Analysis of Public Cognition and Demand of Earthquake Science Popularization and Suggestions—Based on Tianjin Public Questionnaire Survey
-
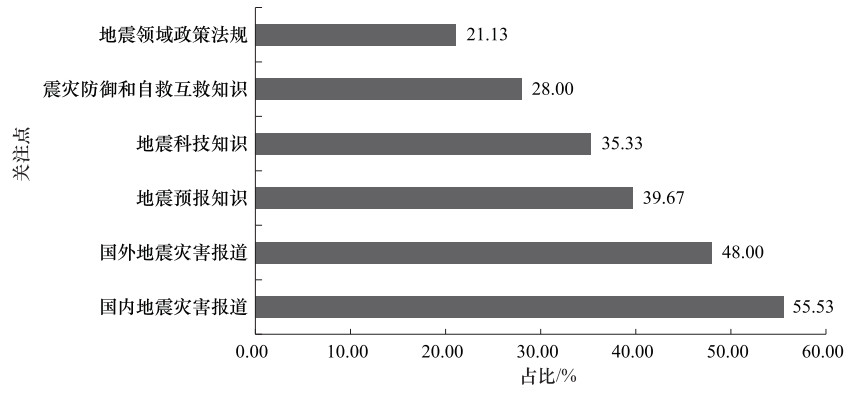
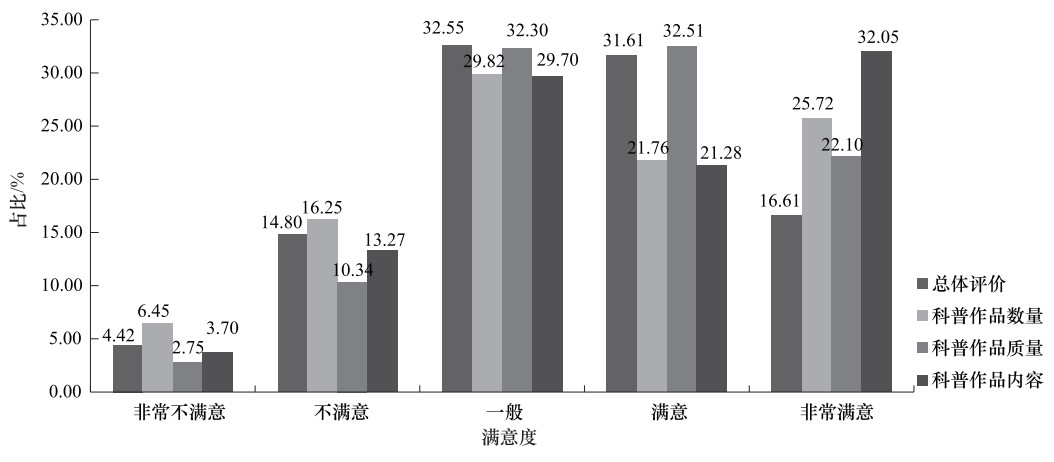
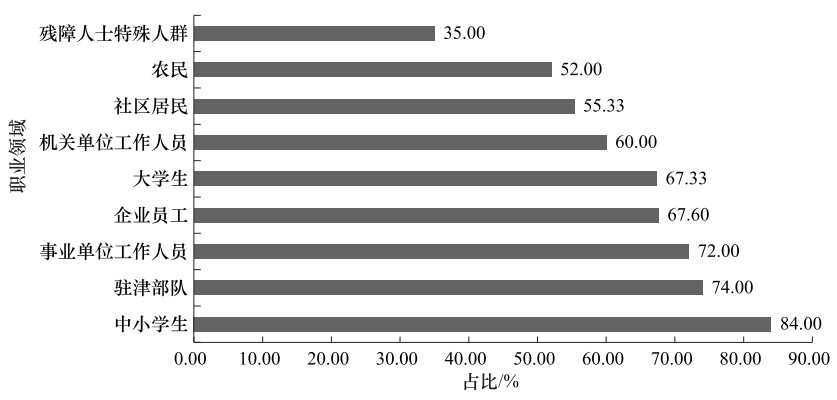
摘要: 为真实了解天津市公众地震科普认知与需求情况,以天津市机关单位工作人员、企业员工、事业单位工作人员、大学生、中小学生、社区居民、农民、驻津部队、残障人士等特殊人群为研究对象,开展专项问卷调查与分析。调查结果显示,天津市公众地震科学知识与地震科普工作的认知度与需求度较高,但仍存在地震科学知识掌握不全面、地震科普产品吸引力不足、科普渠道相对单一等问题,地震科普工作在参与性、互动性与趣味性等方面仍有较大提升空间。基于此,提出提高地震科普工作针对性和有效性及地震科普服务个性化和精准化等建议。Abstract: In order to understand the real situation of the public's cognition and demand for the work of earthquake science popularization, taking Tianjin social public as the research object, by using the method of questionnaire survey, 9 key groups including the office staff, enterprise staff, public institution staff, college students, primary and secondary school students, community residents, farmers, troops and special groups of disabled people were investigated. The survey results show that the public in Tianjin have a high degree of recognition and satisfaction with the knowledge of earthquake science and the work of earthquake science popularization, and the demand for earthquake safety is growing day by day.However, there are still some problems such as the incomplete knowledge of earthquake science, the lack of attraction of the products of earthquake science popularization, and the relatively single channels of science popularization.Based on this, some suggestions are put forward to improve the pertinence and effectiveness of earthquake science popularization, such as broaden the coverage of earthquake science popularization, and improve the accuracy of earthquake science popularization services.
-
表 1 调查样本基本情况
Table 1. Basic data sheet of interviewees in the study
性别 年龄 文化程度 职业 构成 占比/% 构成 占比/% 构成 占比/% 构成 占比/% 男 49.26 <18 10.53 小学 6.73 社区居民 20.00 女 50.74 18—25 15.27 初中 18.57 企业员工 16.67 26—35 28.73 高中 19.78 中小学生 10.00 36—45 25.20 大学专科 10.77 大学生 10.00 46—55 11.53 大学本科 40.17 事业单位 20.00 56—65 6.67 硕士及以上 3.97 特殊人群 6.67 ≥66 2.07 农民 6.67 机关 6.67 驻津部队 3.33 -
薄景山, 李平, 孙有为等, 2019.中国城市抗御地震灾害研究的发展与实践.震灾防御技术, 14(2):259-268. http://zzfy.eq-j.cn/zzfyjs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190201&journal_id=zzfyjs 蓝姝, 胡淑芳, 林岩钊等, 2017.对防震减灾科普工作的思索——基于用户搜索行为的视角.科普研究, 12(2):54-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KUYT201702008.htm 刘子一, 赵甜, 李奇超, 2015.上海市学生人群防震减灾科普工作现状调查研究——以初中生群体为例.国际地震动态, (6):13-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0235-4975.2015.06.007 任福君, 2019.我国科普40年.科学通报, 64(9):885-890. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201909004.htm 王林, 谢碧江, 黄宏生, 2015.基于媒体开展防震减灾科普宣传及其公众认可度的调查研究.灾害学, 30(3):172-175. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2015.03.031 魏本勇, 苏桂武, 陈彪等, 2013.北京市民众地震灾害认知特点的初步分析.地震地质, 35(1):165-176. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2013.01.014 张吕, 余丰晏, 马玉涛, 2019.云南省防震减灾科普宣传教育工作现状调查分析和对策研究.高原地震, 31(2):67-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYDZ201902012.htm 张文佳, 魏本勇, 苏桂武, 2014.少震弱震区民众防震减灾意识现状的调查与分析——以江西萍乡地区为例.地震地质, 36(1):206-221. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201401017.htm 邹文卫, 洪银屏, 翁武明等, 2011.北京市社会公众防震减灾科普认知、需求调查研究.国际地震动态, (6):15-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJZT201106005.htm -



 下载:
下载: