Preliminary Analysis of the Sichuan-Yunnan Block and Surrounding Fault Movement Using GNSS Continuous Observation Data
-
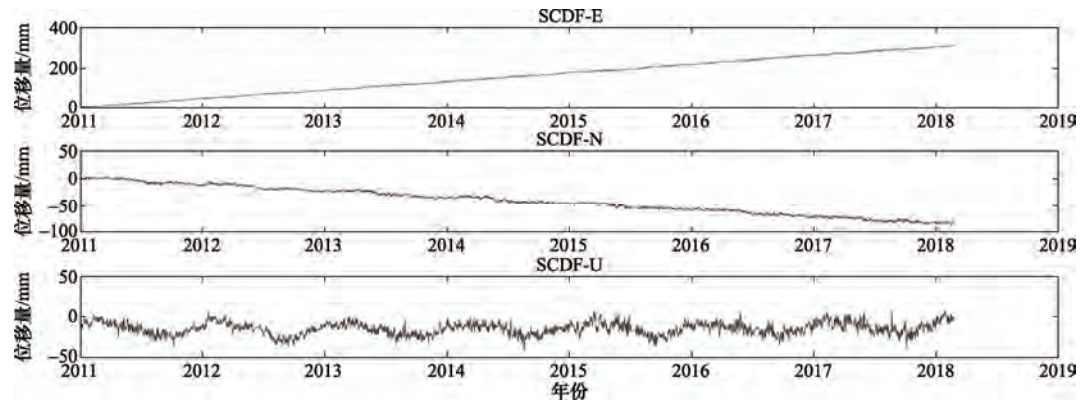
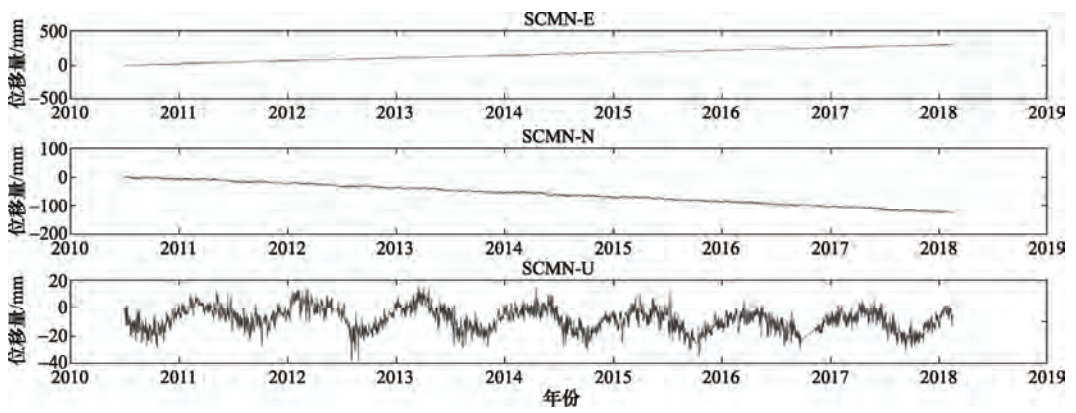
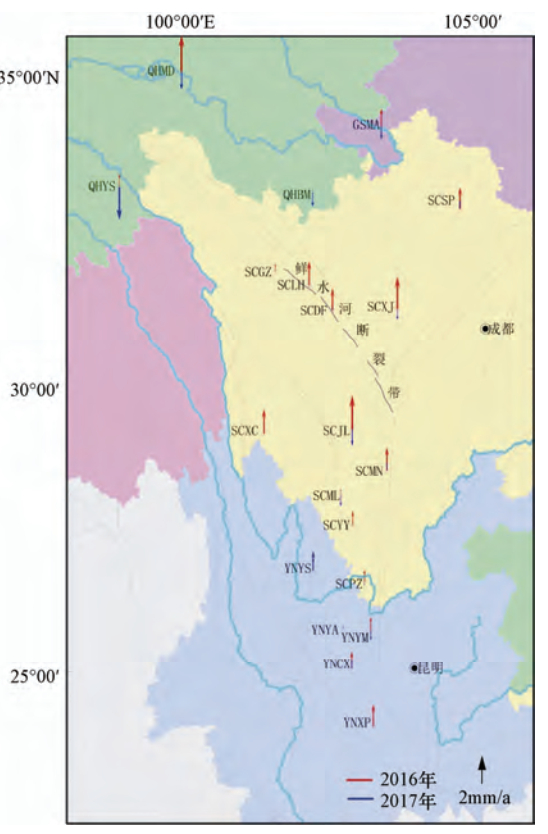
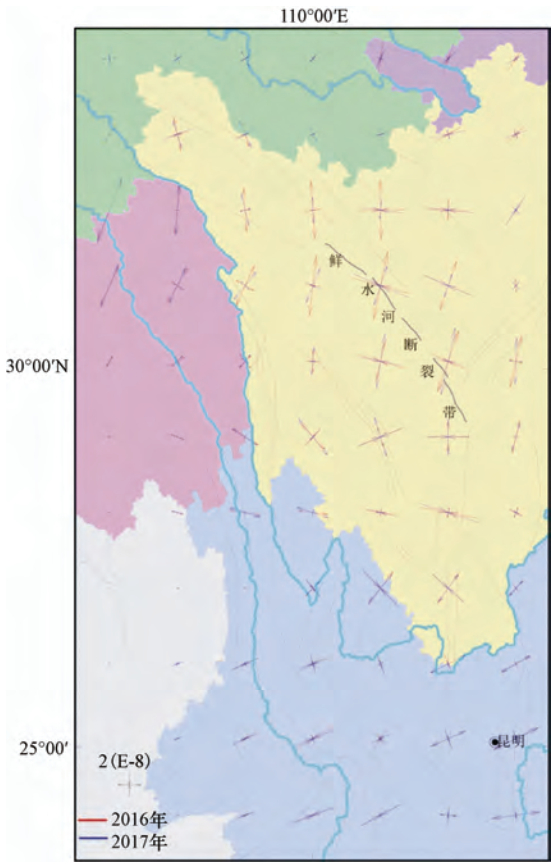
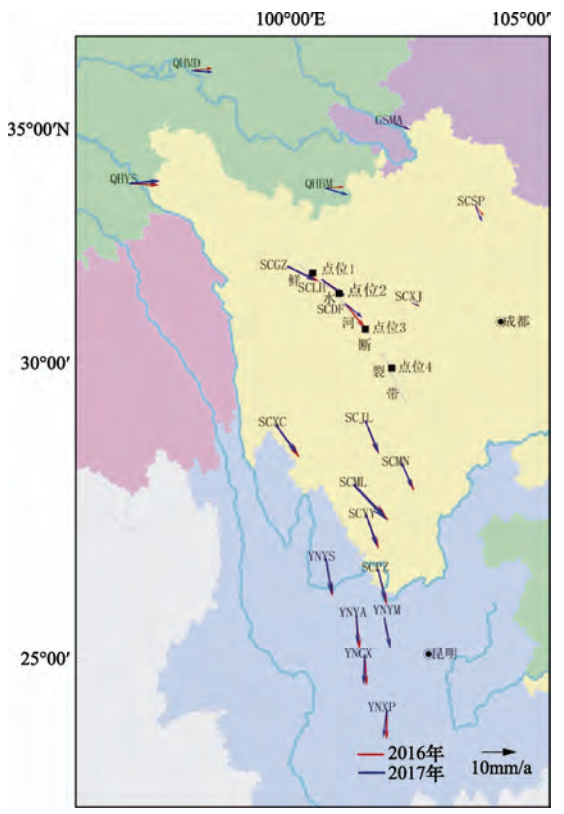
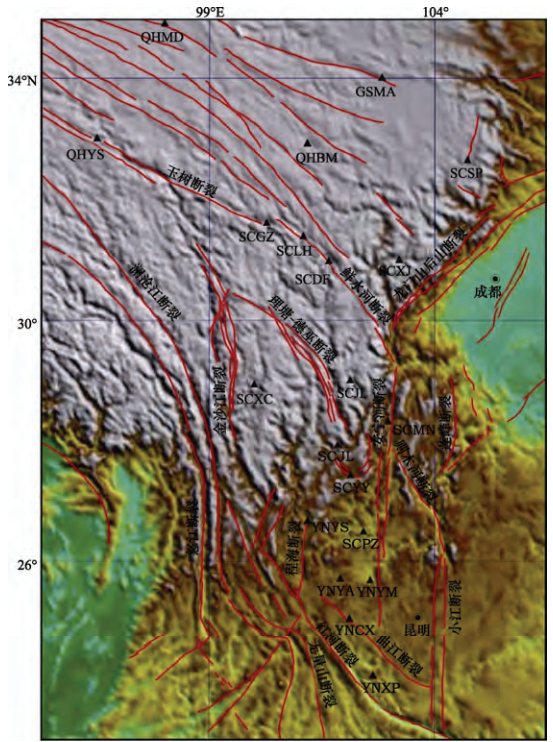
摘要: 本文利用GNSS连续站的资料分析2016、2017年川滇块体和巴彦喀拉块体速度场、应变场特征,认为道孚、西昌和马尔康附近应力积累相对集中。分析GNSS连续站点的相对速度发现,川滇块体内GNSS连续站的运动状态呈明显的顺时针旋转,巴彦喀拉块体也有顺时针旋转态势。此外,利用块体相对运动求解鲜水河断裂运动速率,鲜水河断裂西部的运动速率比东部稍大,约有2—3mm/a的差异。相比2016年,2017年鲜水河断裂运动速率变小,有利于缓解鲜水河断裂应变能的积累。Abstract: In this study, the GNSS continuous station data were analyzed to study the characteristics of the velocity field and strain field of the Sichuan-Yunnan block and the Bayan Har block in 2016-2017, in consideration of that the stress accumulation is relatively concentrated near Dawu, Xichang and Barkam. By analyzing the relative speed of GNSS continuous stations, we found that GNSS continuous station motion in both the Sichuan-Yunnan block and the Bayan Har blocks shows clockwise rotation. By using block relative motion to solve the speed of Xianshuihe fault, we found that the speed of the west of the Xianshuihe fault is slightly faster than that of the east, about 2 to 3 mm/a difference. The movement rate of the Xianshuihe fault in 2017 is smaller than that of 2016, that helps to alleviate the accumulation of strain energy in the Xianshuihe fault. The greater the fault slip difference between the model simulation and the actual measurement, the greater the energy that can be accumulated at the fault. As a result, the seismic energy concentration in the fracture energy concentration area is relatively greater.
-
Key words:
- GNSS continuous station /
- Motion rate /
- Strain /
- Xianshuihe fault
-
表 1 鲜水河断裂不同点位东向和北向运动速率
Table 1. The eastward and northward movement rate of different points on the Xianshuihe fault
年份 点位1(31.50°N,100.50°E)运动速率/mm·a-1 点位2(31.15°N,101.00°E)运动速率/mm·a-1 点位3(30.55°N,101.50°E)运动速率/mm·a-1 点位4(29.90°N,102.00°E)运动速率/mm·a-1 东向 北向 东向 北向 东向 北向 东向 北向 2016 8.2593 -13.499 7.8359 -12.7154 6.8531 -12.0765 5.7652 -11.4543 2017 7.7108 -12.5397 7.2934 -11.8507 6.2555 -11.5369 5.1012 -11.284 备注:东向速率表示为东向为正,西向为负;北向速率表示为北向为正,南向为负。 表 2 鲜水河断裂不同点位走滑和张压运动速率
Table 2. The strike slip and tension movement rate of different points on the Xianshuihe fault
年份 点位1(31.50°N,100.50°E)运动速率/mm·a-1 点位2(31.15°N,101.00°E)运动速率/mm·a-1 点位3(30.55°N,101.50°E)运动速率/mm·a-1 点位4(29.90°N,102.00°E)运动速率/mm·a-1 走滑 张压 走滑 张压 走滑 张压 走滑 张压 2016 13.9023 -7.5608 14.5320 -3.4503 13.3853 -3.6935 12.1760 -4.0228 2017 12.9476 -7.0043 13.5370 -3.2225 12.5811 -3.7345 11.5861 -4.3719 注:走滑速率表示为左旋为正,右旋为负;张压速率表示为张性为正,压性为负。 -
薄万举, 李胜乐, 杨国华等, 2008.流动形变监测系统(中册)-大地形变数据处理软件.北京:地震出版社. 江在森, 马宗晋, 张希等, 2003. GPS初步结果揭示的中国大陆水平应变场与构造变形.地球物理学报, 46(3):352-358. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2003.03.012 李延兴, 杨国华, 李智等, 2003.中国大陆活动地块的运动与应变状态.中国科学(D辑), 33(S1):65-81. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd2003z1008 李延兴, 李智, 张静华等, 2004.中国大陆及周边地区的水平应变场.地球物理学报, 47(2):222-231. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2004.02.008 刘志广, 杨博, 卢双印等, 2013.青藏高原中南部近期地壳水平形变.大地测量与地球动力学, 33(3):l6-20. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gjdzdt201206224 王敏, 沈正康, 牛之俊等, 2003.现今中国大陆地壳运动与活动块体模型.中国科学(D辑), 33(S1):21-32. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd2003z1003 王敏, 2007. GPS数据处理方面的最新进展及其对定位结果的影响.国际地震动态, (7):3-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4975.2007.07.002 徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 郑荣章等, 2003.川滇地区活动块体最新构造变动样式及其动力来源.中国科学(D辑), 33(S1):151-162. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd2003z1017 杨国华, 李延兴, 韩月萍等, 2002.由GPS观测结果推导中国大陆现今水平应变场.地震学报, 24(4):337-347. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2002.04.001 易桂喜, 闻学泽, 范军等, 2004.由地震活动参数分析安宁河-则木河断裂带的现今活动习性及地震危险性.地震学报, 26(3):294-303. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2004.03.008 张培震, 邓起东, 张国民等, 2003.中国大陆的强震活动与活动地块.中国科学(D辑), 33(S1):12-20. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd2003z1002 周伟, 李延兴, 张静华等, 2008.川滇地区现今构造变形分析.大地测量与地球动力学, 28(2):22-27. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dkxbydz200802004 朱爽, 杨国华, 刘辛中等, 2017.川滇地区近期地壳变形动态特征研究.武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 42(12):1765-1772. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/whchkjdxxb201712013 朱爽, 王洪栋, 2018.川滇块体东边界主要断裂带现今运动特征分析.地震工程学报, 40(1):79-85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2018.01.079 -



 下载:
下载: