Based on the Infinite Element Boundary Analysis, the Study of the Effect of Continuous Barrier on the Environmental Vibration of High-speed Railway
-
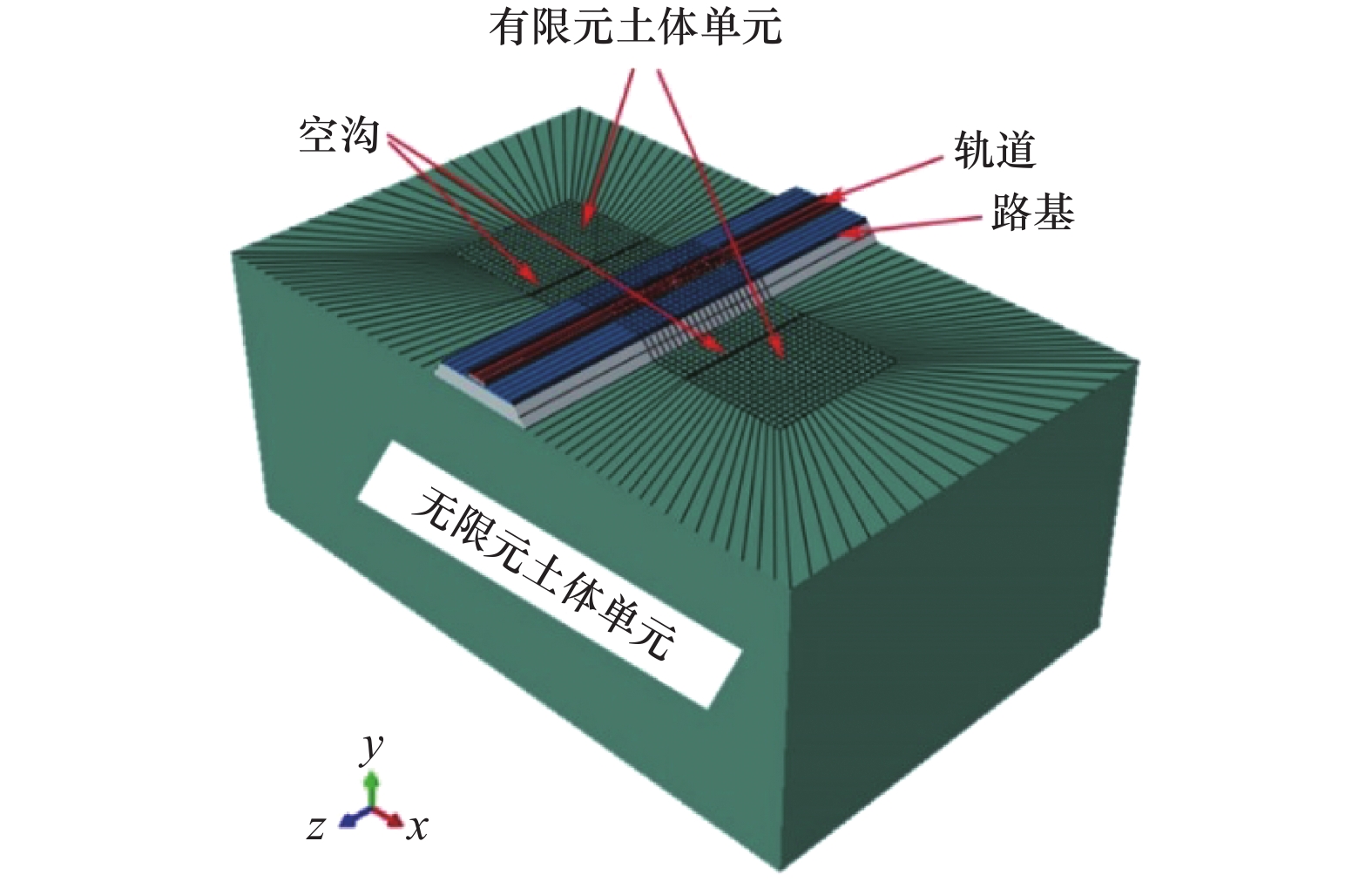
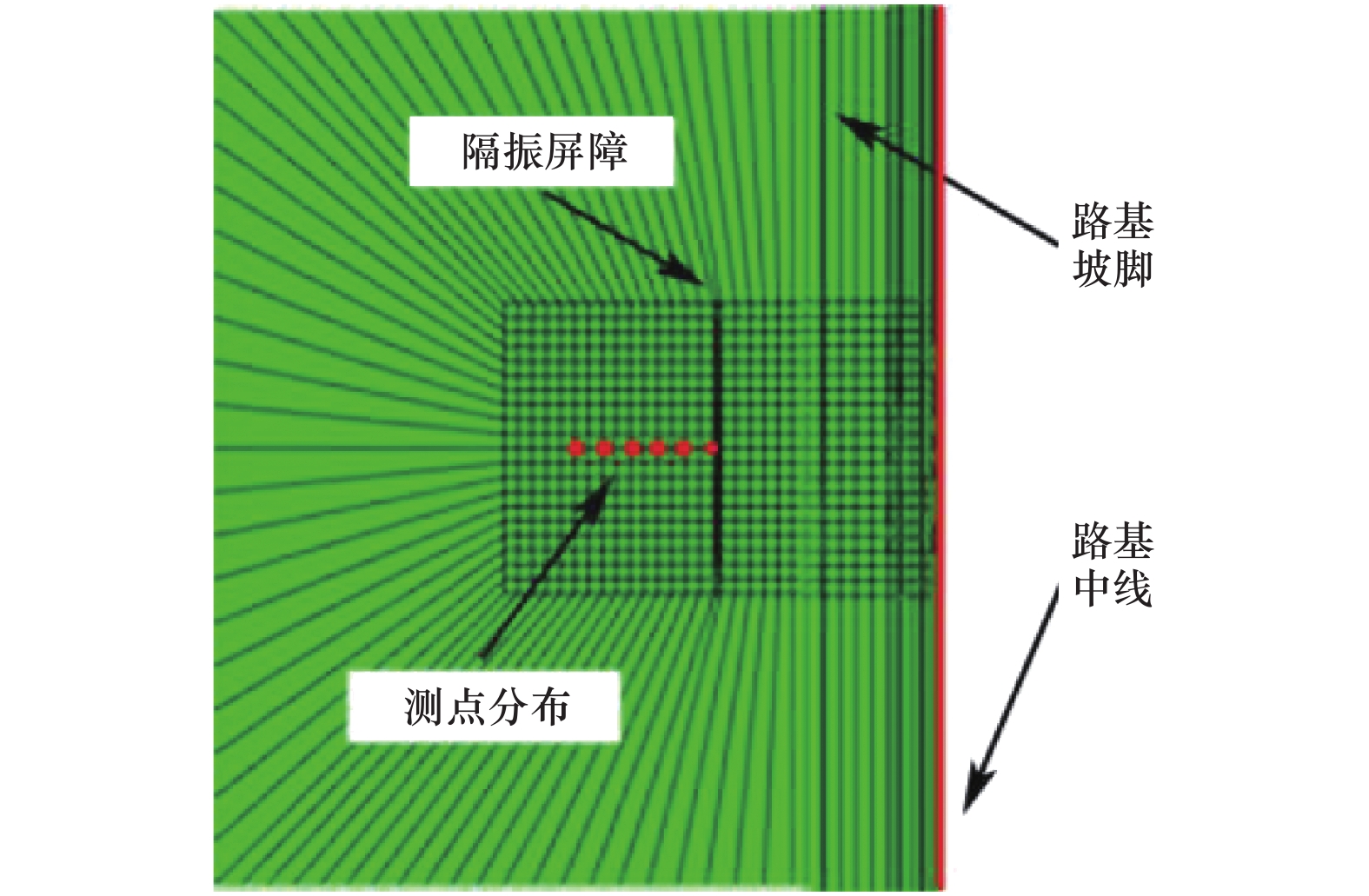
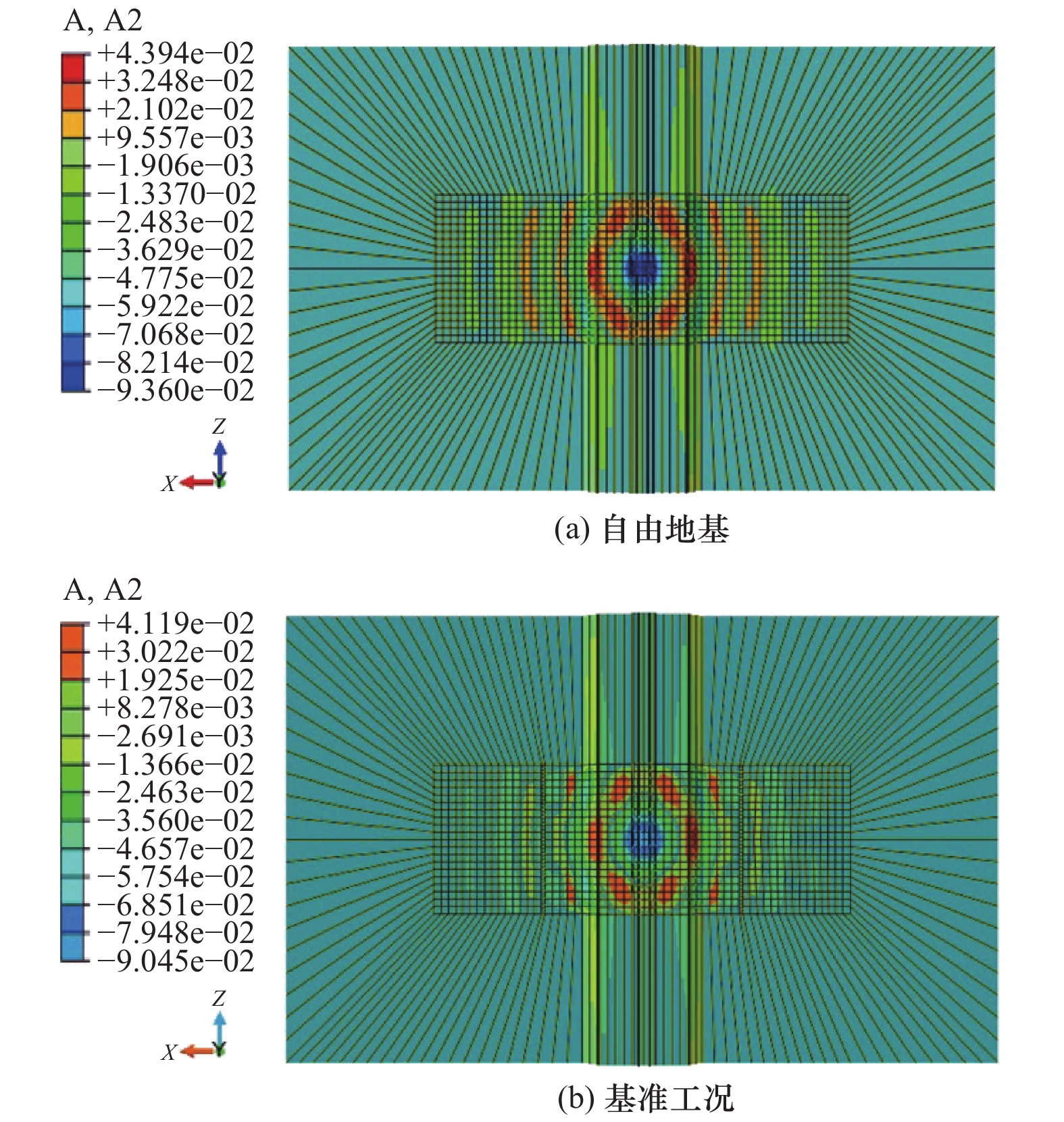
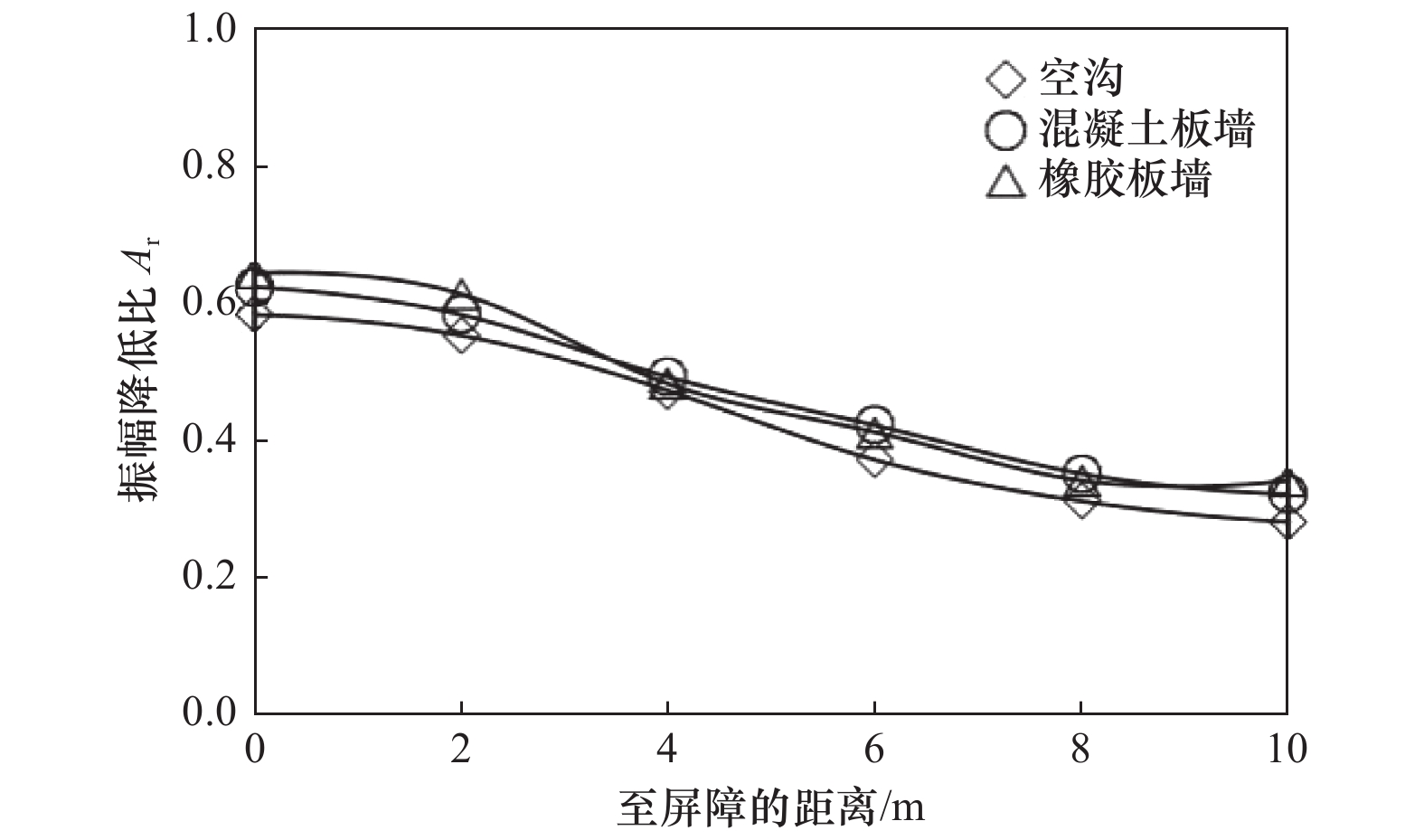
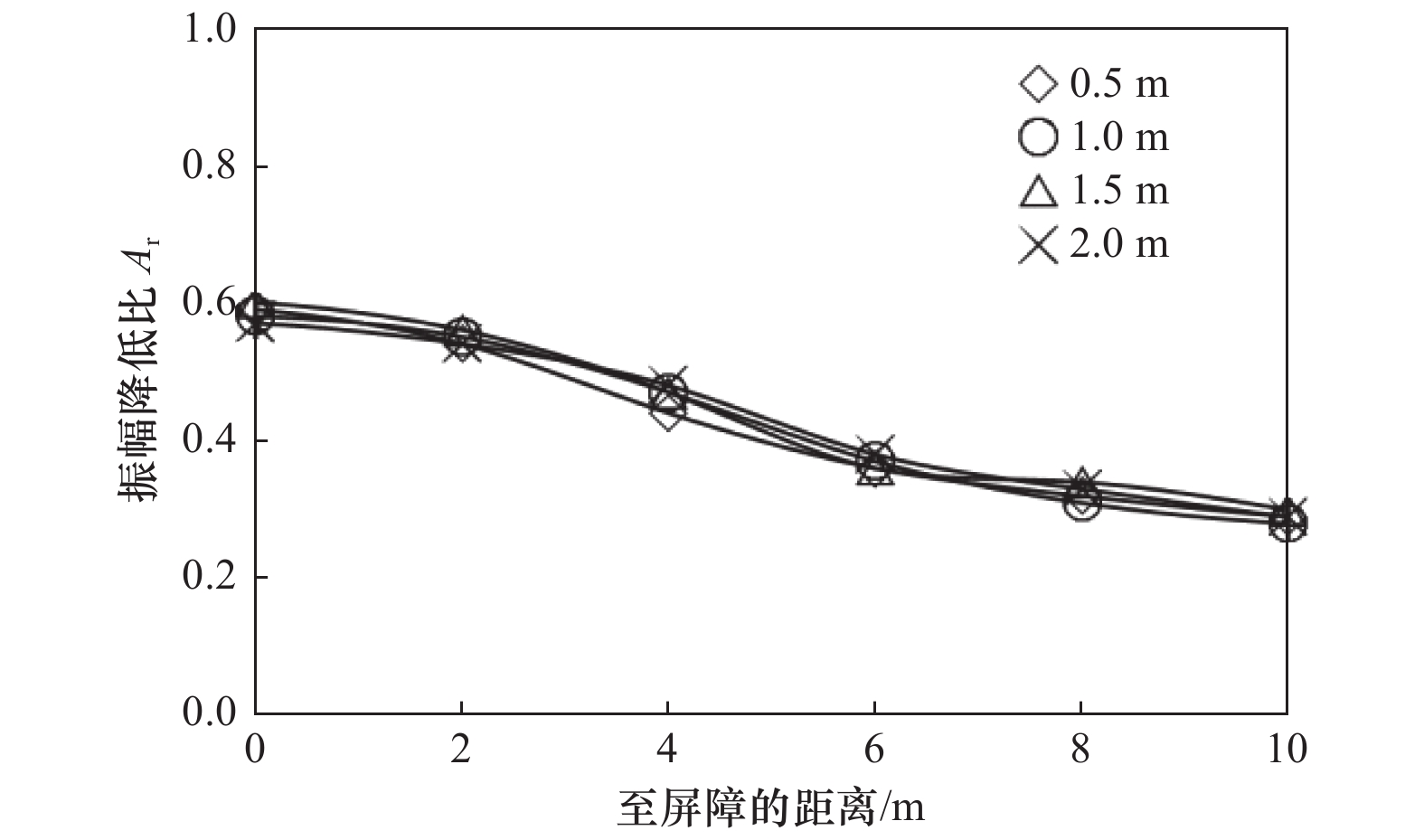
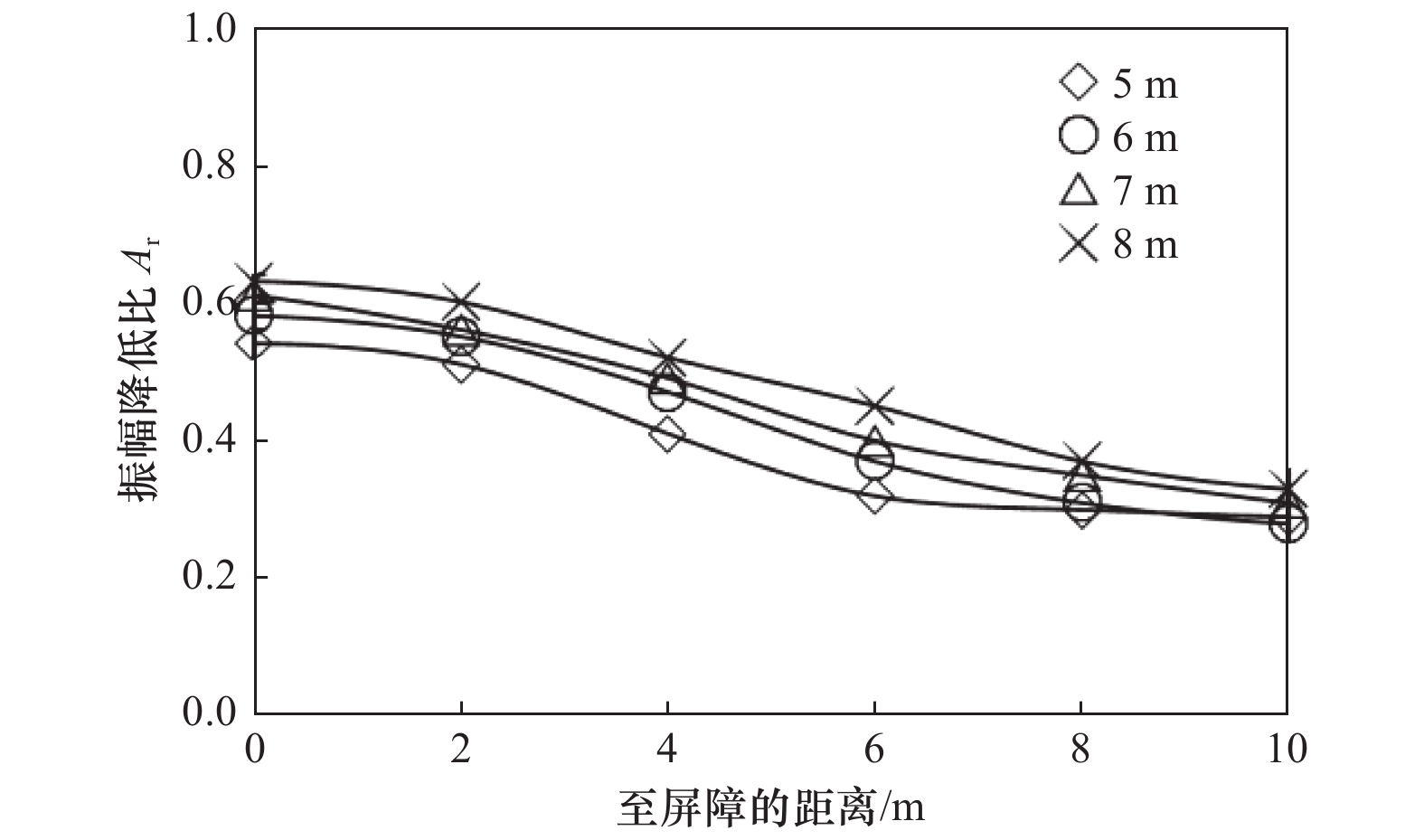
摘要: 为探究高速铁路两侧隔振屏障隔振效果,采用有限元与无限元边界结合的方式进行分析,研究不同连续型隔振屏障及布置形式对隔振效果的影响。通过现场试验与同尺寸、同属性有限元模型对比试验,验证有限元模型合理性。计算结果表明:不同连续型隔振屏障中,空沟隔振效果最优,空沟隔振措施适合高速列车隔振;隔振屏障宽度为0.6~2.5倍波长时,其对隔振效果的影响较小,随着宽度的改变,隔振效果变化幅度较小;隔振屏障深度为3.8~15.2倍波长时,其对隔振效果的影响较明显,随着深度的增加,隔振效果增强;屏障位置对隔振效果的影响较大,建议屏障应靠近路基布置;连续型隔振屏障对高频的隔振效果优于低频。Abstract: In order to explore the vibration isolation effect of the vibration isolation barriers on both sides of high-speed railway, the finite element method combined with infinite element boundary was used to calculate and analyze the influence of different continuous vibration isolation barriers and their layout on the vibration isolation effect. Firstly, the validity of the finite element part was verified by setting experiment and finite element model of the same size and same attribute. The verified results were valid. The results show that the best vibration isolation effect of the gully is obtained by comparing all kinds of continuous vibration isolation barriers, and the gully is suitable for high-speed trains. The width within the range of 0.6~2.5 times of the wavelength has little influence on the vibration isolation effect. With the change of width, the vibration isolation effect changes only slightly. The vibration isolation effect is obviously affected when the depth of the vibration barrier varies from 3.8 to 15.2 wavelength. With the increase of depth, the vibration isolation effect is enhanced. The position of the barrier has great influence on the vibration isolation effect. It is suggested that the barrier should be close to the roadbed. Continuous barrier has better vibration isolation effect at high frequency than at low frequency.
-
Key words:
- High speed railway /
- Continuous barrier /
- Vibration isolation /
- ABAQUS
-
表 1 路基与屏障材料参数
Table 1. Material parameters of subgrade
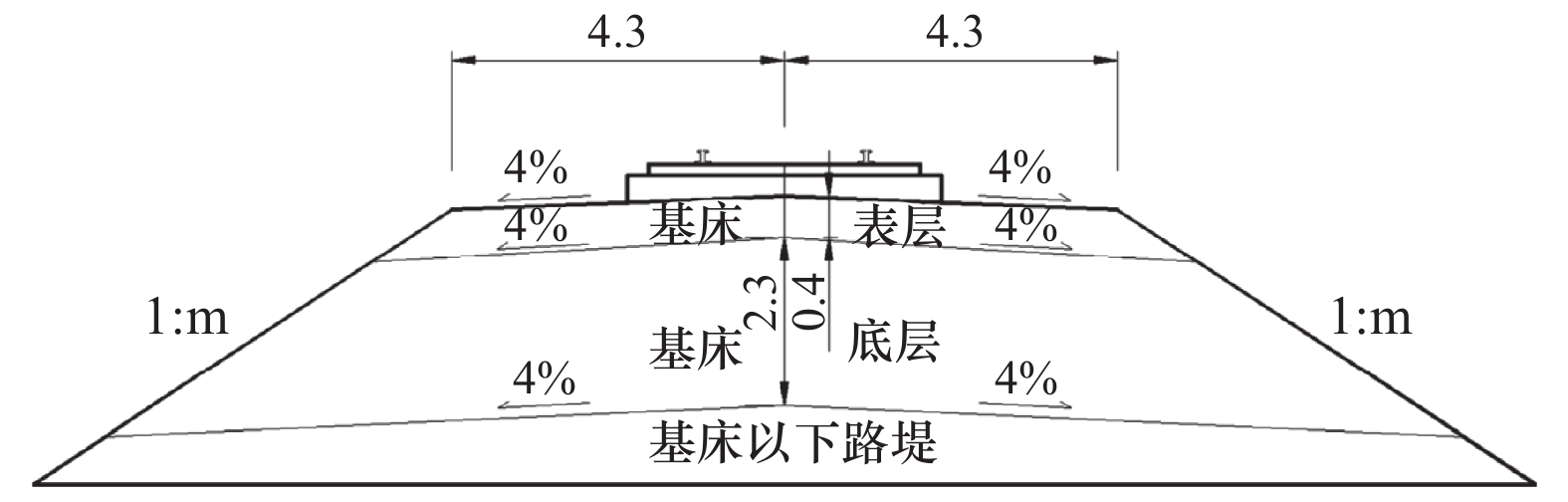
类型 密度/kg·m−3 弹性模量/Pa 泊松比 路基表层 2 000 1.80×108 0.250 路基底层 1 950 1.10×108 0.250 地基土 1 900 2.00×107 0.300 轨道板 2500 3.50×1010 0.167 钢轨 7800 2.10×1011 0.300 支承层 2500 2.70×1010 0.167 混凝土板墙 2400 3.00×1010 0.200 橡胶板墙 1200 7.80×106 0.470 表 2 工况水平组合表
Table 2. Table of combination of parameter levels
水平 类型A 宽度B/m 深度C/m 振源距D/m 激振频率E/Hz 1 空沟 0.5 3.0 5.0 20 2 混凝土板墙 1.0 6.0 6.0 60 3 橡胶板墙 1.5 9.0 7.0 130 4 — 2.0 12.0 8.0 — -
[1] 巴振宁, 梁建文, 张艳菊, 2016. 三维层状黏弹性半空间中球面SH、P和SV波源自由场. 地球物理学报, 59(2): 606—623. doi: 10.6038/cjg20160218Ba Z. N., Liang J. W., Zhang Y. J., 2016. Free-field responses of spherical SH-, P-and SV-wave sources in a layered visco-elastic half space. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 59(2): 606—623. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6038/cjg20160218 [2] 巴振宁, 刘冰松, 张龙等, 2018. 环境振动下德和园大戏楼动力响应分析. 建筑结构, 48(S1): 414—420.Ba Z. N., Liu B. S., Zhang L., et al., 2018. Dynamic response analysis of the Grand Theater in the Garden of Virtuous Harmony under the environmental vibration. Building Structure, 48(S1): 414—420. (in Chinese) [3] 陈行, 晏启祥, 黄希, 2017. 列车振动荷载作用下高速铁路近距地铁平行隧道的动力响应特性分析. 铁道标准设计, 61(6): 116—119, 130.Chen H., Yan Q. X., Huang X., 2017. Research on dynamic response of high-speed train vibration in parallel tunnel close to metro. Railway Standard Design, 61(6): 116—119, 130. (in Chinese) [4] 陈昆, 贾霄, 刘彬等, 2014. 高速铁路空沟隔振措施隔振效果的有限元分析. 地震工程学报, 36(3): 575—579. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2014.03.0575Chen K., Jia X., Liu B., et al., 2014. Finite element analysis of reducing the high-speed railway vibration effect on the environment using open trenches. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 36(3): 575—579. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2014.03.0575 [5] 丁智, 张霄, 吴敏慧等, 2019. 双线地铁运营隔振沟屏障性能研究. 地震工程学报, 41(1): 9—15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2019.01.009Ding Z., Zhang X., Wu M. H., et al., 2019. Vibration isolation effect of isolation trenches during double-line subway operation. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 41(1): 9—15. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2019.01.009 [6] 关歆莹, 刘超, 2011. 地下铁道的振动及其控制措施的研究. 震灾防御技术, 6(1): 77—84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2011.01.008Guan X. Y., Liu C., 2011. The study on the vibration of metro and its control measures. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 6(1): 77—84. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2011.01.008 [7] 国家铁路局, 2015. TB 10621-2014 高速铁路设计规范. 北京: 中国铁道出版社.National Railway Administration of the People’s Republic of China, 2015. TB 10621—2014 Code for design of high speed railway. Beijing: China Railway Publishing House. (in Chinese) [8] 蒋英礼, 赵伯明, 胡晓勇, 2009. 软土地铁车站中柱在强震作用下的响应研究. 防灾减灾工程学报, 29(4): 405—410.Jiang Y. L., Zhao B. M., Hu X. Y., 2009. Study on response of Centre column of metro station in soft soils to strong earthquake. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 29(4): 405—410. (in Chinese) [9] 刘厚毅, 周游, 钟康明等, 2018. 场地条件对高速铁路地基土振动影响的研究. 震灾防御技术, 13(4): 893—902. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20180416Liu H. Y., Zhou Y., Zhong K. M., et al., 2018. Variation characteristics of foundation soil vibration caused by high speed train with depth under different site conditions. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 13(4): 893—902. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11899/zzfy20180416 [10] 刘晶磊, 赵晓玉, 张瑞恒等, 2019. 混凝土排桩深度优化及隔振效果研究. 安全与环境工程, 26(6): 202—208.Liu J. L., Zhao X. Y., Zhang R. H., et al., 2019. Research on depth optimization and vibration isolation effect of concrete row piles. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 26(6): 202—208. (in Chinese) [11] 刘晶磊, 赵倩, 梅名彰等, 2020. 轨道交通荷载下桩板结构主动隔振效果研究. 地震工程学报, 42(1): 7—14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2020.01.007Liu J. L., Zhao Q., Mei M. Z., et al., 2020. Active vibration isolation effect of the pile-plank structures under rail traffic loads. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 42(1): 7—14. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2020.01.007 [12] 孙立强, 李嘉, 刘彬等, 2015. 空沟、碎石填充沟和排桩隔振效果试验研究. 地震工程学报, 37(2): 342—348. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2015.02.0342Sun L. Q., Li J., Liu B., et al., 2015. Experimental study on vibration-isolation effects of open trench, gravel-filled trench, and piles in a row. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 37(2): 342—348. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2015.02.0342 [13] 肖木洋, 2017. 轨道交通地震监测及预警系统现状分析. 地震工程学报, 39(S1): 189—194.Xiao M. Y., 2017. Status analysis of earthquake monitoring and warning system for rail transit. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 39(S1): 189—194. (in Chinese) [14] 肖世伟, 雷长顺, 郭超等, 2011. 高速铁路空沟隔振数值分析. 铁道工程学报, (8): 23—29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2011.08.005Xiao S. W., Lei C. S., Guo C., et al., 2011. Numerical analysis of vibration reduction of open trench for high-speed railway. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, (8): 23—29. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2011.08.005 [15] 徐平, 2017. 空沟对平面纵波隔离效果的理论解答. 振动与冲击, 36(5): 67—71, 101.Xu P., 2017. Theoretical analysis for isolation effect of an open trench on plane longitudinal waves. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 36(5): 67—71, 101. (in Chinese) [16] Adam M., Von Estorff O., 2005. Reduction of train-induced building vibrations by using open and filled trenches. Computers & Structures, 83(1): 11—24. [17] Andersen L., Nielsen S. R. K., 2005. Reduction of ground vibration by means of barriers or soil improvement along a railway track. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 25(7—10): 701—716. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2005.04.007 [18] Ganji V., Gucunski N., Maher A., 1997. Detection of underground obstacles by SASW method-numerical aspects. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 123(3): 212—219. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(1997)123:3(212) [19] Haupt W. A., 1978. Surface waves in nonhomogeneous half-space. In: Prange B, ed., Dynamical Methods in Soil and Rock Mechanics. Rotterdam: Balkema, 335—367. [20] Ju S. H., Lin H. T., 2006. Reduction of vibrations due to foundation slabs. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 132(4): 511—520. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2006)132:4(511) [21] Persson, K., Persson P., Sandberg G., 2016. Numerical study of reduction in ground vibrations by using barriers. Engineering Structures, 115: 18—27. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2016.02.025 [22] Woods R. D., 1968. Screening of surface waves in soils. Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division, 94(4): 951—979. doi: 10.1061/JSFEAQ.0001180 [23] Zhu H. Y., Wang J. W., Cai C. B., et al., 2017. Development of a vibration attenuation track at low frequencies for urban rail transit. Computer‐Aided Civil and infrastructure Engineering, 32(9): 713—726. doi: 10.1111/mice.12285 -




 下载:
下载: