Preliminary Study on Geometry Structure and Activity Features of Luo' erling-Tudiling Fault in Late Quaternary
-
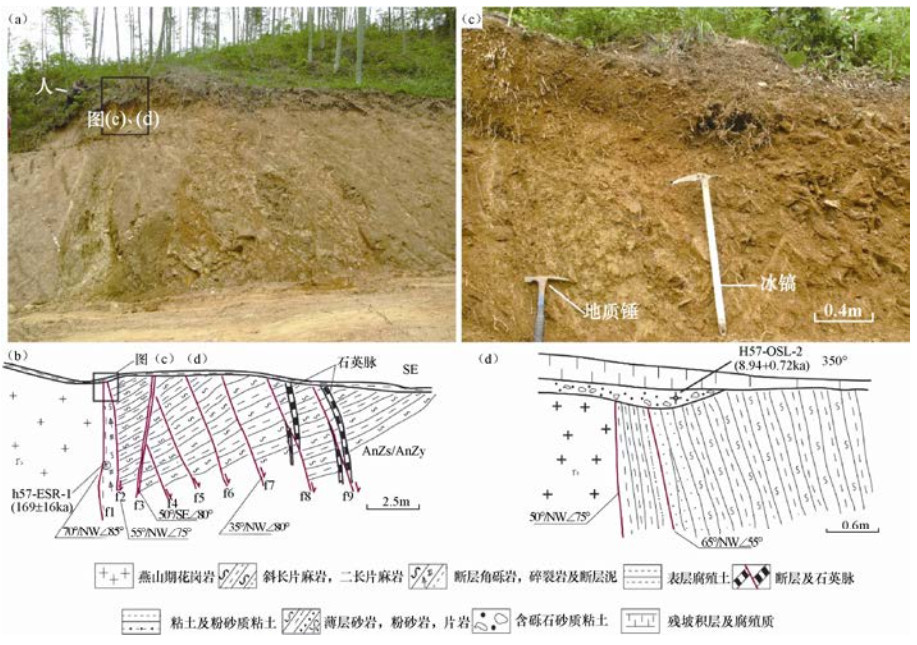
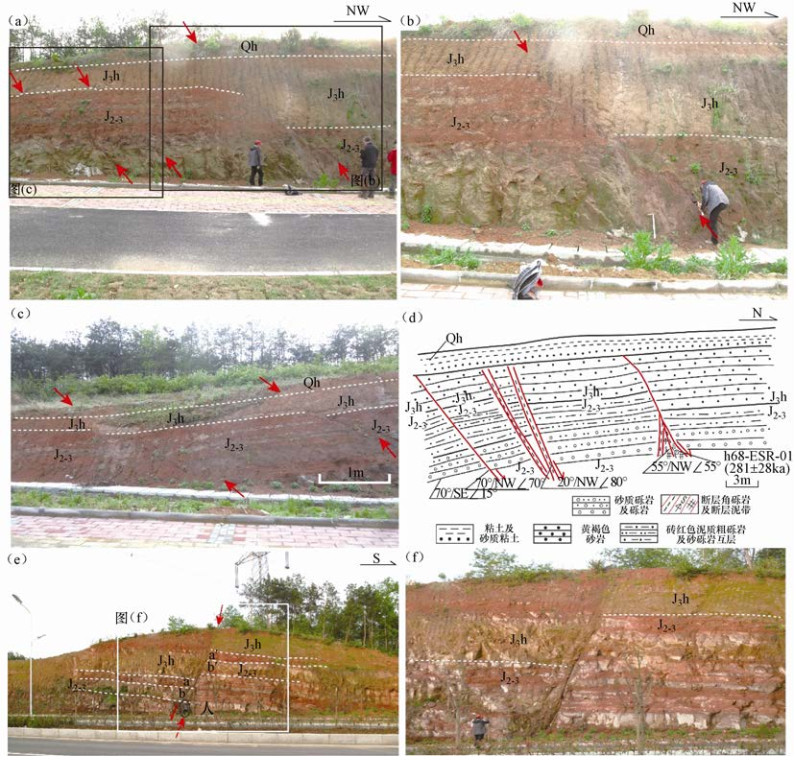
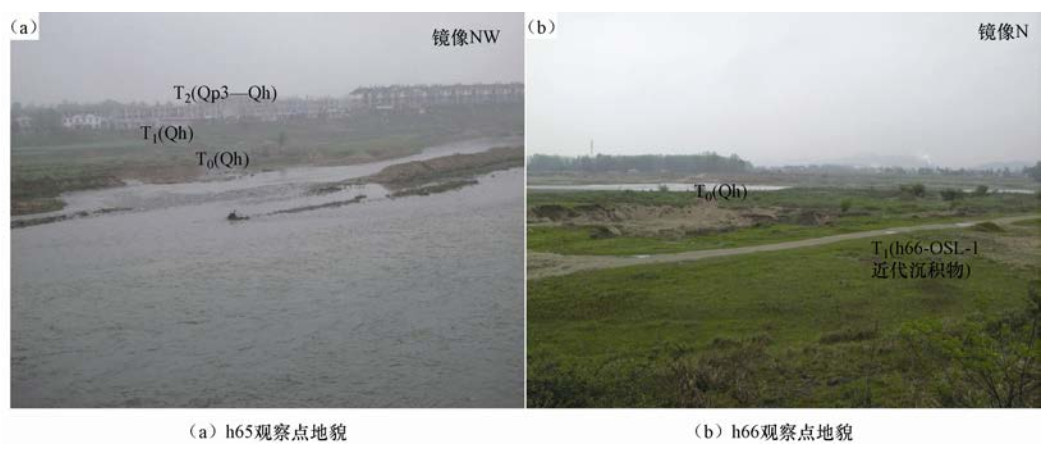
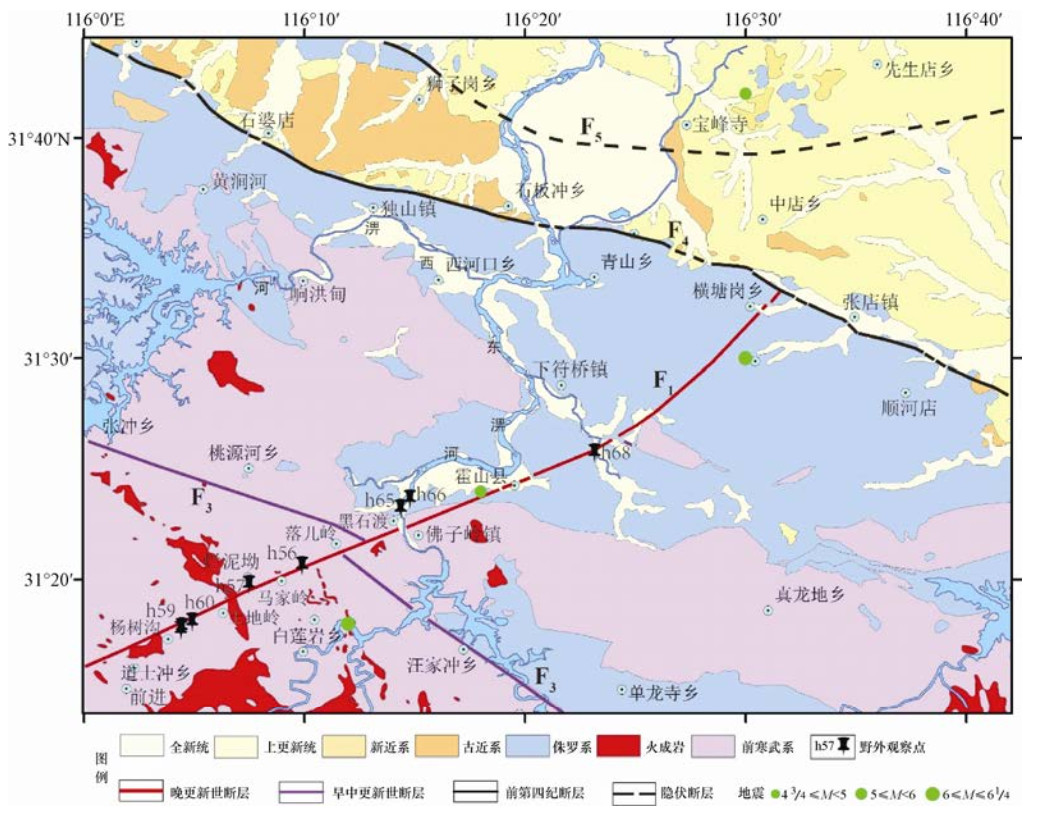
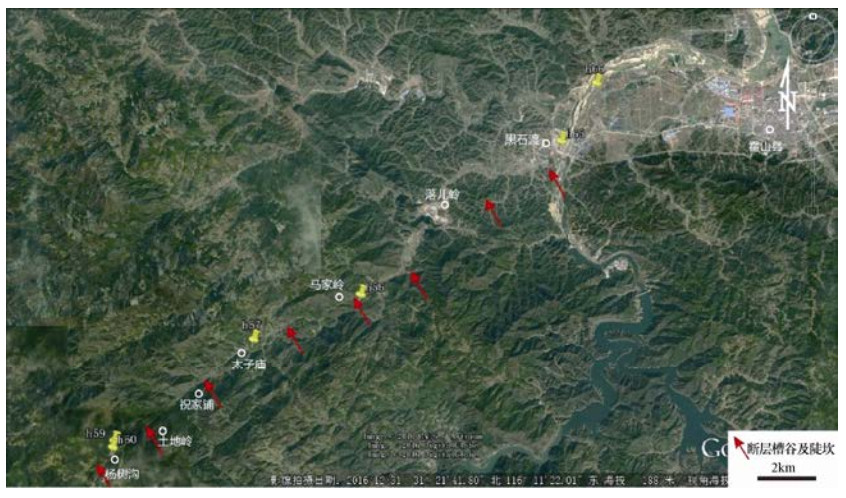
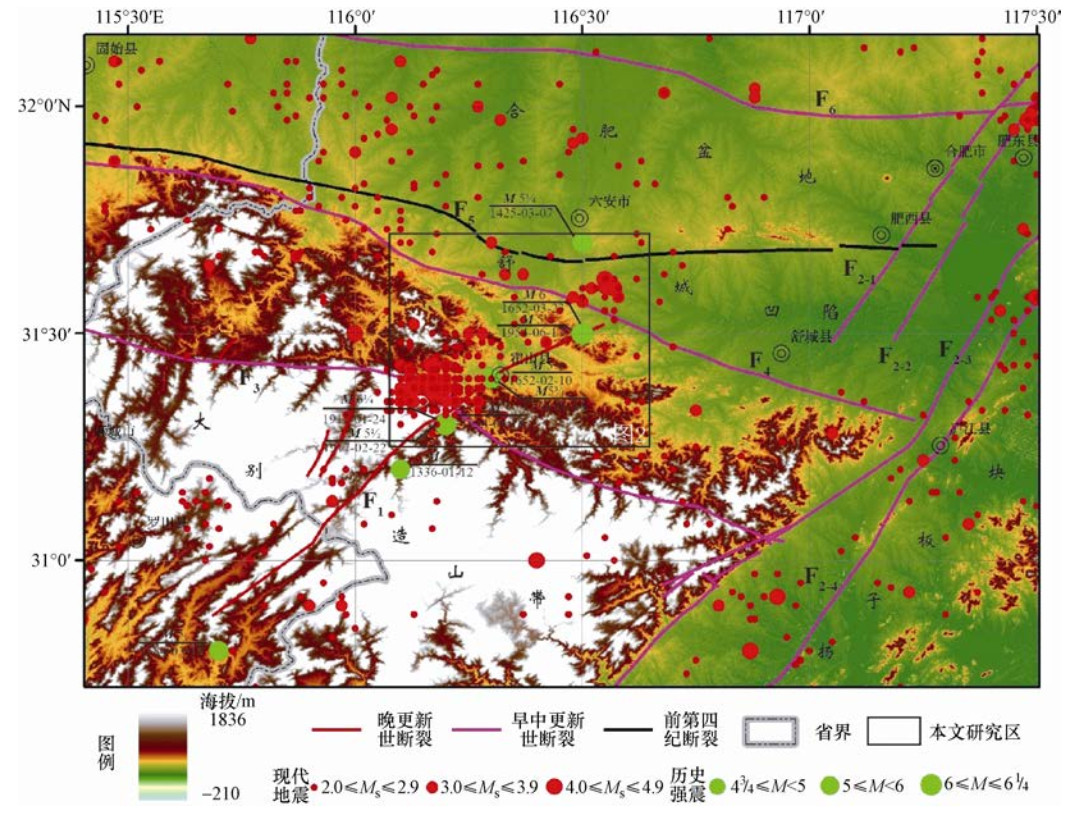
摘要: 落儿岭-土地岭断裂是东大别地区重要的发震构造,然而限于自然地理条件等因素,前人对其的研究并不充分。本文以发生多次中强地震的落儿岭-土地岭断裂为研究对象,在高精度卫星影像解译的基础上,通过详细的野外地质地貌调查,尤其是对典型断层剖面进行分析,研究落儿岭-土地岭断裂的断错地质地貌特征、几何结构及活动特征。通过野外调查并结合其他资料分析认为落儿岭-土地岭断裂为发育于大别造山带内部的一条走向NE、向NW陡倾的断裂带。依据地质地貌特征及地震活动性,断裂可以划分为杨树沟-黑石渡段和黑石渡-横塘岗乡段两个几何段落。断裂最新活动时代为中更新世晚期-晚更新世早期,断裂最新活动继承了中生代以来的运动方式,以兼具右旋走滑的拉张正断为主。Abstract: Luo' erling-Tudiling fault is one of the most important seismogenic structures in east Dabie region. However, there has been no sufficient research on this fault due to its geographical location and natural conditions. Based on interpretation of high-resolution satellite images and detailed field investigation, we take Luo' erling-Tudiling fault as our research object and conduct a systematical study on its geological and geomorphic features, geometry structure and activity features. By field survey and analysis of other related data, we conclude that Luo' erling-Tudingling fault was developed within the Dabie Orogen, stretching northeastward with a deep dip angle to the northwest. According to geological and geomorphic characteristics and seismic activity, this fault is mainly composed two segments, the southern one of which starts from Yangshugou and extends to Heishidu while the northern one stretches from Heishidu to Hengtanggan Town. This study confirmed that Luo' erling-Tudingling fault had experienced multiple extensional normal faulting during middle Mesozoic. Dominated by normal faulting with a certain amount of dextral strike-slip component, its latest activity occurred in early period of late Pleistocene.
-
Key words:
- Luo' erling-Tudingling fault /
- Typical profile /
- Geometry structure /
- Kinematic features /
- Faulting era
-
-
安徽省地震局. 1990.安徽地震目录(公元281-1985年).北京:中国展望出版社. 安徽省地质局. 1974. 区域地质调查报告-六安幅岳西幅. 安徽省地质矿产局. 1987.中华人民共和国地质矿产部:地质专报-区域地质第5号:安徽省区域地质志.北京:地质出版社. 甘家思, 刘锁旺. 1981.鄂豫皖毗邻区的某些地震地质特征.地壳形变与地震, (4):56-64. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dkxb198104008&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 刘东旺, 倪红玉, 沈小七等. 2015.安徽北淮阳构造变形带特征与应力状态研究.地震地磁观测与研究, 36(3):1-8. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZGJ201503002.htm 刘泽民, 黄显良, 倪红玉等. 2015.2014年4月20日霍山MS 4.3地震发震构造研究.地震学报, 37(3):402-410. http://edu.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/Detail/gjdzdt201509113 王清晨, 从柏林. 1998.大别山超高压变质带的大地构造框架.岩石学报, 14(4):481-492. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19980458&journal_id=ysxb 吴利仁. 1998.东秦岭-大别山碰撞造山带的地质演化.北京:科学出版社. 徐树桐, 江来利, 刘贻灿等. 1992.大别山区(安徽部分)的构造格局和演化过程.地质学报, 66(1):1-14. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4874684 徐树桐, 江来利. 1994.大别山的构造格局和演化.北京:科学出版社. 徐锡伟. 2006.活动断层、地震灾害与减灾对策问题.震灾防御技术, 1(1):7-14. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20060102 许志琴, 卢一伦, 汤耀庆等. 1986.东秦岭造山带的变形特征及构造演化.地质学报, 60(3):237-247. http://www.geojournals.cn/dzxb/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19860321 姚大全, 汤有标, 刘加灿等. 1999.大别山东北部基岩区断裂活动习性的综合研究.地震地质, 21(1):63-68. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_dzdz199901007.aspx 姚大全, 刘加灿, 李杰等. 2003.六安-霍山地震危险区地震活动和地震构造.地震地质, 25(2):211-219. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=8008198 张杰, 沈小七, 王行舟等. 2004.安徽历史地震等震线长轴方位分布及地震地质意义.中国地震, 20(2):152-160. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=10019617 Chemenda A. I., Mattauer M., Bokun A. N.. 1996. Continental subduction and a mechanism for exhumation of high-pressure metamorphic rocks:new modelling and field data from Oman. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 143(1-4):173-182. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(96)00123-9 -



 下载:
下载: