The Application of Ultra Shallow Seismic Survey on Wanggezhuang Fault in Qingdao
-
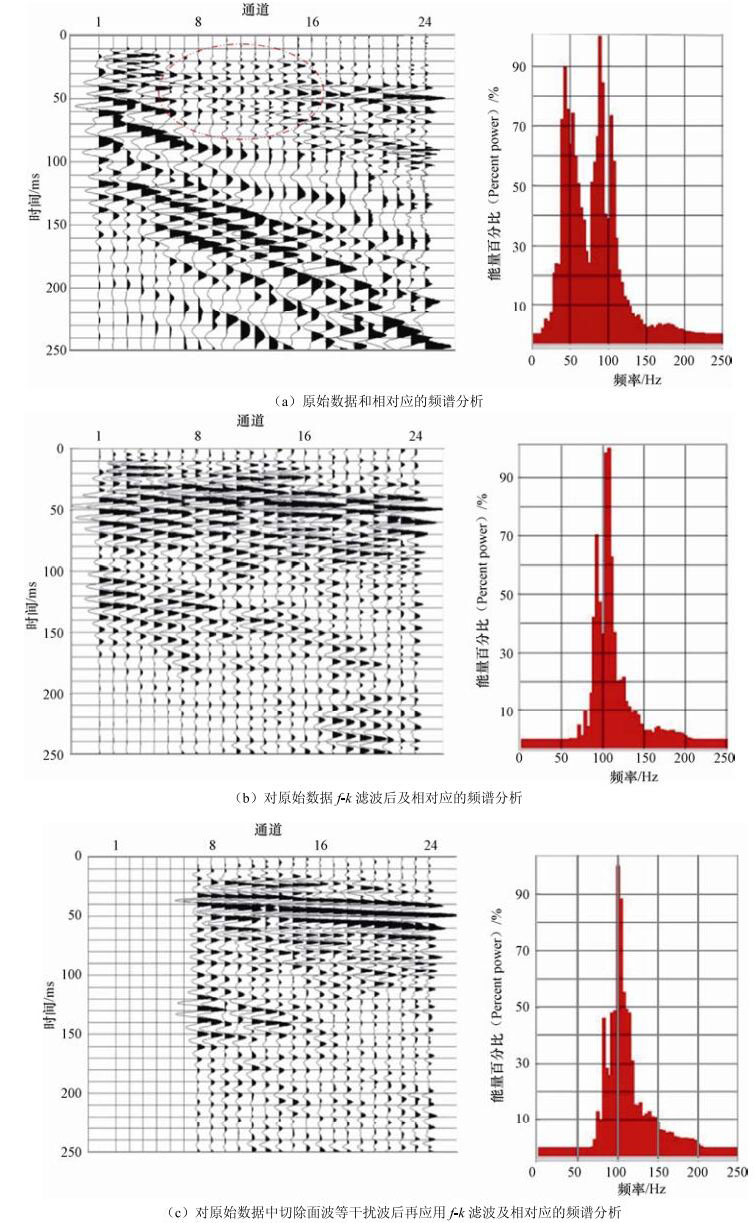
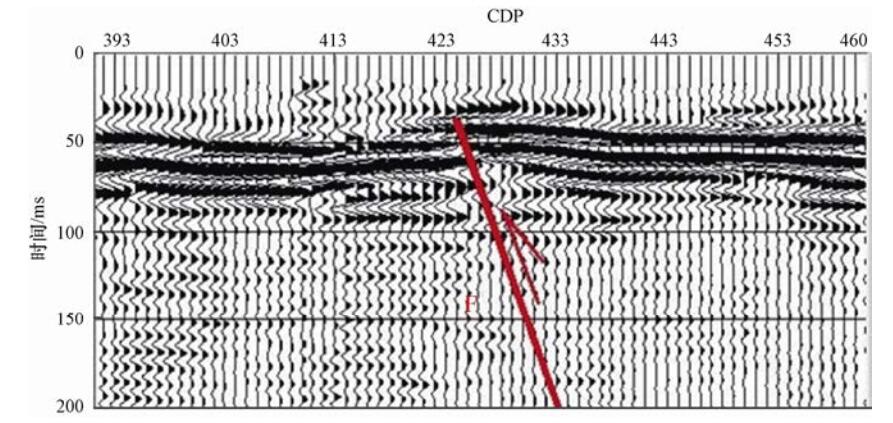
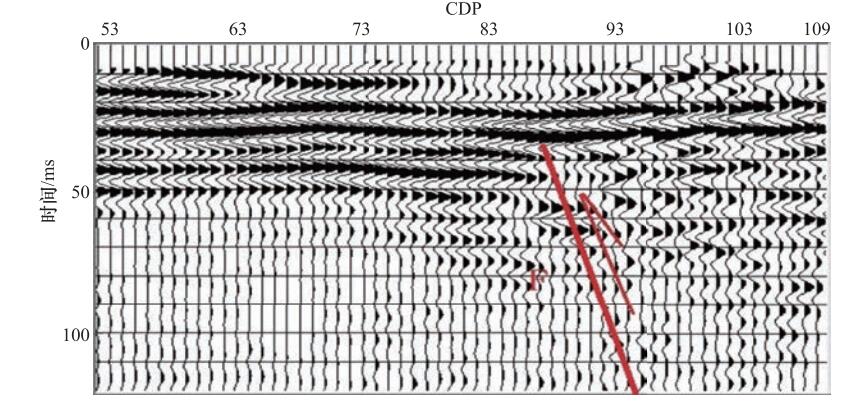
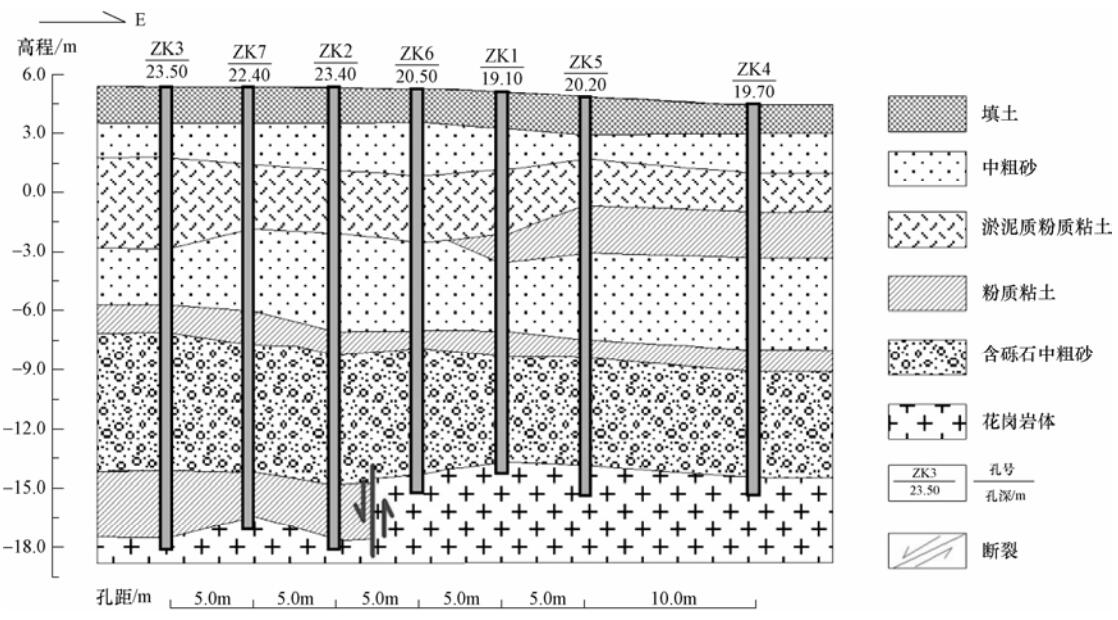
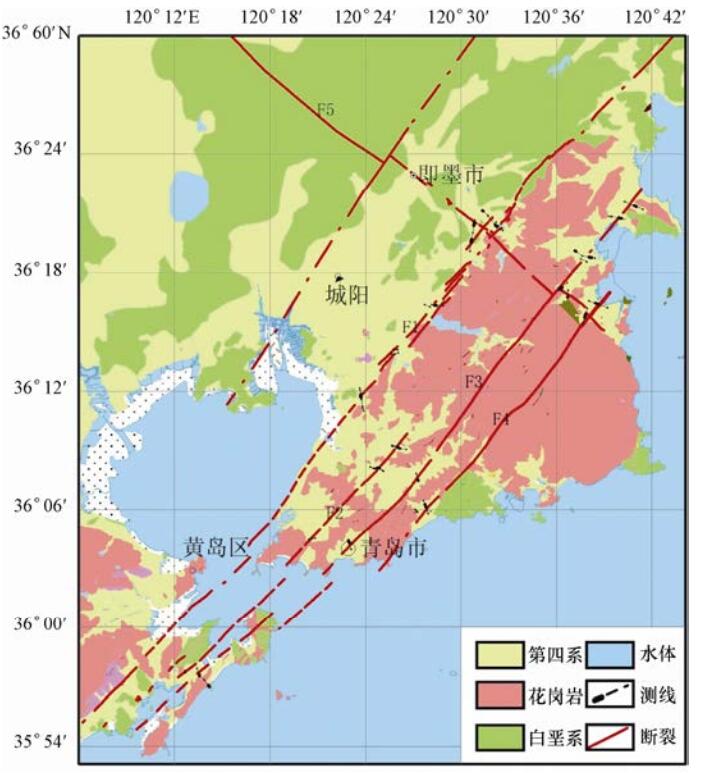
摘要: 目前国内外对目标层埋深仅有几十米(甚至十几米)的超浅层地震勘探经验不多,理论研究也不够深入。本文从城市活断层探测的角度出发,利用地质学、地球物理学及数学等学科中的相关理论和方法,探讨超浅层地震勘探在青岛复杂地质构造背景下取得有效探测结果的前提条件,并对青岛市主要活断层的典型剖面进行重点研究,力求在城市活断层超浅层地震勘探数据采集技术、数据处理等方面有所进展,为青岛及类似地质构造背景的地区开展活动断层超浅层地震探测提供参考。研究表明超浅层地震反射波法可以获取深度仅有十几米的地层反射信号,且大部分反射剖面都可较清楚地揭示出超浅部断层位置和断层特征。Abstract: At present for the target at depth of only tens of meters of ultra-shallow seismic exploration do not have many experiences in practice neither in theoretical research. The depth about decades of meters below the ground surface is the blind area of every kind of deep and shallow seismic exploration, which plays an important role in the research of the location of fault and active structure. Starting from the point of view of detecting urban active faults, we apply related theories and methods of geology and geophysics, probe into the precondition to acquire efficient ultra-shallow seismic results in complicated geological background. Taking the Qingdao area as an example, we study the depth condition of Quaternary deposits, and apply 4-8 stacking folds to satisfy the requirement to get the exploration results with high-resolution and high-SNR. Preliminary results reveal that the selecting proper surveillance layout is one of the keys to acquire authentic exploration results in ultra-shallow P-wave reflection exploration. Our results also show that ultra-shallow seismic reflection method in detecting faults in the Qingdao area has good application prospects.
-
Key words:
- Ultra shallow seismic survey /
- Observation system /
- Wang G Z Fault /
- f-k filtering
-
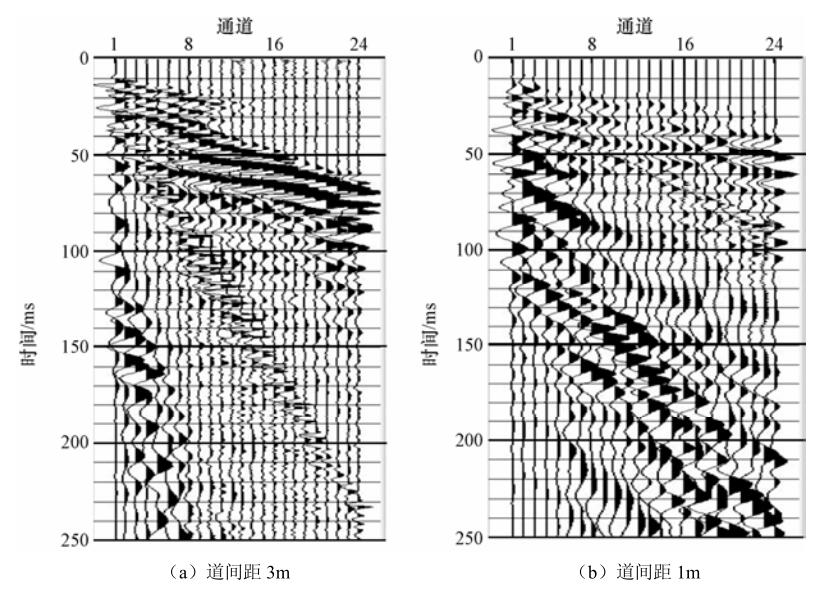
表 1 观测系统参数和地震采集参数表
Table 1. Survey parameters and seismic data acquisition details
剖面编号 道间距/m 偏移距/m 接收道数 覆盖次数 激发震源 检波器固有频率/Hz 采样间隔/ms 记录长度/ms TEST-a 3 6 24 6 人工夯击 60 0.25 256 TEST-b 1 7 24 12 人工锤击 100 0.25 256 -
陈颙, 陈龙生, 于晟, 2003.城市地球物理学发展展望.大地测量与地球动力学, 23(4):1-4. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/f997f82a915f804d2b16c15d.html 邓起东, 2002.城市活动断裂探测和地震危险性评价问题.地震地质, 24(4):601-605. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DZDZ200204015.htm 邓起东, 徐锡伟, 张先康等, 2003.城市活动断裂探测的方法和技术.地学前缘, 10(1):93-104. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200301019.htm 段生全, 贺振华, 黄德济, 2005.HHT方法及其在地震信号处理中的应用.成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 32(4):396-400. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG200504013.htm 方盛明, 张先康, 刘保金等, 2002.探测大城市活断层的地球物理方法.地震地质, 24(4):606-613. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200204016.htm 何正勤, 陈宇坤, 叶太兰等, 2007.浅层地震勘探在沿海地区隐伏断层探测中的应用.地震地质, 29(2):363-372. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzdz200702014 何正勤, 潘华, 胡刚等, 2010.核电厂址隐伏断裂探测中的地震勘探方法研究.地球物理学报, 53(2):326-334. http://manu39.magtech.com.cn/Geophy/CN/abstract/abstract1271.shtml 李大虎, 何强, 邵昌盛等, 2010.综合地球物理勘探在青川县城区活动断层探测中的应用.成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 37(6):666-672. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cdlgxyxb201006012 李万伦, 刘素芳, 田黔宁等, 2018. 城市地球物理学综述. 地球物理学进展. (2018-01-25)http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2982.P.20180125.1015.018.html 刘保金, 张先康, 方盛明等, 2002.城市活断层探测的高分辨率浅层地震数据采集技术.地震地质, 24(4):524-532. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200204006.htm 潘纪顺, 刘保金, 朱金芳等, 2002.城市活断层高分辨率地震勘探震源对比试验研究.地震地质, 24(4):533-541. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95728X/200204/7297242.html 许汉刚, 范小平, 冉勇康等, 2016.郯庐断裂带宿迁段F5断裂浅层地震勘探新证据.地震地质, 38(1):31-43. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzdz201601003 徐明才, 高景华, 刘建勋等, 2005.应用于城市活断层调查的地震方法技术.中国地震, 21(1):17-23. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdz200501002 杨歧焱, 彭远黔, 尼玛等, 2015.日喀则城市活断层地球物理勘探方法和成果.地球物理学报, 58(6):2137-2147. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150627 杨歧焱, 彭远黔, 周月玲等, 2016.综合地质-地球物理方法在山间盆地断裂探测中的应用——以张家口断裂为例.地球物理学进展, 31(6):2451-2457. doi: 10.6038/pg20160613 杨晓平, 郑荣章, 张兰凤等, 2007.浅层地震勘探资料地质解释过程中值得重视的问题.地震地质, 29(2):282-293. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/fad75423192e45361066f5f7-2.html 朱金芳, 徐锡伟, 张先康等, 2005.福州盆地及邻区地壳精细结构的深地震反射与高分辨率折射及宽角反射/折射联合探测研究.中国科学D辑地球科学, 35(8):738-749. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_zgkx-cd200508006 Williams R. A., Odum J. K., Pratt T. L., et al., 1995. Seismic surveys assess earthquake Hazard in the New Madrid area. The Leading Edge, 14(1):30-34. doi: 10.1190/1.1437060 -



 下载:
下载: