Study on Earthquake Disaster Risk Assessment and Countermeasures: A Casa Study on Luodian County in Guizhou
-
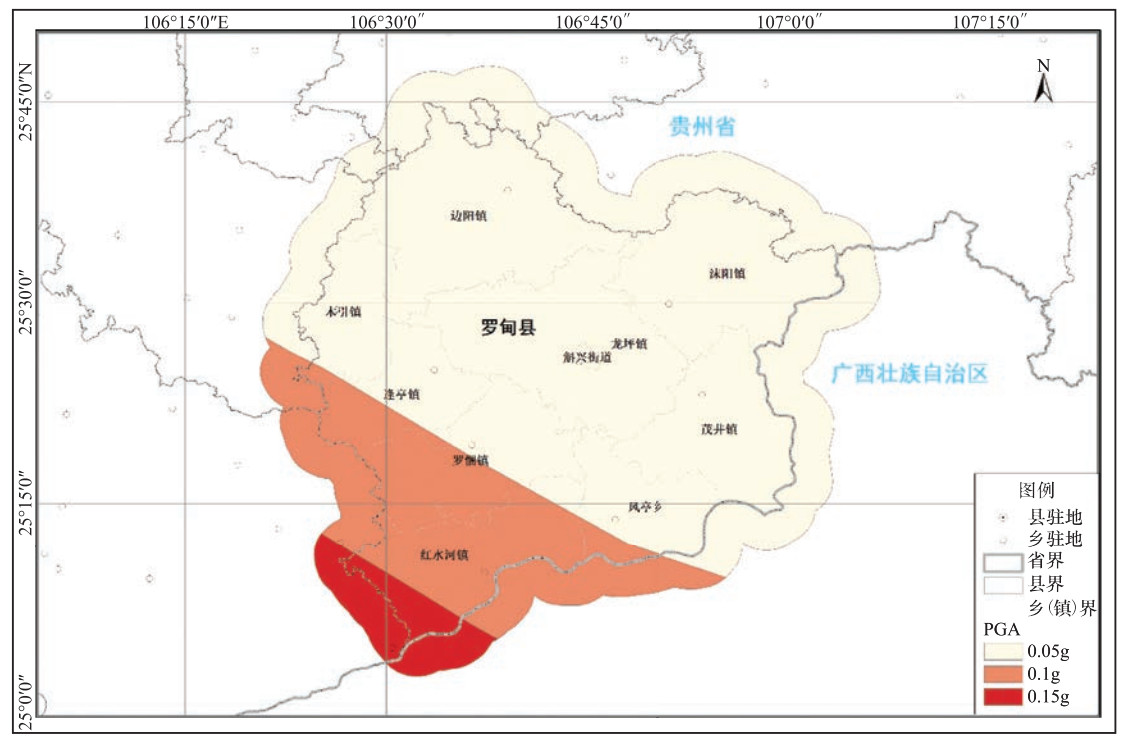
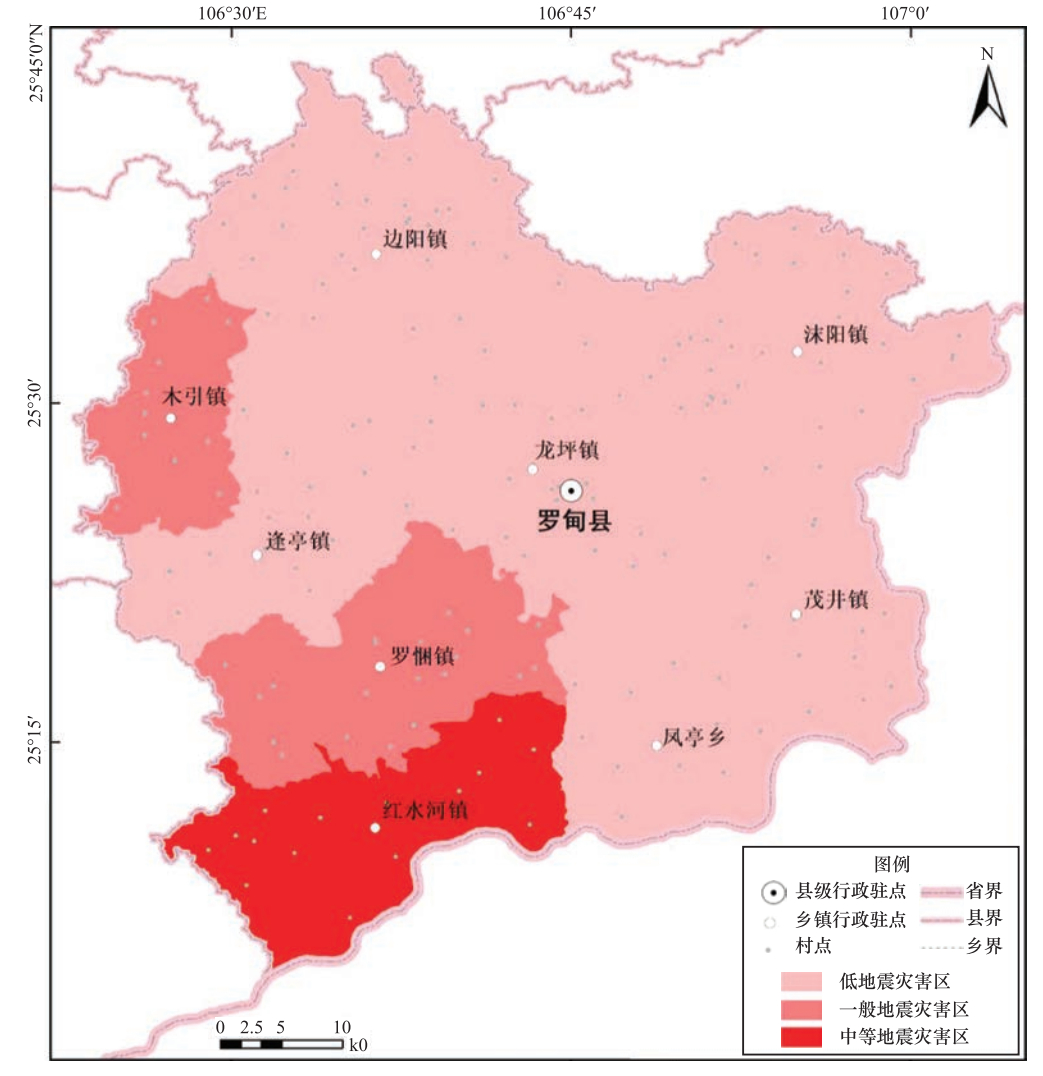
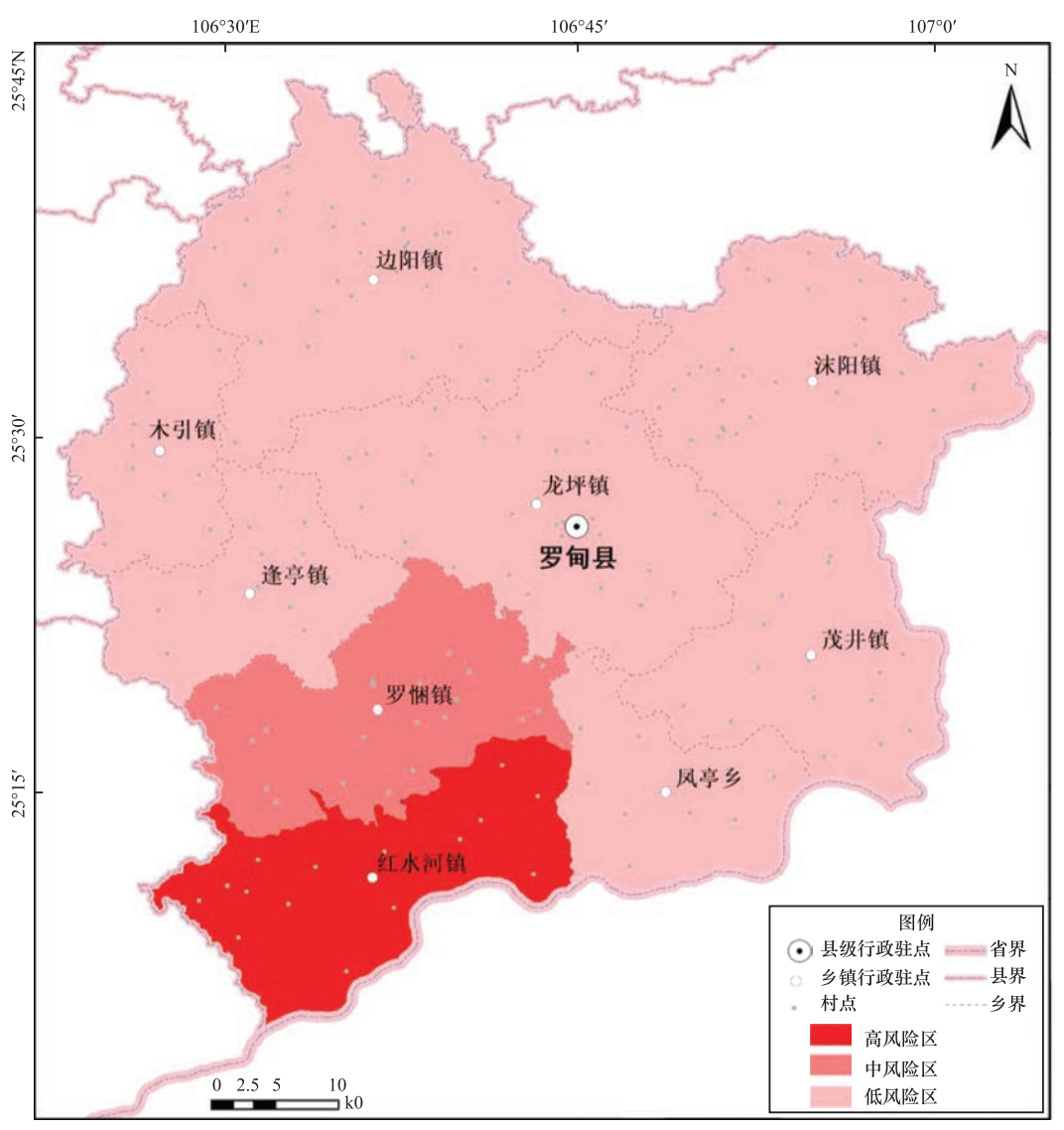
摘要: 为探究贵州省地震灾害风险薄弱环节,减轻地震灾害风险,以贵州省罗甸县为示范,采用地震危险性概率分析方法对各乡镇进行危险性分析,开展地震灾害承灾体现场抽样调查,通过层次分析法和问卷调查的方式,首次构建乡镇级别的地震灾害风险和减灾能力指标体系,评估各乡镇地震灾害综合指数和程度,计算各乡镇地震灾害风险指数,确定红水河镇为高风险区、罗悃镇为中风险区、木引等7个乡镇为低风险区,并从建筑物设防、地震地质灾害及水库地震等角度剖析罗甸县地震灾害特点,从农村危房改造、移民搬迁、地质灾害防护及交通等方面提出减小地震灾害风险的建议。Abstract: In order to explore the weak links of earthquake disaster risk in Guizhou and reduce the risk of earthquake disaster, this paper takes Luodian County of Guizhou as an example, uses the probability analysis method of earthquake risk to carry out a risk analysis on the towns and villages of Luodian County, and carries out the on-site sampling survey of disaster-bearing body. Through adopting the method of AHP and questionnaire survey, a township-level earthquake disaster risk and mitigation capacity index system was constructed for the first time to evaluate the comprehensive index and degree of earthquake disasters for each township in Luodian townships. The calculation of the earthquake disaster risk index determined that 7 townships such as Hongshuihe Town were in a high-risk area, Luopu Town was in a medium-risk area, and Muyin was in a low-risk area. Through the view of building fortification, earthquake geological disasters, and reservoir earthquakes, etc. and the perspective of the analysis of the main characteristics of earthquake disasters in towns and villages of Luodian County, suggestions were put forward to mitigate the risk of earthquake disasters from the perspective of rural dilapidated houses reconstruction, immigration relocation, geological disaster protection and transportation.
-
Key words:
- Earthquake disaster /
- Risk assessment /
- Luodian county /
- Coping strategies
-
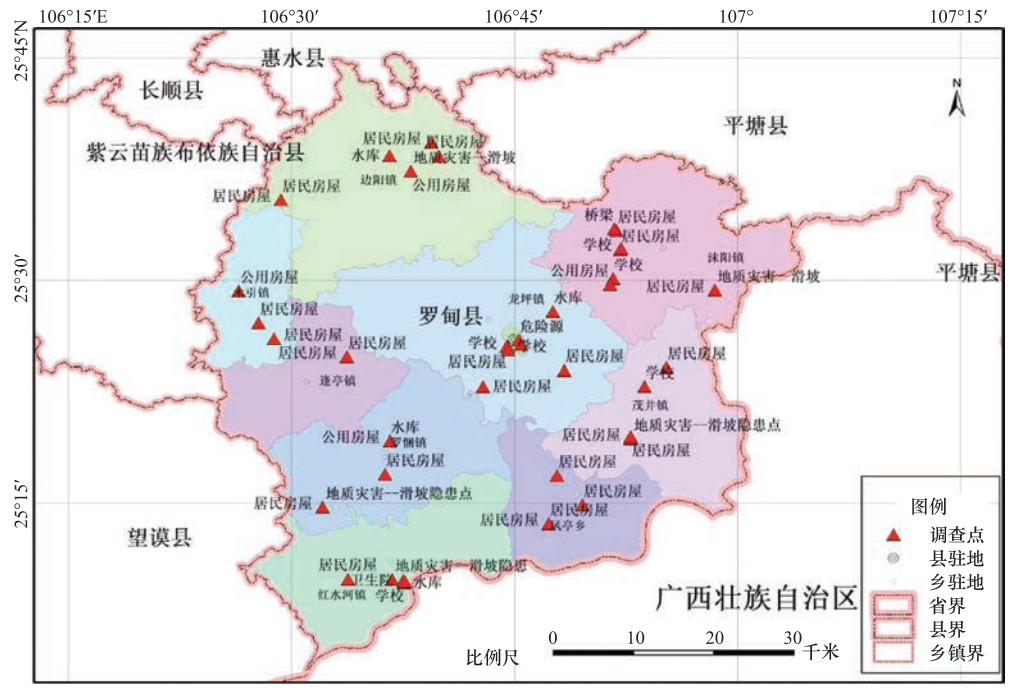
表 1 调查点分布统计
Table 1. Distribution statistics of survey sites of Luodian earthquake disaster victims
乡镇名称 居民房屋 潜在地质灾害点 大型桥梁 水库 医院 学校 重大危险源 公用房屋 调查点总数 边阳镇 1 1 - 1 - 4 1 - 8 逢亭镇 2 - - - - - - - 2 凤亭乡 3 - - - 1 1 - - 5 红水河镇 4 1 - 1 2 2 - - 10 龙坪镇 3 - - - 1 1 - - 5 罗悃镇 1 1 - 1 - - - 2 5 茂井镇 2 1 - - - 4 - - 7 沐阳镇 4 1 1 1 1 3 1 2 14 木引镇 3 - - - - 1 - 1 5 表 2 地震灾害综合程度指数表
Table 2. Index of comprehensive degree of earthquake disasters in each township(town)of Luodian county
乡镇名称 房屋建筑破坏
(Dh)人员死亡
(DP)地震地质灾害
(Dd)水库地震灾害
(Ds)人口经济比
(Li)地震灾害综合程度指数
(EI)风险等级 边阳镇 0.1114 0.1481 0.0990 0.0000 1.3767 0.1481 低风险 逢亭镇 0.1056 0.0741 0.1447 0.0000 2.8382 0.2762 较低风险 凤亭乡 0.0843 0.0741 0.0451 0.0000 2.0438 0.1247 低风险 红水河镇 0.2433 0.2222 0.2360 0.5000 1.9517 0.5084 中风险 龙坪镇 0.0644 0.0370 0.1720 0.0000 0.3560 0.0292 低风险 罗悃镇 0.1554 0.1481 0.0546 0.5000 1.9743 0.3108 较低风险 茂井镇 0.0697 0.0370 0.0945 0.0000 1.1245 0.0679 低风险 沫阳镇 0.0760 0.0370 0.0730 0.0000 1.1028 0.0615 低风险 木引乡 0.0900 0.2222 0.0812 0.0000 3.6121 0.4262 中风险 表 3 减灾能力评价指标及权重表
Table 3. Evaluation indicators and weights of disaster reduction capabilities
指标名称 权重 子指标名称 权重 抗震设防情况(C1) 0.28 建筑物抗震设防情况 0.61 预期地震烈度 0.39 救灾准备能力(C2) 0.24 专业的应急救援队伍建设 0.1050 其他各类应急救援队伍建设 0.0725 应急救援专家队伍建设 0.0725 医疗卫生救援队伍 0.0975 急救医疗网络建设 0.0875 应急救援转运医疗队 0.0650 救灾物资储备网络建设 0.1450 应急物资保障体系建设 0.1050 应急避难场所建设 0.1300 应急避难场所的有效管理 0.1200 应急处置能力(C3) 0.29 应急管理领导机构和办事机构建设 0.1033 应急管理工作制度的制定 0.0567 应急管理工作流程的制定 0.0800 定期开展应急知识培训 0.0933 地方地震应急指挥技术系统建设 0.1467 基础数据库建设 0.0733 技术系统数据库更新与维护 0.1133 完善的灾情获取体系建立 0.1900 调度指挥和联动运行机制建立 0.1433 社会支持能力(C4) 0.19 地震灾害及应急知识宣传教育工作 0.46 日常社会地震应急演练 0.54 表 4 减灾能力指数(PI)
Table 4. Disaster mitigation capacity index (PI) of each town in Luodian
乡镇名称 抗震设防能力
(C1)救灾准备能力
(C2)应急处置能力
(C3)社会支持能力
(C4)减灾能力指数
(PI)边阳镇 0.8333 0.7250 0.3600 0.7000 0.6455 逢亭镇 0.7692 0.4000 0.3300 0.3000 0.4798 凤亭乡 0.7692 0.4500 0.3300 0.7000 0.5348 红水河镇 0.7143 0.4250 0.3300 0.6000 0.5008 龙坪镇 0.8333 0.7250 0.3900 1.0000 0.6845 罗悃镇 0.7692 0.5250 0.3000 0.2000 0.4983 茂井镇 0.8333 0.4000 0.3000 0.2000 0.4800 沫阳镇 0.8333 0.4250 0.3300 0.3000 0.5065 木引乡 0.7692 0.3000 0.3300 0.3000 0.4498 表 5 地震灾害风险指数
Table 5. Earthquake disaster risk coefficients in townships (towns) of Luodian county
乡镇名称 地震灾害综合程度指数
(EI)减灾能力指数
(PI)地震灾害风险系数
(SR)风险等级 红水河镇 0.2605 0.5008 0.5202 高风险 罗悃镇 0.1574 0.4983 0.3159 中风险 木引乡 0.1180 0.4498 0.2623 低风险 逢亭镇 0.0973 0.4798 0.2028 低风险 边阳镇 0.1076 0.6455 0.1667 低风险 茂井镇 0.0604 0.4800 0.1258 低风险 龙坪镇 0.0820 0.6845 0.1198 低风险 凤亭乡 0.0610 0.5348 0.1141 低风险 沫阳镇 0.0558 0.5065 0.1102 低风险 -
黄崇福, 2011.风险分析基本方法探讨.自然灾害学报, 20(5):1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH201105000.htm 李曼, 邹振华, 史培军等, 2015.世界地震灾害风险评价.自然灾害学报, 24(5):1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH201505001.htm 刘军, 程紫燕, 张燕萍等, 2015.贵州地震应急救援中存在的问题及建议.山西地震, (1):46-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6265.2015.01.012 刘军, 苏桂武, 孙甲宁等, 2016.新疆地区县(市)地震应急能力指标体系的建立与区域差异初探.震灾防御技术, 11(4):814-822. http://zzfy.eq-j.cn/zzfyjs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20160412&journal_id=zzfyjs 刘毅, 吴绍洪, 徐中春等, 2011.自然灾害风险评估与分级方法论探研--以山西省地震灾害风险为例.地理研究, 30(2):195-208. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLYJ201102000.htm 罗远模, 张晓东, 徐祥等, 2009.1875年6月8日贵州罗甸地震再考证.贵州地质, 26(4):299-305. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2009.04.013 聂高众, 高建国, 马宗晋等, 2002.中国未来10~15年地震灾害的风险评估.自然灾害学报, 11(1):68-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2002.01.011 申文庄, 朱宝霞, 马明等, 2014.公开地震重点监视防御区信息的风险与控制.灾害学, 29(2):20-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHXU201402005.htm 史培军, 2009.五论灾害系统研究的理论与实践.自然灾害学报, 18(5):1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2009.05.001 苏桂武, 高庆华, 2003.自然灾害风险的分析要素.地学前缘, 10(S1):272-279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY2003S1036.htm 唐丽华, 苗崇刚, 宋立军等, 2013.年度地震危险区地震灾害应急风险评估指标体系构建初探.灾害学, 28(2):153-155. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2013.02.030 王东明, 高永武, 2019.城市建筑群概率地震灾害风险评估研究.工程力学, 36(7):165-173. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCLX201907020.htm 王尚彦, 2014.贵州水库地震的诱发因素分析.科技创新导报, 11(34):97-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-098X.2014.34.068 肖亮, 俞言祥, 2011.中国西部地区地震烈度衰减关系.震灾防御技术, 6(4):358-371. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2011.04.002 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2015.GB/T 19428-2014地震灾害预测及其信息管理系统技术规范.北京: 中国标准出版社. Cornell C. A., 1968.Engineering seismic risk analysis.Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 58(5):1583-1606. Koravos G. C., Tsapanos T. M., ejaichund M., 2006.Probabilistic seismic hazard assessment for Japan.Pure and Applied Geophysics, 163(1):137-151. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/resolve/reference/ADS?id=2006RSPTA.364.1965S Shi P. J., Du J., Ji M. X., et al., 2006.Urban risk assessment research of major natural disasters in China.Advances in Earth Science, 21(2):170-177. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285736416_Urban_risk_assessment_research_of_major_natural_disasters_in_China Smith K., 2013.Environmental hazards:assessing risk and reducing disaster.6th ed.New York:Routledge, 148. Spence R., So E., Jenny S., et al., 2008.The global earthquake vulnerability estimation system (GEVES):an approach for earthquake risk assessment for insurance applications.Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering, 6(3):463-483. doi: 10.1007/s10518-008-9072-7 -



 下载:
下载: