Seismic Performance of the Three-layer Three-span Subway Underground Station Structure With Seismic Isolation Bearings Fixed on the Top of Columns
-
摘要:
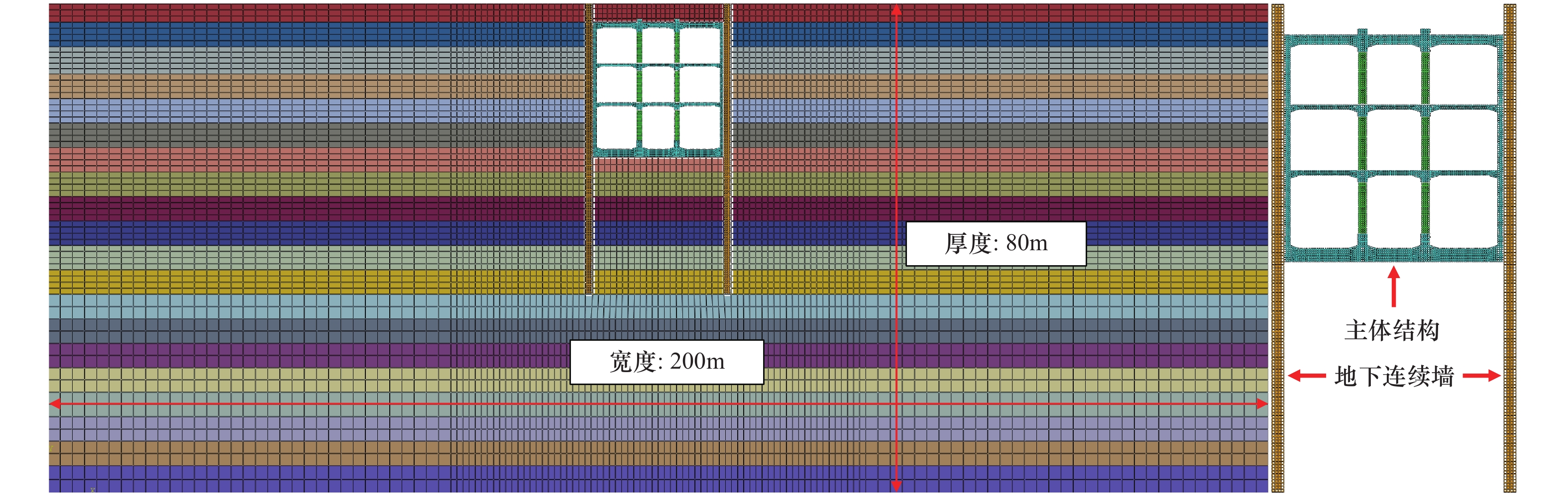
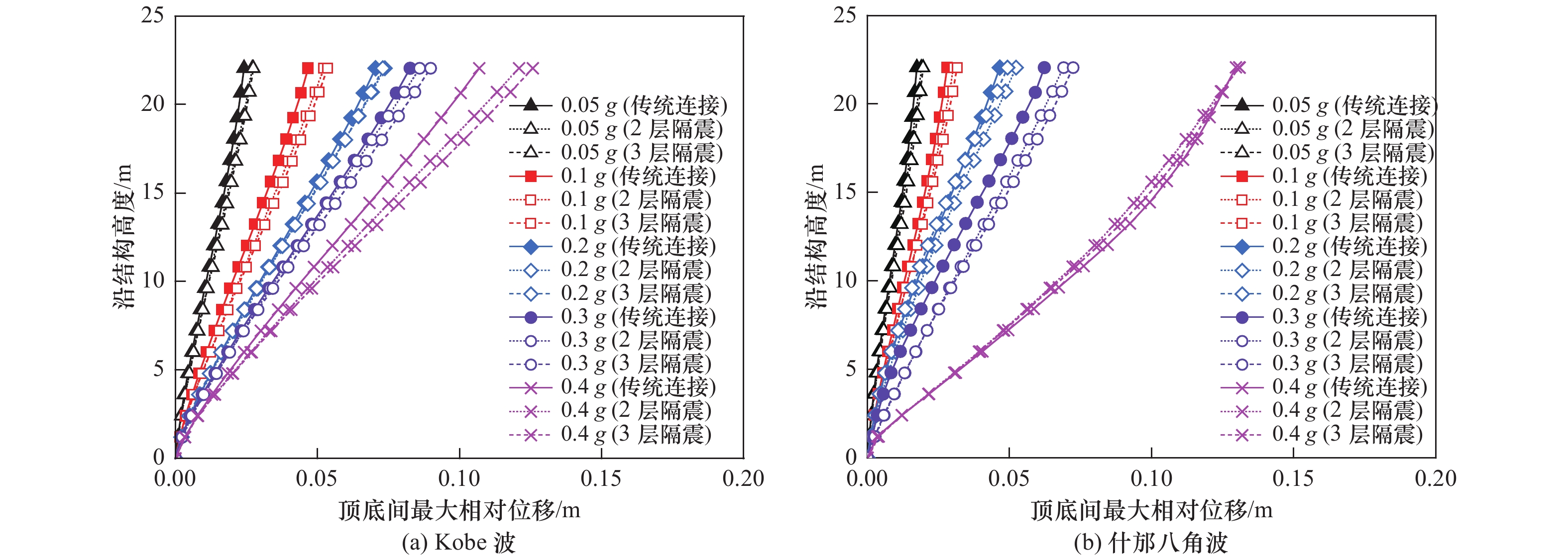
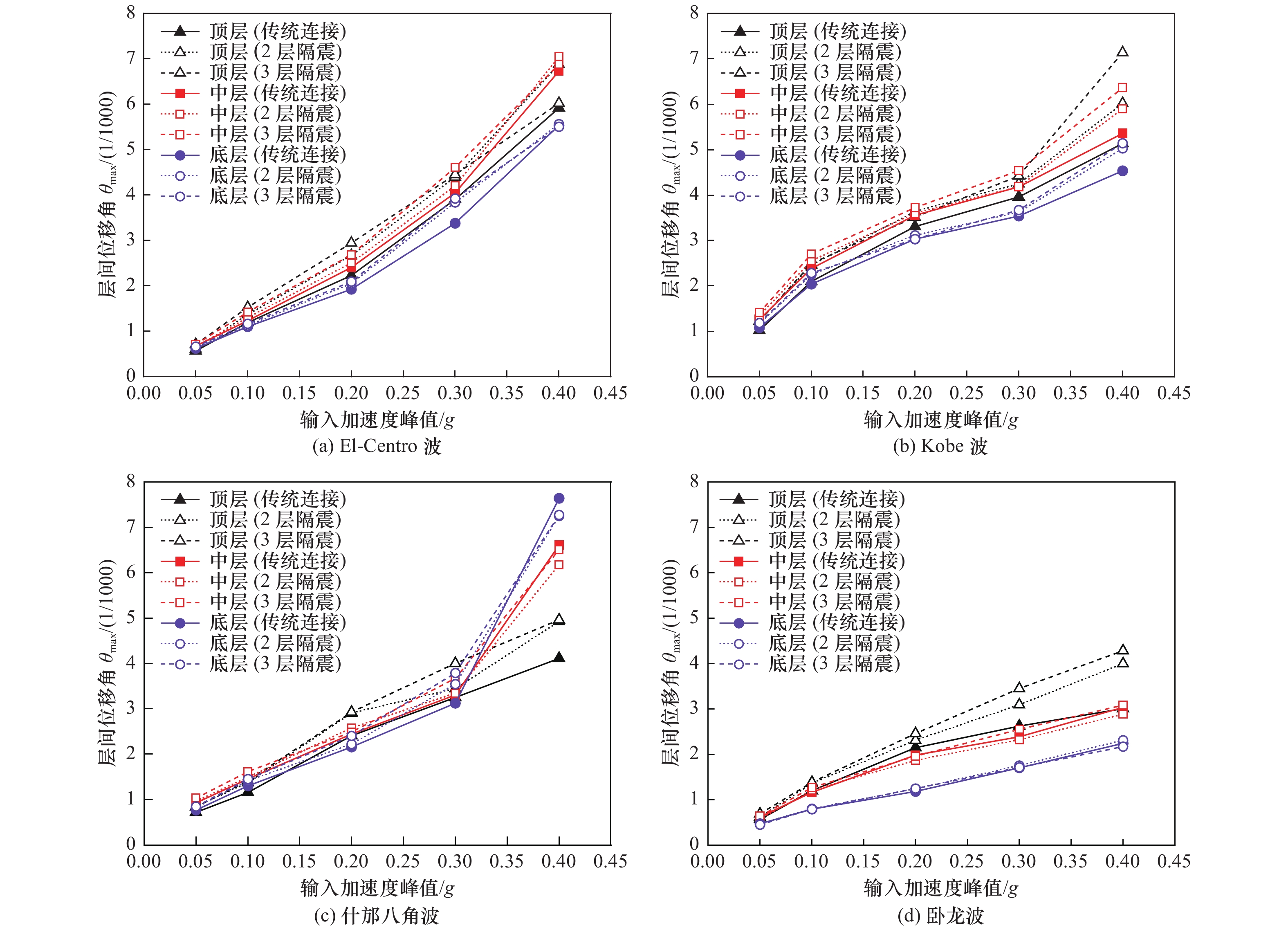
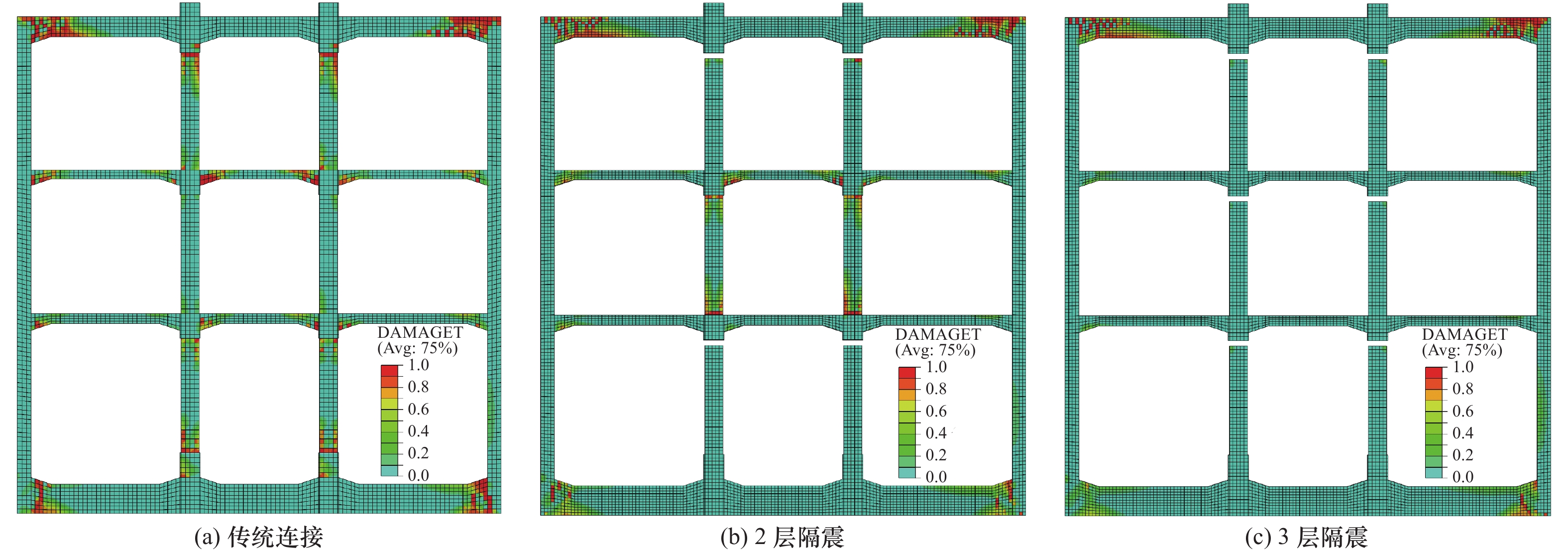
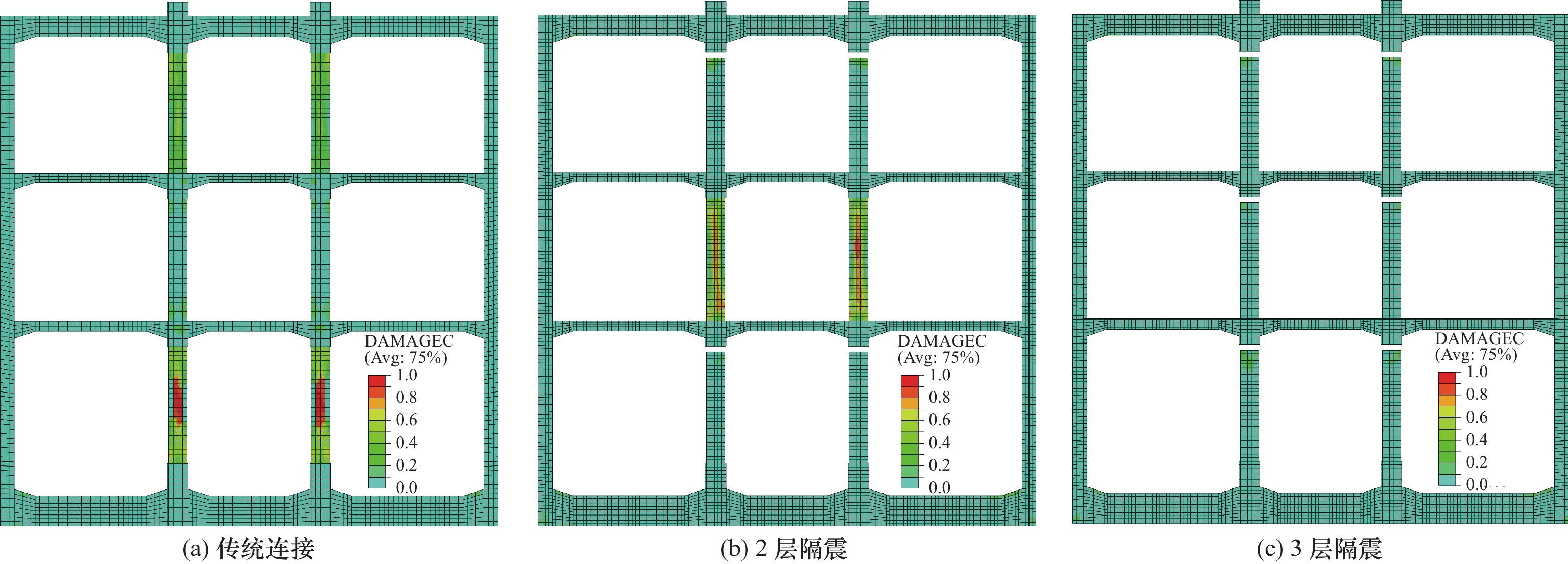
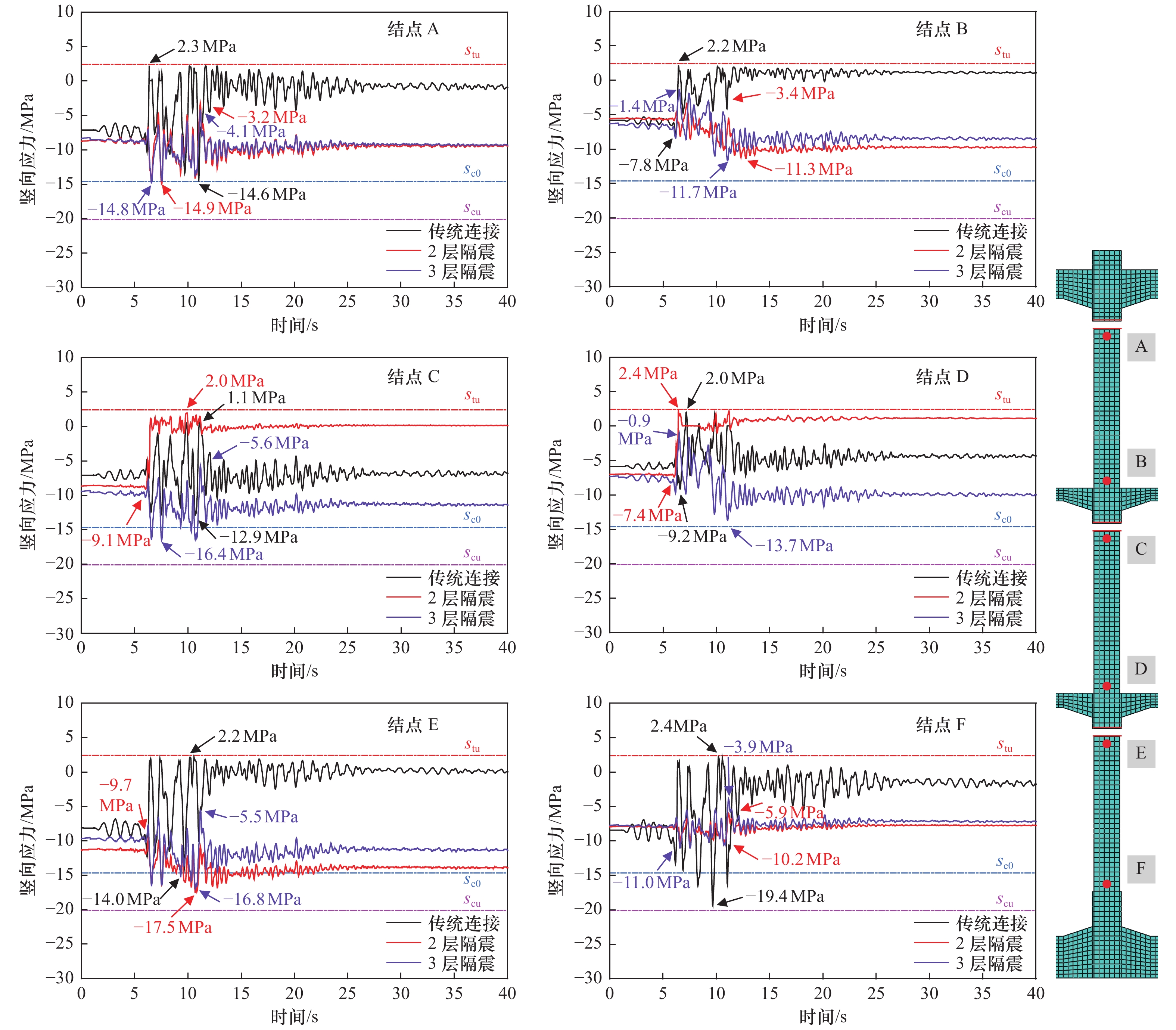
针对3层3跨框架式地铁地下车站结构抗震薄弱构件,采用在柱顶不同位置设置铅芯橡胶隔震支座的方法,建立土-地下连续墙-主体结构非线性静动力耦合相互作用的二维整体时域有限元分析模型,分析柱顶隔震支座对车站主体结构的侧向变形、地震损伤和动应力反应等结构地震反应特性的影响。结果表明,仅在抗震薄弱的顶层和底层中柱柱顶设置2层隔震支座与各层中柱柱顶设置3层隔震支座均可有效减轻中柱地震损伤程度,提高车站结构整体抗震性能。然而,仅在顶、底层中柱柱顶设置2层隔震支座时,会明显加重未设置隔震支座的中间层中柱地震损伤程度。此外,柱顶隔震支座的设置会削弱隔震体系的整体抗侧移能力,从而增大地铁地下车站结构地震侧移。总体上,建议采用各层中柱柱顶均设置隔震支座的措施提升地铁地下车站结构的整体抗震性能。
Abstract:According to the seismic response characteristics of the three-layer three-span frame subway underground station structure, the lead rubber seismic isolation bearings (LRB) were fixed at the different position of the top of columns, a two-dimensional finite element model for the static-dynamic coupling nonlinear interaction among the soil, the diaphragm wall and underground subway station structure was established, analyzing the influence of the position of the LRB fixed on the top of columns on the seismic response of subway station structure, such as the lateral deformation, earthquake damage, and dynamic stress response. It showes that the LRB fixed on the top of upper and lower columns, and fixed on the top of upper, middle and lower columns can effectively reduce the seismic damage of columns, thus improving the overall seismic performance of the isolation structure. However, when the LRB only fixed on the top of upper and lower columns, the seismic damage of the middle columns without the LRB would be severely aggravated. In addition, the LRB fixed on the top of columns can weaken the overall lateral resistance of the isolation structure, which slightly increased the seismic lateral response amplitude of the station structure. In general, it is recommended that the measure of setting the LRB on the top of columns in each floor to improve the overall seismic performance of the three-layer three-span subway underground station structure.
-
表 1 工程场地条件及其参数
Table 1. Soil conditions and physical properties of soils in site
土层编号 土性 重度/kN·m−3 弹性模量/MPa 层厚/m 动泊松比 剪切波速/m·s−1 1 素填土 18.4 3.5 3.0 0.49 200 2 软黏土 19.0 8.0 4.0 0.49 225 3 软黏土 20.5 10.0 4.5 0.49 250 4 黏土 19.4 14.5 4.0 0.49 275 5 砂土 19.4 12.0 4.0 0.49 300 6 砂土 19.4 12.0 4.0 0.49 325 7 砂土 20.9 14.5 4.0 0.49 350 8 砂土 20.9 27.7 4.0 0.49 375 9 砂土 21.2 27.8 4.0 0.49 400 10 砂土 21.2 33.0 4.0 0.49 425 11 砂土 18.9 33.0 4.0 0.49 450 12 老黏土 18.9 33.0 4.0 0.49 475 13 老黏土 18.9 35.0 4.0 0.49 490 14 老黏土 20.5 35.0 4.0 0.49 600 15 老黏土 20.5 35.0 4.0 0.49 700 16 老黏土 20.5 35.0 4.0 0.49 800 17 老黏土 20.5 40.0 4.0 0.49 900 18 老黏土 19.3 40.0 4.0 0.49 1000 19 老黏土 19.3 40.0 4.0 0.49 1000 20 老黏土 19.3 45.0 4.5 0.49 1000 表 2 铅芯橡胶隔震支座主要参数
Table 2. Main parameters of lead rubber seismic isolation bearing
支座
直径/mm安装
高度/mm容许水平
位移/mm竖向
承载力/kN水平等效
刚度/kN·mm−1屈服后
刚度/kN·mm−1竖向压缩
刚度/kN·mm−1等效
阻尼比/%600 251 330 3 600 2.64 1.83 3 627 17.18 -
杜修力, 王刚, 路德春, 2016. 日本阪神地震中大开地铁车站地震破坏机理分析. 防灾减灾工程学报, 36(2): 165—171.Du X. L., Wang G., Lu D. C., 2016. Earthquake damage mechanism analysis of Dakai metro station by Kobe earthquake. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 36(2): 165—171. (in Chinese) 杜修力, 马超, 路德春等, 2017. 大开地铁车站地震破坏模拟与机理分析. 土木工程学报, 50(1): 53—62, 69.Du X. L., Ma C., Lu D. C., et al., 2017. Collapse simulation and failure mechanism analysis of the Daikai subway station under seismic loads. China Civil Engineering Journal, 50(1): 53—62, 69. (in Chinese) 杜修力, 李洋, 许成顺等, 2018. 1995年日本阪神地震大开地铁车站震害原因及成灾机理分析研究进展. 岩土工程学报, 40(2): 223—236. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201802002Du X. L., Li Y., Xu C. S., et al., 2018. Review on damage causes and disaster mechanism of Daikai subway station during 1995 Osaka-Kobe Earthquake. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 40(2): 223—236. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201802002 还毅, 方秦, 柳锦春等, 2011. 提高地铁车站结构抗震能力的理论及数值分析. 振动与冲击, 30(3): 252—257. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2011.03.050Huan Y., Fang Q., Liu J. C., et al., 2011. Theoretical and numerical investigations on enhancement of aseismic capability of metro stations. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 30(3): 252—257. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2011.03.050 楼梦麟, 王文剑, 朱彤等, 2000. 土-结构体系振动台模型试验中土层边界影响问题. 地震工程与工程振动, 20(4): 30—36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1301.2000.04.005Lou M. L., Wang W. J., Zhu T., et al., 2000. Soil lateral boundary effect in shaking table model test of soil-structure system. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 20(4): 30—36. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1301.2000.04.005 王雪剑, 庄海洋, 陈国兴等, 2017. 地下连续墙对叠合墙式地铁车站结构地震反应的影响研究. 岩土工程学报, 39(8): 1435—1443. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201708010Wang X. J., Zhuang H. Y., Chen G. X., et al., 2017. Effect of diaphragm wall on earthquake responses of an underground subway station. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 39(8): 1435—1443. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201708010 杨靖, 云龙, 庄海洋等, 2020. 三层三跨框架式地铁地下车站结构抗震性能水平研究. 岩土工程学报, 42(12): 2240—2248.Yang J., Yun L., Zhuang H. Y., et al., 2020. Seismic performance levels of frame-type subway underground station with three layers and three spans. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 42(12): 2240—2248. (in Chinese) 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 2019. GB/T 51336—2018 地下结构抗震设计标准. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 36.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, 2019. GB/T 51336—2018 Standard for seismic design of underground structures. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 36. (in Chinese) 庄海洋, 陈国兴, 朱定华, 2006. 土体动力粘塑性记忆型嵌套面本构模型及其验证. 岩土工程学报, 28(10): 1267—1272. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2006.10.017Zhuang H. Y., Chen G. X., Zhu D. H., 2006. Dynamic visco-plastic memorial nested yield surface model of soil and its verification. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 28(10): 1267—1272. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2006.10.017 庄海洋, 程绍革, 陈国兴, 2008. 阪神地震中大开地铁车站震害机制数值仿真分析. 岩土力学, 29(1): 245—250. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.01.046Zhuang H. Y., Cheng S. G., Chen G. X., 2008. Numerical simulation and analysis of earthquake damages of Dakai metro station caused by Kobe earthquake. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 29(1): 245—250. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.01.046 庄海洋, 陈国兴, 2009. 对土体动力黏塑性记忆型嵌套面模型的改进. 岩土力学, 30(1): 118—122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.01.019Zhuang H. Y., Chen G. X., 2009. Improvement of dynamic viscoplastic memorial nested yield surface model of soil. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 30(1): 118—122. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.01.019 庄海洋, 吴祥祖, 陈国兴, 2011. 考虑初始静应力状态的土—地下结构非线性静、动力耦合作用研究. 岩石力学与工程学报, 30(S1): 3112—3119.Zhuang H. Y., Wu X. Z., Chen G. X., 2011. Study of nonlinear static and dynamic coupling interaction of soil-underground structure considering initial static stress. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 30(S1): 3112—3119. (in Chinese) 庄海洋, 龙慧, 陈国兴, 2013. 复杂大型地铁地下车站结构非线性地震反应分析. 地震工程与工程振动, 33(2): 192—199.Zhuang H. Y., Long H., Chen G. X., 2013. Analysis of the nonlinear earthquake responses of a large complicated subway underground station. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 33(2): 192—199. (in Chinese) 庄海洋, 王雪剑, 王瑞等, 2017. 土-地铁动力相互作用体系侧向变形特征研究. 岩土工程学报, 39(10): 1761—1769. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201710002Zhuang H. Y., Wang X. J., Wang R., et al., 2017. Characteristics of lateral deformation of soil-subway dynamic interaction system. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 39(10): 1761—1769. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201710002 庄海洋, 付继赛, 朱明轩等, 2019. 柱顶设置滑移支座时地铁地下车站结构抗震性能分析. 隧道与地下工程灾害防治, 1(3): 57—67.Zhuang H. Y., Fu J. S., Zhu M. X., et al., 2019. Seismic performance of underground subway station with elastic slipping bearing fixed on the top of columns. Hazard Control in Tunnelling and Underground Engineering, 1(3): 57—67. (in Chinese) BSI, 2011. BS 5975: 2008 + A1: 2011 Code of practice for temporary works procedures and the permissible stress design of false work. BSI. Chen Z. Y., Chen W., Bian G. Q., 2014. Seismic performance upgrading for underground structures by introducing shear panel dampers. Advances in Structural Engineering, 17(9): 1343—1357. doi: 10.1260/1369-4332.17.9.1343 Chen Z. Y., Liu Z. Q., 2018. Effects of central column aspect ratio on seismic performances of subway station structures. Advances in Structural Engineering, 21(1): 14—29. doi: 10.1177/1369433217706777 Lee J., Fenves G. L., 1998. Plastic-damage model for cyclic loading of concrete structures. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 124(8): 892—900. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(1998)124:8(892) Li W. T., Chen Q. J., 2018. Seismic performance and failure mechanism of a subway station based on nonlinear finite element analysis. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 22(2): 765—776. doi: 10.1007/s12205-017-1840-y Lubliner J., Oliver J., Oller S., et al., 1989. A plastic-damage model for concrete. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 25(3): 299—326. doi: 10.1016/0020-7683(89)90050-4 Ma C., Lu D. C., Du X. L., 2018. Seismic performance upgrading for underground structures by introducing sliding isolation bearings. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 74: 1—9. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2018.01.007 Tso W. K., Zhu T. J., Heidebrecht A. C., 1992. Engineering implication of ground motion A/V ratio. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 11(3): 133—144. doi: 10.1016/0267-7261(92)90027-B -




 下载:
下载: