Characteristics of Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Geomagnetic Field in Chinese Mainland Based on CM4 Model
-
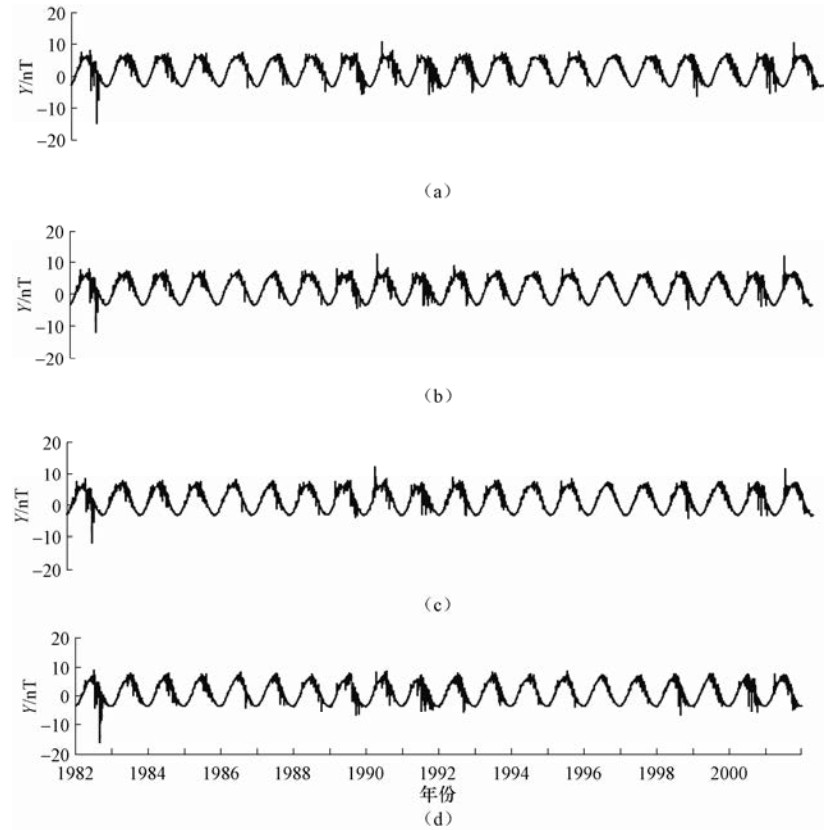
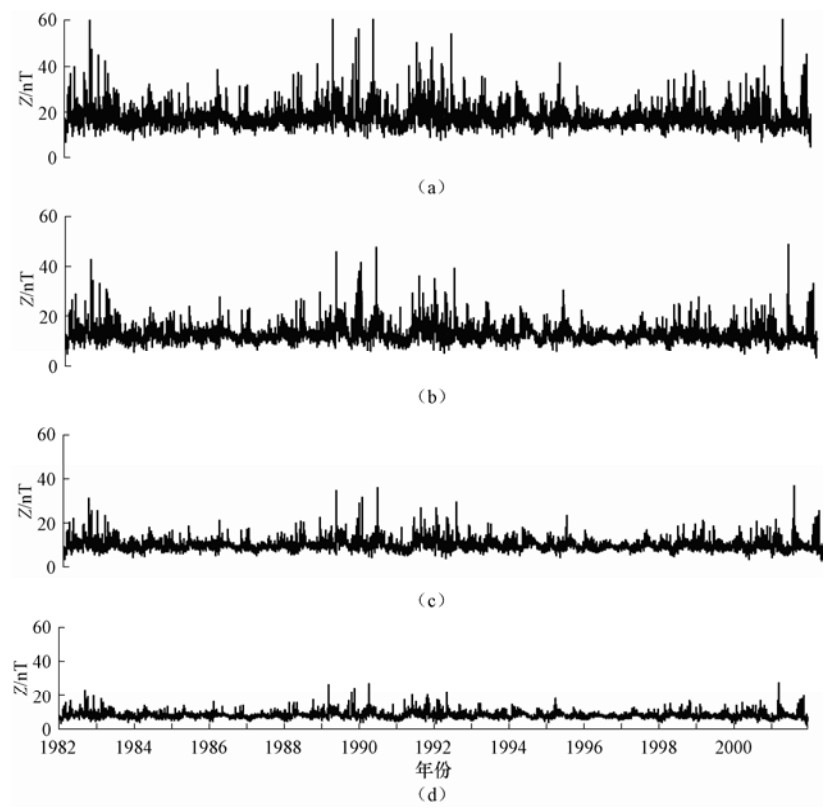
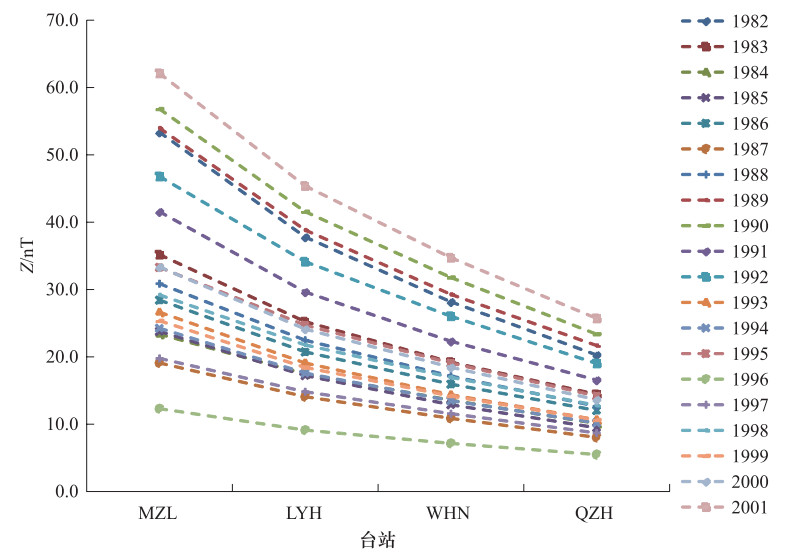
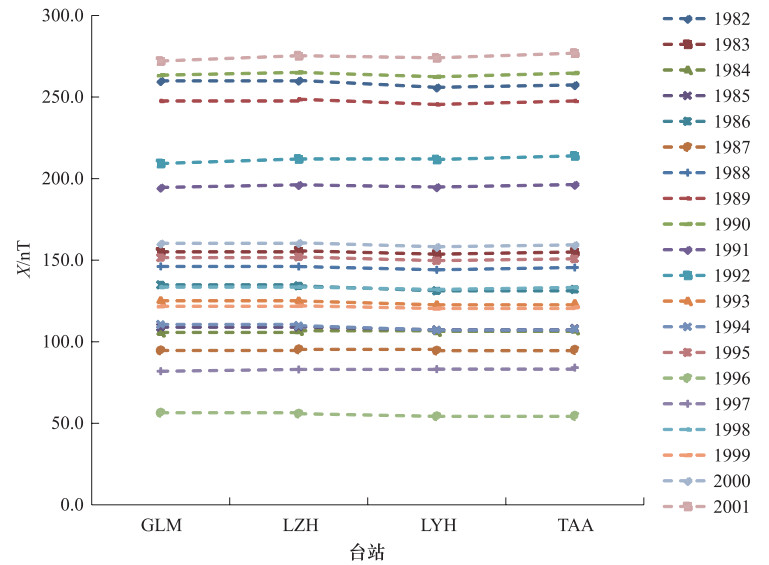
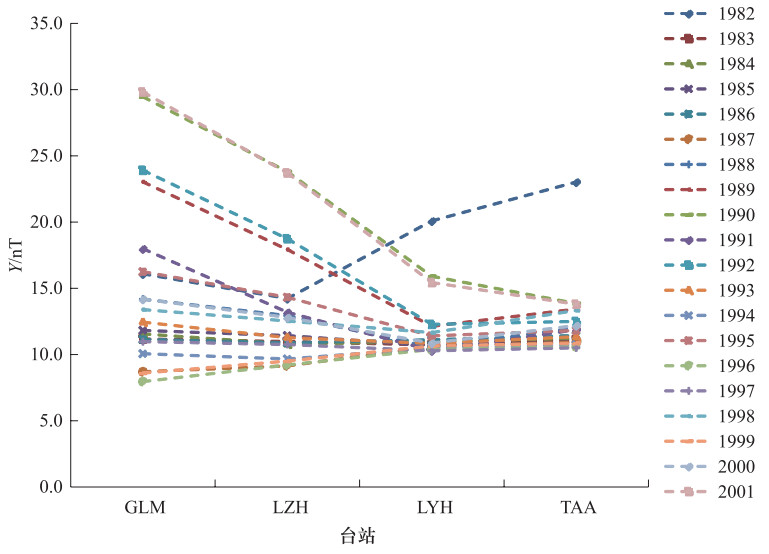
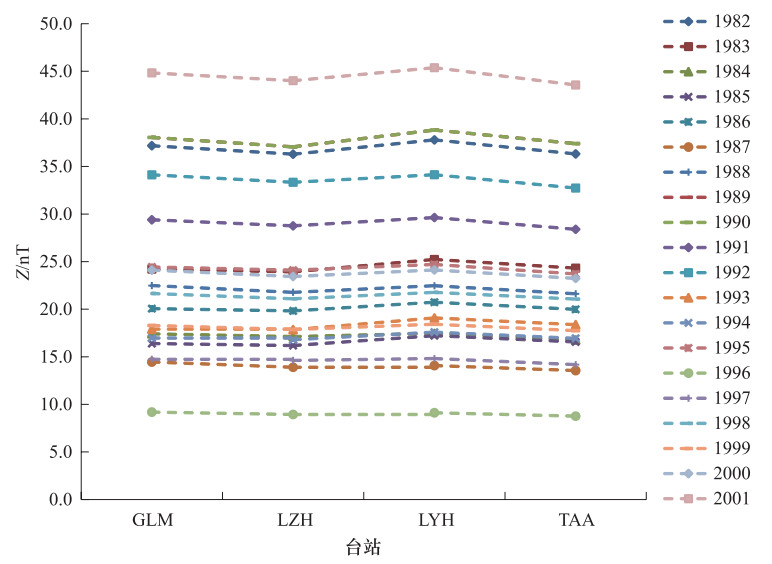
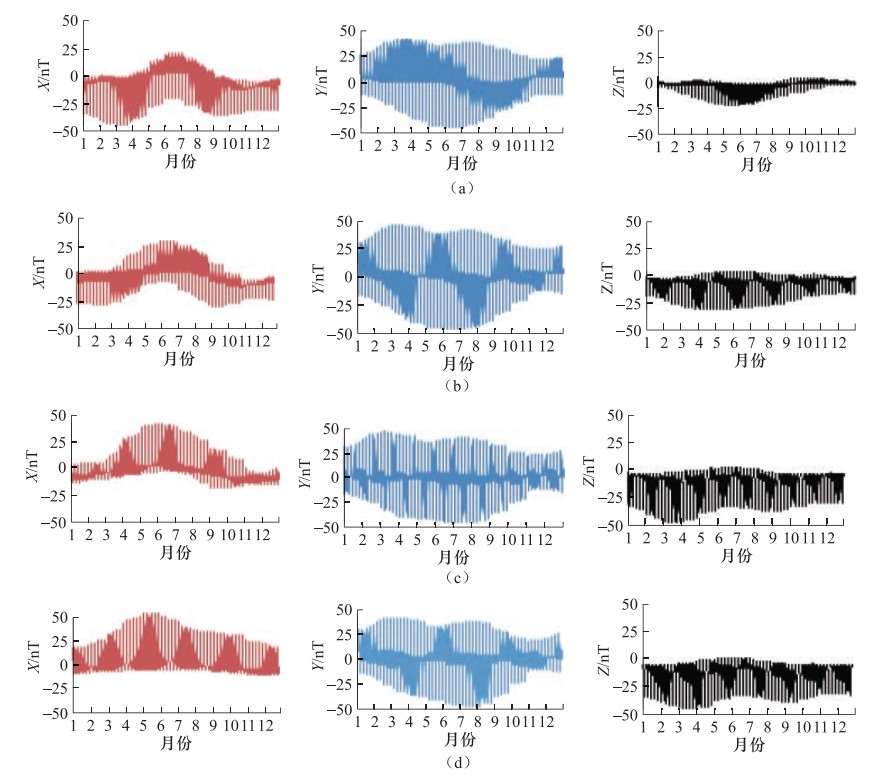
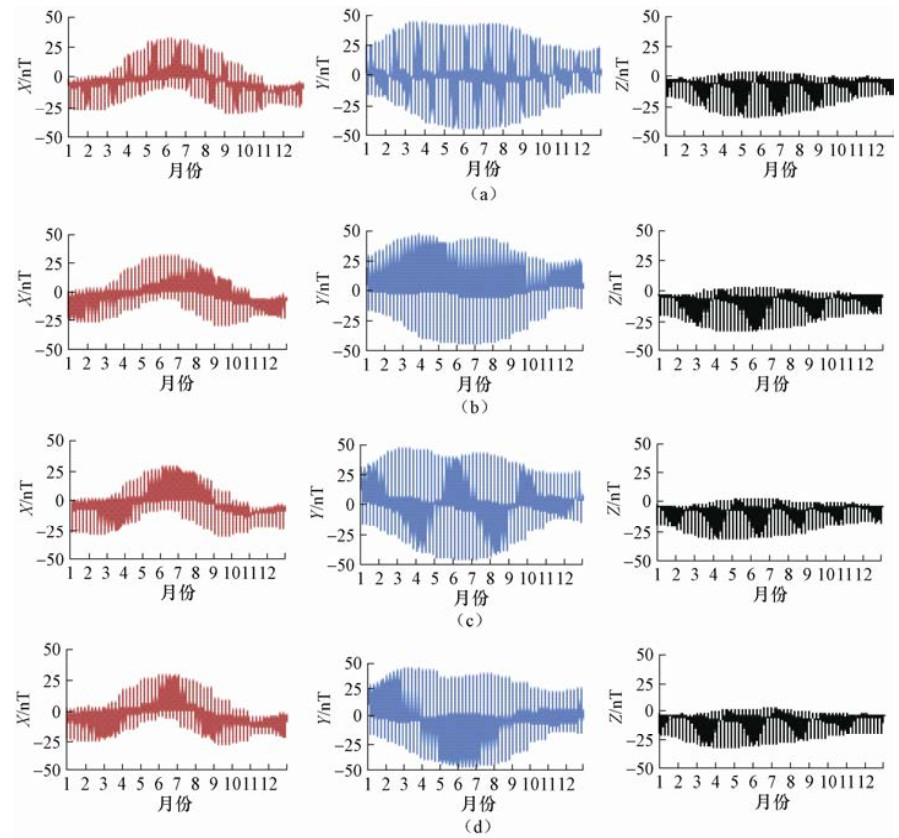
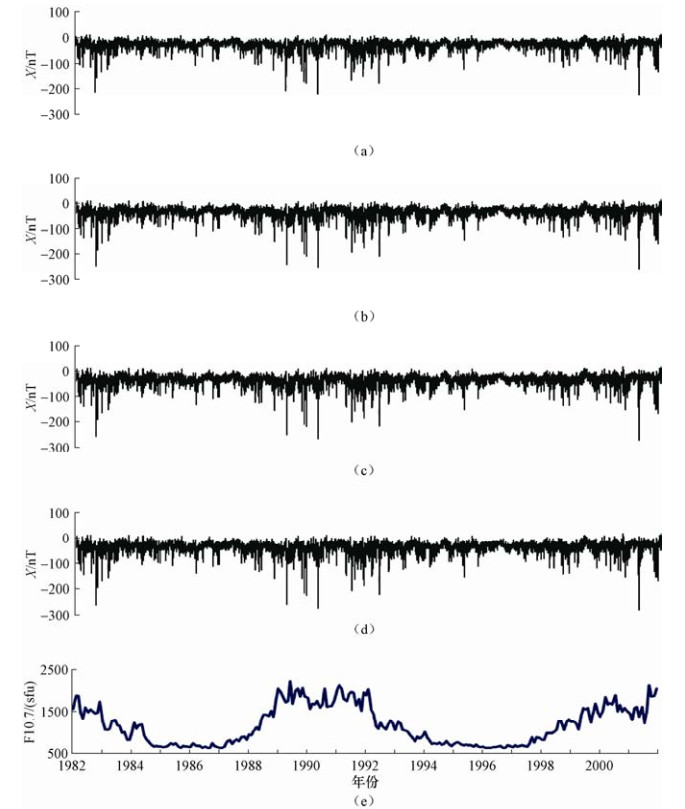
摘要: 本文利用第四代地磁场综合模型(Comprehensive Model 4,CM4),计算了1982-2001年中国大陆地区同一经度链和同一纬度链上地磁台站的磁层源磁场及其感应场、电离层源磁场及其感应场的地磁北向分量X、东向分量Y、垂直分量Z的模型值,分析了各场源磁场随时间和空间的变化特征。结果表明:在时间上,经度链和纬度链台站的磁层源磁场及其感应场均呈现出11年和27天周期性变化。电离层源磁场及其感应场具有明显的季节变化,不同年份相同季节变化形态一致但幅度不同。在空间分布上,经度链和纬度链台站磁层源磁场及其感应场的年变化幅度呈现出不同变化特征,电离层源磁场及其感应场在经度链上变化特征不同,而纬度链台站的数值基本一致。日变化分析显示,磁静日和磁扰日期间,模型数据与台站实测数据变化一致性较好,相关性较高。Abstract: In this paper, based on the comprehensive model4 (CM4), we calculated the latitude and longitude chain stations magnetosphere and its induction magnetic field, ionosphere and its induction magnetic field of the X, Y, Z component from 1982 to 2001 in chinese mainland and also analyzed the change characteristics of the magnetic field with time and space. The results show that the magnetosphere and its induction magnetic field of the longitude chain and latitude chain show periodic variation in 11 years and 27 days. The ionosphere and its induction magnetic field have shown seasonal variation, morphological changes in the same season in which the amplitude is different in the spatial distribution. The annual variation range of the magnetosphere and its induction magnetic field in the longitude chain and latitude chain showed different characteristics. The ionosphere field and its induction magnetic field vary spatially in the longitude chain, but they are about the same of latitude chain station. Diurnal variation analysis showed that the model data is in good consistency with the measured data of the station on the magnetically quiet and disturbed date, and they are highly correlated.
-
Key words:
- CM4 /
- Magnetosphere field /
- Ionosphere field /
- Observatory data /
- Induction field /
- The mean time value /
- Correlation coefficient
-
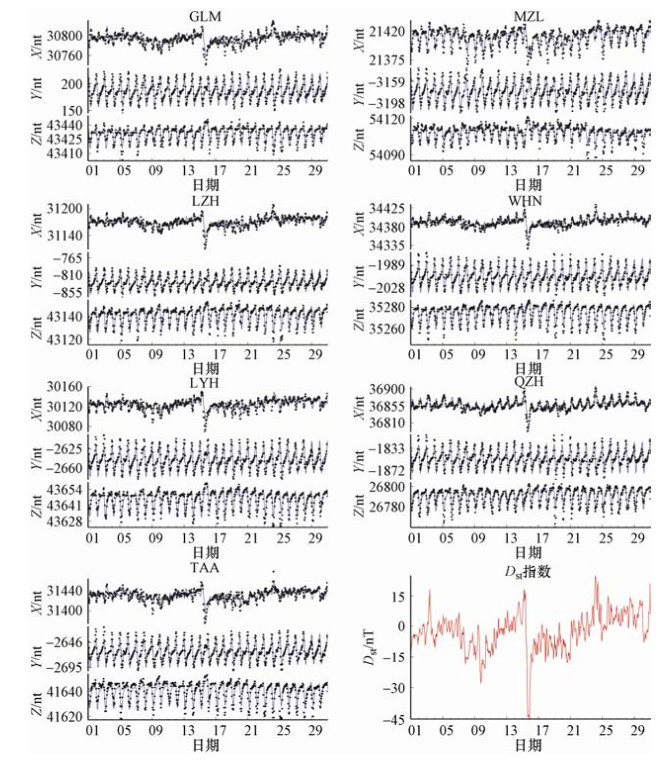
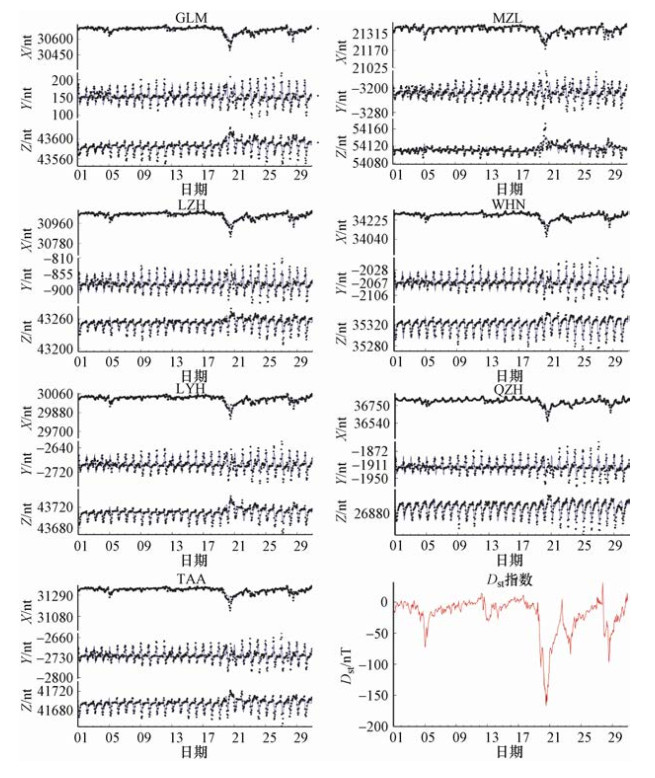
表 1 台站分布
Table 1. Location of the stations
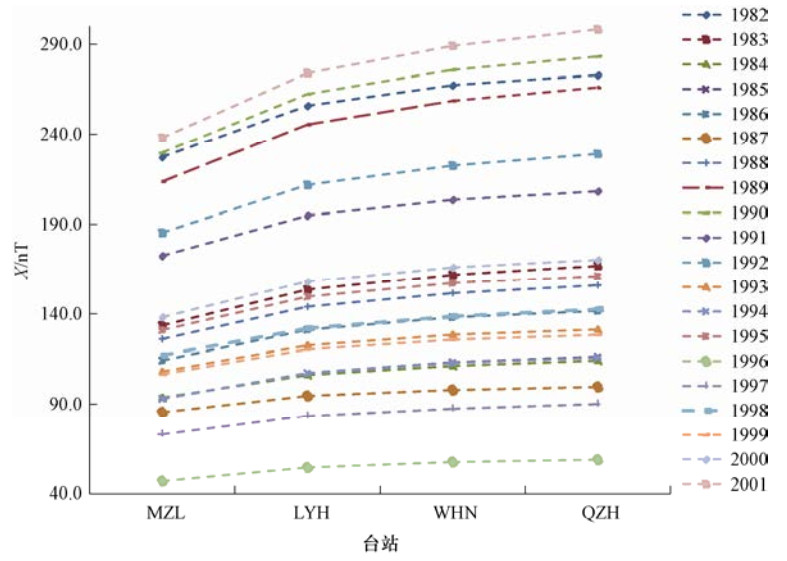
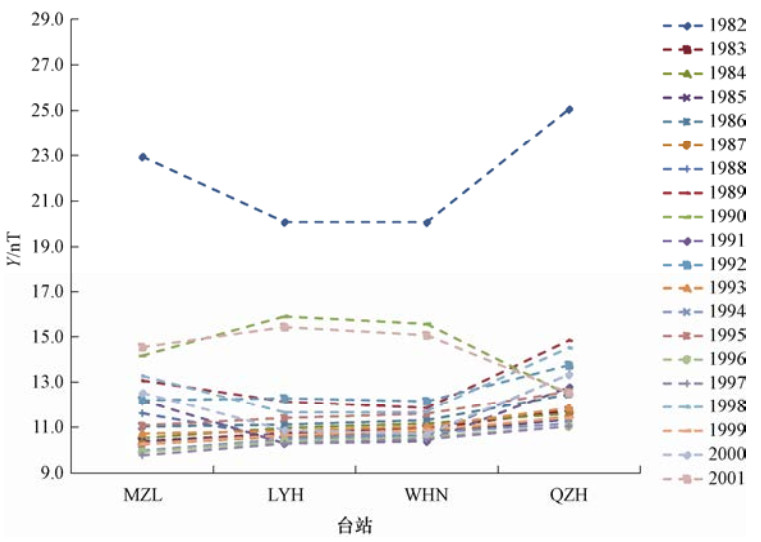
经度链 纬度链 台站 代码 高度/m 台站 代码 高度/m 满洲里 MZL 682 格尔木 GLM 2802 红山 LYH 20 兰州 LZH 1560 武汉 WHN 45 红山 LYH 20 泉州 QZH 41 泰安 TAA 249 表 2 经度链台站X分量年变化幅度
Table 2. Annual variation range of X component in longitude chain
YEAR MZL LYH WHN QZH YEAR MZL LYH WHN QZH 1982 227.2 256.0 267.4 272.9 1992 185.4 211.7 222.4 228.9 1983 133.6 153.7 162.0 167.0 1993 108.1 122.6 128.5 131.4 1984 93.6 106.1 111.2 114.2 1994 93.1 107.2 112.9 115.8 1985 92.9 107.3 113.2 116.3 1995 131.1 149.7 157.4 161.3 1986 114.2 131.2 138.2 141.7 1996 46.7 54.3 57.3 58.6 1987 85.3 94.5 97.9 99.6 1997 72.8 83.2 87.4 90.0 1988 126.1 144.1 151.7 156.1 1998 117.1 132.0 138.7 142.6 1989 213.6 245.5 258.7 266.1 1999 106.6 120.4 125.8 128.5 1990 229.6 262.4 275.9 283.3 2000 138.3 158.2 166.2 170.4 1991 172.7 194.8 203.4 208.2 2001 238.1 274.0 289.2 298.3 表 3 实测值与模型值差值的标准差
Table 3. The standard deviation of the difference between the measured and model values
分量 MZL LYH WHN QZH GLM LZH TAA X 11.2 10.6 8.1 12.8 5.6 11.3 32.1 Y 4.4 4.8 2.0 12.6 6.8 10.7 4.7 Z 21.4 33.9 5.9 34.8 8.9 21.1 24.7 -
白春华, 徐文耀, 康国发, 2008.地球主磁场模型.地球物理学进展, 23(4):1045-1057. http://manu39.magtech.com.cn/Geoprog/CN/abstract/abstract1748.shtml 丁鉴海, 索玉成, 余素荣, 2005.地磁场与电离层异常现象及其与地震的关系.空间科学学报, 25(6):536-542. doi: 10.11728/cjss2005.06.536 冯彦, 安振昌, 孙涵等, 2011.基于第四代地磁场综合模型(CM4)以改善模型边界效应的研究.地球物理学进展, 26(3):850-857. http://manu39.magtech.com.cn/Geophy/CN/abstract/abstract3446.shtml 李细顺, 高登平, 李琪等, 2015.CM4模型数据与台站实测数据的对比研究.震灾防御技术, 10(2):418-425. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20150223 李琪, 杨星, 蔡绍平, 2015.极化方法应用于地磁台阵的震例分析.震灾防御技术, 10(2):412-417. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20150222 王亶文, 2003.国际地磁参考场在中国大陆地区的误差分析.地球物理学报, 46(2):171-174. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94718X/200302/7519358.html 徐文耀, 2002.地球主磁场的NOC模型.中国科学(D辑), 32(7):576-587. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.2002.07.006 徐文耀, 2009.地球电磁现象物理学.合肥:中国科学技术大学出版社, 18-29. 徐文耀, 2011.太阳风-磁层-电离层耦合过程中的能量收支.空间科学学报, 31(1):1-14. doi: 10.11728/cjss2011.01.001 杨云存, 高国明, 2014.1900-2010年地磁场水平分量梯度的全球变化.震灾防御技术, 9(S):557-571. http://zzfy.eq-j.cn/zzfyjs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=2014s101&journal_id=zzfyjs 姚丽, 刘振兴, 左平兵等, 2010.行星际激波对地球磁层的压缩效应分析.空间科学学报, 30(2):113-120. doi: 10.11728/cjss2010.02.113 张素琴, 杨冬梅, 李琪等, 2008.中国部分地磁台站年均值与IGRF模型一致性分析.地震地磁观测与研究, 29(2):42-49. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/96509X/200802/27140315.html Alldredge L. R., 1987. On regional magnetic charts. Journal of Geomagnetism and Geoelectricity, 39:723-738. doi: 10.5636/jgg.39.723 Haines G. V., 1985. Spherical cap harmonic analysis. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 90(B3):2583-2591. doi: 10.1029/JB090iB03p02583 Hemant K., Maus S., 2005. Geological modeling of the new CHAMP magnetic anomaly maps using a geographical information system technique. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 110(B12):B12103. doi: 10.1029/2005JB003837 Hemant K., Thébault E., Mandea M., et al., 2007. Magnetic anomaly map of the world:merging satellite, airborne, marine and ground-based magnetic data sets. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 260(1-2):56-71. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2007.05.040 Langel R. A., Sabaka T. J., Baldwin R. T., et al., 1996. The near-earth magnetic field from magnetospheric and quiet-day ionospheric sources and how it is modeled. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 98(3-4):235-267. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9201(96)03190-1 Lesur V., Wardinski I., Rother M., et al., 2008. GRIMM:the GFZ reference internal magnetic model based on vector satellite and observatory data. Geophysical Journal International, 173(2):382-394. doi: 10.1111/gji.2008.173.issue-2 Sabaka T. J., Olsen N., Langel R. A., 2002. A comprehensive model of the quiet-time, near-Earth magnetic field:phase 3. Geophysical Journal International, 151(1):32-68. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246X.2002.01774.x Sabaka T. J., Olsen N., Purucker M. E., 2004. Extending comprehensive models of the Earth's magnetic field with ørsted and CHAMP data. Geophysical Journal International, 159(2):521-547. doi: 10.1111/gji.2004.159.issue-2 Wardinski I., Holme R., 2006. A time-dependent model of the earth's magnetic field and its secular variation for the period 1980-2000. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 111(B12):B12101. doi: 10.1029/2006JB004401/full -



 下载:
下载: