Exploration for the Shallow Location of Xinzheng-Taikang Fault via Fault Gas H2
-
摘要: 新郑-太康断裂隐伏于河南省东部平原下,是一条规模较大的北西向断裂带,曾于2010年发生太康4.7级地震,确定该断裂准确的浅层位置对防震减灾具有重要意义。根据深部石油勘探资料,应用德尔格X-am 7000型多气体检测仪,在新郑地区布置2条与断裂走向近垂直的地球化学测线进行土壤氢气浓度测试,结果发现解放路和马庄村-前宫村测线异常点位处氢气浓度分别为背景值的16-33倍和40-50倍。2条H2浓度曲线同步解释出一条倾向变化、宽约150m的走滑断裂带,位置与石油勘探资料吻合良好。此次研究表明利用断层气氢探测隐伏断裂的浅层位置在该区具有较好的可行性。Abstract: The Xinzheng-Taikang Fault, striking NW, as a buried fault beneath the eastern plain, is a large-scale fault which induced the earthquake, ML 4.7 in 2010, Taikang county, causing 12 wounded. Confirming the shallow location of the fault is of great significance to seismic hazards defensing. We launched 2 geochemical survey lines across the fault in the Xinzheng area based on the knowledges from Petroleum exploration data, and the outcomes indicated the concentration of H2 at abnormal points in the Jiefang Road survey line is 16-33 times over the background level, while the times of the Mazhuang-Qiangong survey line is 40-50. The two survey lines indicate similar structures of the fault belt, spanning about 150m, and varied inclination and might be filled with fault-clay so as to influence the migration of the gas. More important, the shallow location of the fault from concentration curve of H2 interpretation fits well with that on deep seismic profiles. The research comes out the conclusion that the distribution of the fault gas, H2 is an efficient indicator of the location of buried faults in similar area.
-
Key words:
- Xinzheng-Taikang fault /
- Geochemical exploration /
- Hydrogen /
- Buried fault /
- Petroleum exploration data
-
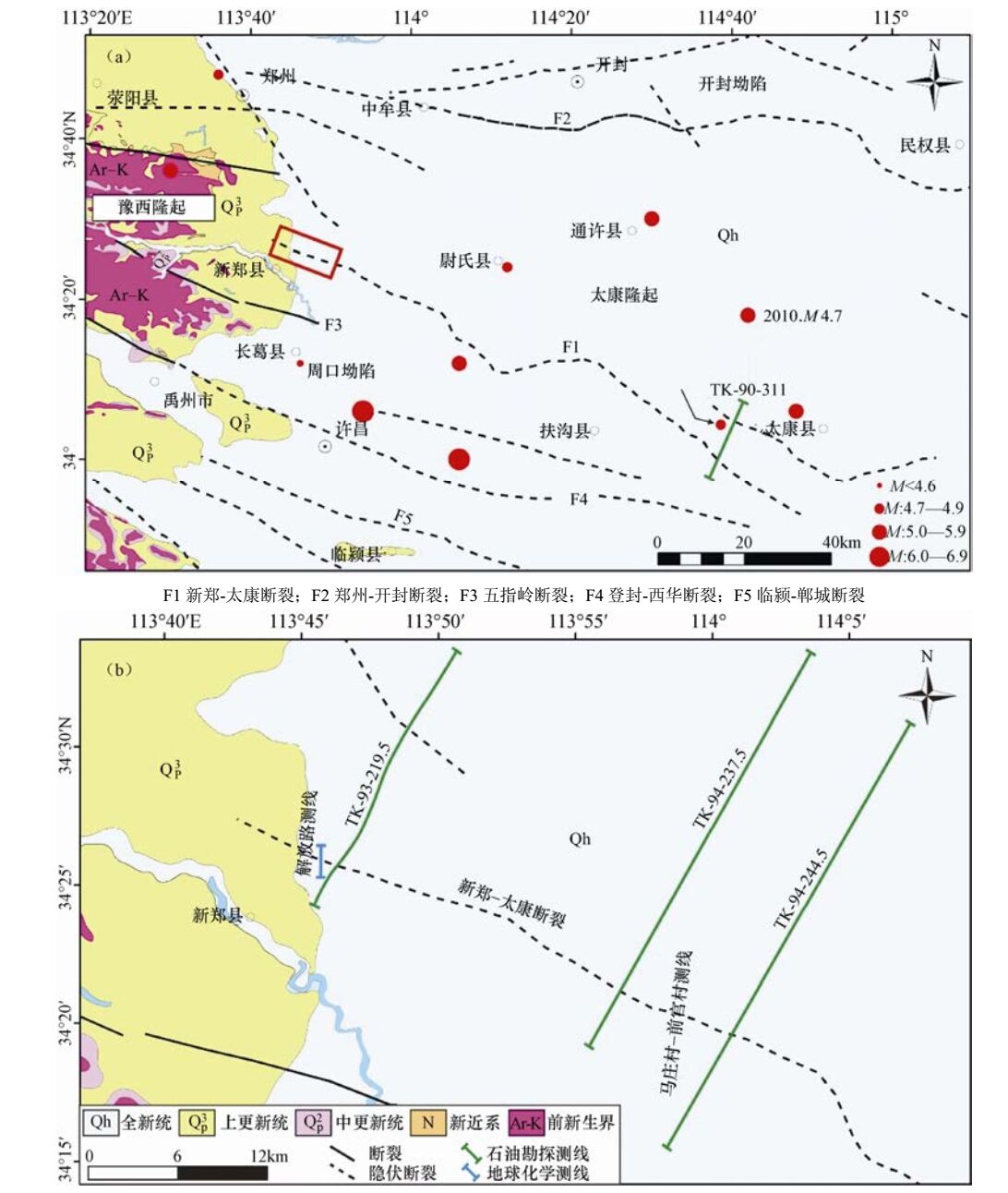
图 2 新郑-太康断裂东段TK-90-311地震偏移剖面(剖面位置见图 1(a))
Figure 2. Seismic profile No.TK-90-311 across the eastern segment of Xinzheng-Taikang fault
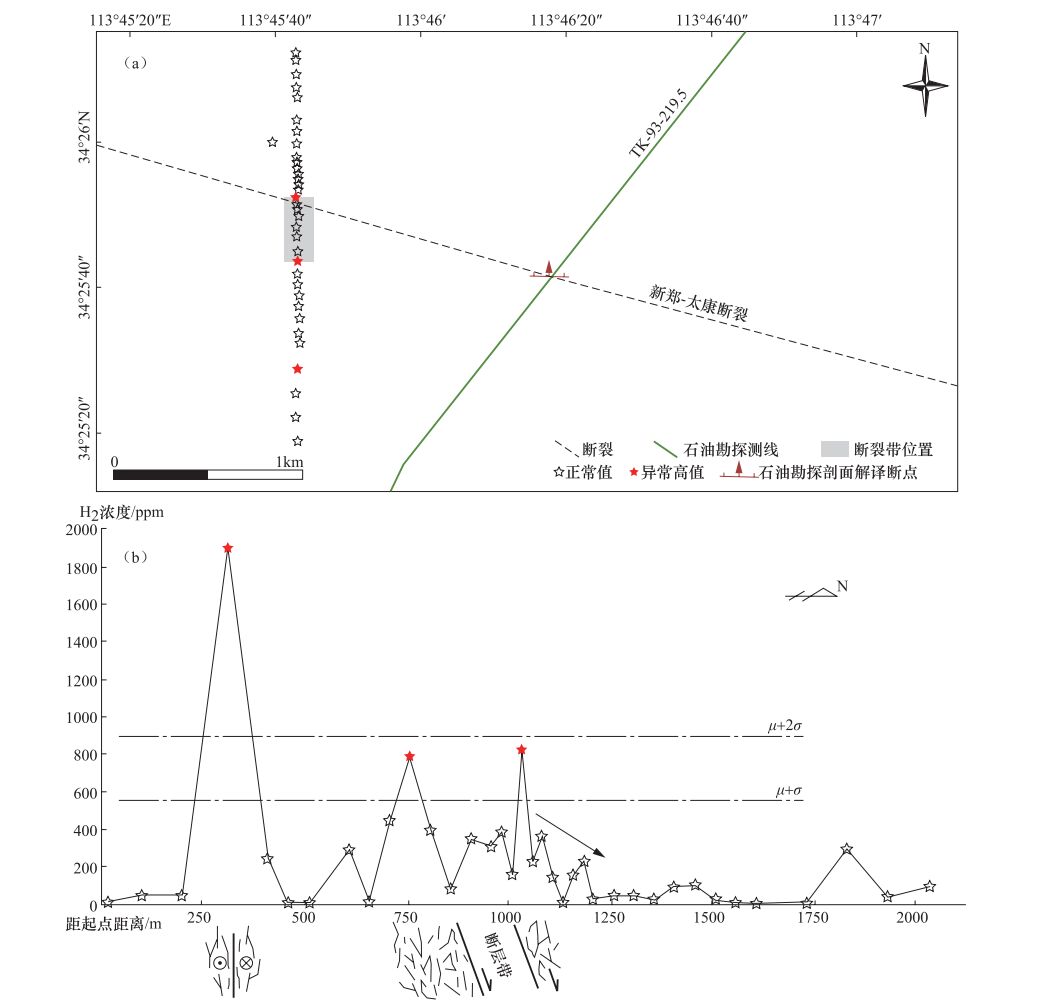
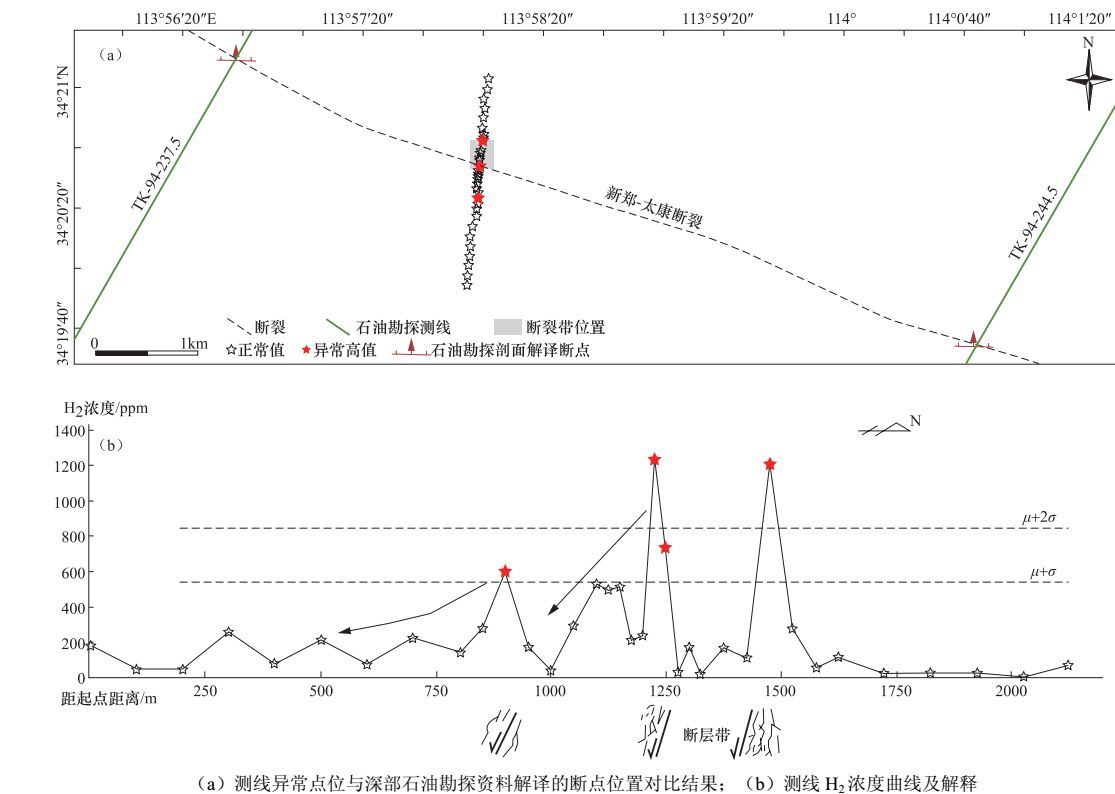
表 1 解放路测线异常点位及类型
Table 1. Location and type of anomalies from the Jiefang road survey line
距测线起始点位置/m H2浓度/ppm 异常类型 断层倾向 310 1901 A 近直立 760 789 B N 1035 814.1 B N 表 2 马庄村-前宫村测线异常点位及类型
Table 2. Location and types of anomalies from the Mazhuang-qiangong survey line
距测线起始点距离/m H2浓度/ppm 异常类型 断层倾向 900 600 B S 1225 1250 A S 1475 1210 A S -
陈刚, 严欣圭, 1995.断层土壤氢气的特征.西北地质, 16(3):22-28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI503.004.htm 冯军, 李红光, 吴涛等, 2011.邢台地区隐伏断裂地球化学探测.震灾防御技术, 6(1):26-35. http://zzfy.eq-j.cn/zzfyjs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20110103&journal_id=zzfyjs 冯希杰, 1988.中国大陆北西-北北西向断裂系统与强震.西安地质学院学报, 10(3):47-55. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX198803005.htm 河南省地质矿产局, 1989.河南省区域地质志.北京:地质出版社. 河南石油勘探指挥部地质大队, 1976. 太康隆起及其周缘古生代地层层序与生储盖组合特征报告. 焦德成, 潘祖寿, 王增光等, 2012.断层气测量用于银川地堑隐伏断裂活动性的研究.防震减灾学报, 28(3):41-47. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DDYJ201203008.htm 李祖武, 1983.中国东部北北西——北西向构造系的基本特征.地震研究, 6(3):339-348. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYJ198303012.htm 刘菁华, 王祝文, 刘树田等, 2006.城市活动断裂带的土壤氡、汞气评价方法.吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 36(2):295-297, 304. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200602024.htm 刘学领, 马建英, 杨绪连等, 2011.断层气探测方法在深隐伏活断层探测中的有效性研究.地震, 31(1):67-74. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZN201101007.htm 孟广魁, 何开明, 班铁等, 1997.氡、汞测量用于断裂活动性和分段的研究.中国地震, 13(1):43-51. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD701.005.htm 漆家福, 肖焕钦, 张卫刚, 2003.东营凹陷主干边界断层(带)构造几何学、运动学特征及成因解释.石油勘探与开发, 30(3):8-12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200303002.htm 燃化部六四六厂研究所, 1972. 周口坳陷研究工作小结. 邵云惠, 1980.试论我国东部的北西向构造及其理论意义.中国地质科学院院报562综合大队分刊, 1(1):19-27. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKD198000004.htm 邵永新, 杨绪连, 李一兵, 2007.海河隐伏活断层探测中土壤气氡和气汞测量及其结果.地震地质, 29(3):627-636. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200703018.htm 石油化工部物探局, 1975. 太康地区及周口地区南部地震勘探成果报告. 宋明春, 张军进, 张丕建等, 2015.胶东三山岛北部海域超大型金矿床的发现及其构造-岩浆背景.地质学报, 89(2):365-383. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201502012.htm 苏鹤军, 张慧, 刘旭宙, 2005.兰州市刘家堡隐伏断层的地球化学探测方法试验.高原地震, 17(1):9-16. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYDZ200501002.htm 孙杰, 胡凤英, 杨龙翔等, 2014. 2010年10月24日周口太康MS 4.6地震的震源机制解.地震地磁观测与研究, 35(3-4):8-14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZGJ2014Z2003.htm 滕吉文, 李松岭, 张永谦等, 2014.秦岭造山带与沉积盆地和结晶基底地震波场及动力学响应.地球物理学报, 57(3):770-788. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-DZDQ201501001043.htm 汪成民, 李宣瑚, 1991.我国断层气测量在地震科学研究中的应用现状.中国地震, 7(2):19-30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD199102002.htm 王志铄, 王明亮, 赵显刚等, 2017.太原隆起南缘新郑-太原断裂的新生代活动形迹与地震活动.地震地质, 39(1):117-129. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201701009.htm 徐杰, 马宗晋, 陈国光等, 2003.中国大陆东部新构造期北西向断裂带的初步探讨.地学前缘, 10(S):193-198. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY2003S1026.htm 姚道平, 卓群, 张艺峰等, 2008.厦门城市隐伏断层控制性地球化学探测.震灾防御技术, 3(4):451-458. http://zzfy.eq-j.cn/zzfyjs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20080415&journal_id=zzfyjs 翟明国, 2011.克拉通化与华北陆块的形成.中国科学:地球科学, 41(8):1037-1046. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201108001.htm 张大其, 1991.利用测汞技术研究隐伏断裂及其活动性.地震学刊, (1):97-100. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXK199101014.htm 张慧, 苏鹤军, 李晨桦, 2013.合作市隐伏断层控制性地球化学探测场地试验.地震工程学报, 35(3):618-624. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ201303036.htm 中国地震局地球物理勘探中心, 2015. 太康县浅层地震勘探报告. 朱日祥, 徐义刚, 朱光等, 2012.华北克拉通破坏.中国科学:地球科学, 42(8):1135-1159. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201404014.htm Annunziatellis A., Beaubien S.E., Bigi S., et al., 2008. Gas migration along fault systems and through the vadose zone in the Latera caldera(central Italy):implications for CO2 geological storage. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2(3):353-372. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2008.02.003 Ciotoli G., Lombardi S., Annunziatellis A., et al., 2007.Geostatistical analysis of soil gas data in a high seismic intermontane basin:Fucino Plain, Central Italy. Journal of Geophysical Research, 112(B5):B05407. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/236845545_Geostatistical_analysis_of_soil_gas_data_in_a_high_seismic_intermontane_basin_Fucino_Plain_central_Italy Giardini A. A., Subbarayudu G. V., Melton C. E., 1976. The emission of occluded gas from rocks as a function of stress:its possible use as a tool for predicting earthquakes. Geophysical Research Letters, 3(6):355-358. doi: 10.1029/GL003i006p00355 Hughes-Schrader S., Schrader F., 1961. The kinetochore of the Hemiptera.Chromosoma, 12(1):327-350. doi: 10.1007/BF00328928 King C.Y., King B.S., Evans W. C., et al., 1996. Spatial radon anomalies on active faults in California. Applied Geochemistry, 11(4):497-510. doi: 10.1016/0883-2927(96)00003-0 Ruff L., Kanamori H., 1980. Seismicity and the subduction process. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 23(3):240-252. doi: 10.1016/0031-9201(80)90117-X Sugisaki R., 1980. Major-element chemistry of argillaceous sediments at Deep Sea Drilling Project Sites 442, 443, and 444, Shikoku Basin. Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project, 58:719-735. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/239528787_23_MAJOR-ELEMENT_CHEMISTRY_OF_ARGILLACEOUS_SEDIMENTS_AT_DEEP_SEA_DRILLING_PROJECT_SITES_442_443_AND_444_SHIKOKU_BASIN Sugisaki R., Ido M., Takeda H., et al, 1983. Origin of hydrogen and carbon dioxide in fault gases and its relation to fault activity. The Journal of Geology, 91(3):239-258. doi: 10.1086/628769 Wakita H., Nakamura Y., Kita I., et al, 1980. Hydrogen release:new indicator of fault activity. Science, 210(4466):188-190. doi: 10.1126/science.210.4466.188 Ware R. H., Roecken C., Wyss M., 1984. The detection and interpretation of hydrogen in fault gases. Pureand Applied Geophysics, 122(2-4):392-402. doi: 10.1007%2FBF00874607.pdf -



 下载:
下载: