Geochemical Characteristics of Volcanic Hot Spring Gas in China and its Applications in Volcanic Monitoring
-
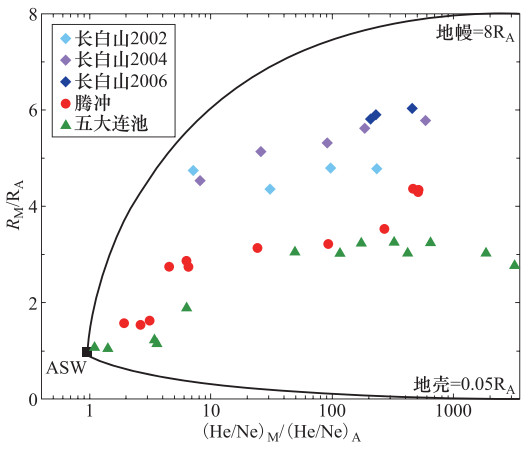
摘要: 中国火山温泉主要分布在吉林长白山、云南腾冲和黑龙江五大连池等火山区。这些火山虽然处于休眠状态,但大面积的温泉分布指示着岩浆房存在的可能性。本文总结了前人研究成果,分析了中国主要火山区温泉气体地球化学特征,并探讨了温泉气体在火山监测中的应用。长白山、腾冲和五大连池火山区温泉气体地球化学性质类似,都以CO2为主要气体,含量在80%以上,最高可达99%以上,其它气体组分包括CH4、N2、O2、SO2、H2S、He和H2等。长白山火山温泉气体中氦同位素比值(3He/4He)最高,约为4—6RA,CO2中碳同位素比值(δ13C)为-7.9‰—-1.3‰,CH4中碳同位素为-48.0‰—-28.7‰;腾冲火山温泉气体氦同位素比值为3—5.5RA,CO2中的碳同位素为-6.49‰—-2.07‰,CH4中碳同位素为-23.5‰—-9.3‰;五大连池火山温泉气体氦同位素比值约为3RA,CO2中的碳同位素比值为-9.6‰—-3.1‰,CH4中碳同位素为-47.2‰—-44.4‰。3个火山区的温泉气体均显示地幔来源的岩浆气体特征,并在上升运移过程中受地壳或古俯冲物质的影响。Abstract: The volcanic hot springs in China are mainly distributed in the Changbaishan volcanic region in Jilin Province, the Tengchong volcanic region in Yunnan Province, and the Wudalianchi volcanic region in Heilongjiang Province. Although these volcanoes are dormant, wide distribution of hot springs indicates the existence of magma chambers. This paper summarizes the results of previous studies, analyzes the geochemical characteristics of hot spring gas in major volcanic regions of China, and discusses the applications of hot spring gases in volcano monitoring. The geochemical characteristics of the hot spring gases in the Changbaishan, Tengchong, and Wudalianchi volcanic regions are similar, with CO2 as the main gas, the content of which is above 80%, and the highest is more than 99%. Other gas components including CH4, N2, O2, SO2, H2S, He and H2. The helium isotopic ratios (3He/4He) in the Changbaishan volcanic hot spring gases are the highest, about 4-6RA. The carbon isotopes (δ13C) in CO2 are from -7.9‰ to -1.3‰ and the carbon isotopes in CH4 are between -48.0‰ and -28.7‰. The helium isotopic ratios of the Tengchong volcanic hot spring gases are 3-5.5RA. The carbon isotopes of CO2 are from -6.49‰ to 2.07‰ and from -22.22‰ to -13.70‰ in CH4. The helium isotopic ratios of the Wudalianchi volcanic hot spring are about 3RA. The carbon isotopic ratios in CO2 are between -9.6‰ and -3.1‰ and from -47.2‰ to -44.4‰ in CH4. The hot spring gases in the three volcanic areas all indicate mantle sources, which may be contaminated by the crustal or ancient subduction materials during the up-immigration processes. Combined with the results of earthquakes and topographic deformation, the geochemical characteristics of gases in volcanic hot springs are of great importance to the monitoring of active volcanoes.
-
Key words:
- Volcanic hot springs /
- Geochemical characteristics /
- Isotopes /
- Volcanic monitoring
-
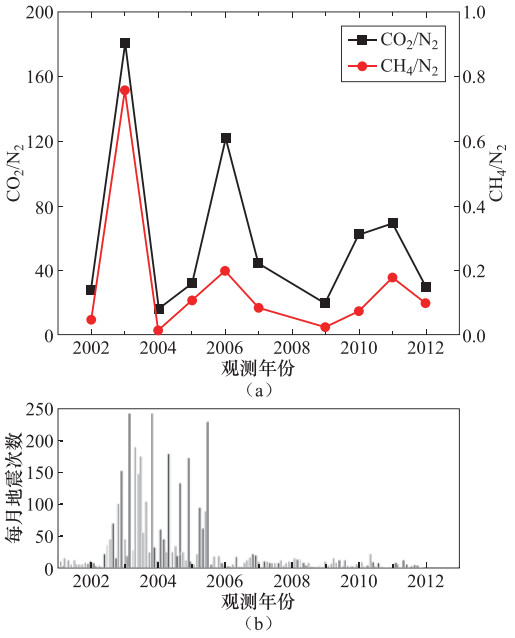
图 1 2002—2012年温泉气体的CO2/N2与CH4/N2比值连续观测图(a)和2001—2012年长白山火山每月地震次数(引自Xu等,2012)(b)
Figure 1. The CO2/N2 and CH4/N2 ratios from 2002 to 2012 (a) and monthly number of earthquakes of Changbaishan Volcano between 2001 and 2012 (revised from Xu et al., 2012)(b)
表 1 长白山聚龙温泉15号采样点温泉气体中CO2、CH4和N2含量及比值
Table 1. Concentrations of CO2, CH4 and N2 and the ratios of Sampling site No.15 of Julong hot spring at Changbaishan Volcano
采样年份 CH4/% CO2/% N2/% CO2/N2 CH4/N2 2002 0.16 95.02 3.44 27.6 0.047 2003 0.41 97.52 0.54 180.6 0.759 2004 0.07 93.23 5.90 15.8 0.012 2005 0.32 95.50 3.02 31.6 0.106 2006 0.16 98.46 0.81 121.6 0.198 2007 0.18 96.46 2.18 44.2 0.083 2009 0.11 93.74 4.77 19.7 0.023 2010 0.12 97.66 1.56 62.6 0.074 2011 0.3 96.90 1.40 69.2 0.179 2012 0.31 94.25 3.17 29.7 0.098 -
陈骏, 王鹤年, 2004.地球化学.北京:科学出版社. 成智慧, 郭正府, 张茂亮等, 2014.腾冲新生代火山区CO2气体释放通量及其成因.岩石学报, 30(12):3657-3670. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201412015 杜建国, 李圣强, 刘连柱等, 1999.五大连池火山区气体地球化学特征.地球化学, 28(2):171-176. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1999.02.008 郭正府, 刘嘉麒, 贺怀宇等, 2003.火山喷出气体的环境、灾害效应及对火山未来喷发的指示意义.地震地质, 25(S1):88-98. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzdz2003z1011 郭正府, 李晓惠, 张茂亮, 2010.火山活动与深部碳循环的关系.第四纪研究, 30(3):497-505. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2010.03.07 郭正府, 张茂亮, 成智慧等, 2014.中国大陆新生代典型火山区温室气体释放的规模及其成因.岩石学报, 30(11):3467-3480. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201411028 姜枚, 谭捍东, 彭淼等, 2016.腾冲火山构造区马站岩浆囊地球物理特征的再探讨.中国地质, 43(5):1688-1696. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201605017 李婷, 刘嘉麒, 王先彬等, 2015.长白山天池火山温泉的气体地球化学特征与成因.矿物岩石地球化学通报, 34(6):1192-1202. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.06.011 刘国明, 孙鸿雁, 郭峰, 2011.长白山火山最新监测信息.岩石学报, 27(10):2905-2911. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201110010 刘嘉麒, 1999.中国火山.北京:科学出版社. 刘嘉麒, 郭正府, 刘强, 1999.火山灾害与监测.第四纪研究, (5):414-422. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1999.05.004 仇根根, 裴发根, 方慧等, 2014.长白山天池火山岩浆系统分析.地球物理学报, 57(10):3466-3477. doi: 10.6038/cjg20141032 冉华, 赵慈平, 陈坤华, 2008.腾冲火山区温泉甲烷气体现场富集取样效果研究.地震研究, 31(S1):599-606. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200802255516 上官志冠, 赵慈平, 高玲, 2006.中国活动火山区甲烷的碳同位素研究.岩石学报, 22(6):1458-1464. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200606002 上官志冠, 武成智, 2008.中国休眠火山区岩浆来源气体地球化学特征.岩石学报, 24(11):2638-2646. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200811019 汤吉, 邓前辉, 赵国泽等, 2001.长白山天池火山区电性结构和岩浆系统.地震地质, 23(2):191-200. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2001.02.008 王先彬, 1989.稀有气体同位素地球化学和宇宙化学.北京:科学出版社. 许建东, 2011.中国活动火山监测进展回顾.矿物岩石地球化学通报, 30(4):390-392. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2011.04.006 杨晓涛, 胥颐, 刘建华等, 2011.腾冲火山区的地震层析成像及其构造意义.地球物理学报, 54(8):2050-2059. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.08.012 詹艳, 赵国泽, 王继军等, 2006.黑龙江五大连池火山群地壳电性结构.岩石学报, 22(6):1494-1502. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200606007 张茂亮, 郭正府, 成智慧等, 2011.长白山火山区温泉温室气体排放通量研究.岩石学报, 27(10):2898-2904. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201110009 张森琦, 贾小丰, 张杨等, 2017.黑龙江省五大连池尾山地区火山岩浆囊探测与干热岩地热地质条件分析.地质学报, 91(7):1506-1521. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.07.007 赵慈平, 冉华, 陈坤华, 2011.腾冲火山区壳内岩浆囊现今温度:来自温泉逸出气体CO2、CH4间碳同位素分馏的估计.岩石学报, 27(10):2883-2897. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201110008 赵慈平, 王云, 周挚等, 2017.宁洱火山区壳内岩浆囊现今温度:来自CO2-CH4碳同位素地质温度计的估计.岩石学报, 33(1):231-249. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201701019 赵宜, 孔令昌, 1989.五大连池火山地区的某些气体地球化学特征.地震地质, 11(3):34-36. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000348864 Aiuppa A., Moretti R., Federico C., et al., 2007. Forecasting Etna eruptions by real-time observation of volcanic gas composition. Geology, 35 (12):1115-1118. doi: 10.1130/G24149A.1 Clarke W. B., Jenkins W. J., Top Z., 1976. Determination of tritium by mass spectrometric measurement of 3He. The International Journal of Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 27 (9):515-522. doi: 10.1016/0020-708X(76)90082-X Fiebig J., Chiodini G., Caliro S., et al., 2004. Chemical and isotopic equilibrium between CO2 and CH4 in fumarolic gas discharges:Generation of CH4 in arc magmatic-hydrothermal systems. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 68 (10):2321-2334. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2003.10.035 Fischer T. P., 2008. Fluxes of volatiles (H2O, CO2, N2, Cl, F) from arc volcanoes. Geochemical Journal, 42 (1):21-38. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.42.21 Gautheron C., Moreira M., 2002. Helium signature of the subcontinental lithospheric mantle. Earth Planetary Science Letter, 199 (1-2):39-47. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00563-0 Giggenbach W. F., 1982. Carbon-13 exchange between CO2 and CH4 under geothermal conditions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 46 (2):159-165. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(82)90243-5 Graham W. D., 2002. Noble gas isotope geochemistry of Mid-Ocean Ridge and Ocean Island Basalts:characterization of mantle source reservoirs. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 47 (1):247-317. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2002.47.8 Hahm D., Hilton D. R., Cho M., et al., 2008. Geothermal He and CO2 variations at Changbaishan intra-plate volcano (NE China) and the nature of the sub-continental lithospheric mantle. Geophysical Research Letters, 35 (22):L22304. doi: 10.1029/2008GL035955 Horita J., 2001. Carbon isotope exchange in the system CO2-CH4 at elevated temperatures. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65 (12):1907-1919. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00570-1 Kim K. H., Nagao K., Tanaka T., et al., 2005. He-Ar and Nd-Sr isotopic compositions of ultramafic xenoliths and host alkali basalts from the Korean peninsula. Geochemical Journal, 39 (4):341-356. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.39.341 Ozima M., Podosek F. A., 2002. Noble gas geochemistry. 2nd ed. Cambridge, UK:Cambridge University Press. Sano Y., Marty B., 1995. Origin of carbon in fumarolic gas from island arcs. Chemical Geology, 119 (1-4):265-274. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)00097-R Schoell M., 1980. The hydrogen and carbon isotopic composition of methane from natural gases of various origins. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 44 (5):649-661. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(80)90155-6 Scott H.P., Hemley R.J., Mao H.K., et al., 2004. Generation of methane in the Earth's mantle:In situ high pressure-temperature measurements of carbonate reduction. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 101 (39):14023-14026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405930101 Shangguan Z. G., Huo W. G., 2002. δD values of escaped H2 from hot springs at the Tengchong Rehai geothermal area and its origin. Chinese Science Bulletin, 47 (2):146-149. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JXTW200202015.htm Sigurdsson H., Houghton B., McNutt S. R., et al., 2015. The encyclopedia of volcanoes. 2nd ed. Cambridge, MA:Academic Press. Wallace P. J., 2005. Volatiles in subduction zone magmas:concentrations and fluxes based on melt inclusion and volcanic gas data. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 140 (1-3):217-240. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2004.07.023 Wallace P. J., Edmonds M. 2011. The sulfur budget in magmas:evidence from melt inclusions, submarine glasses, and volcanic gas emissions. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 73 (1):215-246. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2011.73.8 Wei F. X., Xu J. D., Shangguan Z. G., et al., 2016. Helium and carbon isotopes in the hot springs of Changbaishan Volcano, northeastern China:A material connection between Changbaishan Volcano and the west Pacific plate?. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 327:398-406. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2016.09.005 Weiss R. F., 1971. Solubility of helium and neon in water and seawater. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 16 (2):235-241. doi: 10.1021-je60049a019/ Xu J. D., Liu G. M., Wu J. P., et al., 2012. Recent unrest of Changbaishan volcano, northeast China:A precursor of a future eruption? Geophysical Research Letters, 39 (16):L16305. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258647124_Recent_unrest_of_Changbaishan_volcano_Northeast_China_A_precursor_of_a_future_eruption Xu S., Zheng G. D., Nakai S., et al., 2013. Hydrothermal He and CO2 at Wudalianchi intra-plate volcano, NE China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 62:526-530. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.11.001 Zhang M. L., Guo Z. F., Sano Y., et al., 2015. Stagnant subducted Pacific slab-derived CO2 emissions:Insights into magma degassing at Changbaishan volcano, NE China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 106:49-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.01.029 Zhang M. L., Guo Z. F., Sano Y., et al., 2016. Magma-derived CO2 emissions in the Tengchong volcanic field, SE Tibet:Implications for deep carbon cycle at intra-continent subduction zone. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 127:76-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.06.009 Zhao D. P., Liu L., 2010. Deep structure and origin of active volcanoes in China. Geoscience Frontiers, 1 (1):31-44. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=SciencePaper201401220000012509 -



 下载:
下载: