An Improved Approach for Near-fault Pulse-like Ground Motion Simulation
-
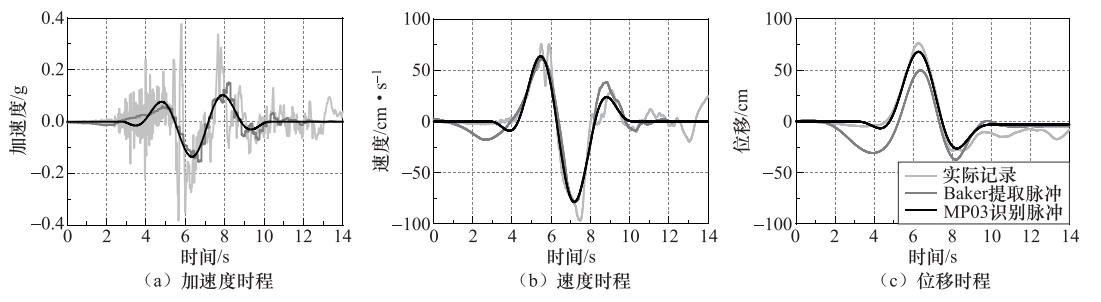
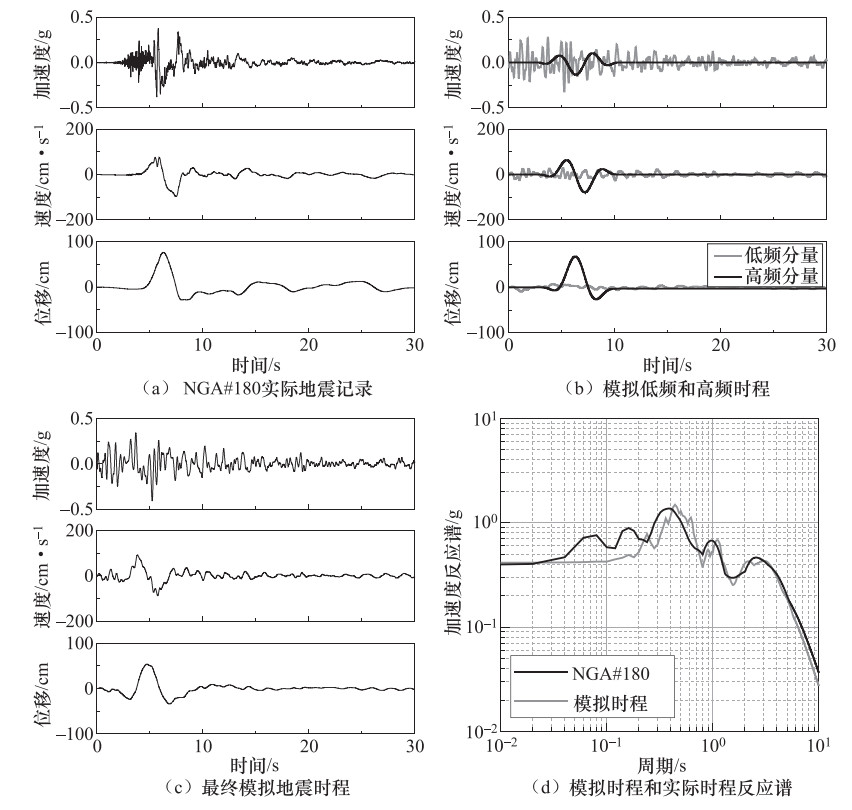
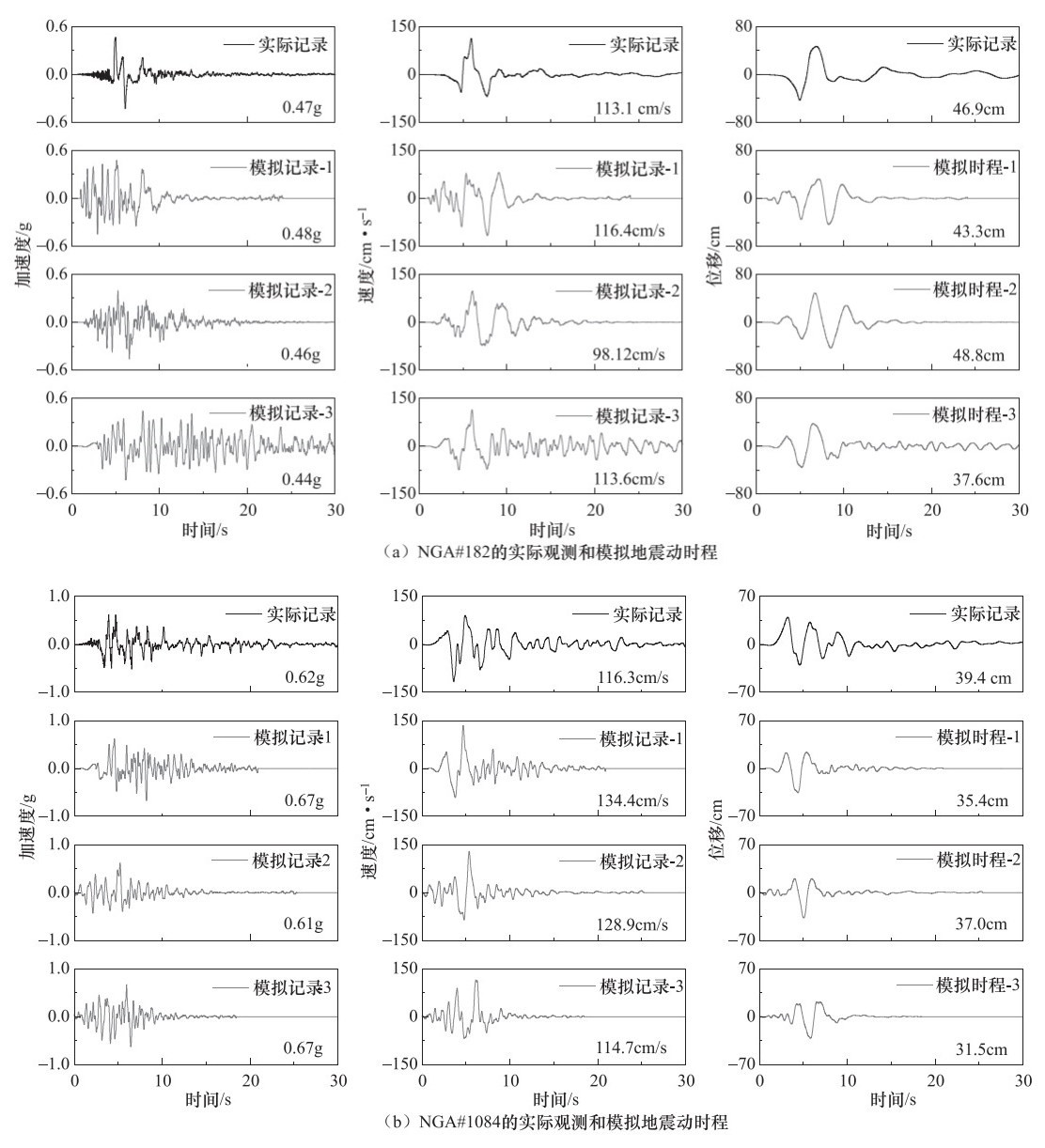
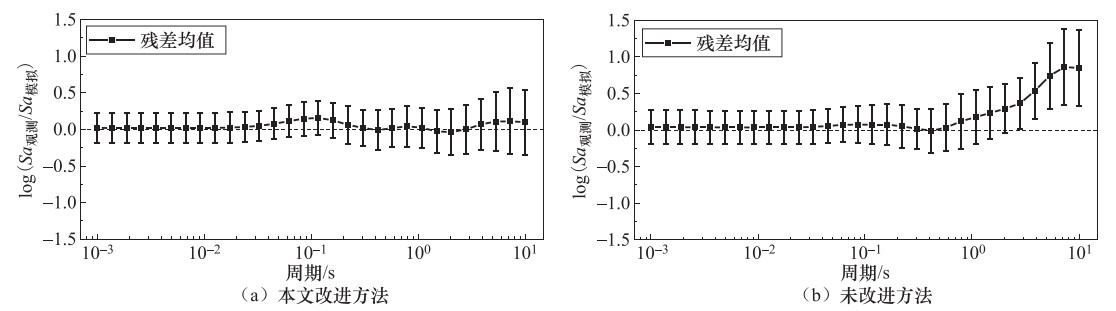
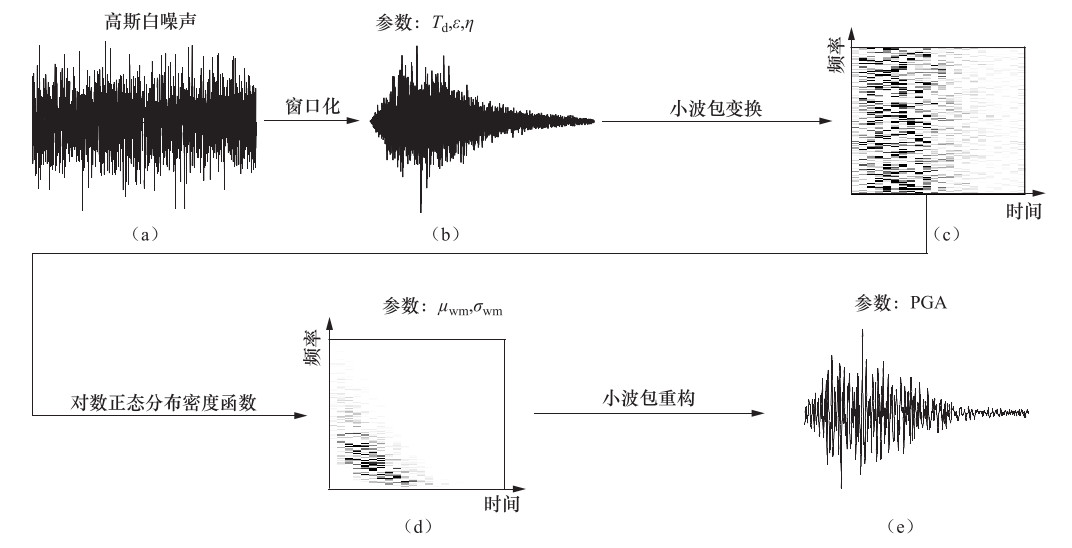
摘要: 本文基于小波包技术的随机地震动模拟方法,提出一种改进的参数化随机近断层脉冲型地震动模拟方法。然后,通过识别和提取近断层脉冲型地震动数据库中脉冲型地震动的特征参数,建立了基于震源、传播路径和场地特征等参数的脉冲模型参数预测方程。最后,通过模拟实际记录和误差分析检验了改进的模拟方法的有效性。结果表明:应用改进的模拟方法得到的地震动时程无论在波形、频率特性还是峰值上均与实际记录具有较好的一致性。改进的模拟方法在保留地震动时频非平稳性的基础上,能够有效地提高近断层脉冲型地震动的模拟效果,并且能够很好地体现脉冲型地震动的主要特征。Abstract: In this paper, an improved parameterized stochastic simulation method of near-fault pulse-like ground motion is proposed based on the stochastic ground motion simulation method using the wavelet packet method. Then, by identifying and extracting the characteristic parameters of pulse-like ground motions in a set near-fault ground motions database, the prediction equation of pulse model parameters in terms of the earthquake source, path and site characteristic parameters is established. Finally, the improved simulation method is verified by simulating recorded pulse-like ground motions and error analysis. Our results illustrate that simulated time histories of pulse-like ground motions by improved simulation method is well consistent with the recorded one in terms of waveform, frequency characteristic and peak value. The improved simulation method can effectively improve the simulation results of near-fault ground motion under retain time-frequency nonstationary of ground motion, and can also well reflect the main characteristics of pulse-like ground motion, which has very important engineering application value.
-
表 1 拟合参数γ和υ的分布系数和限定条件
Table 1. Boundary condition and coefficient of marginal distributions fitted to parameters γ and υ
参数 单位 符合分布 选定下限 选定上限 合适的分布参数 均值 标准差 γ burr 2.0 3.0 α=2.49,c=21.80,k=4.20 2.3 0.14 υ π uniform 0 2 1.0 0.58 表 2 MP03脉冲模型参数的回归系数和标准差
Table 2. Regression coefficients and standard deviations of the MP03 model parameters
参数 α0 α1 α2 β1 β2 β3 β4 β5 ϕ τ σ Vp 1.6784 1.6152 1.6643 0.2201 -0.3060 -0.3230 -0.1231 0.0054 0.132 0.108 0.330 Tp -0.2312 -0.1828 0.1677 0.1762 -0.1295 0.0043 0.261 0.136 0.294 t0 -0.8739 -0.7214 -0.4478 0.2708 0.0551 -0.0455 0.0028 0.285 0.089 0.308 -
樊剑, 涂家祥, 吕超等, 2008.采用时频滤波技术的近断层脉冲地震人工模拟.华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 36(11):116-119. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HZLG200811044.htm 李亚楠, 2016.工程用地震动模拟随机性方法研究.大连: 大连理工大学. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10141-1016204382.htm 罗全波, 陈学良, 高孟潭等, 2018.近断层速度脉冲与震源机制的关系浅析.震灾防御技术, 13(3):646-661. http://zzfy.eq-j.cn/zzfyjs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20180316&journal_id=zzfyjs 田玉基, 杨庆山, 卢明奇, 2007.近断层脉冲型地震动的模拟方法.地震学报, 29(1):77-84. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhen200701009 Atkinson G. M., Assatourians K., Boore D. M., et al., 2009. A guide to differences between stochastic point-source and stochastic finite-fault simulations. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 99(6):3192-3201. doi: 10.1785/0120090058 Baker J. W., 2007. Quantitative classification of near-fault ground motions using wavelet analysis. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 97(5):1486-1501. doi: 10.1785/0120060255 Beresnev I. A., Atkinson G. M., 1997. Modeling finite-fault radiation from the ωn spectrum. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 87(1):67-84. Boore D. M., 1983. Stochastic simulation of high-frequency ground motions based on seismological models of the radiated spectra. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 73(6A):1865-1894. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0aecda90-ca1d-4056-aa8d-57610c62fdb5 Bray J. D., Rodriguez-Marek A., 2004. Characterization of forward-directivity ground motions in the near-fault region. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 24(11):815-828. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2004.05.001 Campbell K. W., 2008. Hybrid empirical ground motion model for PGA and 5% damped linear elastic response spectra from shallow crustal earthquakes in stable continental regions: Example for eastern North America. In: Proceeding of the 14th World Conference Earthquake Engineering. Beijing, China: WCEE. Dabaghi M. N., 2014. Stochastic modeling and simulation of near-fault ground motions for performance-based earthquake engineering. Berkeley: University of California. https://escholarship.org/uc/item/8db18756 Dabaghi M., Der Kiureghian A., 2017. Stochastic model for simulation of near-fault ground motions. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 46(6):963-984. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=080c7eb3415d4053e615dc23bd911f6a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Joyner W. B., Boore D. M., 1993. Methods for regression analysis of strong-motion data. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 83(2):469-487. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=862575101d927d3d6b3b88e6526957a0&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Li Y. N., Wang G. X., 2016. An improved approach for nonstationary strong ground motion simulation. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 173(5):1607-1626. doi: 10.1007/s00024-015-1189-4 Mavroeidis G. P., Papageorgiou A. S., 2003. A mathematical representation of near-fault ground motions. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 93(3):1099-1131. doi: 10.1785/0120020100 Motazedian D., Atkinson G. M., 2005. Stochastic finite-fault modeling based on a dynamic corner frequency. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 95(3):995-1010. doi: 10.1785/0120030207 Somerville P. G., Smith N. F., Graves R. W., et al., 1997. Modification of empirical strong ground motion attenuation relations to include the amplitude and duration effects of rupture directivity. Seismological Research Letters, 68(1):199-222. doi: 10.1785/gssrl.68.1.199 Yamamoto Y., Baker J. W., 2013. Stochastic model for earthquake ground motion using wavelet packets. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 103(6):3044-3056. doi: 10.1785/0120120312 Yang D. X., Zhou J. L., 2015. A stochastic model and synthesis for near-fault impulsive ground motions. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 44(2):243-264. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=720a58f1cf843d0534c204535de9022c -



 下载:
下载: