Application of Geodesy Technology in Deformation Monitoring of Volcanoes
-
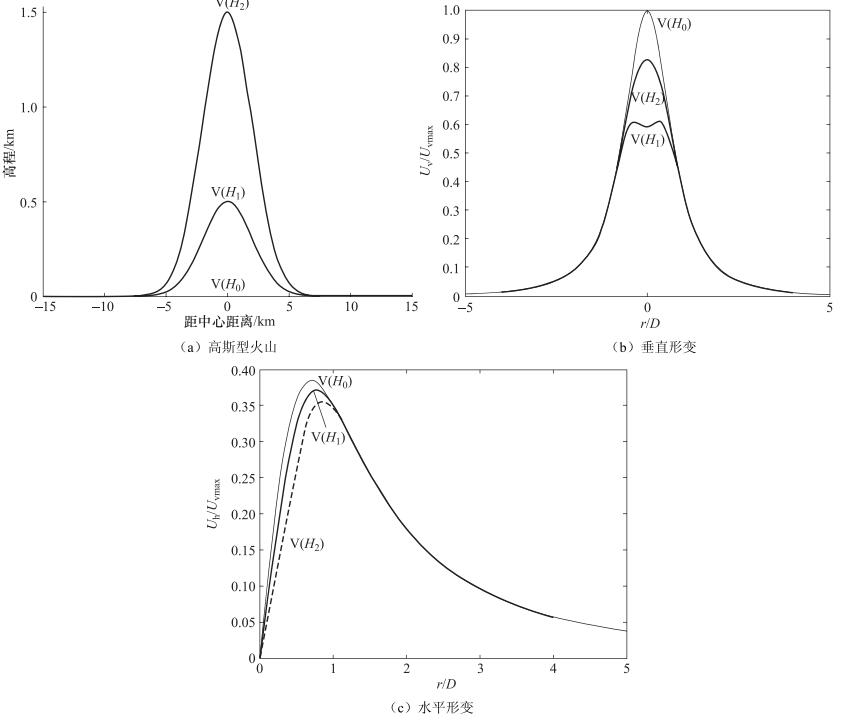
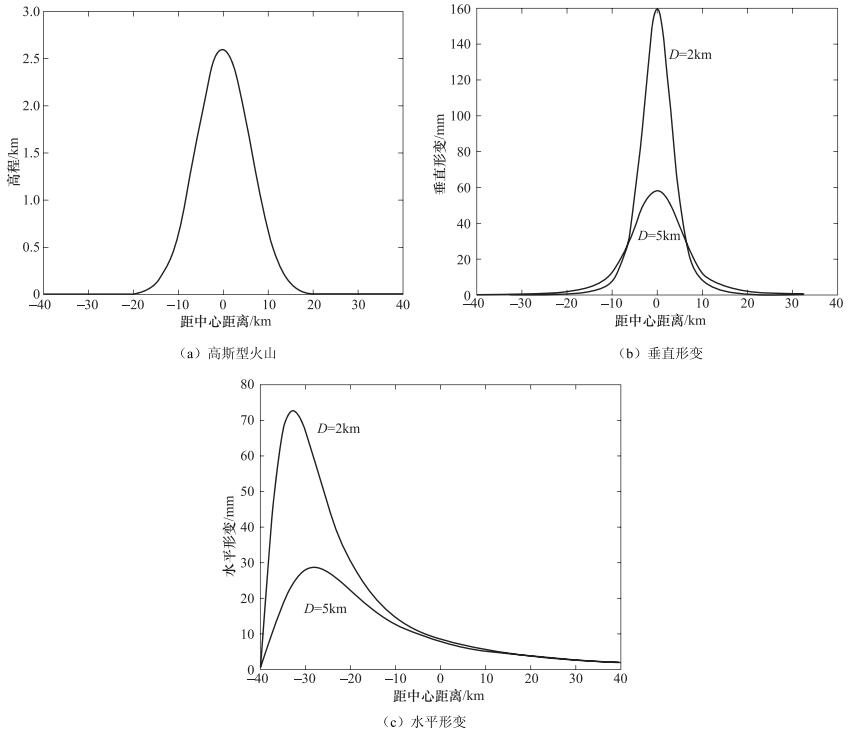
摘要: 岩浆活动的不同阶段引起地表变化不同。地表形变受压力源大小、形状、深度及岩浆运移速率等影响;另外火山类型不同,地形不同,形变特征也不同。地表形变幅度范围很大,为1×10-7—1米量级。火山区形变监测可以了解火山活动状态,有助于进行喷发危险性的预测预报。形变监测从20世纪60年代的传统技术逐渐过渡到20世纪90年代发展起来的GNSS和InSAR等大地测量新技术,火山区形变时空监测能力得到提高,同时缩短了预测时间。我国火山形变监测开始较晚,现已在长白山天池、腾冲以及海南等主要火山区开展监测。传统的连续测量以地倾斜观测为主;新技术主要以流动GNSS监测为主,连续观测站少,InSAR技术研究时间密度不够;目前形变监测还不能实现很好的时空覆盖。Abstract: The surface deformation varies with magmatic activities in different periods. Deformation monitoring can help to understand the activities and to evaluate the potential risk of eruption. Generally, the deformation in volcano area is affected by the magamatic source pressure, size, shape, depth and migration rate and etc. The volcanic types also can cause different deformation on the surface. The range of amplitude is from 1×10-7 to 1 meter-scale. The new geodetic technologies developed in the 1990s, such as GNSS and InSAR, gradually replaced the traditional technique of the 1960s. The monitoring capability has been improved in temporal-spatial domain. The deformation monitoring of active volcanoes in China started late in 1990s, which has been used in the volcano monitoring of Tianchi Changbaishan, Tengchong and Hainan volcanoes. However, the continuous deformation measurement is done only with tilting. The application of new geodesy technologies, such as continuous GNSS, is not enough in these volcano regions.
-
Key words:
- GNSS /
- InSAR /
- Deformation model /
- Deformation monitoring network
-
表 1 大地测量新技术应用于中国活动火山监测情况统计
Table 1. Summary of new geodetic measurement used in active volcano monitoring in China
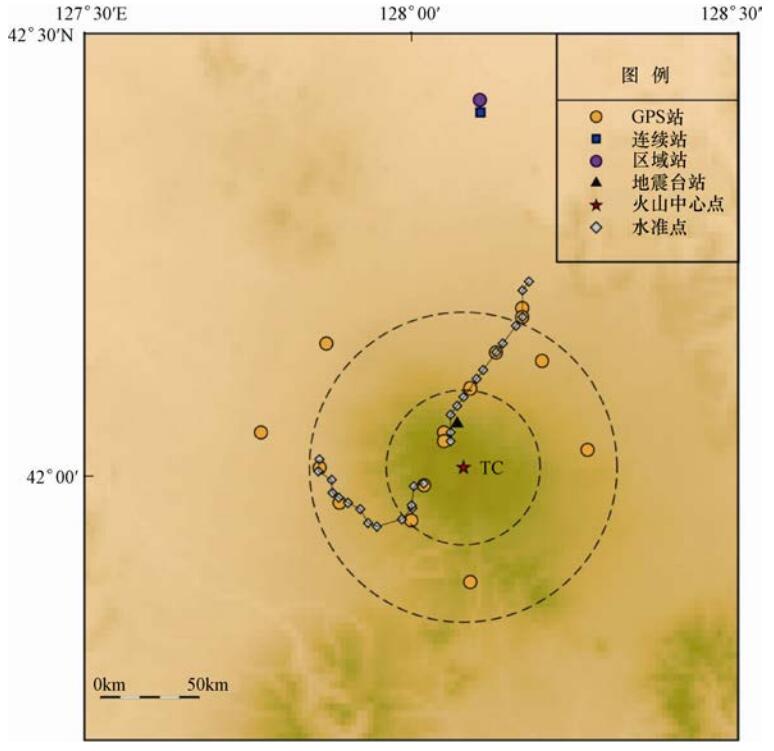
火山 形变观测技术应用 GPS观测成果 InSAR观测成果 模拟深度/km 参考文献 长白山天池 水准(2002年开始、每年) 视线方向:6mm/a(1992—1998)
3mm/a(2007—2010)
视线方向:间白山6—12cm
(1995—1998),隆升最大5mm/a2—60 唐攀攀等,2014
陈国浒等,2008
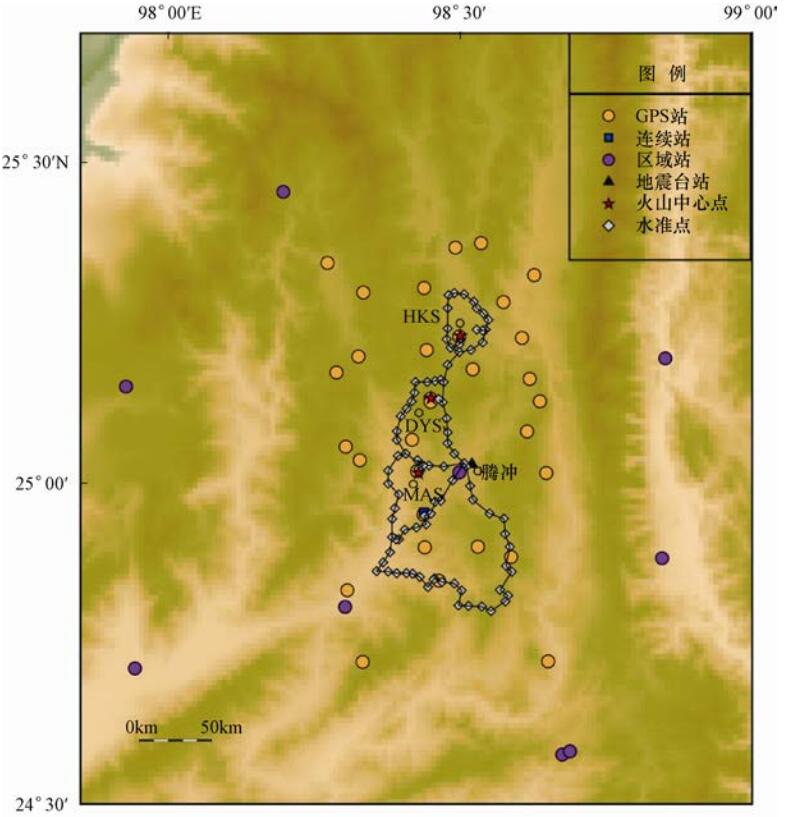
韩宇飞等,2010GPS(2000年开始、每年) 腾冲 水准(1998、1999、2000、2002、2004年) >10mm/a 黑空山:下沉最大12cm
(1995—1997)
打鹰山:隆升最大8cm
(1995—1996),后回落
马鞍山:下沉最大10cm
(1995—1996),后回升季灵运等,2011
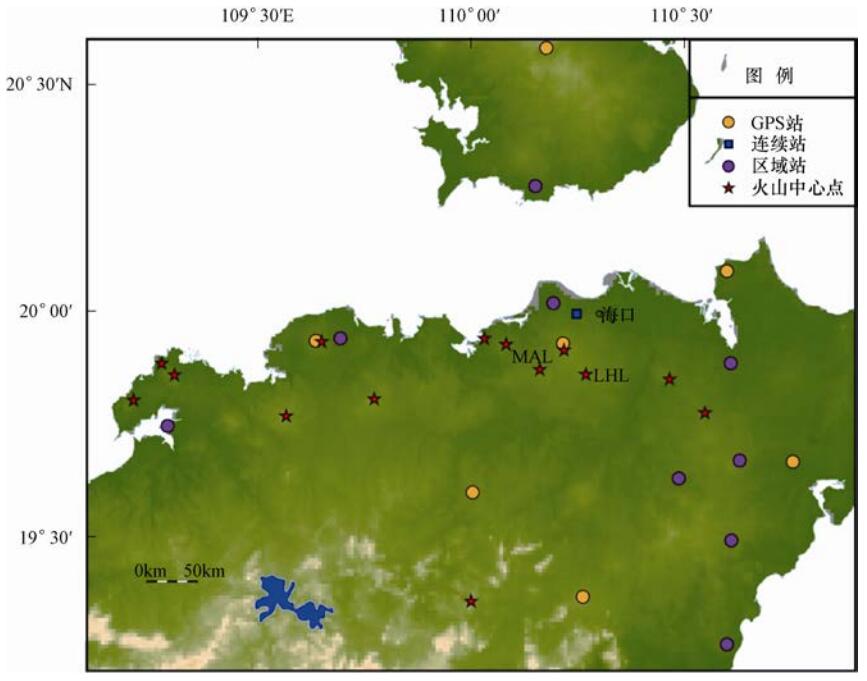
胡亚轩等, 2003, 2007测距仪(1997年) GPS(2002、2003、2004年) 海南 GPS(2008年开始、每年) 4.0—6.7mm/a 垂向相对形变量9mm/a 8—25 Hu等,2016a
Ji等,2015阿什库勒 视线方向:隆升最大约1cm
(2008—2010)许建东等,2014
季灵运等,2013 -
白志达, 徐德斌, 魏海泉等, 2003.琼北马鞍岭地区第四纪火山活动期次划分.地震地质, 25(S1):12-20. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=conference&id=4703962 陈国浒, 单新建, Moon W. M.等, 2008.基于InSAR、GPS形变场的长白山地区火山岩浆囊参数模拟研究.地球物理学报, 51(4):1085-1092. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DQWX200804019.htm 韩宇飞, 宋小刚, 单新建等, 2010. D-InSAR技术在长白山天池火山形变监测中的误差分析与应用.地球物理学报, 53(7):1571-1579. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_dqwlxb201007008 洪汉净, 吴建平, 王庆良等, 2007.中国火山危险性等级与活动性分类.地震地质, 29(3):447-458. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DZDZ200703003.htm 洪汉净, 2013.火山预测与预警.北京:地震出版社, 1-278. 胡久常, 2002.海南有座休眠活火山.防灾博览, (6):43. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/FZBL200206029.htm 胡亚轩, 施行觉, 王庆良等, 2003.腾冲火山区地表垂直形变分析.大地测量与地球动力学, 23(2):37-41. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dkxbydz200302006 胡亚轩, 王庆良, 崔笃信等, 2007.用形变资料分析腾冲火山区岩浆的活动特征.地震研究, 30(2):164-168. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzyj200702011 皇甫岗, 姜朝松, 2000.腾冲火山研究.昆明:云南科技出版社. 季灵运, 王庆良, 崔笃信等, 2011.利用SBAS-DInSAR技术提取腾冲火山区形变时间序列.大地测量与地球动力学, 31(4):149-153, 159. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dkxbydz201104034 季灵运, 许建东, 赵波等, 2013.利用InSAR技术研究新疆阿什库勒火山群现今活动性.地震地质, 35(3):532-541. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Xu_Jiandong/publication/289590683_Present-day_activity_of_Ashikule_volcanic_group_from_InSAR/links/56a6da6808ae860e0253d13b.pdf?origin=publication_detail 李克, 刘俊清, 盘晓东等, 2009. 2000-2007年期间长白山天池火山区地壳变形监测与分析.地震地质, 31(4):639-646. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXLJ201333027.htm 李玉锁, 修济刚, 李继泰等, 1998.火山喷发机制与预报.北京:地震出版社. 刘国明, 孙鸿雁, 郭峰, 2011.长白山火山最新监测信息.岩石学报, 27(10):2905-2911. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/YSXB201110011.htm Scarpa R., Tilling R. I., 1996. 火山监测与减灾. 刘若新等译, 2001. 北京: 地震出版社, 285-303. 唐攀攀, 单新建, 王长林, 2014.基于PSInSAR技术的长白山天池火山形变监测.地震地质, 36(1):177-185. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95728X/201401/49439301.html 王伶俐, 邵德盛, 洪敏, 2015.云南境内陆态网络GNSS观测资料数据处理与初步结果.震灾防御技术, 10(1):141-150. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20150115 许建东, 2006.我国火山灾害的主要类型及火山灾害区划图编制现状探讨.震灾防御技术, 1(3):266-272. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20060312 许建东, 2011.中国活动火山监测进展回顾.矿物岩石地球化学通报, 30(4):390-392. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwysdqhxtb201104006 许建东, 赵波, Sindney H.等, 2014.西昆仑阿什库勒火山群地质特征和活动分期.岩石学报, 30(12):3521-3530. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Xu_Jiandong/publication/278023096_Geological_features_and_eruption_history_of_Ashikule_volcano_clusters_in_western_Kunlun_Mountain/links/557a8a9d08ae75215871875d.pdf?origin=publication_list 张传杰, 李霓, 龚丽文, 2016. 2015年全球火山活动综述.国际地震动态, (11):4-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0235-4975.2016.11.004 Amelung F., Jónsson S., Zebker H., et al., 2000. Widespread uplift and 'trapdoor' faulting on galápagos volcanoes observed with radar interferometry. Nature, 407 (6807):993-996. doi: 10.1038/35039604 Bato M. P., Lagmay A. A., Paguican E. R., 2011. Interferometric SAR persistent scatterer analysis of Mayon volcano, Albay, Philippines. In: American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting. Washington: American Geophysical Union, G23A-0848. Battaglia M., Vasco D. W., 2006. The search for magma reservoirs in Long Valley Caldera:single versus distributed sources. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 269 (1):173-180. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2006.269.01.11 Briole P., Massonnet D., Delacourt C., 1997. Post-eruptive deformation associated with the 1986-87 and 1989 lava flows of etna detected by radar interferometry. Geophysical Research Letters, 24 (1):37-40. doi: 10.1029/96GL03705 Dvorak J. J., 1992. Tracking the movement of Hawaiian volcanoes; Global Positioning System (GPS)measurement. Earthquakes & Volcanoes, 23 (6):255-267. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=713046c690508760406b28d6c99f8ca7&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Dvorak J. J., Dzurisin D., 1997. Volcano geodesy:the search for magma reservoirs and the formation of eruptive vents. Review of Geophysics, 35 (3):343-384. doi: 10.1029/97RG00070 Dzurisin D., 2003. A comprehensive approach to monitoring volcano deformation as a window on the eruption cycle. Reviews of Geophysics, 41 (1):1001. doi: 10.1029/2001RG000107 Fournier T. J., Pritchard M. E., Riddick S. N., 2010. Duration, magnitude, and frequency of subaerial volcano deformation events:new results from Latin America using InSAR and a global synthesis. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 11 (1):Q01003. https://www.deepdyve.com/lp/wiley/duration-magnitude-and-frequency-of-subaerial-volcano-deformation-E7Q7dgQeG0 Harris S. L., 1988. Fire mountains of the west: the cascade and mono lake volcanoes. Missoula: Mountain Press Publishing Company. Hill D. P., 1993. Temperatures at the base of the seismogenic crust beneath Long Valley caldera, California, and the Phlegrean Fields caldera, Italy. In: Gasparini P., Scarpa R., Aki K., Volcanic Seismology. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 432-461. Hooper A., Zebker H., Segall P., 2004. A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers. Geophysical Research Letters, 31 (23):L23611. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=79145d1e618e0a1d609e7886959ca3b0&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Hu Y. X., Hao M., Ji L. Y., et al., 2016a. Three-dimensional crustal movement and the activities of earthquakes, volcanoes and faults in Hainan Island, China. Geodesy and Geodynamics, 7 (4):284-294. doi: 10.1016/j.geog.2016.05.008 Hu Y. X., Cheng L., Wang X., 2016b. Quality analysis of the campaign GPS stations observation in Northeast and North China. Geodesy and Geodynamics, 7 (2):87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.geog.2016.03.008 Ji L. Y., Xu J. D., Wang Q. L., et al., 2013. Episodic deformation at Changbaishan Tianchi volcano, northeast China during 2004 to 2010, observed by persistent scatterer interferometric synthetic aperture radar. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 7 (1):073499. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.7.073499 Ji L. Y., Hu Y. X., Wang Q. L., et al., 2015. Large-scale deformation caused by dyke intrusion beneath eastern Hainan Island, China observed using InSAR. Journal of Geodynamics, 88:52-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jog.2015.04.006 Kiyoo M., 1958. Relations between the eruptions of various volcanoes and the deformations of the ground surfaces around them. Bulletin of the Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo, 36 (2):99-134. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=7da093341b0b321677267858786eeaa8&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Marshall G. A., Langbein J., Stein R. S., et al., 1997. Inflation of Long valley caldera, California, basin and range strain, and possible mono craters dike opening from 1990-94 GPS surveys. Geophysical Research Letters, 24 (9):1003-1006. doi: 10.1029/97GL00885 McTigue D. F., 1987. Elastic stress and deformation near a finite spherical magma body:resolution of the point source paradox. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 92 (B12):12931-12940. doi: 10.1029/JB092iB12p12931 Owen S., Segall P., Lisowski M., et al., 2000a. January 30, 1997 eruptive event on Kilauea volcano, Hawaii, as monitored by continuous GPS. Geophysical Research Letters, 27 (17):2757-2760. doi: 10.1029/1999GL008454 Owen S., Segall P., Lisowski M., et al., 2000b. Rapid deformation of Kilauea Volcano:global positioning system measurements between 1990 and 1996. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 105 (B8):18983-18998. doi: 10.1029/2000JB900109 Parker A. L., Biggs J., Walters R J., et al., 2015. Systematic assessment of atmospheric uncertainties for InSAR data at volcanic arcs using large-scale atmospheric models:application to the cascade volcanoes, United States. Remote Sensing of Environment, 170:102-114. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2015.09.003 Peltier A., Bianchi M., Kaminski E., et al., 2010. PSInSAR as a new tool to monitor pre-eruptive volcano ground deformation:Validation using GPS measurements on Piton de la Fournaise. Geophysical Research Letters, 37 (12):L12301. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=c363096d8930d2430c8c35d96bedfbaa&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Sigmundsson F., Einarsson P., Bilham R., 1992. Magma chamber deflation recorded by the Global Positioning System:The Hekla 1991 eruption. Geophysical Research Letters, 19 (14):1483-1486. doi: 10.1029/92GL01636 Sigurdsson H., Houghton B., McNutt S., et al., 2015. The encyclopedia of volcanoes. 2nd ed. New York:Acadamic Press, 1101-1123. Xu J. D., Liu G. M., Wu J. P., et al., 2012. Recent unrest of Changbaishan volcano, northeast China:A precursor of a future eruption? Geophysical Research Letters, 39 (16):L16305. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2012GeoRL..3916305X Zebker H. A., Amelung F., Jonsson S., 2000. Remote sensing of volcano surface and internal processes using radar interferometry. In: Mouginis-Mark P. J., Crisp J. A., Fink J. H. Remote Sensing of Active Volcanism. Washington DC: Wiley, 179-205. -




 下载:
下载: