Effect Earthquake Response of Seismic Underground Fluid from the Zhaogezhuang Observation Well
-
摘要: 赵各庄井位于首都圈地区,是夏垫断裂带北端的地震观测井。其地下流体同震响应的统计数据显示,在对6级以上远场地震的响应次数上,赵各庄井的水位较水温更显著;在对MS 7.0井水位的响应幅度变化范围为3.0mm—770.0mm,典型水温的响应幅度为0.0129℃,井水位响应幅度明显强于水温,响应形态以振荡型为主。赵各庄井水温、水位的异常变化和夏垫断裂带的活动性密切相关,同时也会影响断裂带的活动性。综合分析认为,在对赵各庄井水温和水位两大测项进行观测时,应以水位为主,还应关注夏垫断裂带的活动性。同时,为了监测夏垫断裂带的活动性,应对赵各庄井水位和水温进行长期监测,以保证首都圈地区的人民生产安全。Abstract: The Zhaogezhuang well is loacated in the capital zone and it's an earthquake observation well along the Xiadian Fault zone. In this poper we conducted sfatistical study of the co-seismic corresponding of and we fand that respcmse of groundwater level is more remarkable than that of temperature for MS ≥ 6.0 earthquakes on responding times and MS ≥ 7.0 earthquakes on responding minute as well; Responding amplitude ranges from 3.0-770.0mm for groundwater level and 0.0129℃ for typical groundwater temperature, and the variation of groundwater level is more obvious than that of temperature. Oscillation mode is the main responsive form. The anomaly of groundwater level and temperature is related to the activity of the Xiadian fault zone in consideration of its location and maybe impact the fault activity. In conclusion, groundwater level of the Zhaogezhuang well should be paid more attention in order to monitor the activity of Xiadian fault zone. Meanwhile, in order to monitor the Xiadian fault zone activity, the observation should be conducted in long-time of the guarantee of production safety of capital circle people.
-
Key words:
- Xiadian active fault /
- Zhaogezhuang well /
- Water temperature /
- Water level
-
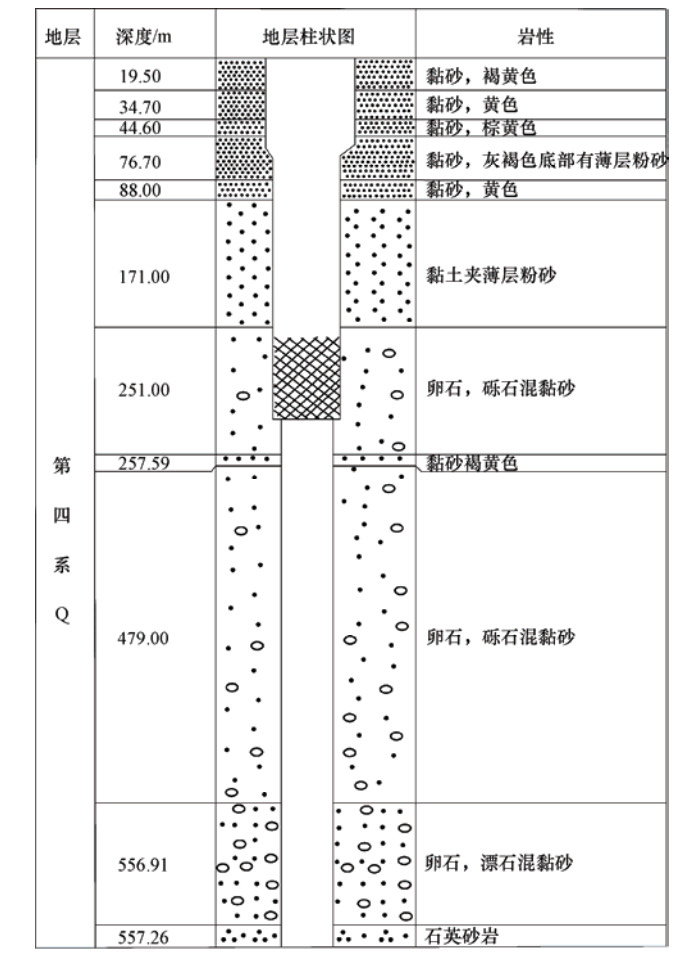
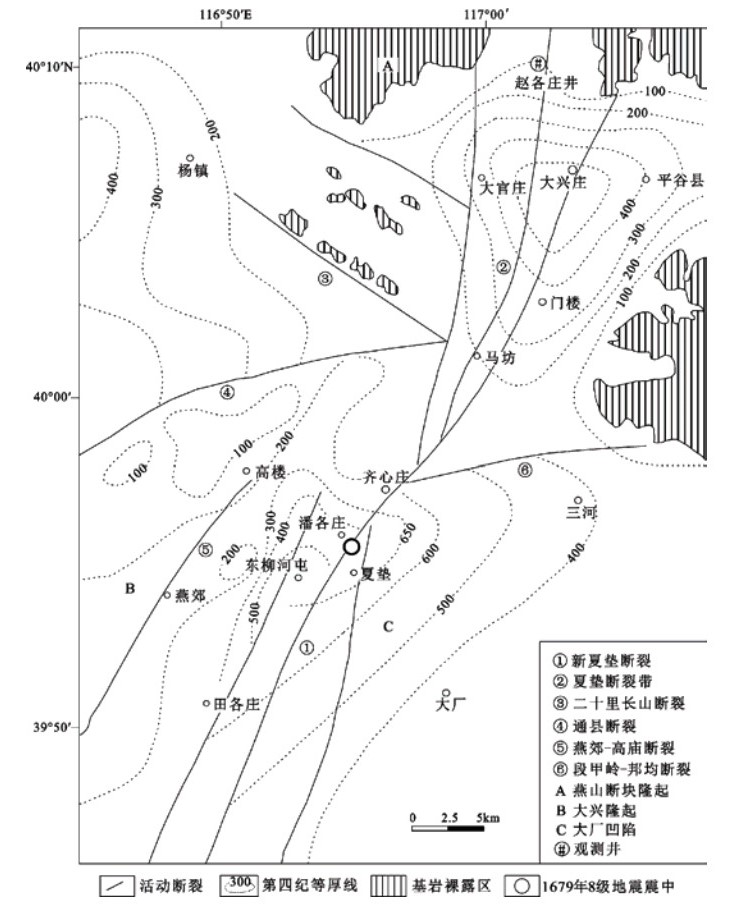
图 1 观测井构造背景示意图(据高战武,2001)
Figure 1. Tectonic background diagram of the observation well
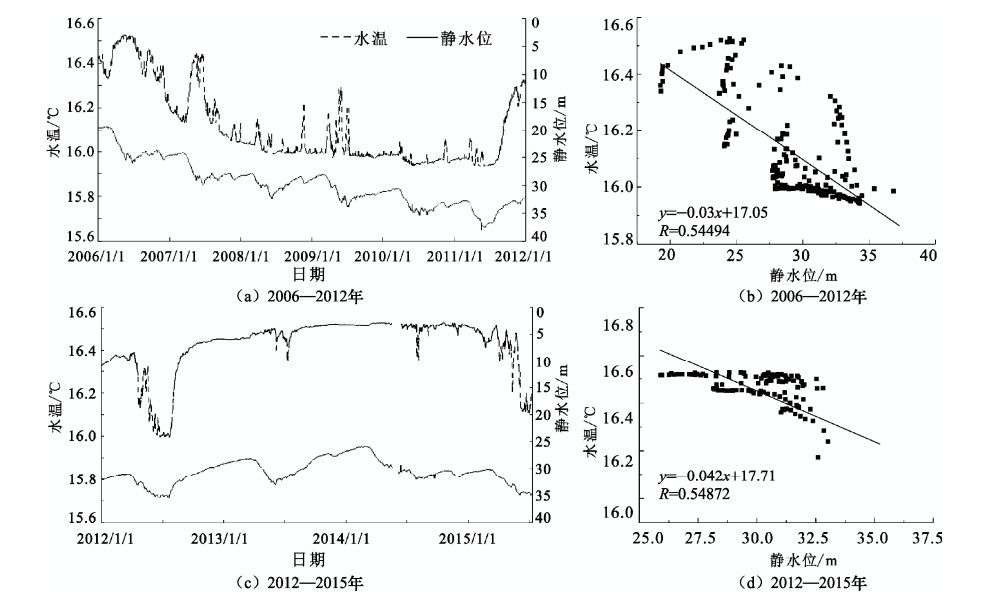
图 2 赵各庄测井井孔柱状图(据韩孔艳等,2016)
Figure 2. The stratigraphy of Zhaogezhuang wellhole
表 1 观测仪器设备参数
Table 1. Parameters of observation instrument
仪器名称 型号 生产厂家 检测线 观测精度 分辨率 探头埋深 测项背景值 水位仪 LN-3 中国地震局分析预报中心 传感器 ±0.2%FS 优于1mm 20.6m 13.7m 数采 ±(0.05%R±2) 0.1mv 水温仪 SZW-1A 地壳所 0—100℃ ±0.05℃ ±0.0001℃ 180.0m 16.46℃ 注:数据源引自北京市地震局(2006)。 表 2 赵各庄井地震及响应次数统计
Table 2. Numbers of earthquakes and response times of observation well
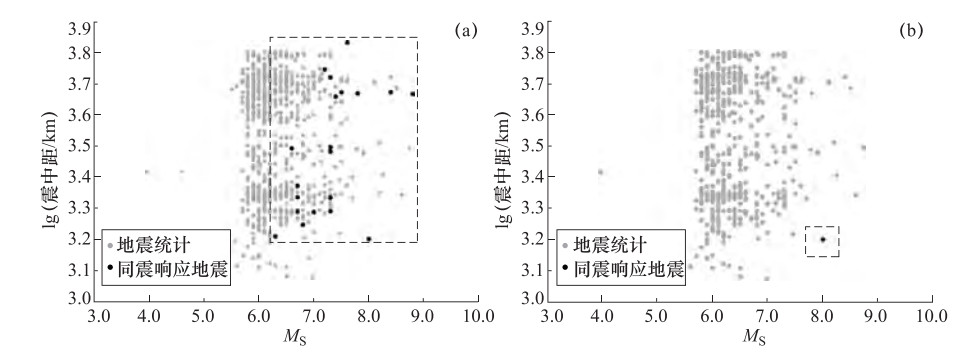
测项 数据时段 次数 MS 4.0—4.9 5.0—5.9 6.0—6.9 7.0—7.9 ≥8.0 静水位 2003-01-01—2015-07-10 发震 2 182 542 91 12 响应 0 0 6 13 4 水温 2006-01-01—2015-07-10 发震 1 126 385 72 9 响应 0 0 0 0 1 表 3 赵各庄井水位及水温同震响应特征
Table 3. The co-seismic responsive characteristic of groundwater level and temperature of Zhaogezhuang well
发震日期 发震时刻 水位开始变化时间 北纬/° 东经/° MS 震源深度
/km震中距/km 参考地点 水位变化幅度
/m同震响应形态类型 水温变化幅度/
℃滞后时间
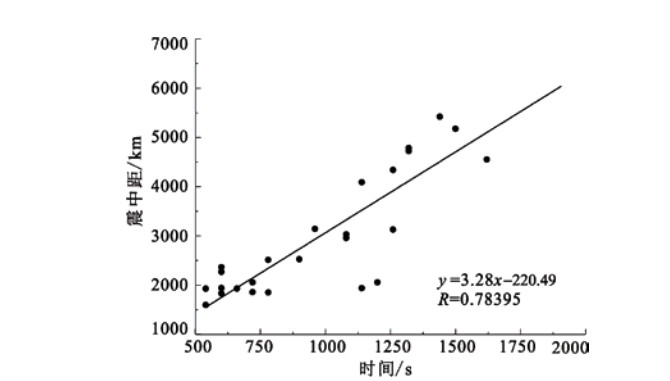
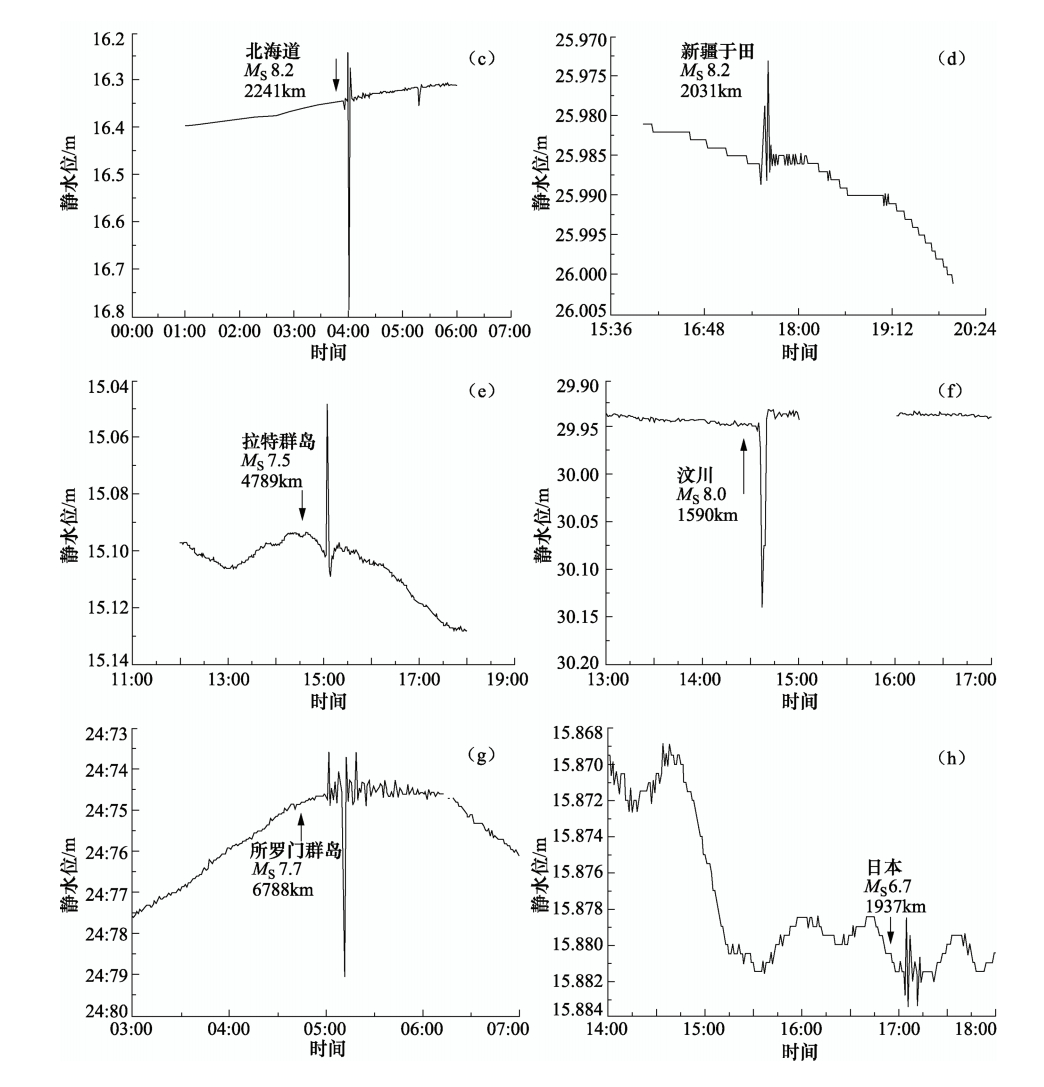
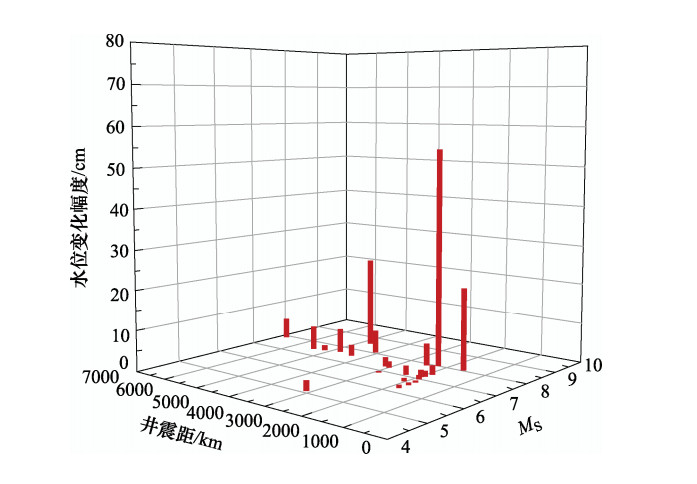
/min2014-02-12 17:19:48 17:37 36.14 82.51 7.3 10 3031 新疆于田 0.0150 振荡—脉冲型 无 18 2008-05-12 14:27:59 14:37 31.01 103.42 8.0 14 1590 四川汶川县 0.2075 脉冲型 0.0129 9 2008-03-21 06:32:59 06:54 35.64 81.54 7.3 21 3131 新疆于田县 0.0240 振荡型 无 21 2008-01-09 16:26:44 16:44 32.39 85.27 6.6 10 2955 西藏改则县 0.0030 振荡型 无 18 2007-04-02 04:39:55 05:12 -8.5 157.00 7.7 10 6788 所罗门群岛 0.0535 振荡—脉冲型 无 33 2006-12-26 20:26:19 20:46 21.86 120.6 7.3 10 2061 中国南海 0.0150 振荡型 无 20 2006-12-26 20:34:10 20:46 21.87 120.73 6.8 10 2060 中国南海 0.0090 振荡型 无 12 2006-04-21 07:24:59 07:44 60.97 167.48 7.9 32 4103 勘查加半岛 0.0590 振荡型 无 19 2005-07-24 23:42:04 00:03 7.83 92.19 7.4 19 4355 尼科巴群岛 0.0280 振荡型 缺数据 21 2005-03-29 00:09:35 00:31 2.03 97.05 8.4 34 4690 印尼苏门答腊 0.2335 振荡型 缺数据 22 2004-12-26 08:58:51 09:25 3.15 95.79 8.8 40 4633 印尼苏门答腊 0.7700 振荡型 缺数据 27 2004-11-29 02:32:13 02:42 43.08 145.14 6.9 41 2351 日本北海道 0.0220 脉冲型 缺数据 10 2004-11-12 05:26:31 05:50 -9.16 125.41 7.2 10 5549 印尼帝汶 0.0620 振荡型 缺数据 24 2004-10-23 16:55:58 17:05 37.10 139.03 6.7 28 1937 日本 0.0050 振荡型 缺数据 9 2004-10-15 12:08:49 12:18 24.51 122.83 6.3 107 1820 中国台湾宜兰以东海中 0.0070 脉冲型 缺数据 10 2004-09-05 18:07:08 18:17 33.02 136.94 7.0 35 1942 日本本州 0.0140 脉冲型 缺数据 10 2004-09-05 22:57:16 23:08 33.15 137.16 7.3 15 1952 日本本州南 0.0230 振荡型 缺数据 11 2004-02-07 10:42:33 11:07 -3.88 135.31 7.3 11 5238 印尼伊里安岛 0.0125 振荡型 缺数据 25 2003-12-10 12:38:11 12:57 23.01 121.51 6.7 13 1950 中国台湾台东近海 0.0095 脉冲型 缺数据 19 2003-11-17 14:43:06 15:05 51.23 178.57 7.5 30 4789 拉特群岛 0.0605 脉冲型 缺数据 22 2003-10-01 09:03:25 09:18 50.13 87.82 7.2 9 2524 俄、蒙、中交界 0.0065 振荡型 缺数据 15 2003-09-27 19:33:25 19:46 50.02 87.87 7.7 16 2517 中蒙边界 0.0550 振荡型 缺数据 13 2003-09-26 03:50:05 04:00 41.79 143.71 8.2 16 2241 日本北海道 0.5455 振荡—脉冲型 缺数据 10 -
北京市地震局, 2006.北京市地震监测志.北京:地震出版社. 车用太, 鱼金子, 刘春国, 1996.我国地震地下水温度动态观测与研究.水文地质工程地质, (4):34-37. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600494353 车用太, 何案华, 鱼金子, 2014.水温微动态形成的水热动力学与地热动力学机制.地震学报, 36(1):106-117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-3782.2014.01.009 陈大庆, 刘耀炜, 杨选辉等, 2007a.远场大震的水位、水温同震响应及其机理研究.地震地质, 29(1):122-132. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzdz200701011 陈大庆, 万永芳, 赵明利, 2007b.北京良乡、赵各庄井水位、水温同震响应对比研究.华南地震, 27(2):69-75. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hndz200702010 陈亮, 丁富雄, 张蕾等, 2012.建水地下流体监测井水位骤降异常分析.地震研究, 35(4):471-476. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2012.04.005 陈运泰, 刘瑞丰, 2004.地震的震级.地震地磁观测与研究, 25(6):1-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3246.2004.06.001 邓前辉, 王继军, 汤吉等, 2000.三河-平谷8级大震区地壳上地幔电性结构特征.见: 中国地震学会第八次学术大会论文摘要集.北京: 地震学报出版社, 282. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGEM200000001282.htm 邓前辉, 王继军, 汤吉等, 2001.三河-平谷8级大震区地壳上地幔电性结构特征研究.地震地质, 23(2):178-185. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2001.02.006 丁锐, 张世民, 毛昌伟等, 2014.夏垫断裂断层陡坎的微地貌分析.见: 2014年中国地球科学联合学术年会——专题15: 活动断层长期滑动习性、深部结构与地震论文集.北京: 中国地球物理学会, 全国岩石学与地球动力学研讨会组委会, 中国地质学会构造地质学与地球动力学专业委员会, 中国地质学会区域地质与成矿专业委员会. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDW201410020016.htm 段美芳, 陆丽娜, 李莹甄等, 2018.张家口-渤海断裂带西段及中西段b值时空扫描.震灾防御技术, 13(1):138-148. http://zzfy.eq-j.cn/zzfyjs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20180112&journal_id=zzfyjs 付虹, 刘丽芳, 王世芹等, 2002.地方震及近震地下水同震震后效应研究.地震, 22(4):55-66. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/diz200204010 高战武, 2001.张家口-蓬莱断裂带地震地质特征研究.北京: 中国地震局地质研究所. 巩浩波, 郭卫英, 李光科等, 2015.重庆井网水位水温同震响应特征分析.震灾防御技术, 10(S1):794-804. doi: 10.11899/zzfy2015s111 郭履灿, 1971.华北地区的地方性震级ML和面波震级MS 经验关系.见: 全国地震工作会议.1-10. 韩孔艳, 赵健, 2016.赵各庄地震观测井观测现状分析及改造方案探讨.煤炭与化工, 39(7):129-132. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hebhg201607043 韩晓昆, 李营, 杜建国等, 2013.夏垫断裂中南段土壤气体地球化学特征.物探与化探, 37(6):976-982. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht201306003 何付兵, 白凌燕, 王继明等, 2013.夏垫断裂带深部构造特征与第四纪活动性讨论.地震地质, 35(3):490-505. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2013.03.004 黄辅琼, 陈顒, 白长清等, 2005.八宝山断层的变形行为与降雨及地下水的关系.地震学报, 27(6):637-646. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2005.06.008 贾辉, 何正勤, 叶太兰, 2008.用瞬态多道瑞利波法研究夏垫隐伏断裂附近的浅层速度结构变化.地震地磁观测与研究, 29(1):15-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3246.2008.01.003 江娃利, 1999.北京平谷地区地表陡坎的成因识别.地震地质, 21(4):309-315. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.1999.04.003 江娃利, 侯治华, 肖振敏等, 2000.北京平原夏垫断裂齐心庄探槽古地震事件分析.地震地质, 22(4):413-422. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2000.04.010 兰双双, 迟宝明, 姜纪沂, 2011.地下水位对近震和远震异常响应的比较——以汶川地震和苏门答腊地震为例.吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 41(1):145-152. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb201101017 李梁, 张世红, 蔡向民等, 2011.北京市平原区夏垫断裂活动性的磁学研究.见: 中国地球物理学会第二十七届年会论文集.长沙: 中国地球物理学会, 161. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDW201110001130.htm 李梁, 2012.北京市平原区夏垫断裂活动性的磁性地层学研究.北京: 中国地质大学(北京). http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1012365104.htm 廖欣, 刘春平, 石云等, 2014.川06井水位固体潮效应变化初探.地震学报, 36(2):299-305. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-3782.2014.02.014 刘瑞丰, 蔡晋安, 彭克银等, 2007.地震科学数据共享工程.地震, 27(2):9-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2007.02.002 刘耀炜, 陆明勇, 付虹等, 2010.地下流体动态信息提取与强震预测技术研究.北京:地震出版社. 陆丽娜, 李静, 沈军等, 2016.夏垫活动断层土壤氡地球化学特征.震灾防御技术, 11(4):736-746. http://zzfy.eq-j.cn/zzfyjs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20160404&journal_id=zzfyjs 陆丽娜, 杨明, 李静等, 2018.土壤气汞探测在夏垫断裂带的应用研究.地质与勘探, 54(1):112-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2018.01.012 陆明勇, 黄辅琼, 刘善华等, 2005.地壳变形与地下水相互作用及其异常关系初探.地震, 25(1):67-73. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/diz200501009 毛昌伟, 丁锐, 龚正等, 2010.1679年三河-平谷8级地震地表断层陡坎的GPS测量.地壳构造与地壳应力文集, (22):11-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SEIS201000003.htm 牛安福, 张晶, 吉平, 2005.强地震引起的同震形变响应.内陆地震, 19(1):1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8956.2005.01.001 冉志杰, 李皓, 吕国军等, 2013.夏垫断裂夏垫段浅部构造特征地震探测.地震工程学报, 35(3):656-663. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2013.03.0651 石耀霖, 曹建玲, 马丽等, 2007.唐山井水温的同震变化及其物理解释.地震学报, 29(3):265-273. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2007.03.005 史浙明, 2015.地下水位同震响应特征及机理研究.北京: 中国地质大学(北京). http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1015391754.htm 宋洋, 谷洪彪, 李海君等, 2016.断裂两盘井水位同震响应特征对比分析——以北京八宝山断裂带中段大灰厂两观测井为例.吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 46(6):1815-1822. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201606018 孙小龙, 刘耀炜, 2008a.苏门答腊8.5级地震引起的水温响应变化.华北地震科学, 26(1):35-40. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hbdzkx200801008 孙小龙, 刘耀炜, 2008b.塔院井水位和水温的同震响应特征及其机理探讨.中国地震, 24(2):105-115. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdz200802002 孙小龙, 刘耀炜, 宴锐, 2011.利用水位资料反演华北地区构造应力场变化.地震, 31(2):42-49. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/diz201102005 孙小龙, 刘耀炜, 晏锐, 2013.云南姚安井2009年10月后水位下降的成因分析.地震学报, 35(3):410-420. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-3782.2013.03.012 田优平, 余达远, 万永革等, 2014.三河-平谷地震区地球物理特征研究.地球物理学进展, 29(4):1563-1572. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQWJ201404010.htm 万永魁, 沈军, 于晓辉等, 2014.北京平原区夏垫活动断裂滑动速率及古地震复发间隔.防灾科技学院学报, 16(3):38-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8047.2014.03.007 王博, 刘耀炜, 孙小龙, 2008.地下流体与断裂活动关系的研究综述.地震研究, 31(3):296-302. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2008.03.018 王芳, 黄辅琼, 2012.安溪一号井水位的同震阶变响应特征.地震地磁观测与研究, 33(5):169-177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3246.2012.05/06.031 王雷, 沈军, 林玲玲等, 2014.北京平原区夏垫断裂的多源遥感影像特征.防灾科技学院学报, 16(4):33-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8047.2014.04.006 武安绪, 李国江, 李平安等, 2010.北京地区流体观测方法记录到的汶川大地震同震变化.地震地磁观测与研究, 31(1):71-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3246.2010.01.014 向阳, 孙小龙, 高小其等, 2017a.新10井水位对九寨沟MS 7.0精河MS 6.6地震同震响应.中国地震, 33(4):563-574. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdz201704012 向阳, 孙小龙, 杨朋涛, 2017b.新疆阿克陶MS 6.7地震引起的新10井水位同震响应研究.地震学报, 39(6):899-909. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhen201706008 徐锡伟, 计凤桔, 于贵华等, 2000.用钻孔地层剖面记录恢复古地震序列:河北夏垫断裂古地震研究.地震地质, 22(1):9-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2000.01.002 杨晓平, 曹景虎, 陈献程, 2012.夏垫活动断裂两盘岩心氧化铁变化.地震地质, 34(4):659-671. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2012.04.010 杨竹转, 邓志辉, 赵云旭等, 2005.云南思茅大寨井水位同震阶变的初步研究.地震学报, 27(5):569-574. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2005.05.012 尹宏伟, 梁丽环, 韩文英等, 2016.黄骅井水位映震效能分析.地震地磁观测与研究, 37(3):23-29. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzdcgcyyj201603004 张超, 沈军, 赵江涛等, 2014.北京平原夏垫断裂沉积旋回研究.防灾科技学院学报, 16(2):49-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8047.2014.02.009 张先康, 赵金仁, 刘国华等, 2002.三河-平谷8.0级大震区震源细结构的深地震反射探测研究.中国地震, 18(4):326-336. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2002.04.002 Cooper Jr. H. H., Bredehoeft J. D., Papadopulos I. S., et al., 1965. The response of well-aquifer systems to seismic waves. Journal of Geophysical Research, 70 (16):3915-3926. doi: 10.1029/JZ070i016p03915 Gu S. Y., Liu B. W., Zhang H., et al., 2013. Numerical simulation of coseismic response and its mechanism of well water temperature to farfield strong earthquakes. Earthquake Research in China, 27 (3):316-330. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdzyj-e201303004 Gutenberg B., Richter C. F., 1956. Magnitude and energy of earthquakes. Annals of Geophysics, 9 (1):1-15. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_e788e8839342702b331c76926f6e3f47 Kim S. W., Choi H. S., Park D. U., et al., 2018. Water level response measurement in a steel cylindrical liquid storage tank using image filter processing under seismic excitation. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 101:274-291. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.08.035 Liu C. Y., Chia Y. P., Chuang P. Y., et al., 2018. Impacts of hydrogeological characteristics on groundwater-level changes induced by earthquakes. Hydrogeology Journal, 26 (2):451-465. http://www.springerlink.com/openurl.asp?id=doi:10.1007/s10040-017-1684-z Mogi K., Mochizuki H., Kurokawa Y., 1989. Temperature changes in an artesian spring at Usami in the Izu Peninsula (Japan) and their relation to earthquakes. Tectonophysics, 159 (1-2):95-108. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(89)90172-8 Montgomery D. R., Manga M., 2003. Streamflow and water well responses to earthquakes. Science, 300 (5628):2047-2049. doi: 10.1126/science.1082980 Petitta M., Mastrorillo L., Preziosi E., et al., 2018. Water-table and discharge changes associated with the 2016-2017 seismic sequence in central Italy:hydrogeological data and a conceptual model for fractured carbonate aquifers. Hydrogeology Journal, 3 (4):1009-1026. Roeloffs E. A., 1998. Persistent water level changes in a well near Parkfield, California, due to local and distant earthquakes. Journal of Geophysical Research, 103 (B1):869-889. doi: 10.1029/97JB02335 Shi Z. M., Wang G. C., Manga M., et al., 2015. Mechanism of co-seismic water level change following four great earthquakes-insights from co-seismic responses throughout the Chinese mainland. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 430:66-74. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.08.012 Sun X. L., Liu Y. W., 2012. Changes in groundwater level and temperature induced by distant earthquakes. Geosciences Journal, 16 (3):327-337. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=96c834f61c6f5f38625cb44f017942a1 Telesca L., do Nascimento A. F., Bezerra F. H. R., et al., 2015. Analysis of the cross-correlation between water level and seismicity at ACU reservoir (Brazil). Tectonophysics, 658:151-158. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2015.07.017 Wang C. Y., Manga M., 2014. Earthquakes and water. Encyclopedia of Complexity and Systems Science. New York: Springer, 1-18. -



 下载:
下载: