Measurement of Shear Wave Velocity of Sand-Silt Mixtures by Bender Element and Resonant Column Tests
-
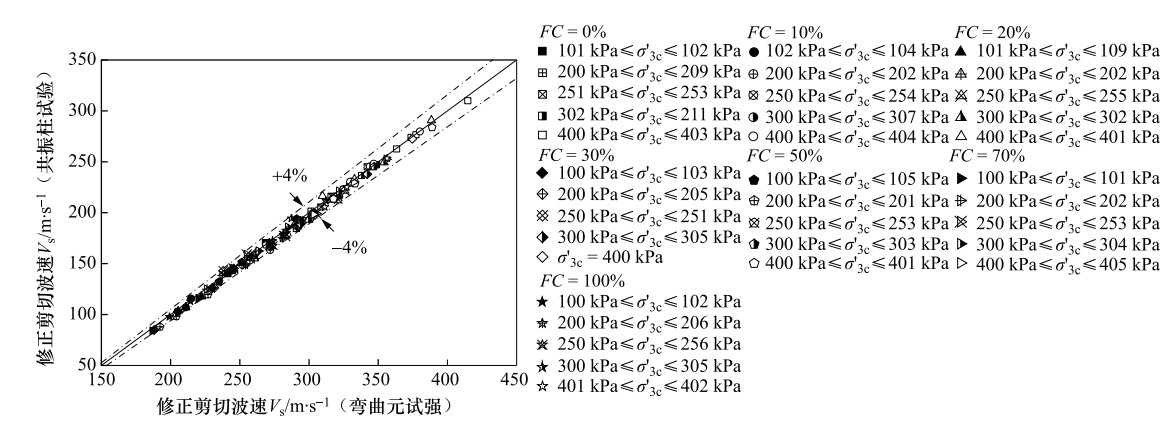
摘要: 为探讨测试方法、试验条件以及级配特征对砂-粉混合料剪切波速的影响,对具有不同细粒含量FC,相对密度Dr以及初始有效围压$\sigma_{3 \mathrm{c}}^{\prime}$的砂-粉混合料进行弯曲元和共振柱试验。结果表明:当Dr =35%或50%时,剪切波速Vs随FC的增大先减小后增大;当Dr =60%时,Vs随FC的增大而减小;弯曲元试验测得的Vs明显大于共振柱试验测得的Vs,随着FC的增大,弯曲元试验与共振试验得到的Vs差值逐渐减小,而当FC>20%时,两种试验得到的Vs基本相同。在考虑Vs弥散性之后,不同FC的混合料弯曲元与共振柱试验得到的Vs结果具有较好的一致性。基于Hardin模型建立的砂-粉混合料Vs预测方法具有较好的预测效果。Abstract: In order to investigate the influence of test method, test conditions and grain size distributions on shear wave velocity of sand-silt mixtures, a series of bender element and resonant column tests were performed on the mixtures with different fines content FC, relative density Dr and initial effective pressure σ′3c. The test results show that when Dr = 35% or 50%, Vs decreases first and then increases with FC increasing, and when Dr = 60%, Vs decreases with the increase of FC. The Vs measured by the bender element test are larger than that measured by the resonance column test, the difference is gradually reduced with FC increasing, and the Vs obtained by the two tests are basically the same when FC > 20%. Based on the theory of Biot two-phase elastic wave propagation, considering the dispersion of shear wave, the shear wave velocity of bending elements of different fine content mixtures are in good agreement with the results of resonant column tests. The Vs prediction method of sand-silt mixture based on Hardin model shows a good prediction effect.
-
表 1 砂-粉混合料的剪切波速测试方案
Table 1. Shear wave velocity test condition of sand-silt mixtures
ID FC/% ρ/g·cm-3 Dr/% e ID FC/% ρ/g·cm-3 Dr/% e Case1 0 1.286 35 1.08 Case12 30 1.506 60 0.79 Case2 0 1.352 50 0.97 Case13 50 1.358 35 1.00 Case3 0 1.412 60 0.89 Case14 50 1.419 50 0.91 Case4 10 1.334 35 1.01 Case15 50 1.497 60 0.81 Case5 10 1.386 50 0.93 Case16 70 1.350 35 1.01 Case6 10 1.424 60 0.88 Case17 70 1.387 50 0.96 Case7 20 1.348 35 0.94 Case18 70 1.453 60 0.87 Case8 20 1.382 50 0.95 Case19 100 1.258 35 1.23 Case9 20 1.475 60 0.82 Case20 100 1.335 50 1.13 Case10 30 1.386 35 0.95 Case21 100 1.409 60 0.99 Case11 30 1.448 50 0.86 注:每组试验工况均进行100、200、250、300、400kPa逐级等压固结并进行剪切波速测试。 表 2 不同FC砂-粉混合料试验参数
Table 2. Test parameters of saturated sand-silt mixtures with different FC
ID FC/% Dr/% σ′3c/kPa f/Hz fc/kHz S1 0 35 101 209 253 311 400 120 136 140 149 158 1.5 1.9 2.2 2.8 3.3 S2 0 50 102 200 252 302 402 118 134 139 143 152 1.7 2.2 2.6 2.8 3.3 S3 0 60 102 200 251 302 403 114 129 137 140 145 1.8 2.3 2.7 2.9 3.5 S4 10 35 102 200 254 307 404 125 149 160 168 179 10.2 11.3 13.4 14.7 15.6 S5 10 50 104 200 252 300 400 111 132 139 144 155 13.1 15.1 16.5 17.1 17.9 S6 10 60 102 202 250 300 401 117 137 144 149 159 15.6 16.7 17.1 18.6 21.9 S7 20 35 109 202 255 302 400 116 138 145 150 161 34.1 44.1 47.7 52.3 55.8 S8 20 50 100 200 250 301 401 114 134 138 145 156 38.2 48.6 52.8 55.7 58.9 S9 20 60 101 200 250 300 400 115 134 143 145 157 42.1 53.8 58.5 63.4 68.9 S10 30 35 101 205 251 300 400 88 117 123 130 148 467.0 594.0 644.0 700.0 756.0 S11 30 50 101 200 250 305 400 121 141 148 155 164 559.0 655.0 690.0 763.0 858.0 S12 30 60 100 202 250 300 400 122 141 148 154 164 580.0 700.0 761.0 779.0 827.0 S13 50 35 105 200 253 303 400 129 148 154 161 168 612.0 725.0 804.0 1000.0 1100.0 S14 50 50 105 201 250 300 401 115 135 144 148 158 646.0 714.0 774.0 844.0 972.0 S15 50 60 100 200 251 300 400 117 138 143 150 162 674.0 751.0 818.0 853.0 1009.0 S16 70 35 100 200 250 300 400 110 131 135 141 152 687.0 841.0 991.0 1080.0 1170.0 S17 70 50 101 201 253 304 405 108 130 138 143 157 718.0 807.0 1043.0 1051.0 1115.0 S18 70 60 101 202 250 300 400 119 134 141 145 159 788.0 975.0 1057.0 1137.0 1147.0 S19 100 35 102 200 251 301 402 96 109 116 119 128 743.0 852.0 897.0 972.0 1010.0 S20 100 50 100 206 250 306 401 110 130 141 150 159 769.0 870.0 939.0 1012.0 1035.0 S21 100 60 100 202 253 300 402 100 119 122 127 140 827.0 897.0 972.0 1082.0 1116.0 注:不同孔隙比下渗透系数的换算釆用Kozeny-Carman建议公式:${k_1}:{k_2} = [e_1^3/(1 + {e_1})]:[e_2^3/(1 + {e_2})]$ -
陈云敏, 周燕国, 黄博, 2006. 利用弯曲元测试砂土剪切模量的国际平行试验. 岩土工程学报, 28(7): 874-880. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2006.07.013 顾晓强, 杨峻, 黄茂松等, 2015. 干砂弹性参数测定的弯曲-伸展元试验. 岩土力学, 36(S1): 220-224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2015S1037.htm 孔令伟, 李新明, 田湖南, 2011. 砂土渗透系数的细粒效应与其状态参数关联性. 岩土力学, 32(S2): 21-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2011S2004.htm 孔梦云, 陈国兴, 李小军等, 2015. 以剪切波速与地表峰值加速度为依据的地震液化确定性及概率判别法. 岩土力学, 36(5): 1239-1252, 1260. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201505003.htm 吴琪, 陈国兴, 周正龙等, 2018. 基于颗粒接触状态理论的粗细粒混合料液化强度试验研究. 岩土工程学报, 40(3): 475-485. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201803014.htm 杨文保, 吴琪, 陈国兴, 2019. 长江入海口原状土动剪切模量预测方法探究. 岩土力学, 40(10): 3889-3896. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201910023.htm 中华人民共和国水利部, 1999. SL 237-1999土工试验规程. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社. 周燕国, 2007. 土结构性的剪切波速表征及对动力特性的影响. 杭州: 浙江大学. Andrus R. D., Stokoe Ⅱ K. H., 2000. Liquefaction resistance of soils from shear-wave velocity. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 126(11): 1015-1025. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2000)126:11(1015) Biot M. A., 1956a. Theory of propagation of elastic waves in a fluid-saturated porous solid. I. Low-frequency range[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 28(2): 168-178. doi: 10.1121/1.1908239 Biot M. A., 1956b. Theory of propagation of elastic waves in a fluid-saturated porous solid. Ⅱ. Higher frequency range[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 28(2): 179-191. doi: 10.1121/1.1908241 Brignoli E. G. M., Gotti M., Stokoe K. H., 1996. Measurement of shear waves in laboratory specimens by means of piezoelectric transducers. Geotechnical Testing Journal, 19(4): 384-397. doi: 10.1520/GTJ10716J Choo H., Burns S. E., 2015. Shear wave velocity of granular mixtures of silica particles as a function of finer fraction, size ratios and void ratios. Granular Matter, 17(5): 567-578. doi: 10.1007/s10035-015-0580-2 Dyvik R., Madshus C., 1985. Lab measurements of Gmax using bender elements. In: Advances in the Art of Testing Soils under Cyclic Conditions. New York: American Society of Civil Engineers, 186-196. Hardin B. O., Richart Jr F. E., 1963. Elastic wave velocities in granular soils. Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division, 89(SM1): 33-65. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/349267063_Elastic_Wave_Velocities_in_Granular_Soils Hardin B. O., Black W. L., 1966. Sand stiffness under various triaxial stresses. Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division, 92(SM2): 27-42. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/349272740_Sand_Stiffness_Under_Various_Triaxial_Stresses Hardin B. O., Drnevich V. P., 1972. Shear modulus and damping in soils: Design equations and curves. Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division, 98(7): 667-692. doi: 10.1061/JSFEAQ.0001760 Huang Y. T., Huang A. B., Kuo Y. C., et al., 2004. A laboratory study on the undrained strength of a silty sand from Central Western Taiwan. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 24(9-10): 733-743. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2004.06.013 Iwasaki T., Tatsuoka F., 1977. Effects of grain size and grading on dynamic shear moduli of sands. Soils and Foundations, 17(3): 19-35. doi: 10.3208/sandf1972.17.3_19 Nagaraj T. S., Pandian N. S., Raju P. S. R. N., 1991. An approach for prediction of compressibility and permeability behaviour of sand-bentonite mixes. Indian Geotechnical Journal, 21(3): 271-282. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285909955_An_approach_for_prediction_of_compressibility_and_permeability_behaviour_of_sand-bentonite_mixes Rahman M. M., Lo S. R., Gnanendran C. T., 2008. On equivalent granular void ratio and steady state behaviour of loose sand with fines. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 45(10): 1439-1456. doi: 10.1139/T08-064 Salgado R., Bandini P., Karim A., 2000. Shear strength and stiffness of silty sand. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 126(5): 451-462. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2000)126:5(451) Santamarina J. C., Klein K. A., Fam M. A., 2001. Soils and waves: Particulate materials behavior, characterization and process monitoring. New York: J. Wiley & Sons, 238-282. Souto A., Hartikainen J., Özüdoğru K., 1994. Measurement of dynamic parameters of road pavement materials by the bender element and resonant column tests. Géotechnique, 44(3): 519-526. doi: 10.1680/geot.1994.44.3.519 Sridharan A., Nagaraj H. B., 2005. Hydraulic conductivity of remolded fine-grained soils versus index properties. Geotechnical & Geological Engineering, 23(1): 43. doi: 10.1007/s10706-003-5396-x Yang J., Yan X. R., 2009. Site response to multi-directional earthquake loading: A practical procedure. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 29(4): 710-721. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2008.07.008 Yang J., Liu X., 2016. Shear wave velocity and stiffness of sand: The role of non-plastic fines[J]. Géotechnique, 66(6): 500-514. doi: 10.1680/jgeot.15.P.205 Youn J. U., Choo Y. W., Kim D. S., 2008. Measurement of small-strain shear modulus Gmax of dry and saturated sands by bender element, resonant column, and torsional shear tests. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 45(10): 1426-1438. doi: 10.1139/T08-069 -



 下载:
下载: