Study on Feature of Surface Rupture and Deformation Caused by Buried Normal Fault Movement
-
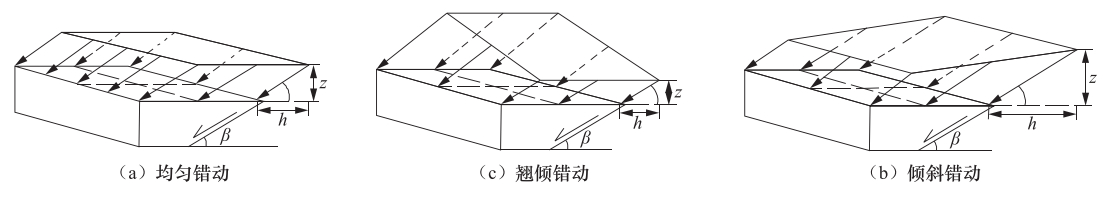
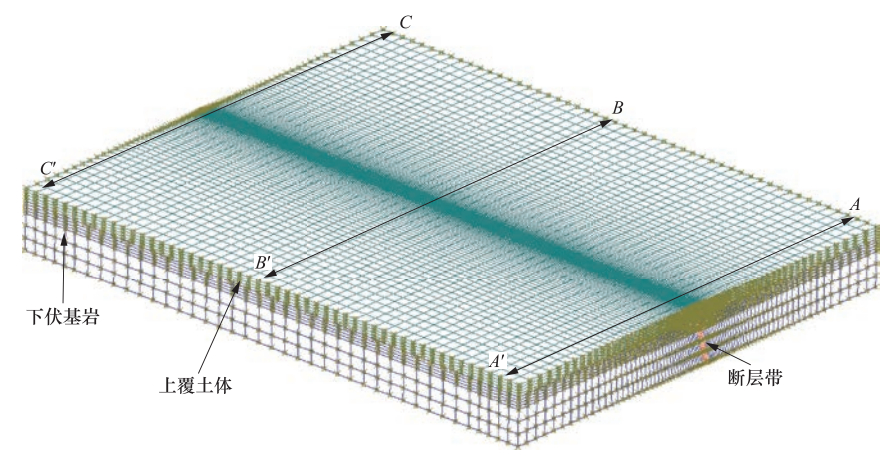
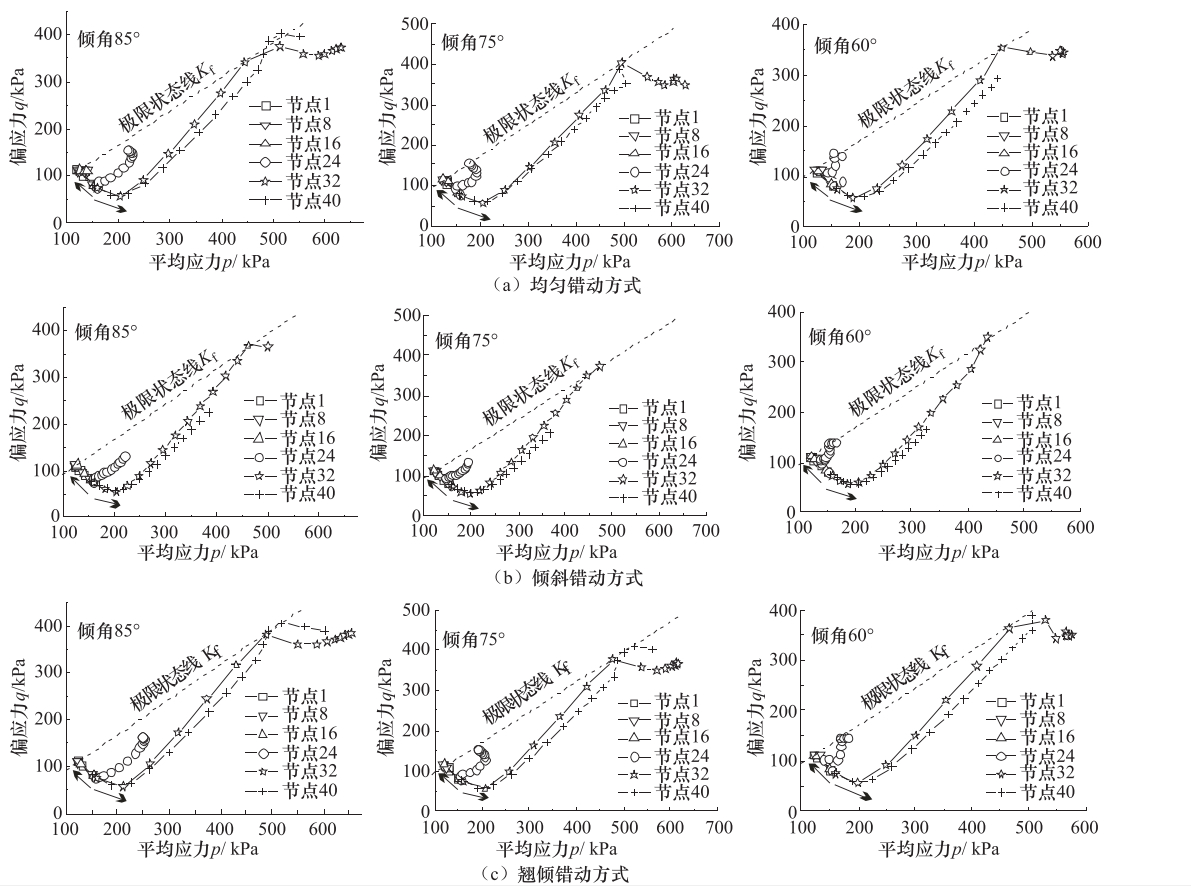
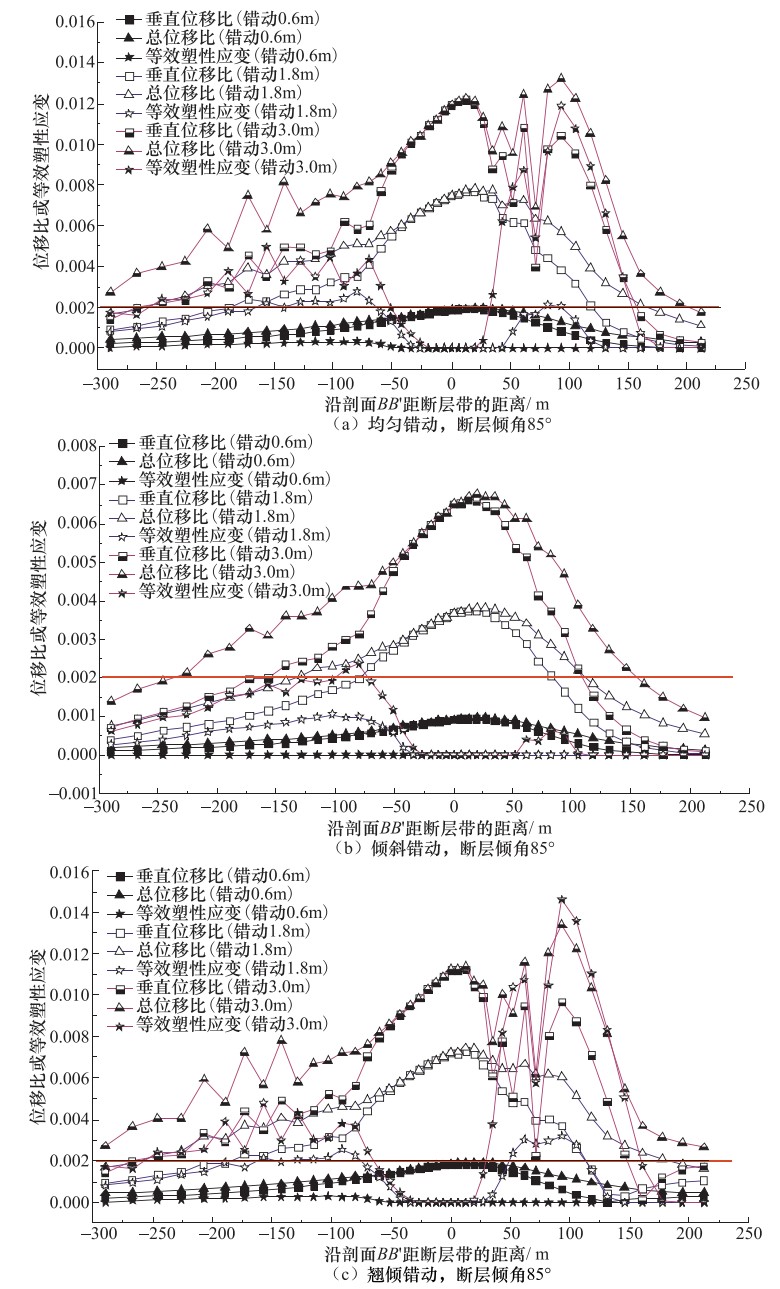
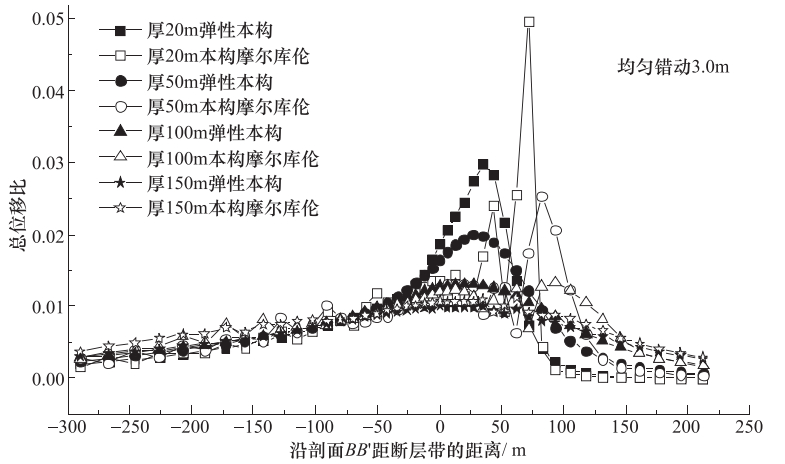
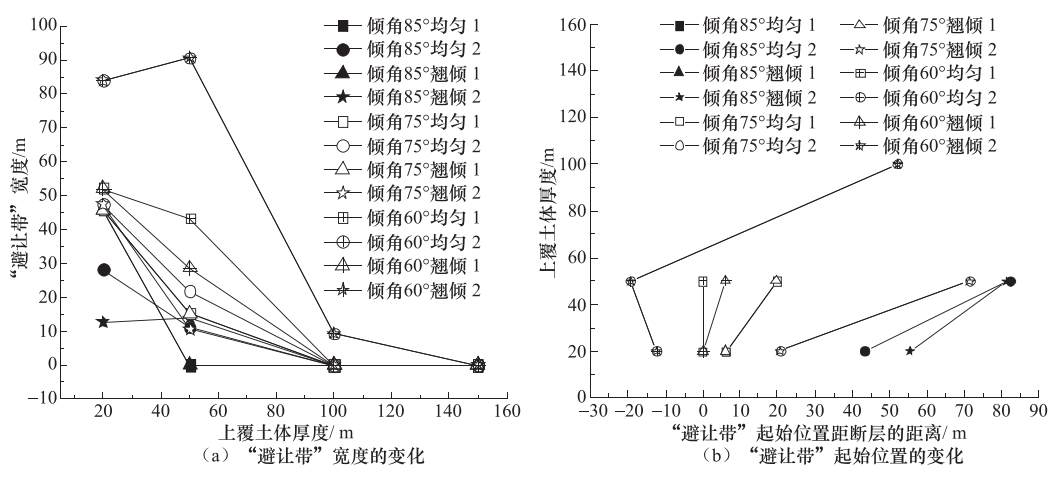
摘要: 通过建立三维计算模型,对隐伏正断层在均匀错动、倾斜错动和翘倾错动方式下地表土体的应力路径、破裂和变形特征进行了研究。根据地表破裂临界值,分析了工程建设“避让带”的宽度和起始位置的变化特征。根据行业规范,提出工程建设“关注带”的确定方法,分析了“关注带”的宽度和起始位置的变化特征,得到以下主要结论:①在断层错动过程中,位于两侧的地表土体应力路径变化明显不同,下盘一侧和上盘一侧分别以三轴拉伸和三轴压缩为主;②地表强变形带与地表破裂带的分布并不一致,需要综合考虑等效塑性应变和总位移比2个指标来评价同震地表错动对建筑物的影响;③当隐伏断层错动的垂直位移达到3m时,工程建设“避让带”的宽度在10—90m范围内变化,受上覆土体厚度和断层倾角的影响最大,而工程建设“关注带”的宽度在150—400m范围内变化,受上覆土体的性质影响最大。Abstract: The serious seismic disaster is often limited in a narrow zone along the fault strike, thus the study on the surface rupture zone and strong deformation zone on both sides of fault is of great significance for engineering seismic fortification. In this paper, a three-dimensional finite element model was constituted to study the stress path, rupture and deformation of surface soil mass caused by the uniform movement, inclined movemen and warped movement of buried normal fault. Based on the critical value of surface rupture, the variation features and influencing factors of width and starting position of the "avoiding zone" in engineering construction are analyzed in accordance to industry standards. The main results are as follows:① the variations of stress path are obviously different for the surface soil on upper wall to footwall of the fault, and are respecively triaxial-tension and triaxial-compression stress state. ② The distribution of strong deformation zone is not consistent with that of rupture zone, so it is necessary to consider the equivalent plastic strain and the total displacement ratio to evaluate the effect of the seismic ground movement on buildings. ③ When the vertical displacement of buried fault is 3m, the width of "avoiding zone" in engineering construction changes within the range of 10-90 m, which is most affected by the thickness of overlying soil and the fault dip angle, whereas the width of "attention zone" in engineering construction changes within the range of 150-400 m, which is most affected by the properties of overlying soil mass.
-
Key words:
- Buried normal fault /
- Surface rupture /
- Stress path /
- Avoiding zone /
- Attention zone
-
表 1 模型参数
Table 1. Model parameters
名称 变形模量/Pa 泊松比 密度/kg·m-3 内摩擦角/° 黏聚力/kPa 土层 2.4x108 0.3 1970 35 38.5 岩石 2.25x1010 0.2 2140 断层带 6.8x109 0.21 2040 表 2 节点的位置及编号
Table 2. The location and number of the nodes
节点号 距离/m 1 -289.5 2 -267.0 3 -245.8 4 -225.8 5 -207.0 6 -189.3 7 -172.6 8 -156.9 9 -142.1 10 -128.2 11 -115.1 12 -102.7 13 -91.0 14 -80.1 15 -69.7 16 -60.0 17 -50.8 18 -42.2 19 -34.1 20 -26.4 21 -19.2 22 -12.4 23 -6.0 24 0 25 6.2 26 12.7 27 19.7 28 27.1 29 35.0 30 43.3 31 52.2 32 61.6 33 71.5 34 82.1 35 93.4 36 105.3 37 118.0 38 131.5 39 145.8 40 161.0 41 177.1 42 194.2 43 212.4 44 231.7 -
崔光耀, 伍修刚, 王明年等. 2018.黏滑断层隧道减错措施参数对减错效果的影响分析.震灾防御技术, 13(3):502-511. http://zzfy.eq-j.cn/zzfyjs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20180302&journal_id=zzfyjs 丁国瑜. 1995.活断层的分段模型.地学前缘, 2(1-2):195-202. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DXQY502.014.htm 韩竹军, 冉勇康, 徐锡伟. 2002.隐伏活断层未来地表破裂带宽度与位错量初步研究.地震地质, 24(4):484-494. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.002 马野, 袁志丹, 曹金凤. 2011.ADINA有限元经典实例分析.北京:机械工业出版社, 118-120. 徐锡伟, 于贵华, 马文涛等. 2002.活断层地震地表破裂"避让带"宽度确定的依据与方法.地震地质, 24(4):470-483. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.001 徐锡伟, 赵伯明, 马胜利等. 2011.活动断层地震灾害预测方法与应用.北京:科学出版社, 132-165. 张学言, 闫澍旺. 2004.岩土塑性力学基础.天津:天津大学出版社, 35-36. 赵雷, 李小军, 霍达. 2007.数值模拟软夹层对基岩上覆土层破裂的影响.北京工业大学学报, 33(3):289-292. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0037.2007.03.013 赵颖, 郭恩栋, 王琼等. 2013.走滑断层地震地表断裂位错估计方法研究.岩土力学, 34(5):1403-1408. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201305029 中华人民共和国建设部, 国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 2001.建筑抗震设计规范(GB 50011-2001).北京:中国建筑工业出版社. 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2011, 建筑地基基础设计规范(GB 50007-2011).北京: 中国建筑工业出版社. 庄妍, 王康宇. 2016.基于Von-Mises屈服准则的结构安定性研究.地下空间与工程学报, 12(S1):170-174, 191. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxkj2016z1028 Hernandez-Marin M., BurbeyT. J.. 2012. Fault-controlled deformation and stress from pumping-induced groundwater flow. Journal of Hydrology, 428-429:80-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.01.025 Li B., Su J. Y., Ma D. H., et al.. 2015. The study on forecasting the surface rupture width under strong earthquake based on information diffusion methodology. Natural Hazards, 75(2):1871-1882. doi: 10.1007/s11069-014-1403-1 Loukidis D., Bouckovalas G. D., Papadimitriou A. G., et al.. 2009. Analysis of fault rupture propagation through uniform soil cover. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 29(11-12):1389-1404. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2009.04.003 Okada B. Y.. 1992. Internal Deformation due to shear and tensile faults in a half-space. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 82(2):1018-1040. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1dc6d1fe123d7f2601f38d1e724b4764 Xu L. Q., Li S. Z., Cao X. Z., et al.. 2016. Holocene intracontinental deformation of the northern North China Plain:Evidence of tectonic ground fissures. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 119:49-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.01.003 -




 下载:
下载: