Application of Double-difference Relocation Method Combined with Waveforms Cross-correlation on Earthquakes in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area
-
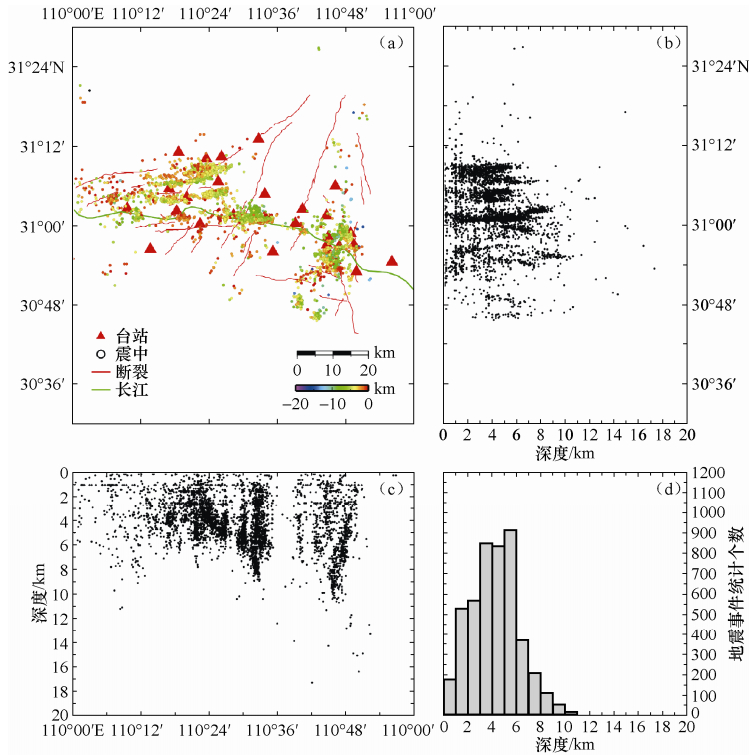
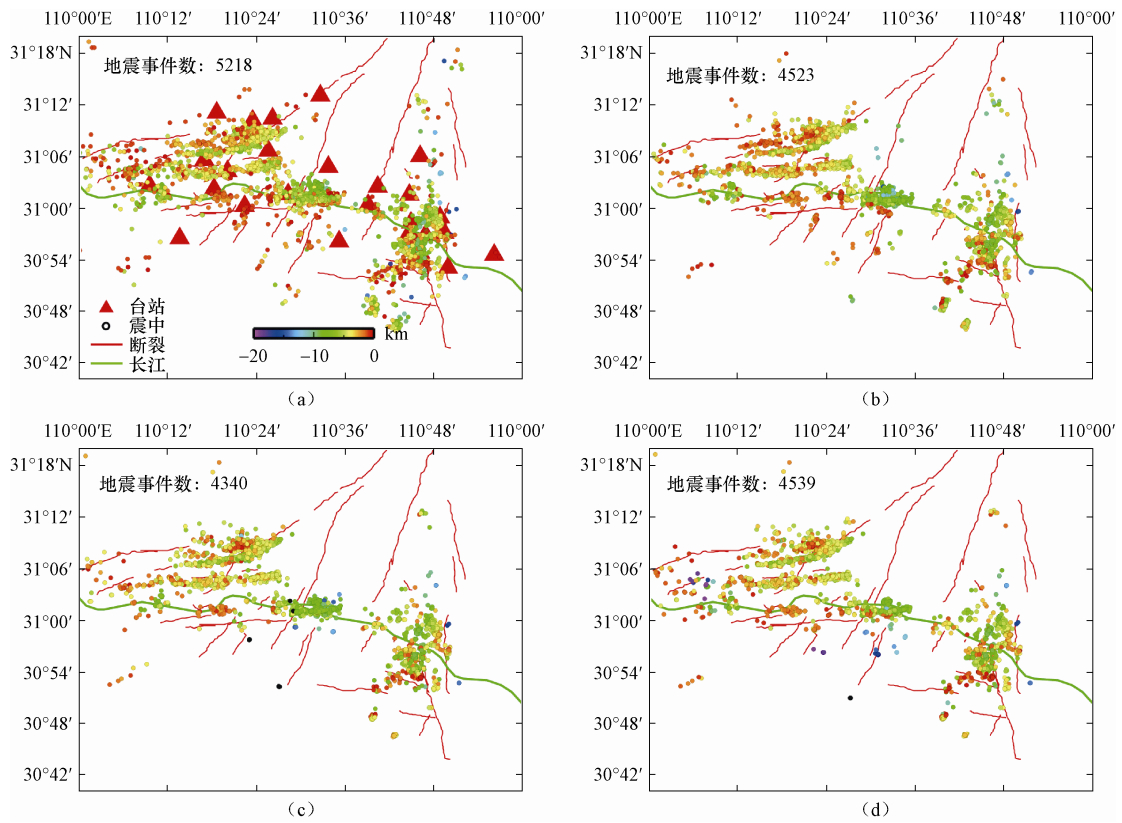
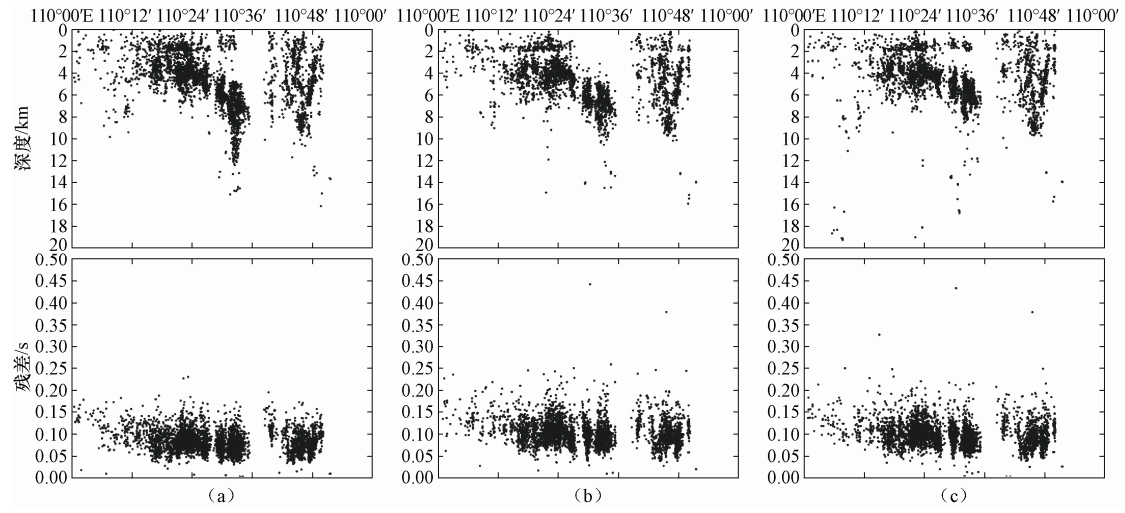
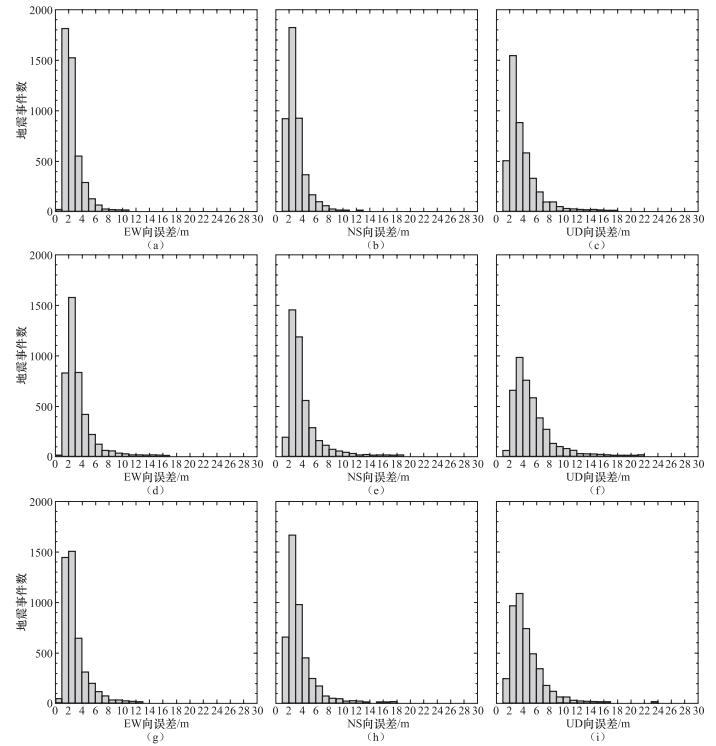
摘要: 本文采用基于波形互相关算法的双差定位方法对三峡水库地震进行精定位和地震活动性分析。首先使用双谱互相关方法分析了三峡库区加密台网于2009年3月至2010年12月观测到的地震波形数据,并对波形互相关分析的结果进行了评价。基于结合获得的波形互相关数据使用双差定位方法对地震事件进行精定位研究,结果表明使用双谱法验证的波形互相关数据的定位精度要高于其他数据的结果,其东西向震源位置平均误差为3.2m、南北向为3.9m、垂直向为6.2m。重定位震中结果显示巴东神龙溪两岸微震分布明显呈现出3条近东西向的线性条带状,与地表小规模断裂和碳酸盐岩地层走向一致,揭示了库水主要沿着溶洞或者地下暗河渗透进而诱发地震活动,较强地震可能是微小地震贯穿活动面的结果。Abstract: In this paper, we applied the double difference location method based on waveform cross-correlation algorithm for earthquake precision positioning of the Three Gorges Reservoir (TGR). First we used bispectrum cross-correlation method to analyze the seismic waveform data of TGR encrypted networks in March 2009 to December 2010, and evaluate the quality of waveform cross-correlation analysis. Combining the waveform cross-correlation of data obtained, we used the double difference method to relocate the position of quakes. The results show that the location by using bispectrum verified waveform cross-correlation data is higher than other type of data, and the mean 2sig-errors in EW, NS and UD are 3.2m, 3.9m and 6.2m, respectively. The results also show that the Badong and Shenlong River quake in reservoir distribution is characterized by linear distribution of three nearly east-west, which is in accordance with the small faults and carbonate strata line of new tectonic period, revealing reservoir water main along the underground river or cave penetration induced seismic activity. A strong earthquake may be the result of a small earthquakes that broken through the active plane.
-
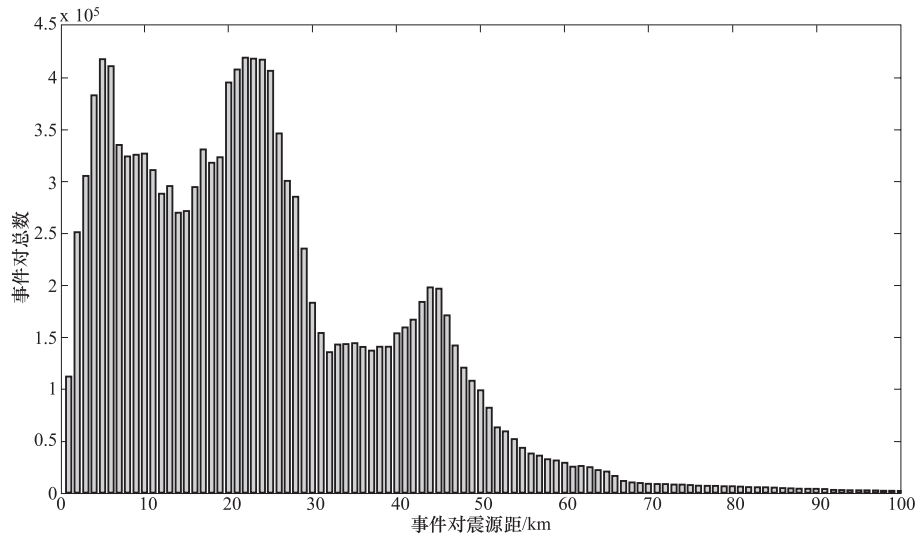
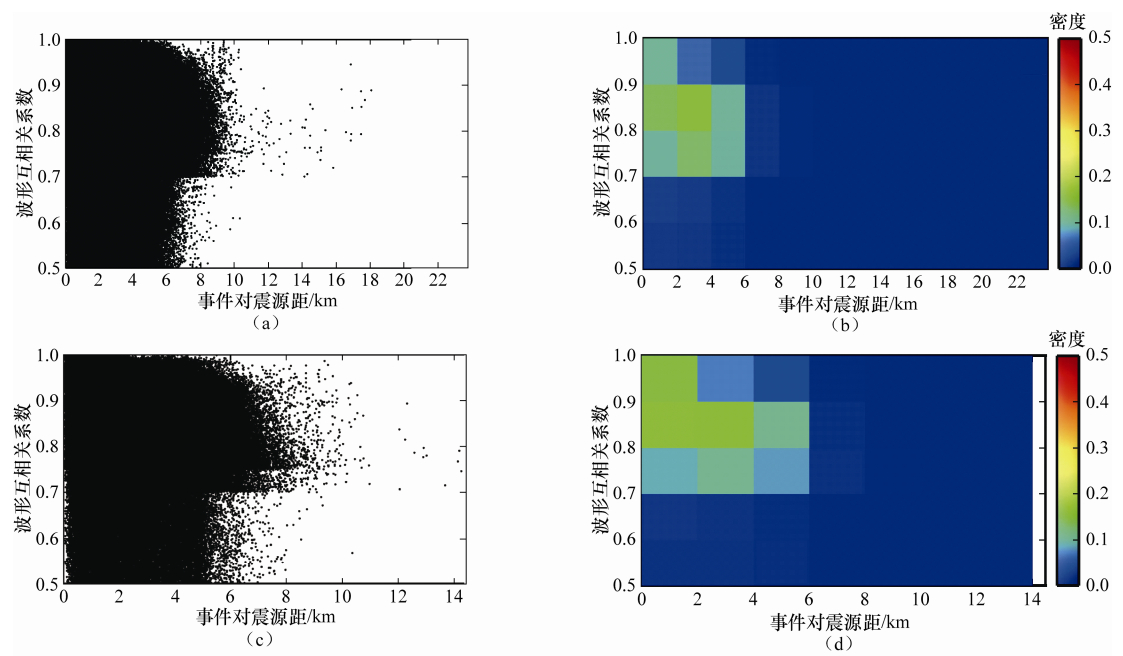
图 3 三峡库区2种互相关系数评估柱状统计图
(a)P波传统互相分析结果统计图,纵坐标括号内数值为互相关记录条数,互相关系数统计间隔为0.01;(b)P波双谱验证互相关分析结果统计图,纵坐标括号内的第一个数值为互相关系数大于0.7的记录个数,第二个为总记录个数,3条竖线表示了CClim (l)=0.5,CClim=0.7,CClim (u)=0.9;(c)S波传统互相关分析结果统计,其余同图(a);(d)S波双谱验证互相关分析结果统计图,其余同图(b)
Figure 3. Histogram of two kinds of cross-correlation coefficients in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area
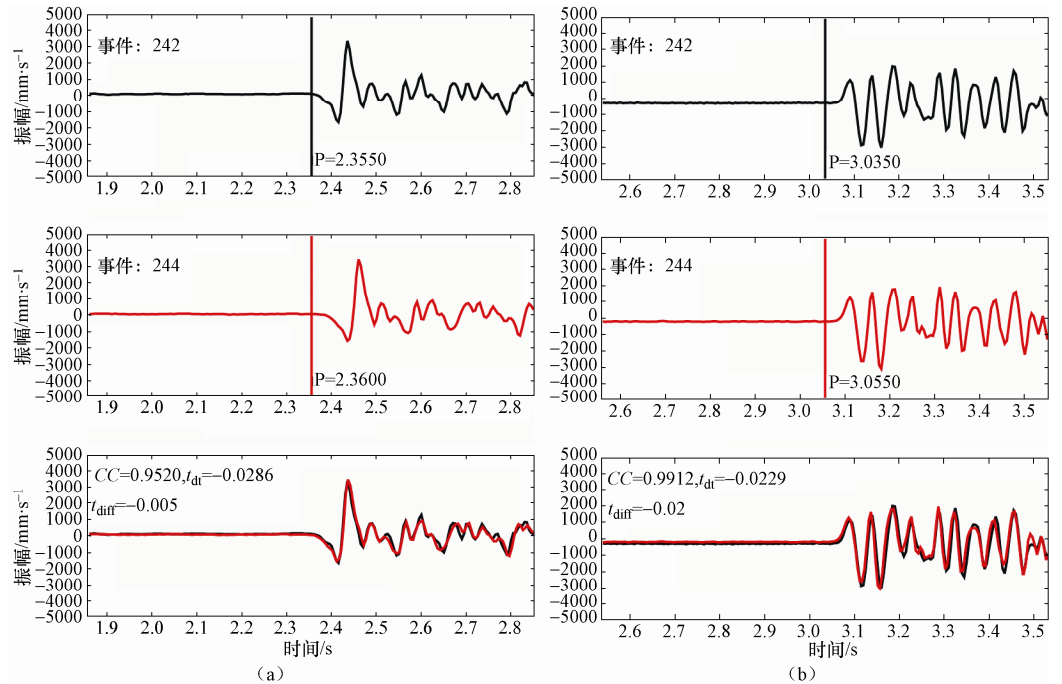
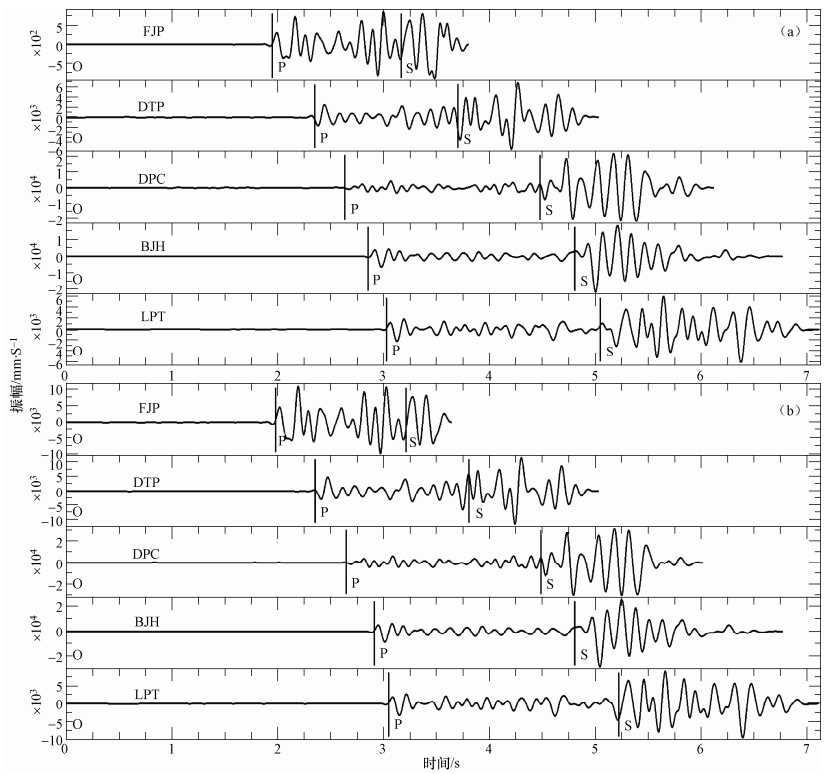
事件对242;244 2009-03-25 22:16:21.3 ML1.3;2009-03-25 22:17:17.3 ML 1.5 台站 互相关延时/s 互相关系数 震相 台站 互相关延时/s 互相关系数 震相 BJH -0.033 0.9852 P JJP -0.035 0.986 P CJP -0.03 0.9733 P LPT -0.023 0.9912 P DJW -0.016 0.9848 P BJH -0.04 0.9876 S DPC -0.015 0.9813 P CJP -0.039 0.9635 S DTP -0.029 0.952 P DJW -0.009 0.9976 S FJP -0.027 0.9887 P GJY -0.04 0.9719 S GJY -0.033 0.984 P LPT -0.015 0.9132 S -
黄媛, 2008.结合波形互相关技术的双差算法在地震定位中的应用探讨.国际地震动态, (4):29-34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJZT200804005.htm 黄媛, 杨建思, 张天中, 2006.2003年新疆巴楚-伽师地震序列的双差法重新定位研究.地球物理学报, 49(1):162-169. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200601022.htm 李强, 赵旭, 蔡晋安等, 2009.三峡水库坝址及邻区中上地壳P波速度结构.中国科学D辑:地球科学, 39(4):427-436. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200904005.htm 蔺永, 马文涛, 2014.基于Matlab的三峡水库地震数据处理与分析.震灾防御技术, 9(3):447-453. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20140311 马文涛, 徐长朋, 李海鸥等, 2010.长江三峡水库诱发地震加密观测及地震成因初步分析.地震地质, 32(4):552-563. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201004004.htm 王清东, 朱良保, 苏有锦等, 2015.2012年9月7日彝良地震及余震序列双差定位研究.地球物理学报, 58(9):3205-3221. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150916 张广伟, 雷建设, 2015.2011年云南腾冲5.2级双震发震机理.地球物理学报, 58(4):1194-1204. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150409 赵翠萍, 2006.1997-2003年新疆伽师震源区特征的地震学方法研究.北京:中国地震局地球物理研究所. 赵旭, 李强, 蔡晋安, 2007.三峡库首区最小一维速度模型研究.大地测量与地球动力学, 27(专刊):1-7. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB2007S1000.htm Bannister S., Fry B., Reyners M., et al., 2011. Fine-scale Relocation of Aftershocks of the 22 February MW6.2 Christchurch Earthquake using Double-difference Tomography. Seismological Research Letters, 82(6):839-845. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Stephen_Bannister/publication/234114637_Fine-scale_Relocation_of_Aftershocks_of_the_22_February_M-w_62_Christchurch_Earthquake_Using_Double-difference_Tomography/links/0912f50f50b07d1b1e000000/Fine-scale-Relocation-of-Aftershocks-of-the-22-February-M-w-62-Christchurch-Earthquake-Using-Double-difference-Tomography.pdf Bourguignon S., Bannister S., Henderson C. M., et al., 2015. Structural heterogeneity of the midcrust adjacent to the central Alpine Fault, New Zealand:Inferences from seismic tomography and seismicity between Harihari and Ross. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 16(4):1017-1043. doi: 10.1002/2014GC005702 Du W. X., Thurber C. H., Eberhart-Phillips D., 2004. Earthquake relocation using cross-correlation time delay estimates verified with the bispectrum method. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 94(3):856-866. doi: 10.1785/0120030084 Hansen S. E., DeShon H. R., Moore-Driskell M. M., et al., 2013. Investigating the P wave velocity structure beneath Harrat Lunayyir, northwestern Saudi Arabia, using double-difference tomography and earthquakes from the 2009 seismic swarm. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 118(9):4814-4826. doi: 10.1002/jgrb.50286 Poupinet G., Ellsworth W., Frechet J., 1984. Monitoring velocity variations in the crust using earthquake doublets:An application to the Calaveras Fault, California. Journal of Geophysical Research, 89(B7):5719-5731. doi: 10.1029/JB089iB07p05719 Schaff D. P., Bokelmann G. H. R., Ellsworth W. L., et al., 2004. Optimizing correlation techniques for improved earthquake location. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 94(2):705-721. doi: 10.1785/0120020238 Schaff D. P., Waldhauser F., 2005. Waveform cross-correlation-based differential travel-time measurements at the Northern California Seismic Network. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 95(6):2446-2461. doi: 10.1785/0120040221 Waldhauser F., Ellsworth W. L., 2000. A double-difference earthquake location algorithm:Method and application to the northern Hayward fault, California. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 90(6):1353-1368. doi: 10.1785/0120000006 Wessel P., Smith W. H. F., 1995. New version of the generic mapping tools. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 76(33):329. https://www.soest.hawaii.edu/gmt/gmt/pdf/GMT_Tutorial.pdf -



 下载:
下载: