Study on Influence of the Dynamic Characteristics of Ramp Bridge Setting Different Constrainting Forms
-
摘要: 近年来,地震作用下的匝道桥表现出较高的地震易损性。为建立匝道桥的有效约束方式,以减小其地震损伤,本文基于汶川地震中连续梁桥约束方式的调研结果,建立了4种不同匝道桥支座约束方式,并以石家庄石环线某匝道桥为例,对比分析了不同约束方式下匝道桥的自振特性及地震响应。结果表明:板式橡胶支座具有一定的剪切变形能力,可降低桥墩与支座组成的体系刚度,有效分散了上部结构的地震惯性力,保护了下部结构,但应注意其引起的较大主梁位移;固定支座或墩梁固结形式会放大桥墩受力,增加下部结构的损坏,不宜设置在高度较矮、刚度较大的桥墩上;双层挡块和垫石凹槽分级限位支座具有较好的限位能力,并可耗散部分地震能量。Abstract: In recent years, it has been shown that the ramp bridge has relatively high seismic vulnerability under earthquake. In order to reduce the seismic damage, effective constrainting forms of the ramp bridge should be established. Based on the investigation results of the constrainting forms supported on the continuous girder bridges in the Wenchuan earthquake, 4 different constrainting forms supported on the ramp bridges are established. Taking a ramp bridge in Shijiazhuang as an example, we compare the vibration characteristics and the seismic response of the ramp bridge with different constrains. The results show that the elastomeric pad bearings have a certain shear deformation ability, which could reduce the stiffness of the system of the piers and the bearings. Using these bearings, the seismic force of the upper structure could be effectively distributed which could protect the lower structure, but engineers should also pay attention to the larger beam displacements. Fixed bearings or piers beam consolidation form setting on the bridges will enlarge the pier internal force and increase the damage probability of the lower structure. So it is not suitable to set them on the short piers with higher stiffness. The proposed seismic double-layer stopper and grading limit bearing in this paper have good limiting ability and can dissipate the seismic energy.
-
Key words:
- Bridge engineering /
- Constrainting form /
- Ramp bridge /
- Dynamic characteristics /
- Seismic performance
-
表 1 一联约束形式
Table 1. Constrainting form
约束方式 左侧联端(0号桥台) 1号墩 2号墩 右侧联端(3号墩) 1 抗扭竖向约束 抗扭竖向约束 抗扭竖向约束 抗扭竖向约束 2 抗扭竖向约束 固定 抗竖向约束 抗扭竖向约束 3 抗扭竖向约束 固定 固定 抗扭竖向约束 4 抗扭竖向切径向约束 抗扭竖径向约束 抗扭竖径向约束 抗扭竖向切径向约束 表 2 不同约束方式的匝道桥自振特性对比
Table 2. Comparison of the vibration characteristics of the ramp bridge by using different constrainting forms
约束方式 振型 周期/s 频率/Hz 振型描述 约束1 1 1.123 0.891 第二、三联切向平动 2 1.064 0.94 第二、三联径向平动 3 1.044 0.958 各联切向平动,二、三联切向反向 约束2 1 0.959 1.042 第二联水平转动 2 0.92 1.087 第三联转动 3 0.883 1.132 第一联转动 约束3 1 0.617 1.621 第二、三联水平转动 2 0.589 1.699 第三联桥墩径向弯曲 3 0.562 1.781 第二联转动 约束4 1 0.827 1.21 第三联切向平动 2 0.575 1.74 第二联切向平动 3 0.496 2.017 第二、三联桥墩径向弯曲 -
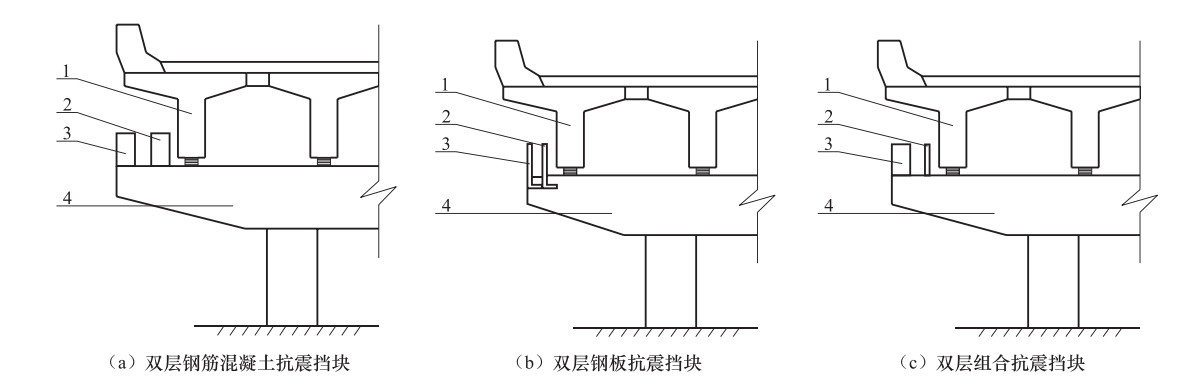
陈乐生, 庄卫林, 赵河清等, 2012.汶川地震公路震害调查——桥梁.北京:人民交通出版社. 黄勇, 王君杰, 韩鹏等, 2010.考虑支座破坏的连续梁桥地震反应分析.土木工程学报, 43(S2):217-223. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8521383 李冲, 2015.中小跨径梁桥基于性能的抗震设计方法研究.南京: 东南大学. 聂利英, 李建中, 胡世德等, 2006.地震作用下板式橡胶支座滑动引起的城市立交中的动力耦合作用.工程力学, 23(11):14-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2006.11.003 孙治国, 王东升, 郭迅等, 2009.汶川大地震绵竹市回澜立交桥震害调查.地震工程与工程振动, 29(4):132-138. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzgcygczd200904019 王克海, 韦韩, 李茜, 2011a.双层钢筋混凝土抗震挡块: 中国, 201020662424.1. 王克海, 韦韩, 李茜, 2011b.双层钢板抗震挡块: 中国, 201020662462.7. 王克海, 韦韩, 李茜, 2011c.双层组合抗震挡块: 中国, 201020662461.2. 王克海, 2014.桥梁抗震研究(2版).北京:中国铁道出版社. 王克海, 李冲, 2014a.垫石凹槽分级限位无顶钢板和底钢板的橡胶支座: 中国, 201420086825.5. 王克海, 惠迎新, 吴刚, 2014b.新型双层抗震挡块抗震性能研究.地震工程与工程振动, 34(S1):505-510. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8707280 张菊辉, 梁磊, 管仲国, 2017.城市高架匝道桥部分隔震体系地震响应分析.振动与冲击, 36(7):141-148. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zdycj201707022 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2016.中国地震动参数区划图(GB 18306-2015).北京:中国标准出版社. 中华人民共和国交通运输部, 2008.公路桥梁抗震设计细则(JTG/T B02-01-2008).北京:人民交通出版社. Kim S. H., Mha H. S., Lee S. W., 2006. Effects of bearing damage upon seismic behaviors of a multi-span girder bridge. Engineering Structures, 28 (7):1071-1080. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2005.11.015 Samaan M., Kennedy J. B., Sennah K., 2007. Dynamic analysis of curved continuous multiple-box girder bridges. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 12 (2):184-193. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0702(2007)12:2(184) Seo J., Linzell D. G., 2013. Nonlinear seismic response and parametric examination of horizontally curved steel bridges using 3D Computational models. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 18 (3):220-231. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0000345 -




 下载:
下载: