Focal Mechanism Solution for Jiashi Ms5.5 Earthquake Sequence on September 4, 2018 and the Characteristics of Stress Field in the Source Area
-
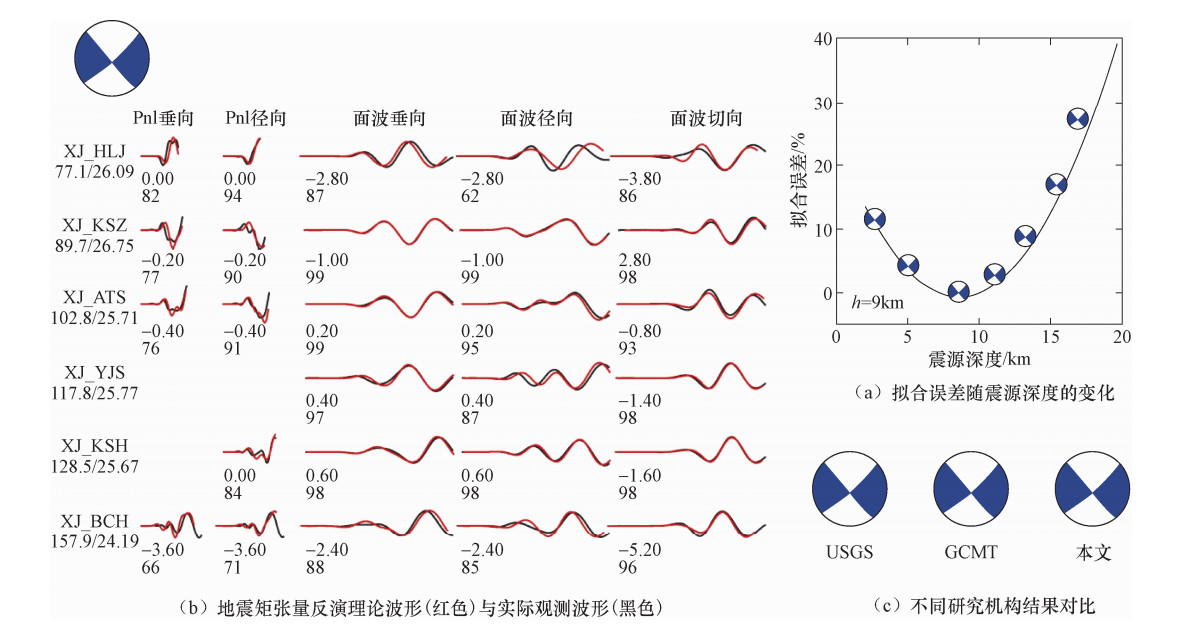
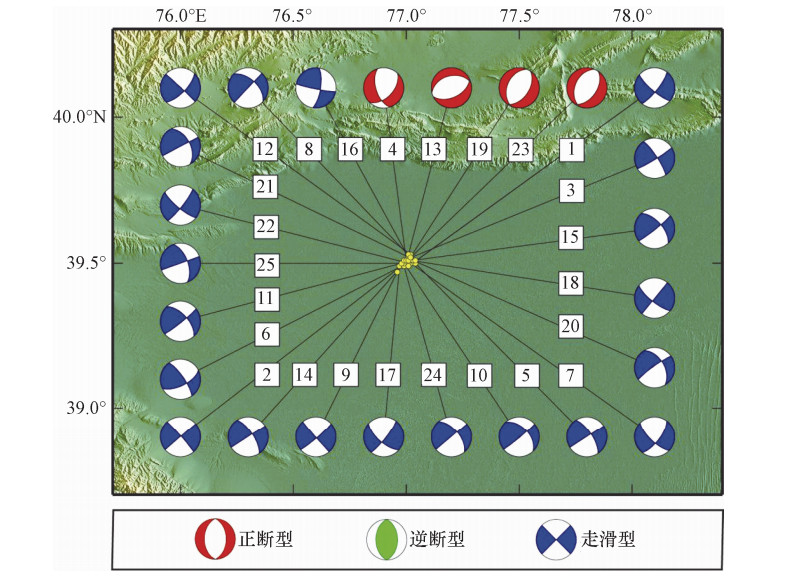
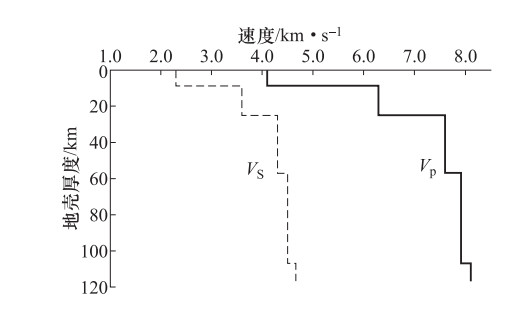
摘要: 本文采用新疆测震台网数字波形记录,利用CAP和P、S波初动和振幅比方法计算2018年9月4日伽师5.5级地震序列中MS≥2.5地震的震源机制解,结合地震烈度等震线和双差重定位后的地震序列空间展布等特征分析了此次地震的发震构造,反演了震源处应力场。结果表明,伽师5.5级地震呈NE向的节面I为发震断层面,属于左旋走滑断层,震源深度为9km,发震构造可能为浅部超基底断裂;地震序列中有21次为走滑型,4次为正断型,说明绝大多数序列的破裂方式与主震相近,表明余震应力场主要受主震震源应力场控制;P轴方位在NNE向有明显的优势分布且倾伏角较小,T轴方位在NWW向有明显的优势分布且倾伏角较小,说明震源处主要以NNE向水平挤压和NWW向水平拉张作用为主;此次伽师5.5级地震序列表现的浅部应力场与已有研究得出的震源区深部应力场基本一致,应力形因子R的最优解为0.17,说明震源处近NE向中间主应力σ2有一定挤压成分。Abstract: Based on the digital waveforms record of Xinjiang seismic network,the CAP and P-wave,S-wave initial motion and amplitude ratio methods were used to calculate the focal mechanism solution of the MS≥2.5 earthquake sequence of Jiashi Ms5.5 earthquake on September 4,2018. The seismogenic structure of this earthquake was analyzed based on the seismic intensity isoseismic lines and the spatial distribution of the earthquake sequence after double differential relocation,and the stress field in the source area was inverted. The results show that the nodal plane I is the seismogenic fault,which is northeast trend and nearly upright left-lateral strike slip fault. The focal depth of main shock is about 9km. It is preliminarily inferred that the seismogenic structure may be superficial ultra crystalline basement fault. The 21 earthquake sequences are strike-slip and 4 earthquake sequences are normal faults. The rupture pattern of most earthquake sequences is similar to that of the main shock,indicating that the aftershock stress field is mainly controlled by the main shock source area stress field. P axis is near north-northeast,and the inclination angle is small. T axis is near northwest-west,and the inclination angle is small. It indicates that the stress field of source area is mainly under action of north-northeast horizontal compression and the northwest-west horizontal tensional. The shallow stress field shown in Jiashi 5.5 earthquake sequences is basically the same as the deep stress field obtained from previous research. The stress shape ratio is 0.17,and it shows that there is a certain compression of σ2.
-
Key words:
- Jiashi MS5.5 earthquake /
- Focal mechanism solution /
- Stress field /
- CAP /
- First motion /
- Amplitude ratio /
- Double difference location
-
表 1 伽师5.5级地震和早期24次MS≥2.5地震序列震源机制解
Table 1. Focal mechanism solutions of Jiashi MS5.5 earthquake and the early 24 MS≥2.5 earthquake sequences
序号 发震时刻 震中/(°) 震级MS 节面Ⅰ/(°) 节面Ⅱ/(°) P轴 T轴 B轴 方法 东经 北纬 走向 倾角 滑动角 走向 倾角 滑动角 方位 倾伏角 方位 倾伏角 方位 倾伏角 1 2018-09-04
05:51:4477.01 39.49 4.7 38 78 -13 130 77 -167 354 17 84 1 176 72 CAP 2 2018-09-04
05:52:5577.01 39.51 5.5 49 90 3 319 87 -180 183 2 274 2 49 87 CAP 3 2018-09-04
06:48:2676.99 39.51 3.3 9 58 85 327 80 175 192 3 283 9 83 80 Snoke 4 2018-09-04
06:52:5877.00 39.51 3.3 43 51 -42 163 58 -132 17 54 282 4 189 35 Snoke 5 2018-09-04
07:10:1577.04 39.50 2.6 57 90 20 327 70 180 190 14 284 14 57 70 Snoke 6 2018-09-04
07:20:3877.03 39.51 3.2 63 64 16 326 75 153 16 7 282 28 120 60 Snoke 7 2018-09-04
08:25:2477.02 39.50 3.8 37 70 -20 134 71 -158 355 28 265 1 173 62 CAP 8 2018-09-04
09:31:3577.02 39.52 2.7 43 90 35 313 55 180 173 23 274 23 43 55 Snoke 9 2018-09-04
10:51:2476.96 39.47 4.6 49 84 -2 139 88 -174 4 6 274 3 158 84 CAP 10 2018-09-04
11:26:1776.99 39.50 3.1 50 86 39 318 50 175 177 24 282 29 54 50 Snoke 11 2018-09-04
15:11:5476.98 39.50 3.0 51 85 29 318 60 174 181 16 278 24 60 60 Snoke 12 2018-09-04
16:12:2077.02 39.53 2.6 44 70 2 314 88 160 1 12 267 15 129 70 Snoke 13 2018-09-04
21:11:4477.01 39.53 3.2 255 40 -82 65 50 -96 295 82 160 5 70 5 Snoke 14 2018-09-04
21:57:5776.98 39.49 3.4 57 90 20 327 70 180 190 14 284 14 57 70 Snoke 15 2018-09-05
01:10:4177.03 39.51 2.6 51 85 29 318 60 174 181 16 278 24 60 60 Snoke 16 2018-09-05
01:52:5077.01 39.52 3.0 101 85 19 9 70 174 233 10 326 17 115 70 Snoke 17 2018-09-05
02:44:0876.97 39.49 3.6 38 81 -23 131 67 -170 352 22 87 9 197 65 CAP 18 2018-09-05
11:15:2177.02 39.51 3.7 39 90 -15 129 75 180 353 10 85 10 219 75 CAP 19 2018-09-07
02:05:4277.01 39.51 2.6 34 50 -83 204 40 -97 344 82 119 5 209 5 Snoke 20 2018-09-07
02:42:4577.03 39.51 3.3 234 83 -39 329 50 -171 184 31 288 21 46 50 Snoke 21 2018-09-07
04:06:4277.04 39.51 3.1 62 90 40 332 50 180 190 27 295 27 62 50 Snoke 22 2018-09-07
09:01:2377.01 39.50 3.0 38 82 -13 130 77 -172 353 14 84 4 189 75 Snoke 23 2018-09-07
17:14:5677.02 39.52 2.5 34 50 -83 204 40 -97 344 83 119 5 209 5 Snoke 24 2018-09-08
21:49:2876.99 39.49 2.6 50 90 30 320 60 180 180 20 279 20 50 60 Snoke 25 2018-09-20
13:24:0576.98 39.50 3.0 70 90 30 340 60 180 200 20 299 20 70 60 Snoke 表 2 伽师5.5级地震震源处应力反演结果
Table 2. Source stress field of Jiashi MS5.5 earthquake
σ1 σ2 σ3 应力形因子 应力结构 方位/(°) 倾角/(°) 方位/(°) 倾角/(°) 方位/(°) 倾角/(°) R -163
-320— -21824
-63—8640
12—20164
-23—88-69
-80— -609
1—200.17
0.01—0.45走滑 注:表中数值范围为各参数95%置信度的不确定性范围 -
刁桂苓, 王海涛, 高国英等, 2005.伽师强震系列应力场的转向过程.地球物理学报, 48(5):1062-1068. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2005.05.012 高国英, 聂晓红, 夏爱国, 2004.2003年伽师6.8级地震序列特征和震源机制的初步研究.中国地震, 20(2):179-186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2004.02.008 高国英, 王海涛, 温和平等, 2001.帕米尔东北侧中强地震前应力场动态变化特征分析.西北地震学报, 23(4):389-394. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdzxb200104012 李艳永, 王成虎, 杨佳佳, 2018.呼图壁地区震源机制解及构造应力场特征分析.大地测量与地球动力学, 38(12):1246-1250. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dkxbydz201812007 刘启元, 陈九辉, 李顺成等, 2000.新疆伽师强震群区三维地壳上地幔S波速度结构及其地震成因的探讨.地球物理学报, 43(3):356-365, 433. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2000.03.009 龙海英, 高国英, 聂晓红, 2007.1997-1998年伽师强震群震源区应力场特征.西北地震学报, 29(2):145-149. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdzxb200702010 单新建, 何玉梅, 朱燕等, 2002.伽师强震群震源破裂特征的初步分析.地球物理学报, 45(3):416-425. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2002.03.013 苏廼秦, 2003.新疆伽师强震群强震主破裂面走向初探.西北地震学报, 25(3):269-274. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdzxb200303014 屠泓为, 万秀红, 高歌等, 2008.1977年至2006年新疆伽师地震断层性质及应力场变化原因初探.地球物理学进展, 23(4):1038-1044. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxjz200804007 万永革, 2008.美国Landers地震和Hector Mine地震前震源机制与主震机制一致现象的研究.中国地震, 24(3):216-225. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2008.03.003 万永革, 2019.同一地震多个震源机制中心解的确定.地球物理学报, 62(12):4718-4728. doi: 10.6038/cjg2019M0553 王晓楠, 唐方头, 邵翠茹, 2018.南迦巴瓦构造结周边地区主要断裂现今运动特征.震灾防御技术, 13(2):267-275. http://zzfy.eq-j.cn/zzfyjs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20180202&journal_id=zzfyjs 王筱荣, 孙甲宁, 王季达, 2005.1997-2004年伽师地区6级地震序列特征研究.内陆地震, 19(1):44-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8956.2005.01.007 徐朝繁, 段永红, 田晓峰等, 2007.新疆伽师强震群区基底界面结构特征.地震学报, 29(5):477-482. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2007.05.004 张志斌, 金花, 朱皓清, 2019a.2018年9月4日伽师MS 5.5地震与97年及03年伽师强震属于同一发震构造吗?.地球物理学进展, 34(6):2232-2238. 张志斌, 冉慧敏, 金花, 2019b.2016年12月8日新疆呼图壁MS6.2地震发震构造初步研究.地震工程学报, 41(4):962-969. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdzxb201904020 赵翠萍, 陈章立, 郑斯华等, 2008.伽师震源区中等强度地震矩张量反演及其应力场特征.地球物理学报, 51(3):782-792. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2008.03.019 周仕勇, 许忠淮, 陈晓非, 2001.伽师强震群震源特征及震源机制力学成因分析.地球物理学报, 44(3):654-662. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxb200105009 周仕勇, 许忠淮, 韩京等, 1999.主地震定位法分析以及1997年新疆伽师强震群高精度定位.地震学报, 21(3):258-265. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.1999.03.005 Efron B. R., Tibshirani, 1986. Bootstrap methods for standard errors, confidence intervals, and other measures of statistical accuracy. Stat. Sci, 1(1):54-75. http://doi.ieeecomputersociety.org/resolve?ref_id=doi:10.1214/ss/1177013815&rfr_id=trans/tk/2010/04/ttk2010040565.htm Hardebeck J. L., Michael A. J., 2006. Damped regional-scale stress inversions:Methodology and examples for southern California and the Coalinga aftershock sequence. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 111 (B11):B11310. Kagan Y. Y., 1991.3-D rotation of double-couple earthquake source.Geophys J Int, 106 (3):709-716. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1991.tb06343.x Kagan Y. Y., 2003. Accuracy of modern global earthquake catalogs. Phys Earth planet Inter, 135 (2-3):173-209. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9201(02)00214-5 Kagan Y. Y., Jackson D. D., 2000. Probabilistic forecasting of earthquakes. Geophys J Int, l43 (2):438-453. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246X.2000.01267.x Martínez-Garzón P., Kwiatek G., Ickrath M., et al., 2014. MSATSI:A MATLAB package for stress inversion, combining solid classic methodology, a new simplified user handling, and a visualization tool. Seismological Research Letters, 85 (4):896-904. doi: 10.1785/0220130189 Snoke J. A., Munsey J. W., Teague A. G., et al., 1984. A program for focal mechanism determination by combined use of polarity and SV-P amplitude ratio data. Earthquake Notes, 55 (3):15. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1111/j.1528-1167.2006.00001_8.x Waldhauser F., Ellsworth W. L., 2000. A double difference earthquake location algorithm:Method and application to the Northern Hayward Faul, Califomia. Bul1. Seism. Soc. Am, 90 (6):1353-1368. doi: 10.1785/0120000006 Zhao L. S., Helmberger D. V., 1994. Source estimation from broadband regional seismograms.Bull Seismol Soc Amer, 84 (1):91-104. Zhu L. P., Helmberger D. V., 1996. Advancement in source estimation techniques using broadband regional seismograms. Bull Seismol Soc Amer, 86 (5):1634-l641. -



 下载:
下载: