Application of Micro Tremor Observation on Vibration Characteristic and Rapid Seismic Capacity Evaluation for Brick Concrete Buildings
-
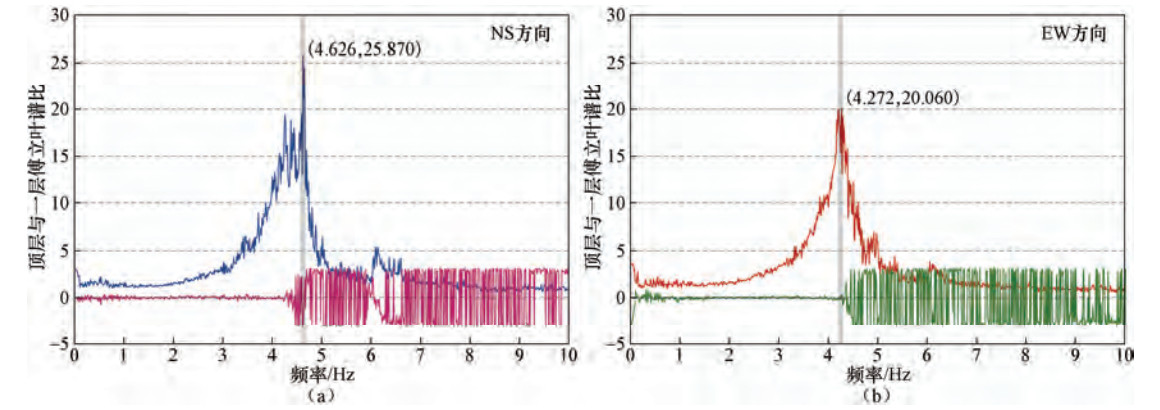
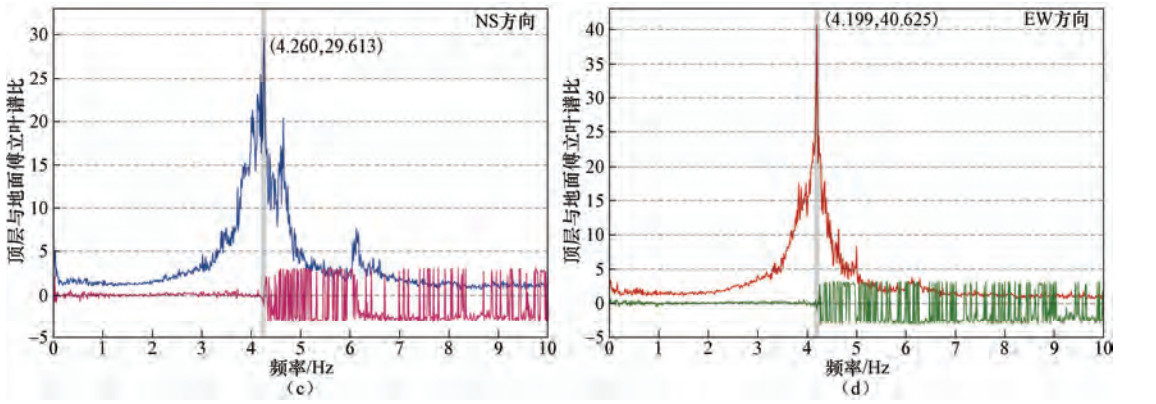
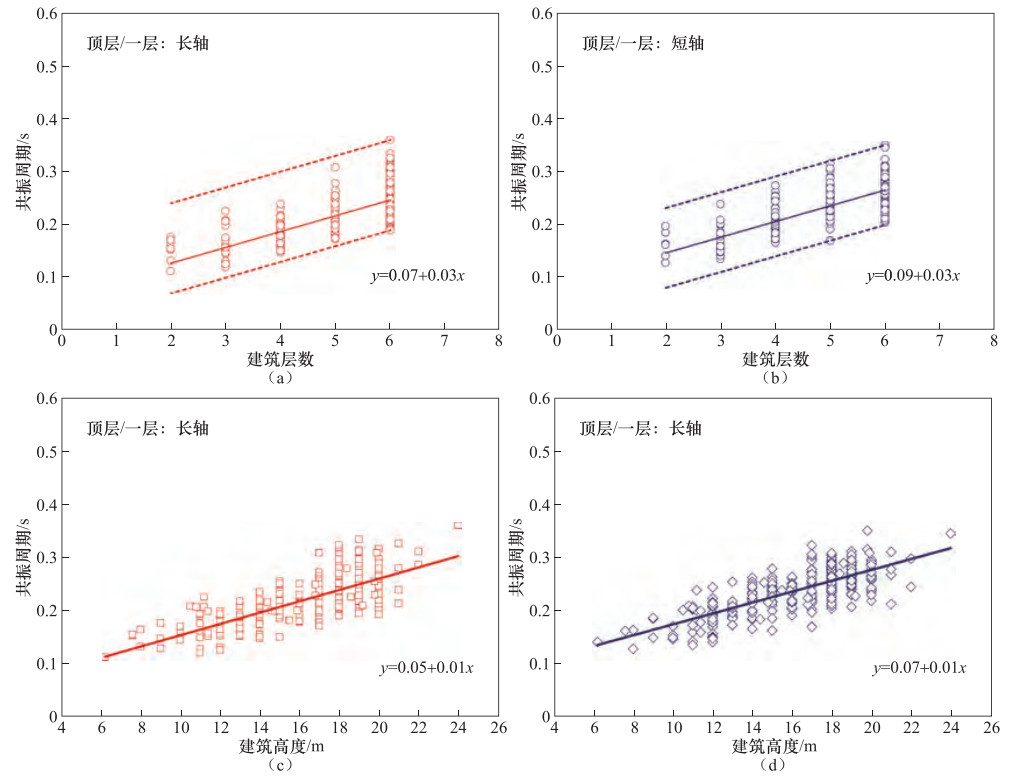
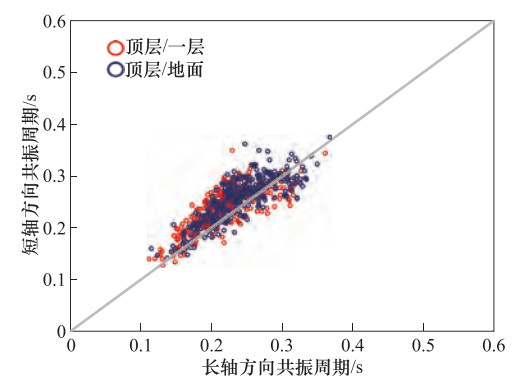
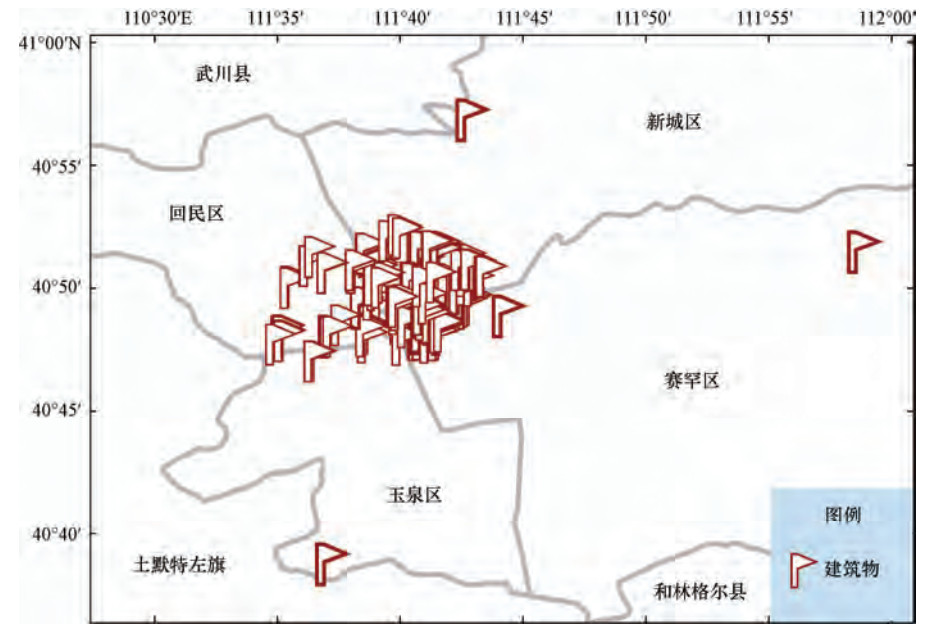
摘要: 城市建筑群中砖混结构建筑数量众多,抗震性能较弱,在地震中的破损率较高,逐一进行抗震性能测定难度巨大。本文提出基于常时微动观测的城市砖混结构建筑群抗震性能快速评价方法,提供初步的决策参考建议,适用于在大范围城市建筑群中快捷地筛选易损建筑。选取呼和浩特市区331栋砖混结构建筑物进行振动特性分析,分别建立适用于研究区域建筑物长轴和短轴平均共振周期与建筑物楼层数的回归关系,作为衡量研究区砖混结构建筑群抗震能力的快速判断标准。筛选出82栋抗震能力较弱的易损建筑,其中24栋为重点关注对象,主要分布于人口较为密集的老旧城区,多为4层(含)以上住宅类型,建筑年代较为久远,具有面临潜在地震危害的风险,为下一步有针对性地进行抗震加固和防震减灾工作提供参考依据。Abstract: At present, a large number of brick concrete structure buildings in urban areas of China are poor in anti-seismic performance in destructive earthquakes. It is hard to determine these buildings in detailed aseismic properties one by one. Based on the micro tremor observation, we put forward a rapid method to evaluate the anti- seismic ability of these brick concrete structure buildings in urban areas. Our method is suitable for determining the buildings that may be vulnerable in large areas of the city and providing preliminary decision-making reference. In this paper, vibration characteristic analysis is carried out for 331 buildings of brick concrete in the urban district in Hohhot. Then regression analysis of the relations between number of floors and major and minor axis average period resonance are established, respectively, and which are taken as the rapid judge criterion for anti-seismic capability of brick concrete structure buildings. We selected 82 buildings with poor anti-seismic capacity, in which 24 buildings are chosen to be the critical representatives, which mainly distributed in heavily populated areas of older neighborhoods. Most of these buildings are residential with over four floors (including four floors) and in great potential seismic hazard risks. The results will provide scientific reference for further anti-seismic strengthening and earthquake prevention and disaster mitigation.
-
Key words:
- Hohhot /
- Brick concrete structure /
- Vibration characteristic /
- Aseismic capability /
- Rapid evaluation
-
表 1 平均绝对共振周期
Table 1. List of absolute average period resonance
楼层 平均绝对共振周期T/s 标准差σ 长轴方向 短轴方向 长轴方向 短轴方向 2 0.152 0.163 0.0228 0.0236 3 0.161 0.170 0.0292 0.0268 4 0.182 0.204 0.0209 0.0228 5 0.212 0.238 0.0250 0.0263 6 0.249 0.264 0.0353 0.0272 -
布仁, 那仁满都拉, 包玉海等, 2014.基于常时微动观测的呼和浩特市区地基土振动特性及分类研究.内蒙古师范大学学报(自然科学汉文版), 43(1):86-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8735.2014.01.018 蔡彩君, 2012.常时微动测试在工程场地评价中的应用与发展.建筑技术开发, 39(11):24-30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JZKF201211013.htm 傅唯一, 1991.地基震动特性及常时微动测定.国外地质勘探技术, (3):20-27. 黄博, 夏唐代, 赵晴等, 2015.老旧小区砖混结构房屋振动与减振.地震工程学报, 37(1):126-130. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbdzxb201501022 贾洁, 黄银莹, 王超等, 2011.汶川地震中砖混结构震害分析.建筑结构, 41(2):81-84, 80. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/shanxjz200932037 金井清, 1987.工程地震学.常宝琦, 张虎男, 译.北京: 地震出版社, 81-137. 孔芳芳, 2017.砖混结构震后安全性定量评价方法研究.大连:大连理工大学, 1-10. 刘曾武, 1992.概述常时微动的研究及在工程中的应用.世界地震工程, (1):17-29. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000004586906 满特格尔, 2015.基于常时微动观测的呼和浩特市区地基土深度推测研究.呼和浩特:内蒙古师范大学, 7-22. 那仁满都拉, 满特格尔, 包玉海等, 2015.基于常时微动观测的呼和浩特市RC建筑物振动特性.国际地震动态, (9):164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4975.2015.09.164 那仁满都拉, 布仁, 宝音图等, 2016.基于常时微动观测的钢筋混凝土建筑物振动特性及其地域差异.振动与冲击, 35(4):22-27, 41. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zdycj201604005 彭远黔, 路正, 李雪英等, 2000.场地脉动卓越周期在工程抗震中的应用.华北地震科学, 18(4):61-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1375.2000.04.012 谭皓, 李杰, 张电吉等, 2011.玉树地震灾区底框砖混结构建筑的震害调查.浙江建筑, 28(1):20-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3707.2011.01.006 王涛, 张永群, 金波等, 2013.芦山7.0级强烈地震砖混民居震害调查与分析.地震工程与工程振动, 33(3):9-19. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb201305035 吴永芳, 2011.提高砖混结构房屋抗震能力的有效方法.工程抗震与加固改造, 33(3):111-116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8412.2011.03.020 吴亚男, 2014.砌体结构建筑抗震能力快速评估方法研究.青岛:中国海洋大学, 1-20. 吴志坚, 车爱兰, 王兰民等, 2009.常时微动测试在汶川地震甘肃灾区建筑结构震害调查中的应用.西北地震学报, 31(1):86-90. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbdzxb200901017 杨娜, 王龙, 刘爱文等, 2018.青海东南部农村民居结构特点及抗震能力分析.震灾防御技术, 13(1):206-214. http://zzfy.eq-j.cn/zzfyjs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20180119&journal_id=zzfyjs 杨彦明, 姜立新, 王祯祥, 2017.基于Levenberg-Marquardt方法的内蒙古及邻区地震烈度影响场改进技术.地震, 37(3):117-126. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/diz201703012 杨永强, 公茂盛, 谢礼立等, 2014.芦山M 7.0级地震中砖混结构民居震害特征分析.建筑结构, 44(18):68-70, 93. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jzjg201418015 张合, 吕国军, 孙丽娜, 2017.邢台市重要建筑中砖混结构震害预测.华北地震科学, 35(1):73-77. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hbdzkx201701012 张卫华, 2007.常时微动测试在抗震设计上的应用.华南地震, 27(3):96-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8662.2007.03.010 中国工程建设标准化协会, 1995. CECS 74:95场地微振动测量技术规程.北京:中国计划出版社, 1-16. Abe Y., Mori K., Konno M., 1986. Fundamental study on the relation between sismic indexes and natural periods through microtremor measurement of renforced concrete buildings. In:Proceedings of Summaries of Technical Papers of Annual Meeting. Tokyo:Architectural Institute of Japan, 611-612. Ho N., Kawase H., 2006. Evaluation of earthquake response and dynamic characteristics of RC and wooden buildings in Fukuoka city obtained from aftershocks of the west off Fukuoka earthquake and microtremor data. Journal of Structural and Construction Engineering (Transactions of AIJ), 71(605):63-70. doi: 10.3130/aijs.71.63_3 Izumi M., Katukura H., Tobita J., 1990. Properties of ambient vibration system of structures. Journal of Structural and Construction Engineering (Transactions of AIJ), 409:83-93. doi: 10.3130/aijsx.409.0_83 Li M., Li H. N., 2011. Effects of strain rate on reinforced concrete beam. Advanced Materials Research, 243-249:4033-4036. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.243-249 -



 下载:
下载: