Analysis on Seismic Responses of Immersed Tunnel Under Inclined P Waves
-
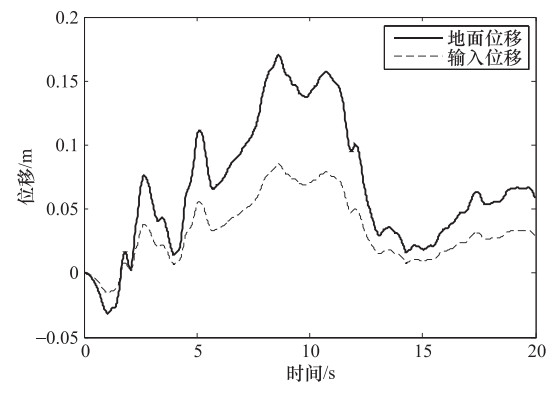
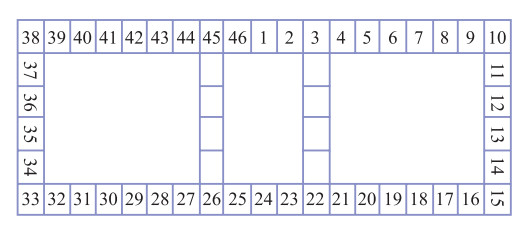
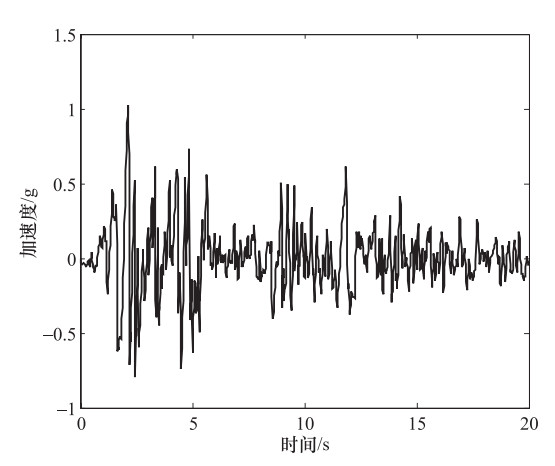
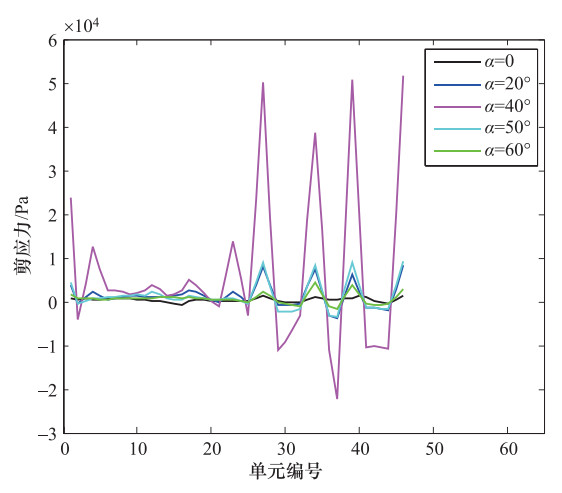
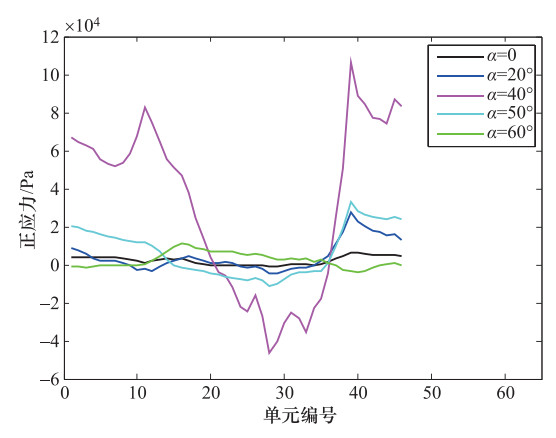
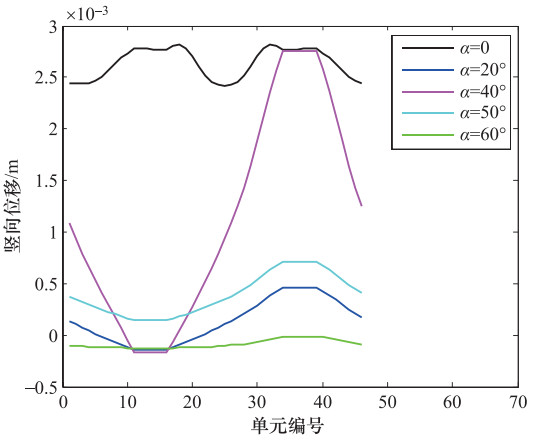
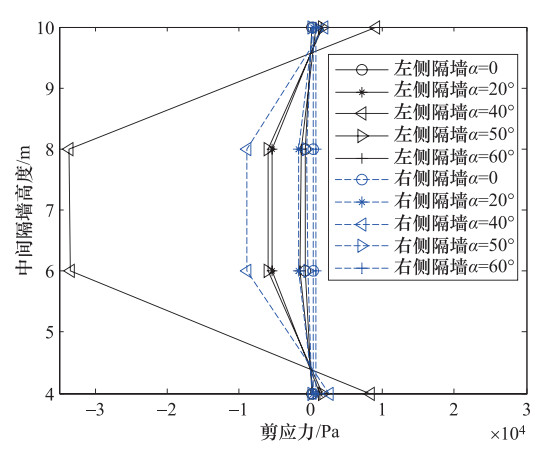
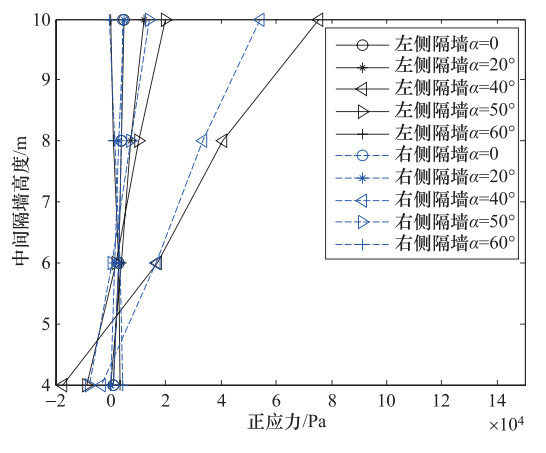
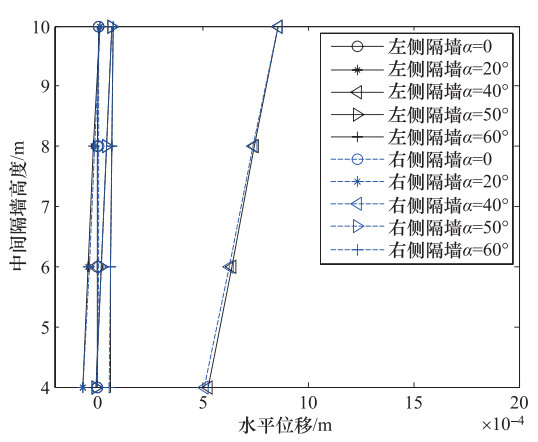
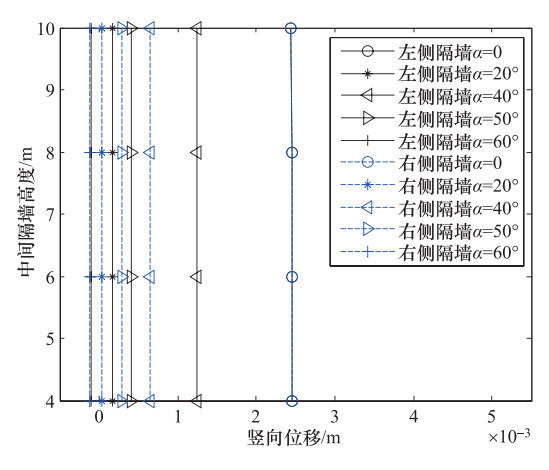
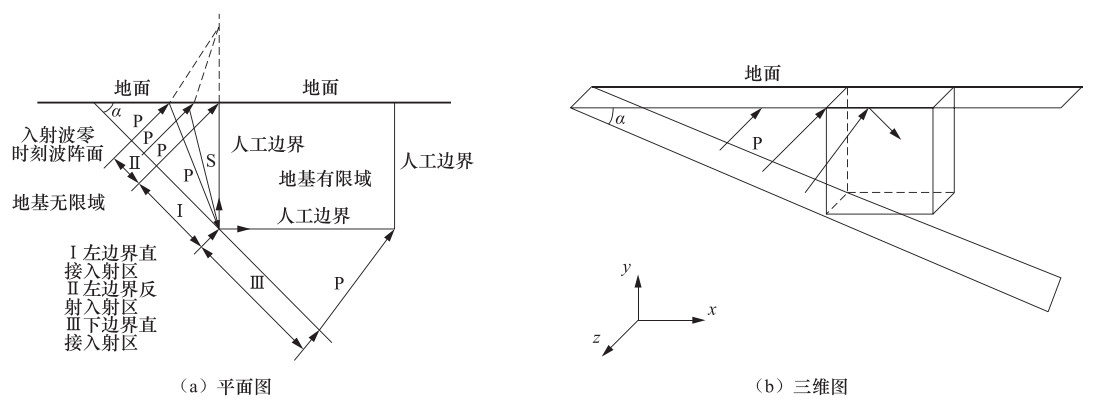
摘要: 为了研究P波斜入射对沉管隧道地震响应的影响,以港珠澳大桥沉管隧道为工程背景,考虑上覆海水与海床、沉管隧道之间耦合作用,采用粘弹性边界和等效力的地震荷载输入方式,利用ADINA软件建立三维有限元模型进行地震响应分析。分析入射角为0°、20°、40°、50°、60°时P波对沉管隧道环向应力峰值(正应力峰值、剪应力峰值)和位移峰值的影响,结果表明:入射角为40°时,沉管隧道应力峰值最大;入射角为0°—40°时,隧道的应力峰值逐渐增大,入射角为40°—60°时,隧道的应力峰值逐渐减小;隧道截面4个转角处及隔墙与顶板、底板的连接处为隧道剪应力峰值最大处;隧道截面左侧剪应力峰值远大于右侧;隧道顶板正应力峰值最大,顶板的正应力峰值大约为底板的2倍;隧道截面左侧位移峰值远大于隧道截面右侧。Abstract: To study the seismic response of immersed tunnel under inclined P waves, we carried out a series of simulation analysis. In this paper, we presented 3D analytical models of immersed tunnel which is based on the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge immersed tunnel taking account of viscous-spring artificial boundary and solid-fluid interaction modeled by ADINA, and analyzed the seismic response of immersed tunnel under P waves with angle of incidence 0°, 20°, 40°, 50°, 60°. It is shown that peak value of stress of tunnel under P waves with angle of incidence 40° reached maximum. The peak value of stress of tunnel had shown a magnifying trend when P-wave angle of incidence 0° increased to 40° and a decreasing trend when P-wave angle of incidence 40° increased to 60°. The larger peak stress point on the immersed tunnel takes place in the four corners of the tunnel and the connection between the partition wall and the bottom plate and the roof. The peak value of shear stress of left side of tunnel cross section is larger than the right side of the tunnel section. The largest peak value of normal stress of tunnel appears on roof, and the peak value of normal stress of roof is about 2 times of on the floor. The peak value of displacement of left side of tunnel cross section is larger than the right side of the tunnel section.
-
Key words:
- Immersed tunnel /
- Inclined P waves /
- Earthquake response /
- Tunnel-soil-fluid interaction
-
表 1 土和隧道参数
Table 1. Parameters of soil and immersed tunnel
名称 参数 单位 数值 土体 泊松比 0.33 渗透系数 m/s 6×10-4 饱和度 1 密度 kg/m3 1900 杨氏模量 MPa 50 隧道 隧道埋深 m 6 泊松比 0.2 密度 kg/m3 2400 杨氏模量 MPa 30000 -
陈贵红, 2002.沉管隧道抗震数值分析.成都: 西南交通大学. 陈向红, 2013.大型水下隧道与附属竖井的地震响应研究.北京: 北京交通大学. 韩大建, 周阿兴, 1999.沉管隧道地震响应分析的等效质点系模型探讨.华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 27(11):108-114. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-565X.1999.11.017 李鹏, 2013.饱和地基中隧道纵向地震反应的数值分析.北京: 清华大学. 廖振鹏, 2002.工程波动理论导论.2版.北京:科学出版社. 刘晶波, 谷音, 杜义欣, 2006.一致粘弹性人工边界及粘弹性边界单元.岩土工程学报, 28(9):1070-1075. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2006.09.004 刘鹏, 丁文其, 金跃郎等, 2014.沉管隧道接头三维非线性刚度力学模型.同济大学学报(自然科学版), 42(2):232-237. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tjdxxb201402010 袁勇, 禹海涛, 燕晓等, 2016.超长沉管隧道多点振动台试验模拟与分析.中国公路学报, 29(12):157-165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2016.12.020 岳戈, 2010.ADINA流体与流固耦合功能的高级应用.北京:人民交通出版社. 赵密, 2009.近场波动有限元模拟的应力型时域人工边界条件及其应用.北京: 北京工业大学. 周晓洁, 张越宇, 何颖等, 2017.地震SV波斜入射下沉管隧道的地震响应分析.地震工程学报, 39(4):600-608. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2017.04.0600 Choi J. S., Lee J. S., Kim J. M., 2002. Nonlinear earthquake response analysis of 2-D underground structures with soil-structure interaction including separation and sliding at interface. In: Proceedings of the 15th ASCE Engineering Mechanics Conference. New York: Columbia, 1-8. Huo H. B., Bobet A., 2003. Seismic design of cut and cover rectangular tunnels-evaluation of observed behavior of Dakai station during Kobe earthquake. In: Proceedings of 1st World Forum of Chinese Scholars in Geotechnical Engineering. Shanghai: Tongji University Press, 456-466. Uenishi K., Sakurai S., 2000. Characteristic of the vertical seismic waves associated with the 1995 Hyogo-ken Nanbu (Kobe), Japan earthquake estimated from the failure of the Daikai Underground Station. Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 29(6):813-821. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-9845 -



 下载:
下载: