Mortise-tenon Joints of Traditional Wood Residences in North China Villages
-
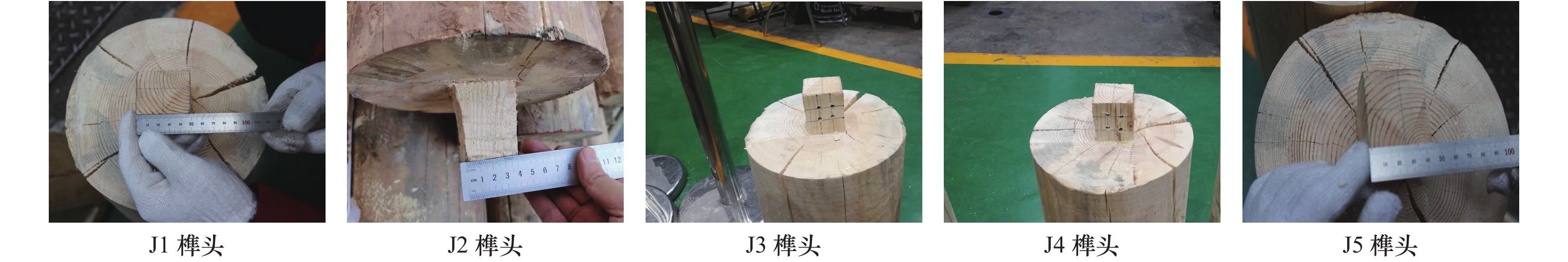
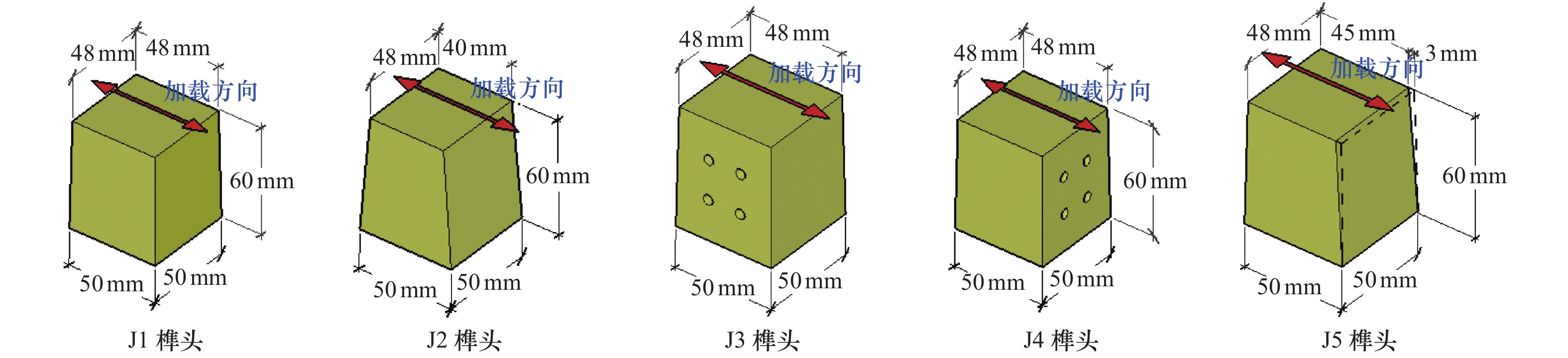
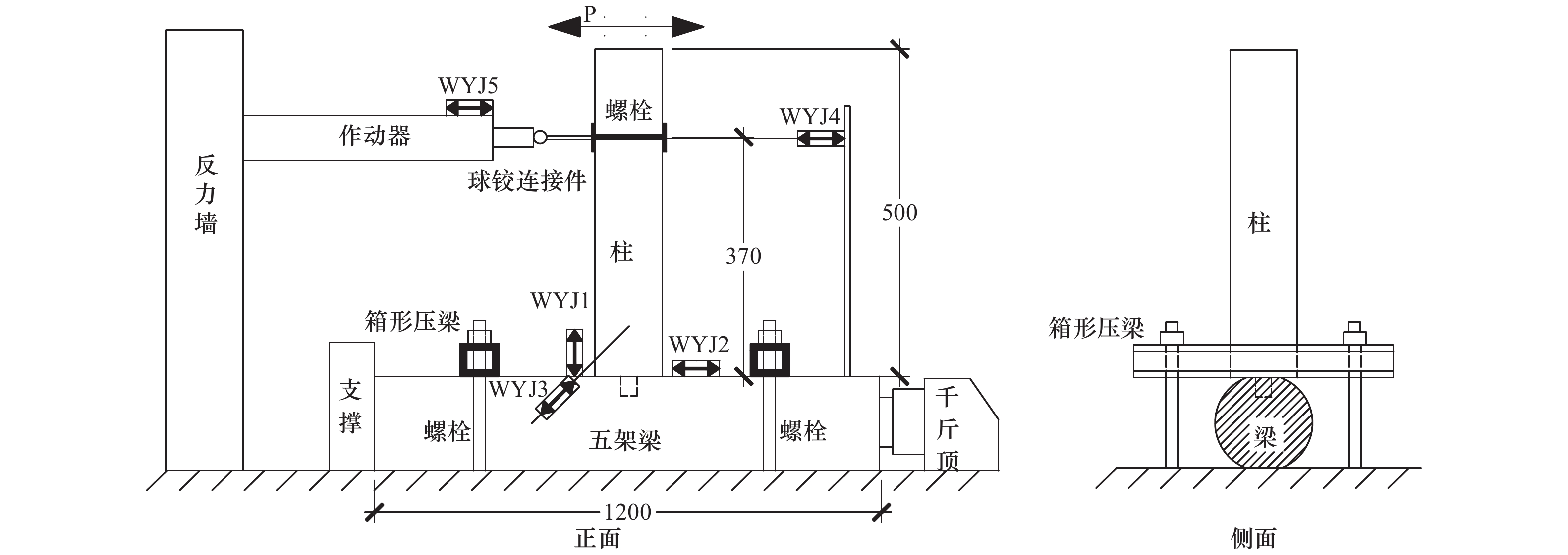
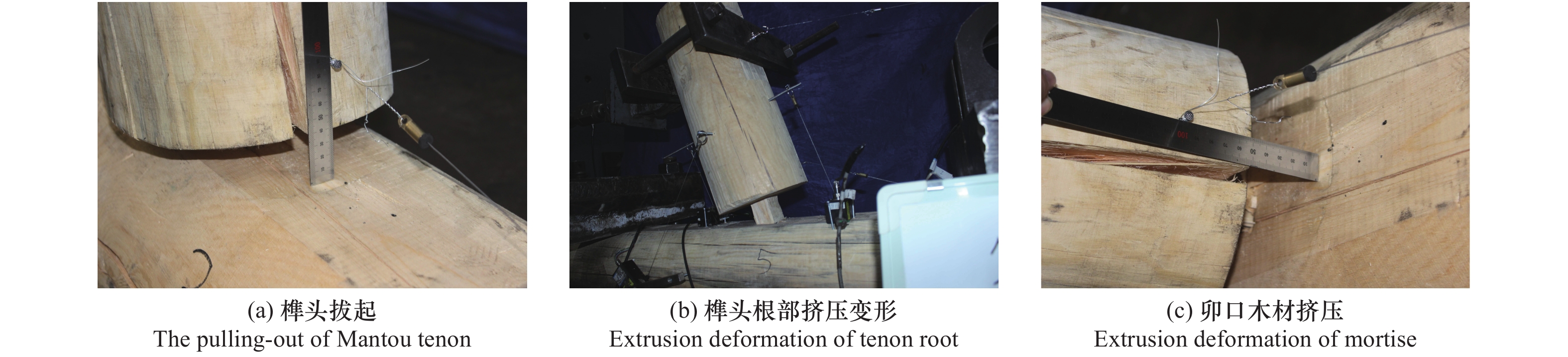
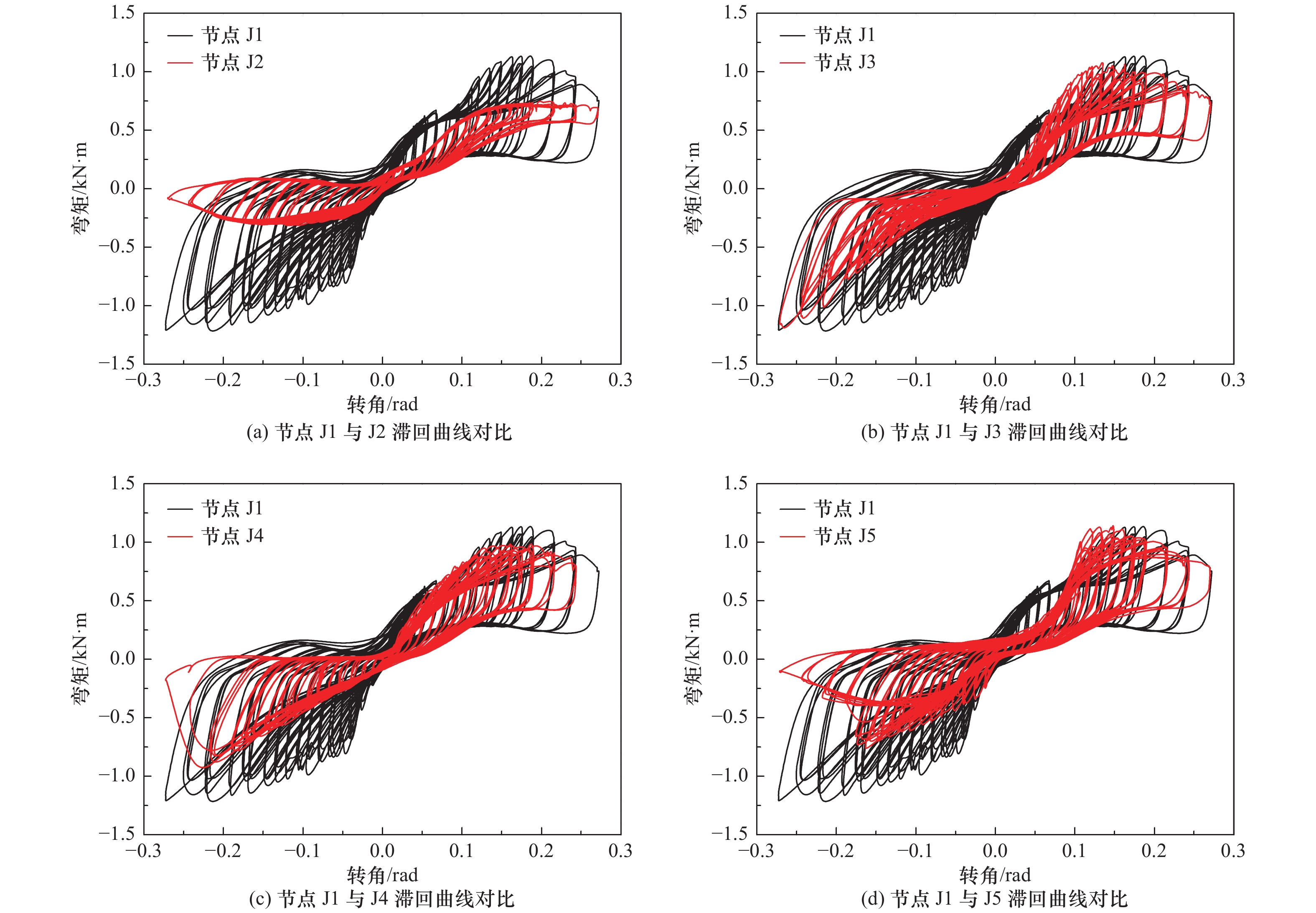
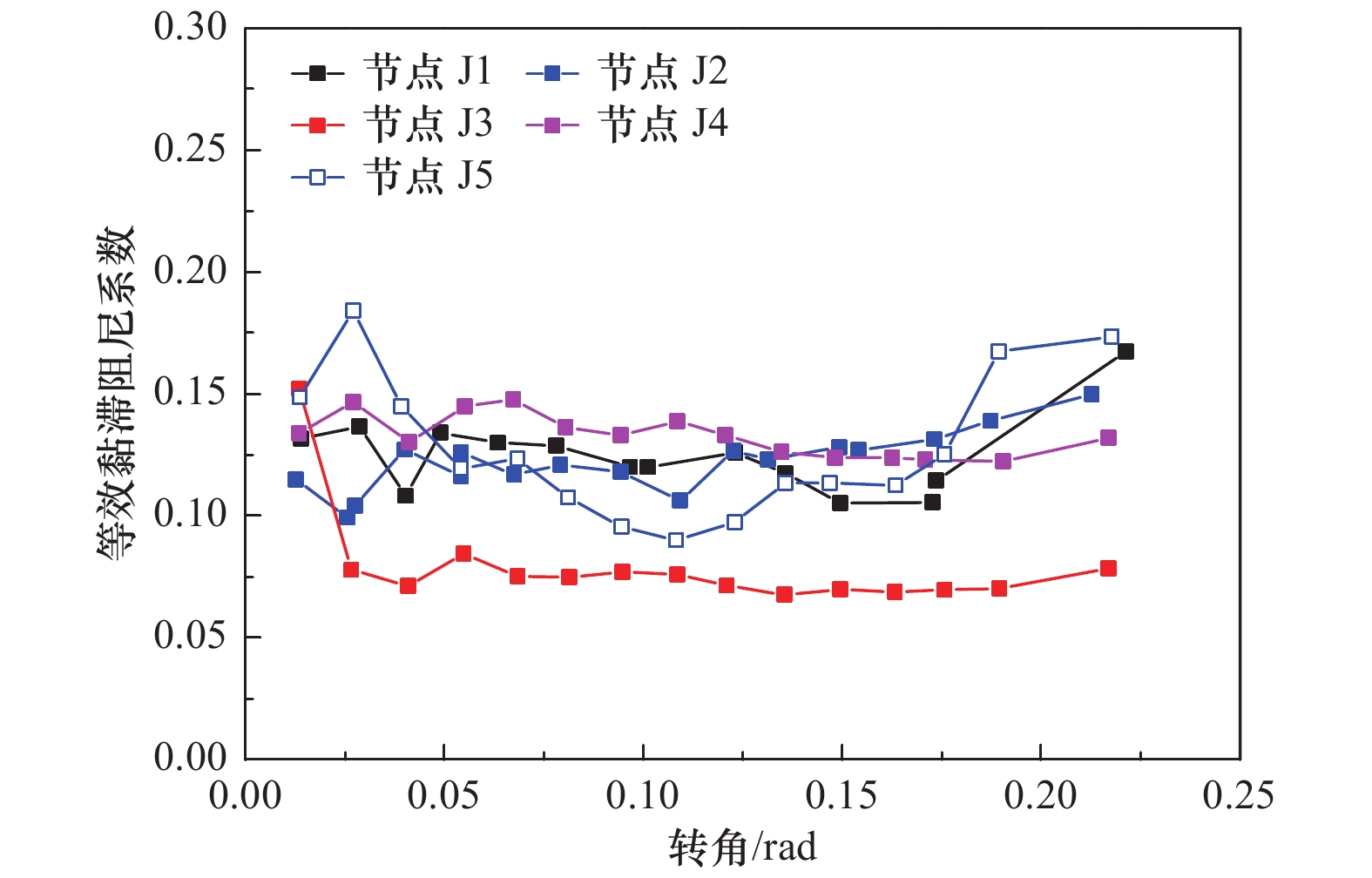
摘要: 现存的传统村落木结构民居,由于受风雨侵蚀及战乱、地震、火灾的破坏,发生不同程度的损伤和破坏,榫卯节点残损情况直接影响整个民居房屋结构的安全。以北方地区传统村落“四梁八柱”木结构民居榫卯节点(馒头榫)为研究对象,考虑不同残损类型及程度,制作5个足尺梁柱节点模型,通过拟静力低周往复加载试验研究其破坏模式、弯矩-转角滞回响应及骨架曲线、加载刚度、变形、强度及耗能能力等力学性能。试验结果表明:馒头榫节点破坏模式表现为榫头拔出、榫与卯口挤压变形;相比于完好节点,残损馒头榫节点抗弯承载力、加载刚度和耗能能力明显降低,且“捏拢”效应加剧;榫头松动是导致节点力学性能降低的直接原因;垂直加载方向虫蛀节点力学性能劣化程度强于平行加载方向虫蛀节点,更易导致耗能能力降低。Abstract: The existing traditional wood residences in villages have experienced different levels of degradation of structural performance, due to long-term weatherworn and damage from war, earthquake and fire. The damaged mortise-tenon joints play a critical role on the safety of these buildings. In this study, taking mortise-tenon joints of “four beams and eight pillars” wood residences in ancient villages of North China as the research object, five full size beam-column joints (Mantou joints) were fabricated with different manually simulated damage types and degrees. The failure modes, hysteretic curves of moment-angle, envelope curves, stiffness, strength, deformation and energy dissipation of theses joists were studied by low-reversed cyclic loading test. It indicates the tenon pulling out and extrusion deformation between mortise and tenon are main failure modes. The rotational moment, strength, stiffness and energy dissipation capacity of damaged joints are significantly lower than those of the intact joint, and the pinch effect of damaged joints are more obvious. The looseness of tenon is the direct reason for degradation of mechanical properties of joints. The termites decay direction perpendicular to loading direction has more serious deterioration for mechanical performance of joints than that of parallel direction, which more easily results in decrease of energy dissipation.
-
Key words:
- Traditional village buildings /
- Matou joints /
- Damage /
- Quasi-static test
-
表 1 樟子松清材试件力学性能
Table 1. Mechanical property of Pinus sylvestris clean specimens
顺纹抗压强度
/MPa顺纹抗拉强度
/MPa顺纹抗压弹性模量
/MPa横纹(径向)弹性模模
/MPa横纹(弦向)弹性模量
/MPa含水率
/%横纹抗压(全表面)强度
/MPa横纹抗压(局部)强度
/MPa抗弯强度
/MPa28.6 88.6 9420 112 139 24.3 3.3 6.1 64.4 表 2 各节点力学性能参数
Table 2. Mechanical property parameters of Mantou mortise-tenon joints
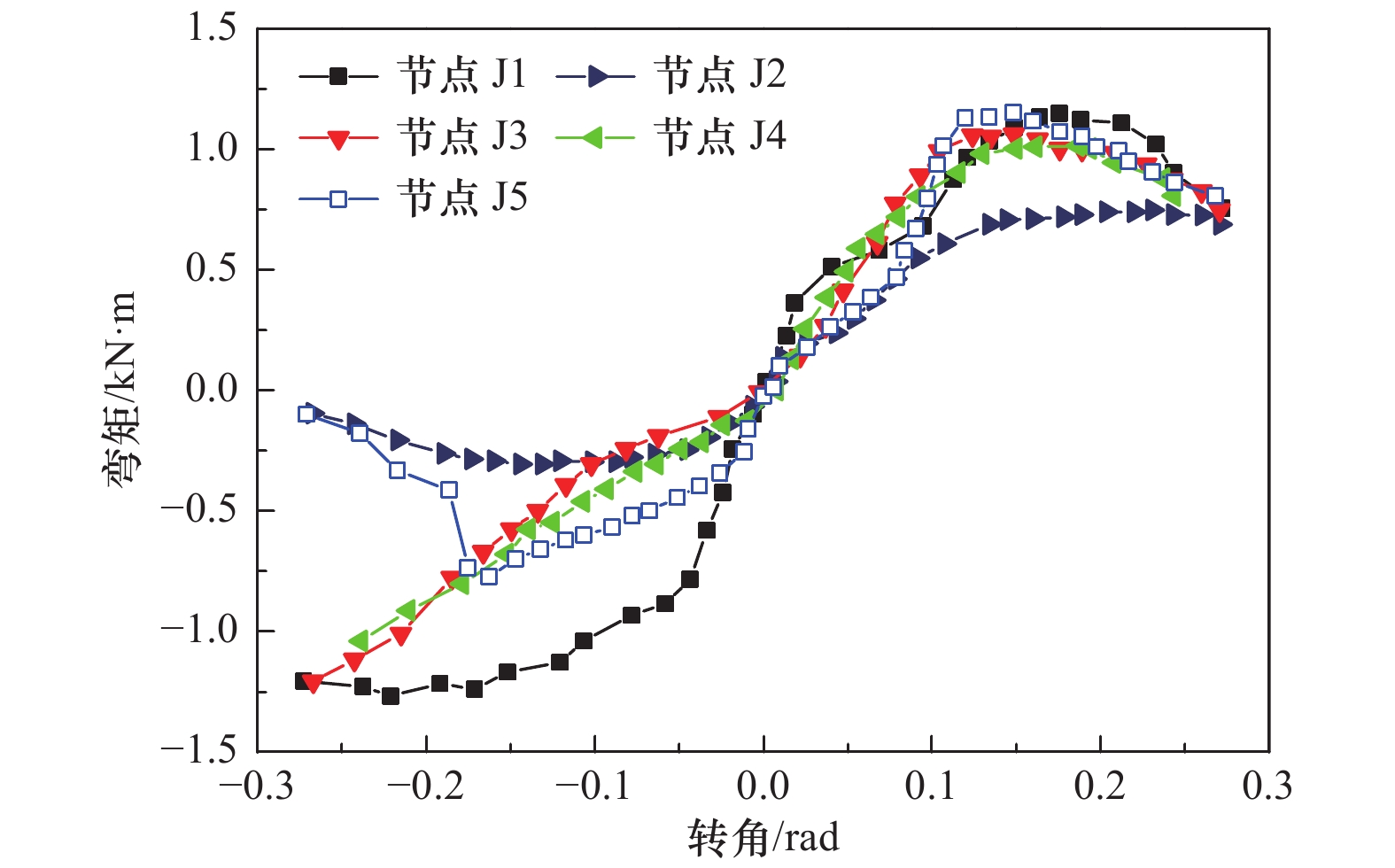
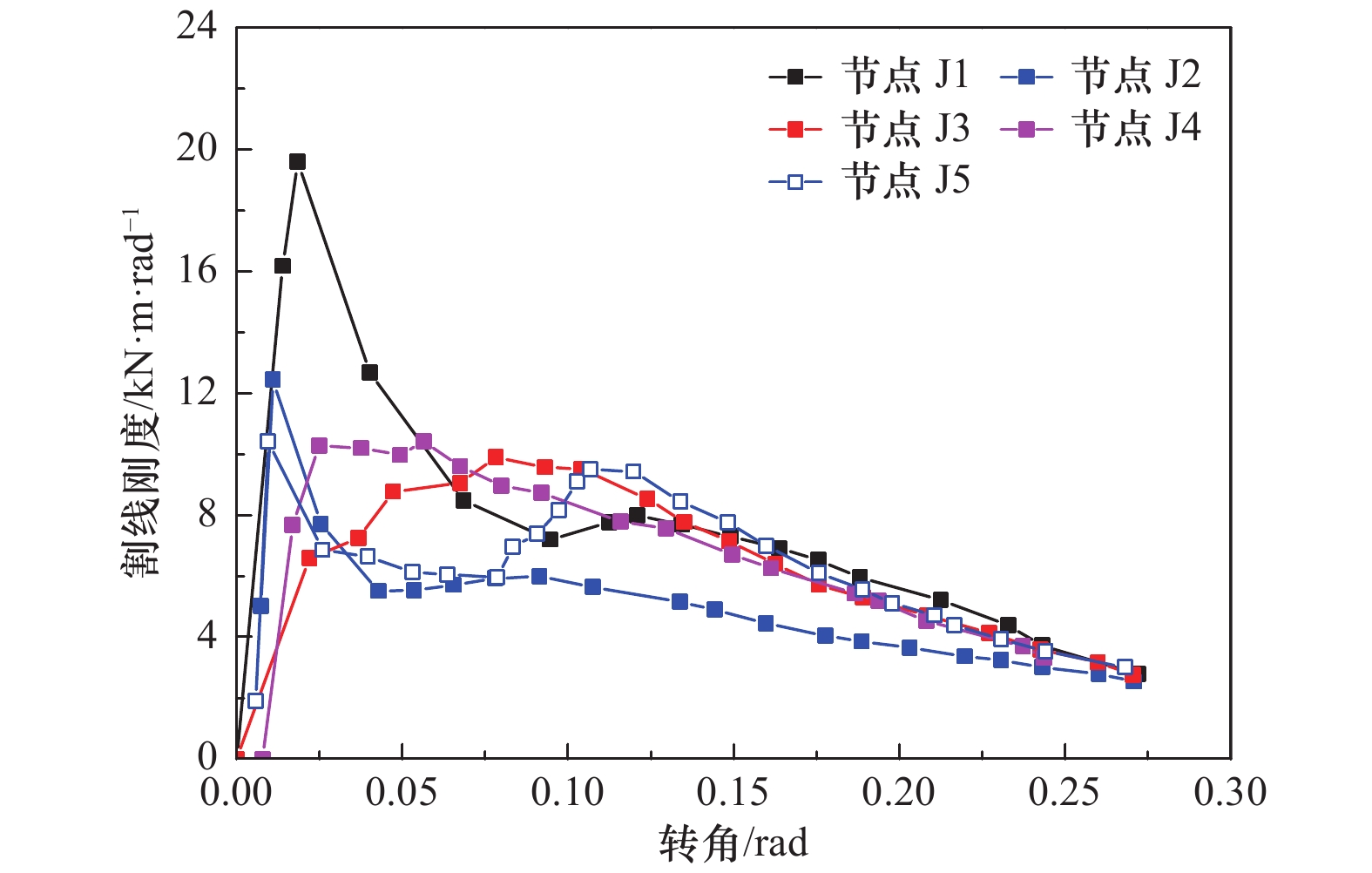
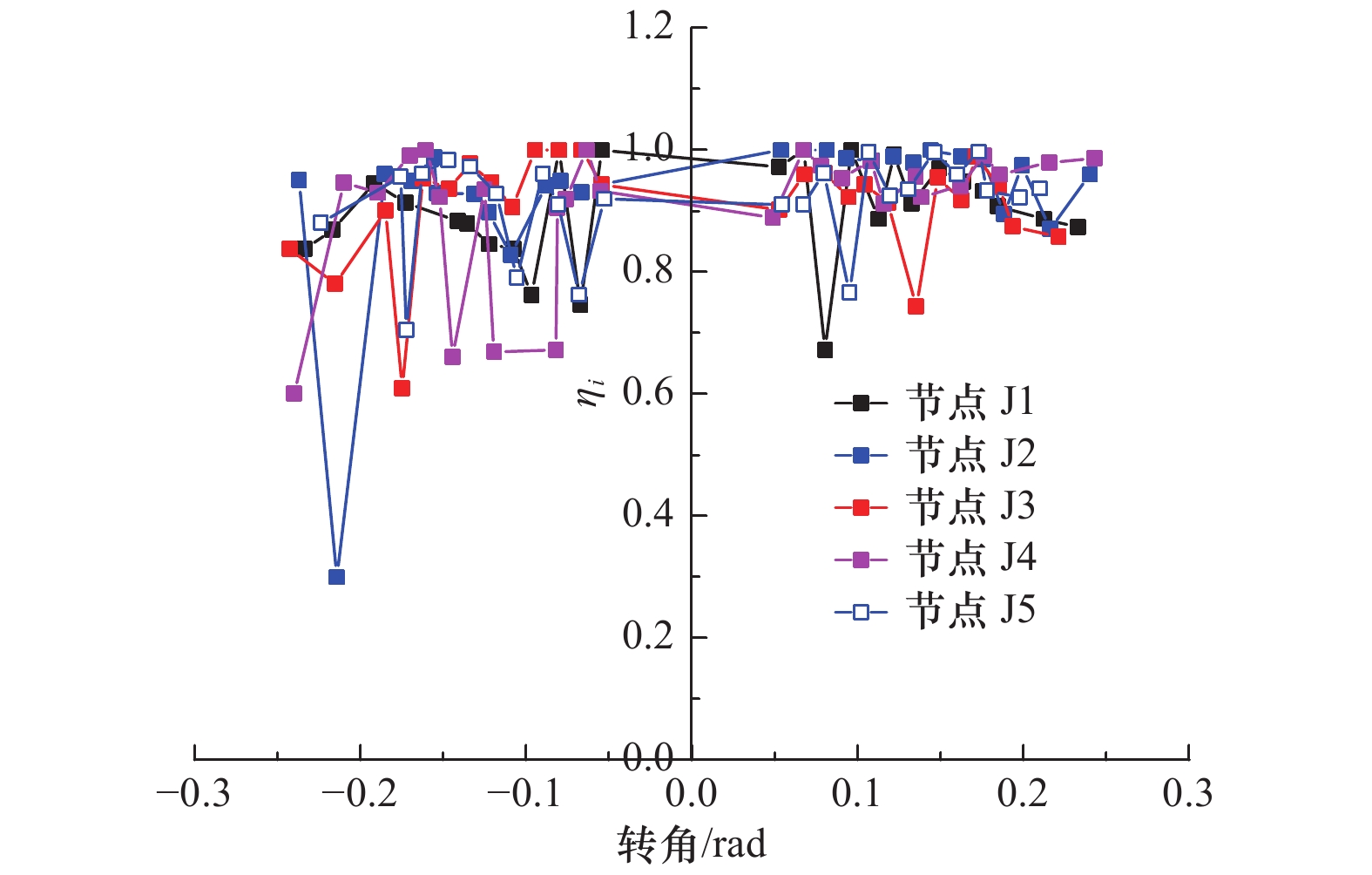
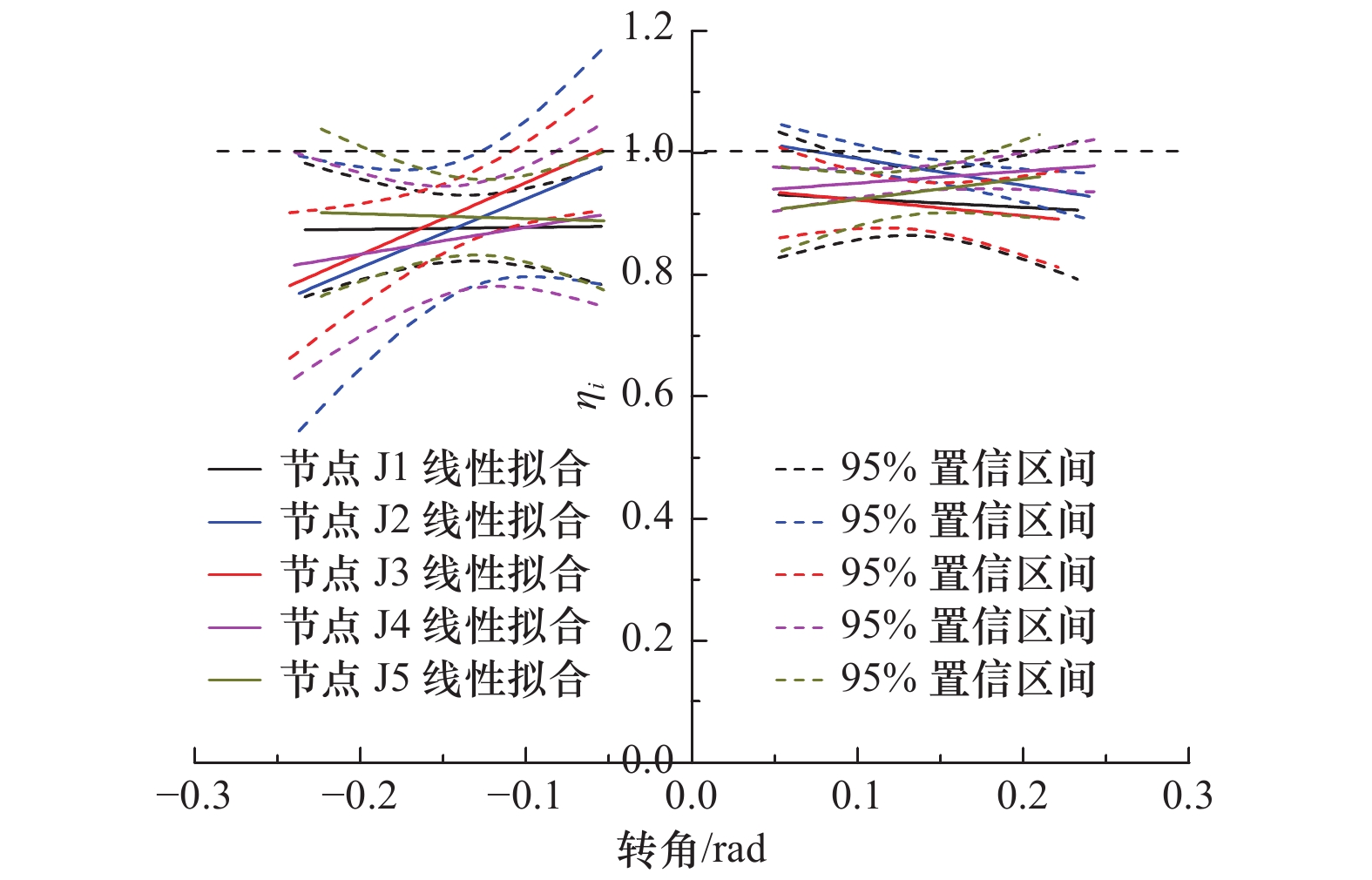
节点编号 加载方向 θy/rad θmax/rad Mmax/(kN∙m) θu/rad Mu/(kN∙m) μ 降低幅度/% 延性系数 承载力 J1 正向 0.064 0.176 1.153 1.212 0.237 0.922 3.70 — — 负向 0.066 0.221 1.27 — — — J2 正向 0.119 0.230 0.750 0.532 — — — 18 56 负向 0.062 0.142 0.314 −0.19 0.251 3.04 J3 正向 0.105 0.126 1.053 1.132 0.229 0.842 2.18 41 7 负向 0.070 0.264 1.210 — — — J4 正向 0.085 0.173 1.017 1.031 0.239 0.814 2.81 24 15 负向 0.066 0.239 1.045 — — — J5 正向 0.075 0.148 1.146 0.962 0.213 0.917 2.84 17 21 负向 0.052 0.164 0.778 0.174 0.622 3.32 -
[1] 淳庆, 潘建伍, 2015. 江南地区抬梁木构建筑馒头榫节点受力性能研究. 四川大学学报(工程科学版), 47(5): 23—29.Chun Q., Pan J. W., 2015. Research on mechanical properties of Mantou mortise-tenon joints in the post-and-lintel constructions of the traditional timber buildings in the South Yangtze River regions. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition), 47(5): 23—29. (in Chinese) [2] 淳庆, 潘建伍, 韩宜丹, 2016a. 江南地区传统木构建筑半榫节点受力性能研究. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 43(1): 124—131.Chun Q., Pan J. W., Han Y. D., 2016a. Research on mechanical properties of ban mortise-tenon joint of the traditional timber buildings in the South Yangtze river regions. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 43(1): 124—131. (in Chinese) [3] 淳庆, 潘建伍, 董运宏, 2016b. 江南地区传统木构建筑透榫节点受力性能研究. 西南交通大学学报, 51(5): 862—869.Chun Q., Pan J. W., Dong Y. H., 2016b. Mechanical properties of Tou mortise-tenon joints of the traditional timber buildings in the South Yangtze river regions. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 51(5): 862—869. (in Chinese) [4] 隋䶮, 赵鸿铁, 薛建阳等, 2010. 古建筑木结构直榫和燕尾榫节点试验研究. 世界地震工程, 26(2): 88—92.Duo Y., Zhao H. T., Xue J. Y., et al., 2010. Experimental study on characteristics of mortise-tenon joints in historic timber buildings. World Earthquake Engineering, 26(2): 88—92. (in Chinese) [5] 高大峰, 邓红仙, 刘静等, 2014. 明清木结构榫卯节点拟静力试验研究. 世界地震工程, 30(4): 8—16.Gao D. F., Deng H. X., Liu J., et al., 2014. Pseudostatic experimental study on mortise and Tenon joints of timber structures of Chinese Ming and Qing Dynasties. World Earthquake Engineering, 30(4): 8—16. (in Chinese) [6] 高永林, 陶忠, 叶燎原等, 2015. 传统木结构典型榫卯节点基于摩擦机理特性的低周反复加载试验研究. 建筑结构学报, 36(10): 139—145.Gao Y. L., Tao Z., Ye L. Y., et al., 2015. Low-cycle reversed loading tests study on typical mortise-tenon joints of traditional timber building based on friction mechanism. Journal of Building Structures, 36(10): 139—145. (in Chinese) [7] 郭光玲, 张敏, 2019. 汉中村镇砖木结构房屋抗震现状及处理方法研究. 震灾防御技术, 14(4): 760—768. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20190407Guo G. L., Zhang M., 2019. Study on seismic resistance situation and treatment methods on brick-wood structure houses in towns and villages of Hanzhong. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 14(4): 760—768. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20190407 [8] 郭光玲, 2020. 陕南村镇住宅结构体系抗震能力评价研究——以汉中市留坝县为例. 震灾防御技术, 15(1): 56—65. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20200106Guo G. L., 2020. Research on evaluation of seismic capability of rural residential structure system in Southern Shaanxi Province-in the Case of Liuba County, Hanzhong City. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 15(1): 56—65. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20200106 [9] 李佳韦, 林金禄, 林敏郎等, 2007. 台湾传统建筑直榫木接头力学行为研究. 台湾林业科学, 22(2): 125—134.Lee C. W., Lin C. L., Lin M. L., et al., 2007. Studies of the mechanical behavior of tenon and mortise wood joints used in traditional Taiwanese construction. Taiwan Journal Forest Science, 22(2): 125—134. [10] 李佳韦, 2006. 中国传统建筑直榫木接头力学行为研究. 台湾, 中国: 台湾大学.Lee C. W., 2006. The structural behavior of defective plug-in joint in Chinese traditional wooden frames.Taiwan, China: National Chung Hsing University. (in Chinese) [11] 李忠献, 2004. 工程结构试验理论与技术. 天津: 天津大学出版社.Li Z. X., 2004. Theory and technique of engineering structure experiments. Tianjin: Tianjin University Press. (in Chinese) [12] 马炳坚, 2018. 中国古建筑木作营造技术. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社.Ma B. J., 2018. Wooden construction technology of Chinese ancient architecture. 2nd ed. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) [13] 王满生, 杨威, 陈俞等, 2012. 北京地区农村砖木结构振动台试验研究. 地震工程与工程振动, 32(1): 128—133.Wang M. S., Yang W., Chen Y., et al., 2012. Shaking table test on a typical brick-timber structure model in rural areas of Beijing. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 32(1): 128—133. (in Chinese) [14] 王满生, 赵晓敏, 纪晓东等, 2015. 北京地区典型砖木结构农宅抗震加固性能研究. 土木建筑与环境工程, 37(6): 62—69.Wang M. S., Zhao X. M., Ji X. D., et al., 2015. Earthquake resistant behavior on seismic strengthening of typical rural brick-wood structure in Beijing. Journal of Civil, Architectural & Environmental Engineering, 37(6): 62—69. (in Chinese) [15] 谢启芳, 郑培君, 向伟等, 2014. 残损古建筑木结构单向直榫榫卯节点抗震性能试验研究. 建筑结构学报, 35(11): 143—150.Xie Q. F., Zheng P. J., Xiang W., et al., 2014. Experimental study on seismic behavior of damaged straight mortise-tenon joints of ancient timber buildings. Journal of Building Structures, 35(11): 143—150. (in Chinese) [16] 谢启芳, 杜彬, 向伟等, 2015. 古建筑木结构燕尾榫节点抗震性能及尺寸效应试验研究. 建筑结构学报, 36(3): 112—120.Xie Q. F., Du B., Xiang W., et al., 2015. Experimental study on seismic behavior and size effect of dovetail mortise-tenon joints of ancient timber buildings. Journal of Building Structures, 36(3): 112—120. (in Chinese) [17] 熊立红, 阳超, 2017. 砌体结构的抗震研究现状. 地震工程与工程振动, 37(3): 111—119.Xiong L. H., Yang C., 2017. An overview of research on seismic behavior of masonry structures. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics, 37(3): 111—119. (in Chinese) [18] 薛建阳, 夏海伦, 李义柱等, 2017. 不同松动程度下古建筑透榫节点抗震性能试验研究. 西安建筑科技大学学报(自然科学版), 49(4): 463—469, 477.Xue J. Y., Xia H. L., Li Y. Z., et al., 2017. Experimental study on seismic behavior of penetrated mortise-tenon joints under different degree of looseness in ancient buildings. Journal of Xi′an University of Architecture & Technology (Natural Science Edition), 49(4): 463—469, 477. (in Chinese) [19] 杨娜, 王龙, 刘爱文等, 2018. 青海东南部农村民居结构特点及抗震能力分析. 震灾防御技术, 13(1): 206—214. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20180119Yang N., Wang L., Liu A. W., et al., 2018. Structural characteristics and seismic capacity analysis of rural buildings in the southeast of Qinghai Province. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 13(1): 206—214. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20180119 [20] 杨威, 王满生, 纪晓东等, 2014. 北京农村砖木结构抗震加固动力特性分析. 土木工程学报, 47(3): 26—32.Yang W., Wang M. S., Ji X. D., et al., 2014. Dynamic characteristic analysis on seismic strengthening of existing rural masonry-timber buildings in Beijing. China Civil Engineering Journal, 47(3): 26—32. (in Chinese) [21] 姚侃, 赵鸿铁, 葛鸿鹏, 2006. 古建木结构榫卯连接特性的试验研究. 工程力学, 23(10): 168—173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2006.10.032Yao K., Zhao H. T., Ge H. P., 2006. Experimental studies on the characteristic of mortise-tenon joint in historic timber buildings. Engineering Mechanics, 23(10): 168—173. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2006.10.032 [22] Han S. R., Lee J. J., 2006. Mechanical performance of Korean traditional wooden building of the column-girder tenon-joint by joint type. In: Proceedings of the 9th World Conference on Timber Engineering. Portland, USA. [23] King W. S., Yen J. Y. R., Yen Y. N. A., 1996. Joint characteristics of traditional Chinese wooden frames. Engineering Structures, 18(8): 635—644. doi: 10.1016/0141-0296(96)00203-9 -




 下载:
下载: