Identification and Analysis of Micro-earthquake Events in Open-pit Ore Area Based on Waveform Characters——A Case Study of Zhuozishan Molybdenum Mine
-
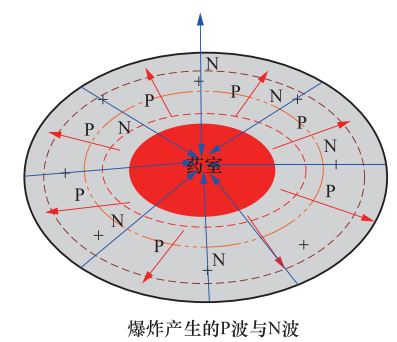
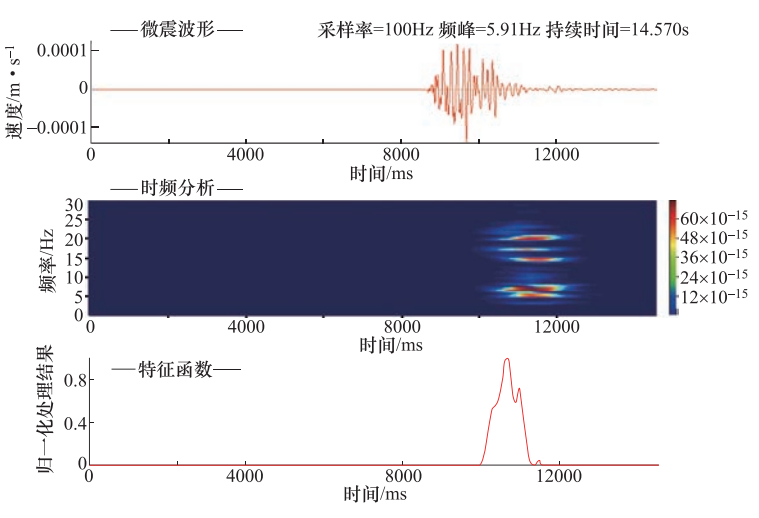
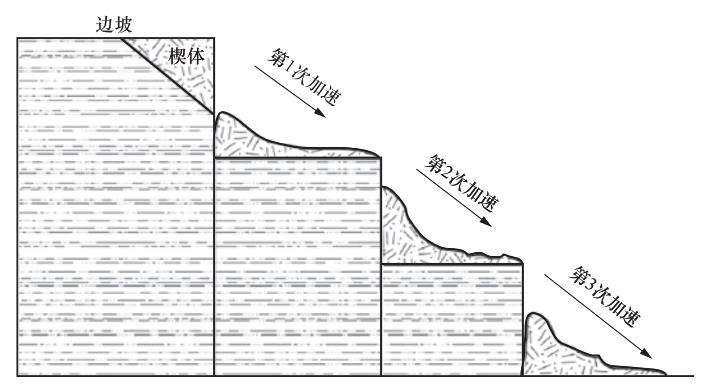
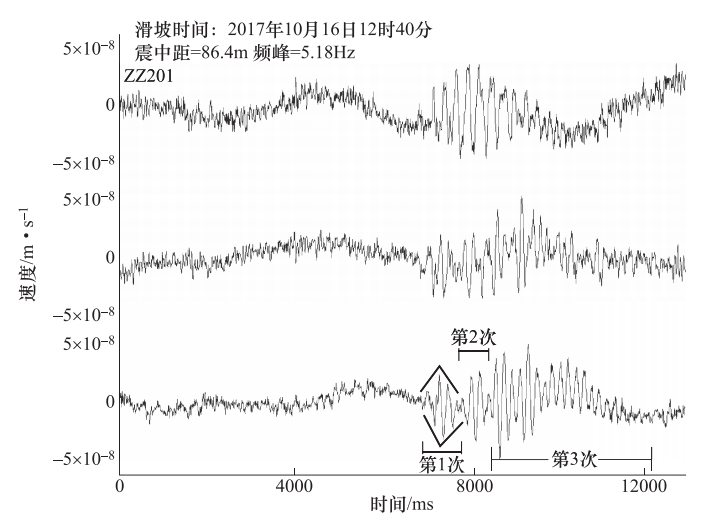
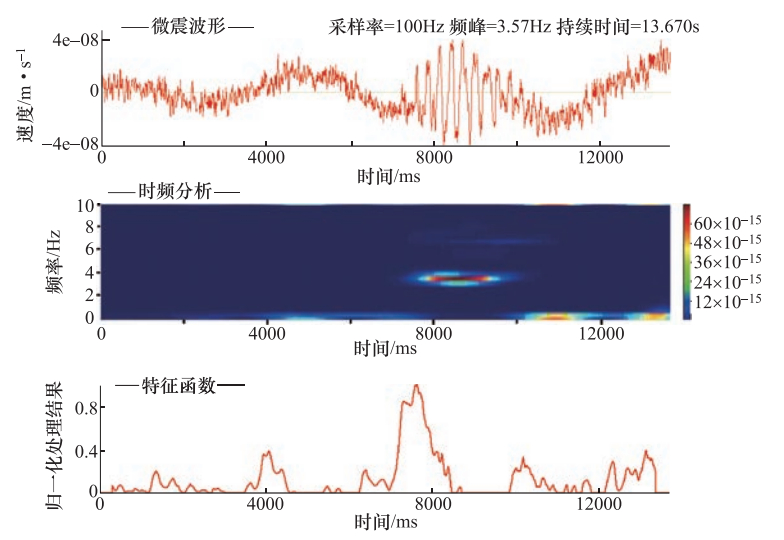
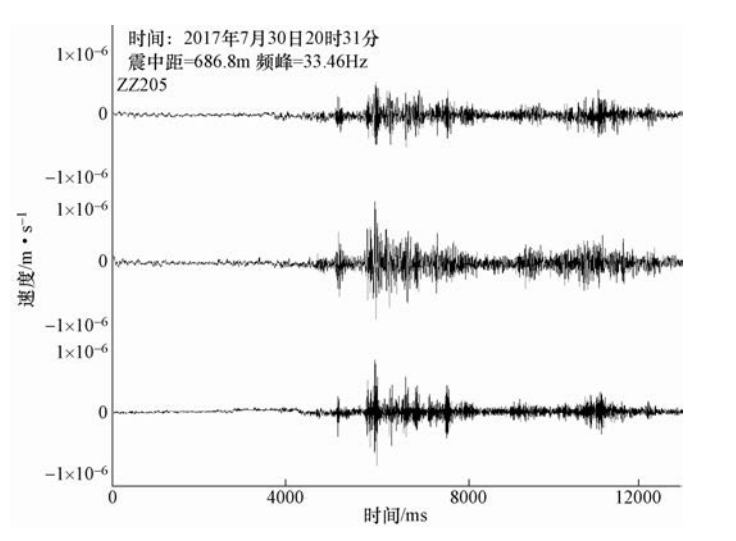
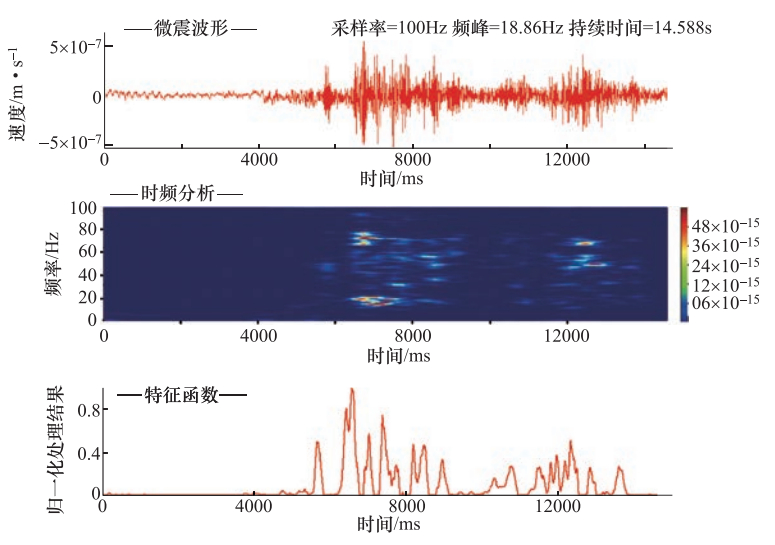
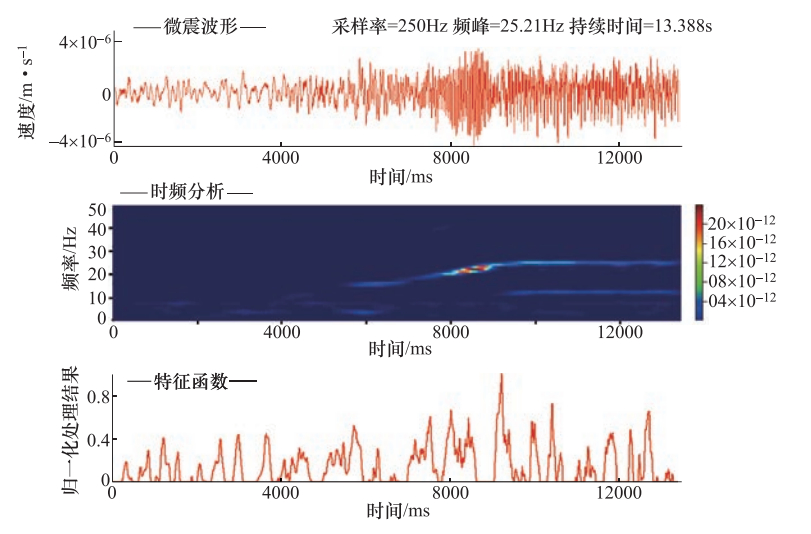
摘要: 基于前人研究成果以及现场的实测结果,采用卓资山露天钼矿微震监测项目产出资料,提取了5类微震事件的波形特征和时频特征。波形特征显示:微地震的振幅、辐射均匀性和频率变化特征表明微地震是由于岩层受到单力偶和剪切力作用破裂而产生;爆破具有P波初动方向向上、S波不易识别的特点,包含“初震段、主震段、尾波段”三段变化形态;小型边坡滑坡波事件属楔体滑坡,是由多个“加速—缓冲—终止”构成,波形是由包络线呈“V”字形的多组脉冲波列组成;机械开采震动事件具有自振能量不变、脉冲幅度相差很大、持续时间间隔不确定的特点;运输车辆波形振幅具有形态“弱—强—弱”、等频率、包络线呈多段纺锤形的特征。时频空间分布可以分为相对独立、界限分明的两类:一类包含微地震、爆破、机械开采、小型边坡滑坡事件,另一类只包含车辆运输事件。Abstract: Based on the previous research results and the field measurements, taking Zhuozishan open-pit molybdenum mine as an example, we analyzed the waveform and time-frequency characteristics of five kinds of micro-seismic events in the region. The amplitude, radiation uniformity and frequency variation of the microearthquakes show that the microearthquakes are caused by the single force couple and shear force. The blasting has a upward P wave initial direction, whereas the initial direction of S wave is not easy to identify, characterized with three section changes of initial earthquake, main shock and tail band". The event of small slope landslide belongs to wedge-body landslide, and the total process is composed of several so-called acceleration-buffer terminations, in which the waveform is composed of multiple sets of pulse wave trains with "V" shape of envelope line. The vibration event of mechanical mining is characterized by constant natural vibration energy, great difference in pulse amplitude and uncertain duration interval. The wave amplitude of the transport vehicle has the shape of "weak-strong-weak", equal frequency and multi-segment spindle shape. The time-frequency spatial distribution can be divided into two categories. The first contains micro-earthquakes, blasting, mechanical mining and small slope landslides, and the second contains only vehicle transport events. The research results provide a reference for the identification of microseismic events in open pit mines.
-
表 1 5种类型事件波形特征统计表
Table 1. Statistical results of waveform characteristics of five typical events
事件类型 个数 震级范围
ML事件波形形态 频率集中度 持续时间
均值/s衰减
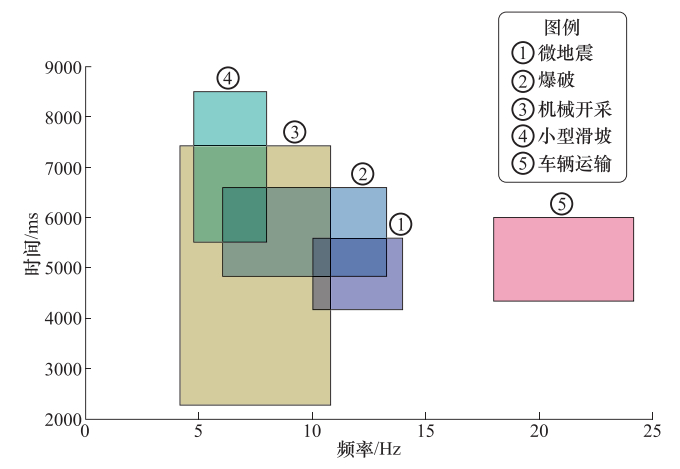
方式微地震 56 -0.5—1.9 包含P波、S波,面波发育,是能量较小的地震波 72×10-15 11.33 指数衰减,较快 爆破 79 -0.65—0.9 P波尖锐(初动向上)、S波不易识别,包含“初震”、“主震”、“尾波”三段 75×10-15 12.81 幂函数衰,减快 小型滑坡 23 1.5—1.9 由包络线呈“V”字型的波列组成 75×10-15 11.53 起伏不定,较慢 机械开采 206 -0.9—1.8 由“密集”、“尖锐”的波列组成 70×10-15 11.06 不规律 运输车辆 367 -0.6—1.0 由近似连续的、多组波形尖锐、包络线呈“纺缍”形的密集波列组成 30×10-15 10.70 不规律 表 2 5种事件类型时频分布特征
Table 2. Time-frequency distribution characteristics of five typical events
事件类型 时间均值范围/ms 频率均值范围/Hz 微地震 4150—5583 10—14 爆破 4800—6600 6—13.3 小型边坡滑坡 5500—8500 4.8—8 机械开采 2250—7400 4.2—10.8 车辆运输 4333—6000 18—24.2 -
董世华, 2009, 基于微震监测技术在深井矿山地震波形的识别, 现代矿业, (7):129-131 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2009.07.044 科恩, 1998, 时频分析: 理论与应用, 白居宪, 译.西安: 西安交通大学出版社 李夕兵, 李地元, 赵国彦等, 2006, 金属矿地下采空区探测、处理与安全评判, 采矿与安全工程学报, 23(1):24-29 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3363.2006.01.005 刘芳, 曹井泉, 赵蒙生等, 2005, 乌拉特前旗爆破与地震识别.高原地震, 17(2):22-27 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-586X.2005.02.002 刘先锋, 张瑞明, 2013, 微震波形识别技术在监测边坡岩体中的应用.山西冶金, 36(6):27-29 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1152.2013.06.011 马举, 2014, 基于波形特征的矿山微震与爆破信号模式识别.长沙:中南大学. 宋维琪, 陈泽东, 毛中华, 2008, 水力压裂裂缝微地震监测技术.东营:中国石油大学出版社, 3-5. 姚家骏, 杨立明, 冯建刚. 2011.常用时频分析方法在数字地震波特征量分析中的应用.西北地震学报, 33(2):105-110. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbdzxb201102001 张华, 姚宏, 陈鑫等. 2014.矿震识别及成因研究进展.国际地震动态, (3):4-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0235-4975.2014.03.002 张萍, 高艳玲, 肖健等. 2001.辽宁台网记录爆破、矿震与地震的识别.地震地磁观测与研究, 22(5):29-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3246.2001.05.004 张青成, 王家磊, 李德璇等. 2013.露天矿山爆破振动影响因素分析研究.辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版), 32(10):1334-1338. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0562.2013.10.008 赵淑红. 2006.时频分析方法及其在地震数据处理中的应用.西安:长安大学. 赵永, 刘卫红, 高艳玲. 1995.北京地区地震、爆破和矿震的记录图识别.地震地磁观测与研究, 16(4):48-54. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1995-DZGJ504.006.htm Cohen L.1995. Time-frequency analysis. New York:Prentice - Hall. -




 下载:
下载: