Application Study of Seismic Isolation Design on A Shear Wall Structure in High Intensity Area
-
摘要: 对于近断层处高烈度区高层剪力墙结构,传统设计难以解决墙体太厚、配筋太大等难题。为研究在考虑近断层影响下高烈度区剪力墙住宅采用隔震设计的技术可行性,采用隔震设计对某剪力墙结构工程进行全面分析。对比分析常规剪力墙结构方案及增设橡胶隔震支座的隔震方案,分析结果表明,隔震方案较常规方案前3阶结构自振周期延长约3倍,从而有效减小了上部结构的地震作用;在设防烈度地震作用下,结构水平向减震系数为0.281,上部结构所受水平地震作用和抗震措施可按降低一度进行设计;罕遇地震作用下隔震支座性能稳定,上部结构基本处于弹性工作状态。研究结论可为隔震支座设计和进一步研究提供参考。Abstract: For the high-rise shear wall structure with high intensity near the fault, the traditional design is difficult to solve such problems as "the wall is too thick and the reinforcement is too big". In order to study the technical feasibility of adopting seismic isolation design for shear wall structures in high intensity area considering the influence of fault, a comprehensive analysis and comparison were made on the seismic isolation design of a shear wall structure project. Through the comparative analysis of the conventional frame structure scheme and the isolation scheme with rubber isolation support, the isolation scheme extends the first three order period of the structure by over 2.7 times under the action of earthquake. And it can effectively reduce the seismic action of the structure. Under the seismic fortification intensity, the horizontal damping coefficient of the structure is 0.281. The horizontal seismic action and the seismic measures of the superstructure can be reduced by one degree. Under the action of rare earthquake, the performance of isolation support is stable and the superstructure is in elastic working state. The results can provide reference for the design and further research of isolation bearing.
-
Key words:
- High-rise buildings /
- Isolation technology /
- Rubber bearing /
- Time history analysis
-
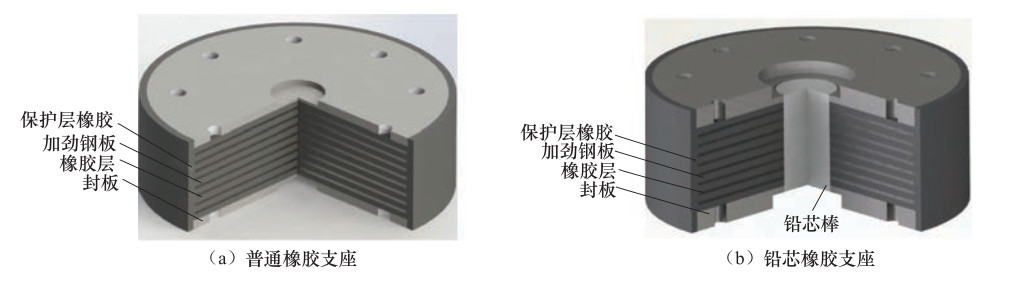
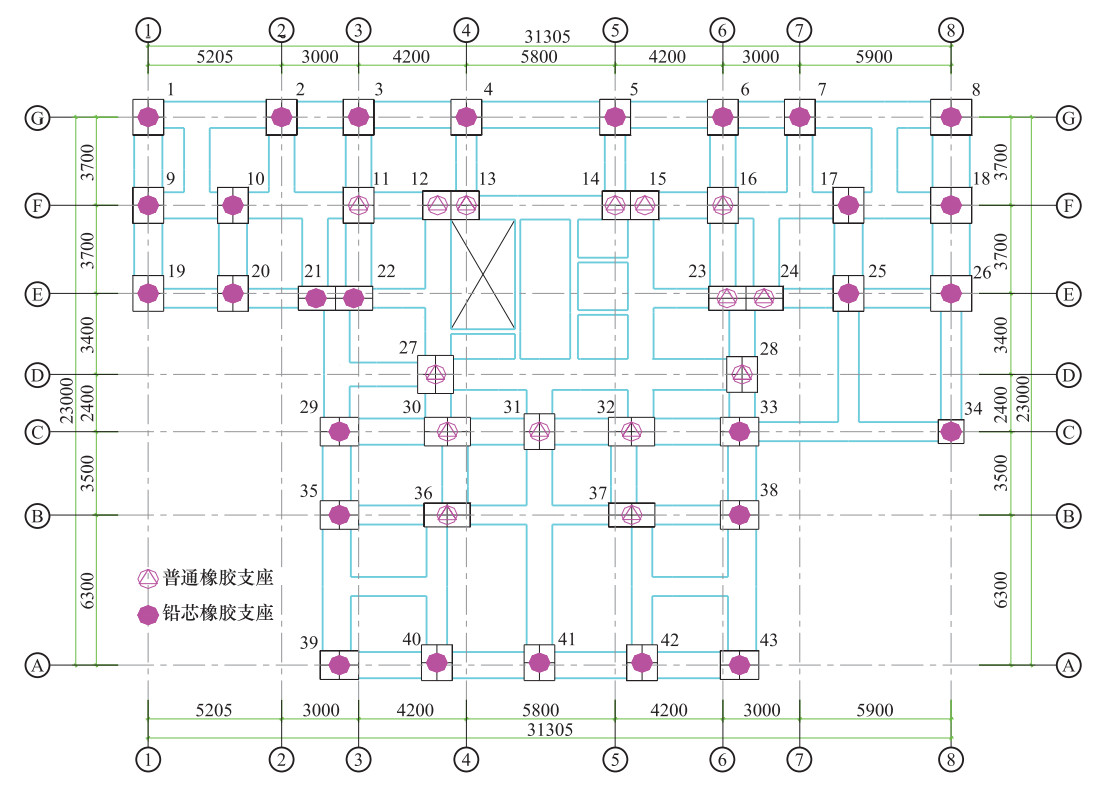
表 1 隔震支座参数
Table 1. Isolation bearing parameters
阻尼器型号 竖向刚度/kN·mm-1 等效水平刚度/kN·mm-1 支座直径/mm 屈服前刚度/kN·mm-1 屈服后刚度/kN·mm-1 屈服力/kN 支座总高度/mm LRB1000 4252 2.76 1000 14.64 1.54 267 370 28 LNB1000 3200 1.59 1000 — — — 370 15 表 2 前3阶振型周期对比
Table 2. Periodic comparison of the first three modes
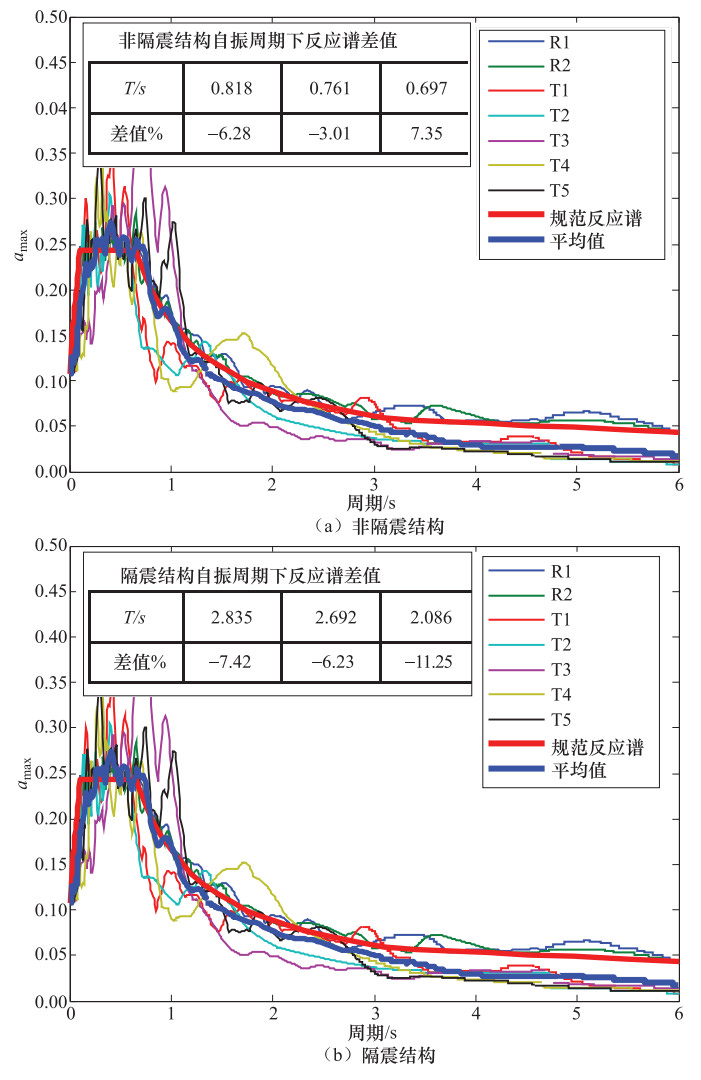
振型 非隔震结构/s ETABS隔震/s 周期放大系数 SATWE 有效质量系数(X+Y+Z)/% ETABS 有效质量系数(X+Y+Z)/% 周期误差/% 1 0.791 60+14+0 0.818 65+12+0 3.41 2.835 3.58 2 0.785 17+55+0 0.761 14+61+0 3.06 2.692 3.43 3 0.764 0+0+72 0.697 0+0+68 8.77 2.086 2.73 表 3 结构基底剪力对比
Table 3. Comparison table of bottom shear force of structure
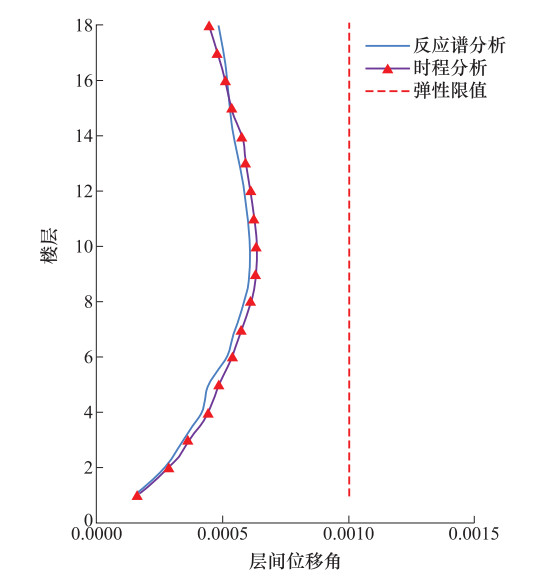
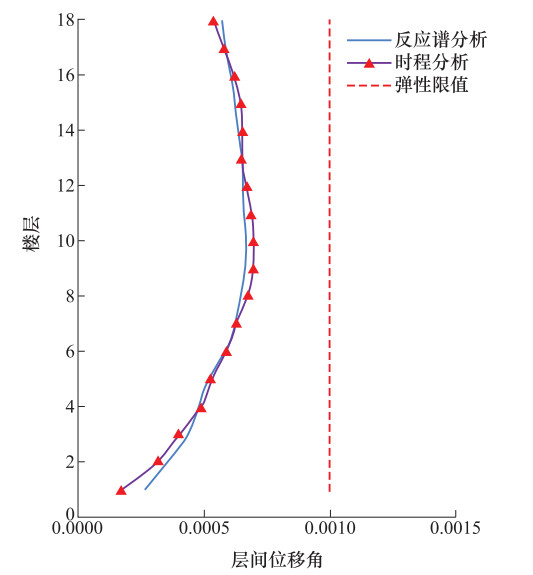
工况 反应谱分析结果/kN 时程分析结果/kN 差值/% 非隔震模型(x向) 9832 9395 -4.44 非隔震模型(y向) 10704 10252 -4.22 隔震模型(x向) 17938 17052 -4.94 隔震模型(y向) 19420 18120 -6.69 表 4 偏心率计算结果
Table 4. Results of eccentricity
项目 重心/m 刚心/m 偏心距/m 抗扭刚度/kN·m-1 回转半径/m 偏心率/% x向 31.02 31.27 0.25 9.133×107 20.28 1.2 y向 13.69 13.49 0.20 9.133×107 20.28 1.0 表 5 非隔震结构与隔震结构层间剪力及倾覆弯矩
Table 5. Comparison table of bottom shear force of structure
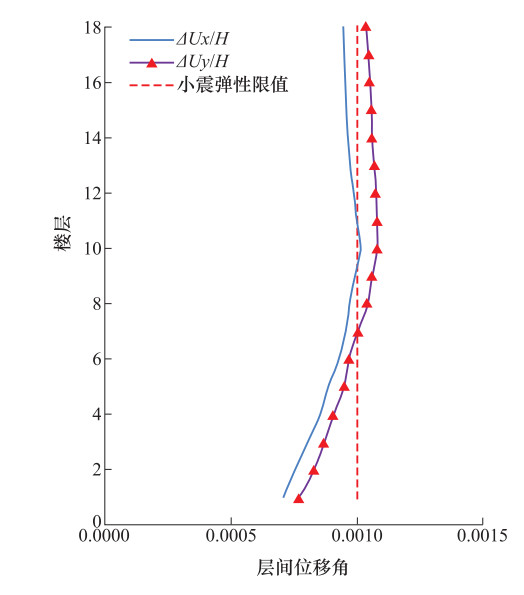
楼层 层间剪力Vx 层间剪力Vy 倾覆弯矩Mx 倾覆弯矩My 最大值 非隔震 隔震 比值 非隔震 隔震 比值 非隔震 隔震 比值 非隔震 隔震 比值 18 6461 1529 0.237 6455 1543 0.239 16697 3979 0.238 16685 3956 0.237 0.239 17 12271 2900 0.236 12168 2994 0.246 50282 12213 0.243 50567 11933 0.236 0.246 16 16970 4093 0.241 16814 4253 0.253 97692 24095 0.247 98390 23425 0.238 0.253 15 21038 5168 0.246 20747 5239 0.253 155893 38993 0.250 156922 38043 0.242 0.253 14 24481 6119 0.250 23947 6104 0.255 222857 56410 0.253 225053 55415 0.246 0.255 13 27237 6884 0.253 26761 6970 0.260 298040 76292 0.256 302368 74924 0.248 0.260 12 29435 7562 0.257 29048 7776 0.268 378482 98465 0.260 385318 96375 0.250 0.268 11 31448 8245 0.262 30931 8300 0.268 463211 122122 0.264 472297 119968 0.254 0.268 10 33188 8757 0.264 32590 8538 0.262 553200 146497 0.265 563903 145050 0.257 0.265 9 34645 8978 0.259 33905 8855 0.261 646886 171643 0.265 658340 170647 0.259 0.265 8 36352 9180 0.253 35240 9427 0.267 742136 200564 0.270 753707 196565 0.261 0.270 7 38453 9633 0.251 36490 9959 0.273 838940 225472 0.269 855000 223425 0.261 0.273 6 40640 10000 0.246 38111 9914 0.260 935047 252793 0.270 959786 250982 0.261 0.270 5 42978 9961 0.232 40130 9698 0.242 1030607 279590 0.271 1065000 278765 0.262 0.271 4 44890 9908 0.221 42263 9905 0.234 1131750 306365 0.271 1170965 305540 0.261 0.271 3 46700 10358 0.222 44219 10943 0.247 1235036 335100 0.271 1279286 332732 0.260 0.271 2 48190 11257 0.234 46028 12210 0.265 1342393 377080 0.281 1393178 361703 0.260 0.281 1 49145 11743 0.239 47418 12722 0.268 1475250 395410 0.268 1535036 396836 0.259 0.268 表 6 罕遇地震作用下支座最大压应力和最小压应力(MPa)
Table 6. Maximum and minimum compressive stress of bearing under rare earthquake (MPa)
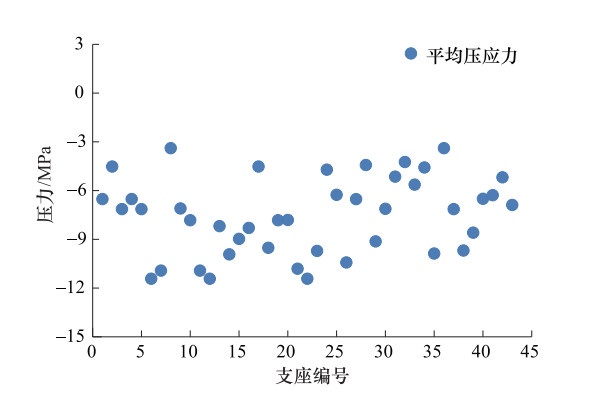
地震波 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 R1 R2 最值 最大压应力 -15.46 -14.03 -14.72 -15.28 -16.22 -16.56 -15.95 -16.56 平均压应力 -9.96 -8.93 -9.71 -9.78 -9.85 -10.04 -9.97 -10.04 最大拉应力 0.32 0.23 0.24 0.19 0.25 0.24 0.23 0.32 表 7 罕遇地震作用下x、y向作为主方向输入地震波时隔震层支座位移(mm)
Table 7. The support displacement of time-isolation layer in X and Y directions (mm)
地震方向 比较项 x向位移 y向位移 合位移 位移容许值 x向 最大值 270 220 348 550 最小值 260 211 335 550 y向 最大值 218 267 345 550 最小值 214 262 338 550 -
杜东升, 王曙光, 刘伟庆等, 2010.高层建筑组合隔震的设计方法及应用.东南大学学报(自然科学版), 40(5):1039—1046. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=35499044 傅金华, 2011.日本抗震结构及隔震结构的设计方法.北京:中国建筑工业出版社. 李爱群, 2012.日本东北大地震之隔减震建筑考察与思考.工程力学, 29(S2):69—77, 106. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gclx2012z2008 罗佳俊, 2017.高烈度区抗震与隔震结构设计对比分析.广州: 华南理工大学. 齐杰, 2018.高烈度区高层RC剪力墙隔震结构抗震性能研究.兰州: 兰州交通大学. 肖从真, 薛彦涛, 曾德民等, 2009.成都凯德风尚高层建筑隔震设计与研究.建筑结构, 39(6):93—97. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jzjg200906023 徐至钧, 李景, 2013.建筑隔震技术与工程应用.北京:中国标准出版社. 徐至钧, 徐卓, 赵尧钟等, 2014.建筑结构隔震技术与应用.上海:同济大学出版社. 薛彦涛, 2011.建筑结构隔震技术现状与应用.建筑结构, 41(11):82—87. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jzjg201111017 中国工程建设标准化协会, 2001.CECS 126:2001叠层橡胶支座隔震技术规程.北京:中国建筑工业出版社. 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2016.GB 50011—2010建筑抗震设计规范[2016版].北京: 中国建筑工业出版社. Takewaki I., 2008. Robustness of base-isolated high-rise buildings under code-specified ground motions. The Structural Design of Tall & Special Buildings, 17(2):257—271. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dcf37cfed0c118124250c3e297b42c68 -



 下载:
下载: