Discussion of Relationship between the Wenchuan Earthquake and Lushan Earthquake from the Viewpoint of Coulomb Failure Stress Change and Spatial Distribution of Aftershocks
-
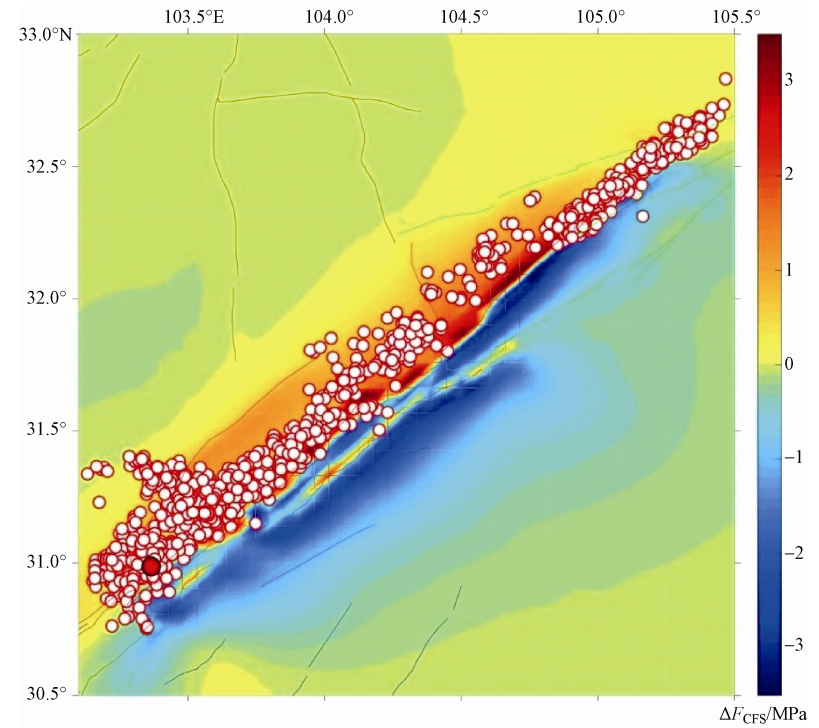
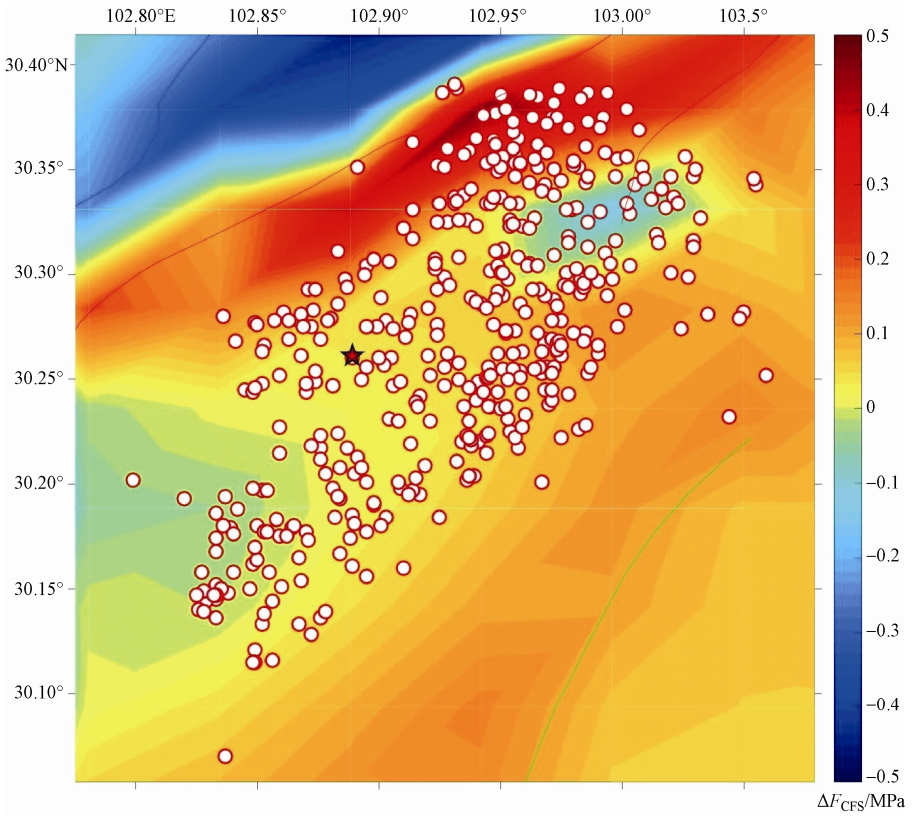
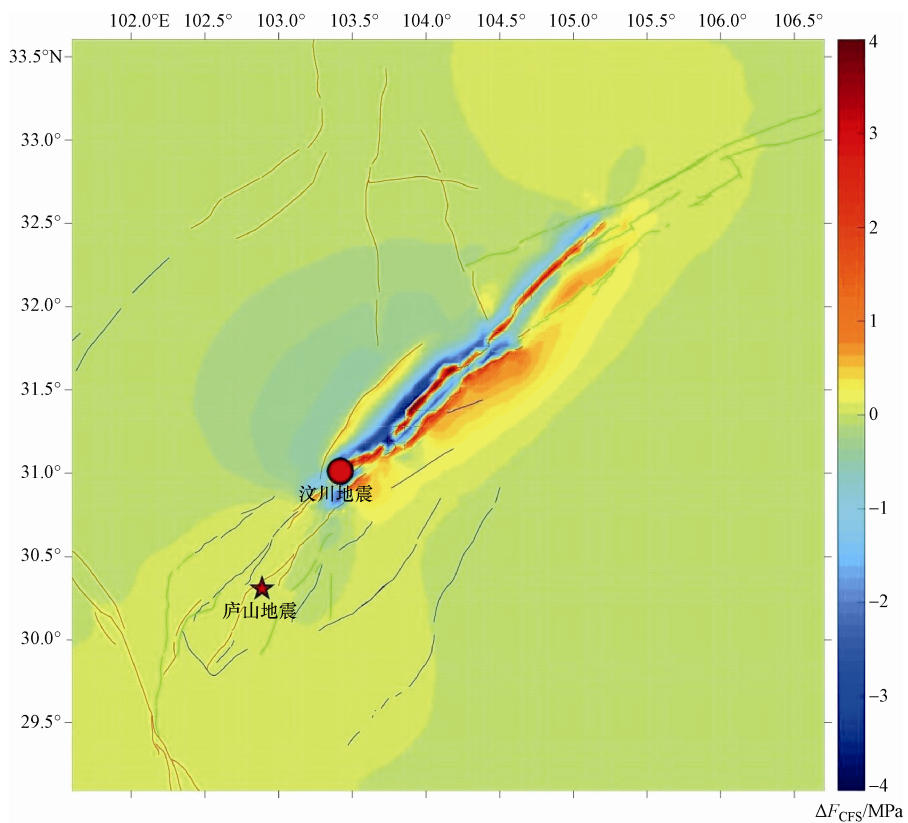
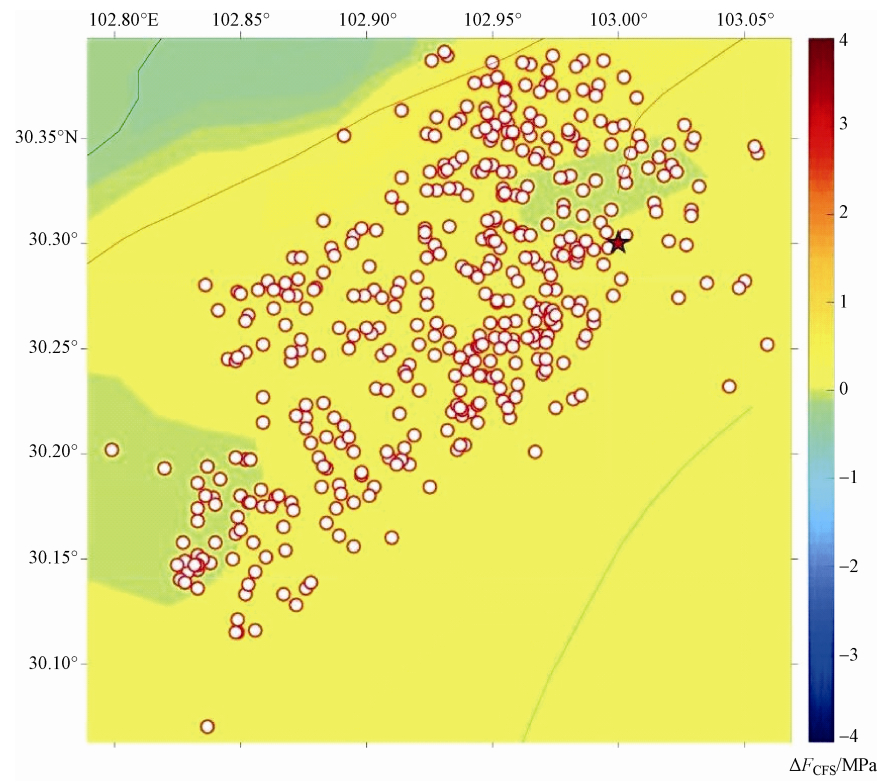
摘要: 本文以龙门山及周边地区为研究对象,考虑区域地质构造差异、主要活动断裂带、地表附加重力影响,建立能反映地表起伏和岩石圈分层结构的龙门山地区三维粘弹性有限元模型。以地壳水平运动速率观测值为约束条件重建研究区现今构造背景应力场,在此基础上分别模拟了汶川地震和芦山地震的发生机理。通过分析同震库仑破裂应力变化与余震空间分布的关系,探讨了2次地震主震对余震的触发作用以及汶川地震对芦山地震的影响。研究表明,汶川地震和芦山地震的余震大部分由其主震触发,汶川地震对芦山地震的余震有约6.78%的触发作用。汶川地震的同震库仑破裂应力在芦山地震主震位置的增加值约为0.016MPa,如果龙门山断裂带南段库仑破裂应力年累积速率按照0.4×10-3-0.6×10-3MPa·a-1计算,汶川地震使芦山地震提前了约27-40年。计算还表明汶川地震和芦山地震的发生使鲜水河断裂带南段和虎牙断裂的库仑破裂应力增加,这些断裂带在未来发生地震的可能性增加。Abstract: Taking the Longmenshan and its surrounding area as the research area, with consideration of the difference of regional geological structure, the main active fault zone, additional surface gravity, we constructed the 3-D viscoelastic finite element model of the Longmenshan area with irregular topography and the layered lithosphere structure. Using the observed values of crustal horizontal movement as constraint condition, the present tectonic background stress field in the research area is reconstructed. Based on it, the occurrence of Wenchuan earthquake and Lushan earthquake are simulated respectively. Through the analysis the relationship between coseismic Coulomb stress change and the spatial distribution of aftershocks, the trigger action of main shock to aftershock and the influence of Wenchuan earthquake on Lushan earthquake is investigated. The results show that the most aftershocks of Wenchuan earthquake and Lushan earthquake are triggered by their main shock, and only 6.78% aftershock of Lushan earthquake is triggered by Wenchuan earthquake. The coseismic Coulomb stress of the location of Lushan earthquake caused by Wenchuan earthquake is about 0.016MPa. Assuming tha the annual cumulative rate of Coulomb stress in the southern segment of the Longmenshan fault zone is 0.4-0.6×10-3MPa·a-1, the occurrence of Wenchuan earthquake causes the occurrence of Lushan earthquake nearly 27-40 years earlier than it should. Our results also show that the Wenchuan earthquake and Lushan earthquake cause the Coulomb stress increase in the southern segment of the Xianshuihe fault zone and Huya fault, which increases the possibility of earthquake in this area in the future.
-
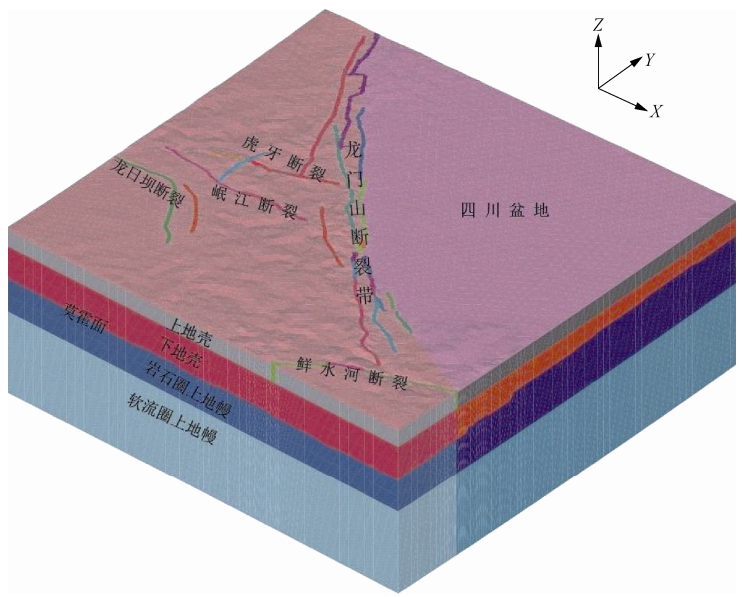
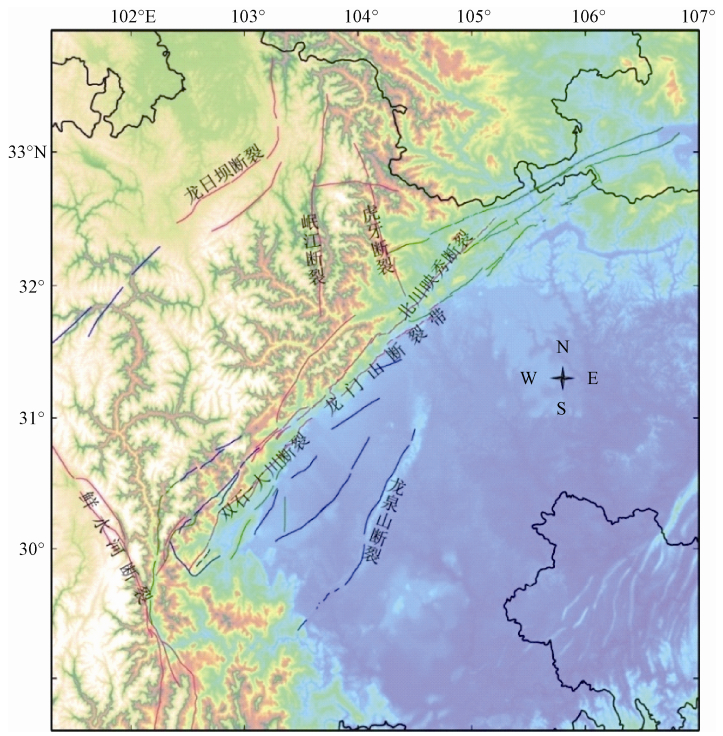
图 1 研究区域 (根据邓起东等,2011)
Figure 1. Research area of this study (after Deng et al., 2011)
表 1 研究区介质分层材料参数
Table 1. Material parameters of the layered medium in the research area
分层 深度/km 四川盆地 青藏高原东缘 E/1010·Pa υ η/1022·Pa·s E/1010·Pa υ η/1022·Pa·s 地表 0-0.5 3.75 0.21 0.8 3.75 0.21 0.8 上地壳 0.5-20 7.2 0.246 9.96 7.39 0.25 10.3 下地壳 20-Moho面 12.5 0.253 0.925 11.9 0.254 2.02 岩石圈 Moho面-100 17.5 0.265 0.05 17.50 0.265 0.05 软流圈 100-200 17.5 0.265 0.5 17.50 0.265 0.5 表 2 汶川地震和芦山地震参数
Table 2. Earthquake parameters of the Wenchuan earthquake and Lushan earthquake
事件 经度 纬度 走向 倾角 滑动角 最大水平滑动量/m 破裂长度/km 数据来源 汶川 103.4°E 31.0°N 231° 35° 138° 4.9 > 300 中国地震台网中心;Global CMT;徐锡伟等,2008 芦山 102.89°E 30.31°N 212° 44° 92° 1.3 46.7 USGS;曾祥方等,2013;徐锡伟,2013;张勇等,2013 表 3 研究区内主要活动断层参数及汶川地震和芦山地震共同引起的库仑破裂应力变化
Table 3. Parameters of the main active faults in research area and the Coulomb stress change caused by the Wenchuan earthquake and Lushan earthquake
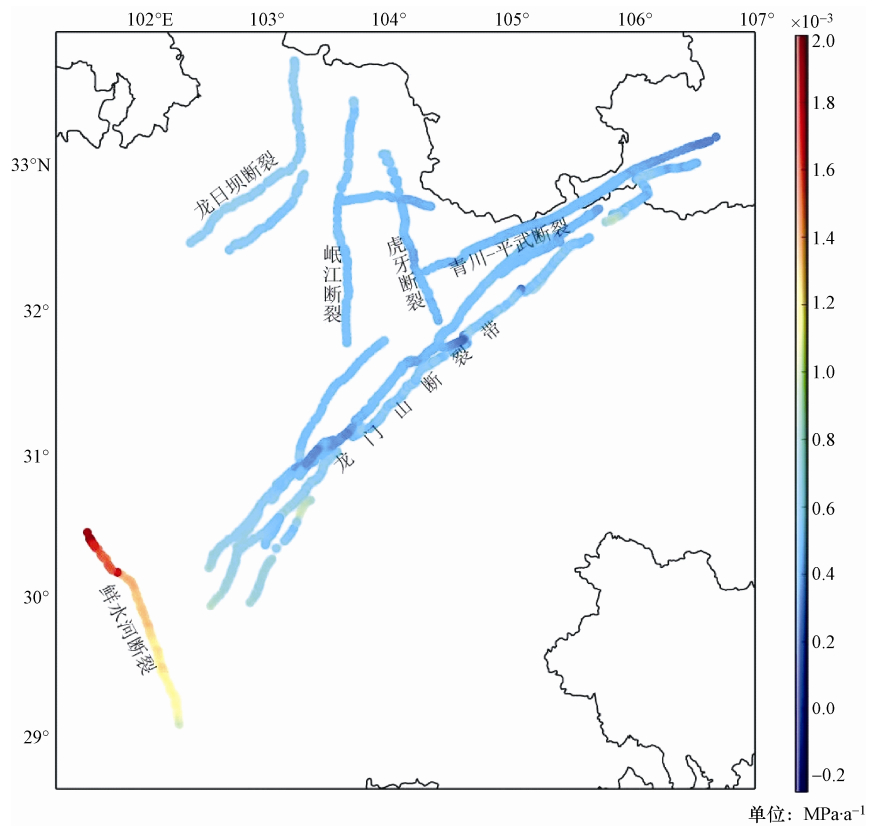
断裂名称 走向/° 倾角/° 滑动角/° 库仑破裂应力变化/MPa 龙门山断裂带东北段 225 60 180 -4.2-3.2 龙门山断裂带南段 220 60 90 -2-1.8 鲜水河断裂带南段 142-159.5 90 0-45 0.005-0.15 龙日坝断裂 205-229 60 135 -0.067-0 岷江断裂 180 45-60 45-70 -2.96-0 虎牙断裂 150 75 45 0~0.08 -
曹建玲, 石耀霖, 张怀, 王辉, 2009.青藏高原GPS位移绕喜马拉雅东构造结顺时针旋转成因的数值模拟.科学通报, 54(2):224-234. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200902017.htm 陈立春, 冉勇康, 王虎等, 2013.芦山地震与龙门山断裂带南段活动性.科学通报, 58(20):1925-1932. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201320007.htm 陈连旺, 陆远忠, 刘杰等, 2001.1966年邢台地震引起的华北地区应力场动态演化过程的三维粘弹性模拟.地震学报, 23(5):480-491. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXB200105003.htm 陈连旺, 张培震, 陆远忠等, 2008.川滇地区强震序列库仑破裂应力加卸载效应的数值模拟.地球物理学报, 51(5):1411-1421. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200805015.htm 陈运泰, 杨智娴, 张勇, 刘超, 2013.从汶川地震到芦山地震.中国科学:地球科学, 43(6):1064-1072. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSCD201701022.htm 董培育, 程惠红, 曾祥方, 石耀霖, 2013.四川芦山MS 7.0级地震导致周边断层的应力变化.科技导报 (北京), 31(12):19-22. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=kjdb201312015&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 邓起东, 陈社发, 赵小麟, 1994.龙门山及其邻区的构造和地震活动及动力学.地震地质, 16(4):389-403. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ404.013.htm 邓起东, 陈桂华, 朱艾斓, 2011.关于2008年汶川MS 8.0地震震源断裂破裂机制几个问题的讨论.中国科学:地球科学, 41(11):1559-1576. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jdxk201111002&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 房立华, 吴建平, 王未来等, 2013.四川芦山MS 7.0级地震及其余震序列重定位.科学通报, 58(20):901-1909. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=kxtb201320004&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 李传友, 宋方敏, 冉勇康, 2004.龙门山断裂带北段晚第四纪活动性讨论.地震地质, 26(2):248-258. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200402006.htm 李玉江, 陈连旺, 陆远忠, 詹自敏, 2013a.汶川地震的发生对周围断层稳定性影响的数值模拟.地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 38(2):398-410. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201302023.htm 李玉江, 陈连旺, 杨树新, 2013b.基于应变能变化的芦山强震同震效应的数值模拟.震灾防御技术, 8(4):361-369. http://zzfy.eq-j.cn/zzfyjs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20130403&journal_id=zzfyjs 李玉江, 陈连旺, 刘少峰, 杨树新, 荆燕, 2014.芦山地震的发生对周围断层影响的数值模拟.地球学报, 35(5):627-634. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2014.05.13 刘杰, 易桂喜, 张致伟等, 2013.2013年4月20日四川芦山M 7.0级地震介绍.地球物理学报, 56(4):1404-1407. doi: 10.6038/cjg20130434 缪淼, 朱守彪, 2013.2013年芦山MS7.0地震产生的静态库仑应力变化及其对余震空间分布的影响.地震学报, 35(5):619-631. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDW201310008003.htm 单斌, 熊熊, 郑勇, 刁法启, 2009.2008年5月12日MW7.9汶川地震导致的周边断层应力变化.中国科学 (D辑), 39(5):537-545. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jdxk200905001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 单斌, 熊熊, 郑勇等, 2013.2013年芦山地震导致的周边断层应力变化及其与2008年汶川地震的关系.中国科学:地球科学, 43(6):1002-1009. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201306008.htm 邵志刚, 周龙泉, 蒋长胜, 马宏生, 张浪平, 2010.2008年汶川MS 8.0地震对周边断层地震活动的影响.地球物理学报, 53(8):1784-1795. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dqwx201008005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 石耀霖, 曹建玲, 2008.中国大陆岩石圈等效粘滞系数的计算和讨论.地学前缘, 15(3):82-95. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200803006.htm 史翔, 冉勇康, 陈立春, 王虎, 刘瑞春, 2009.龙门山中央断裂北川-邓家一带古地震初步研究.第四纪研究, 29(3):494-501. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200903010.htm 万永革, 吴忠良, 周公威等, 2000.几次复杂地震中不同破裂事件之间的"应力触发"问题.地震学报, 22(6):568-576. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXB200006001.htm 万永革, 沈正康, 盛书中, 徐晓枫, 2009.2008年汶川大地震对周围断层的影响.地震学报, 31(2):128-139. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXB200902002.htm 王椿镛, 楼海, 吕智勇等, 2008.青藏高原东部地壳上地幔S波速度结构——下地壳流的深部环.中国科学 (D辑), 38(1):22-32. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200801003.htm 王辉, 刘杰, 石耀霖, 张怀, 张国民, 2008.鲜水河断裂带强震相互作用的动力学模拟研究.中国科学 (D辑), 38(7):808-818. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200807003.htm 王敏中, 王炜, 武际可, 2011.弹性力学教程.北京:北京大学出版社. 吴建平, 明跃红, 王椿镛, 2006.川滇地区速度结构的区域地震波形反演研究.地球物理学报, 49(5):1369-1376. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200605015.htm 徐晶, 邵志刚, 马宏生, 张浪平, 2013.鲜水河断裂带库仑应力演化与强震间关系.地球物理学报, 56(4):1146-1158. doi: 10.6038/cjg20130410 徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 叶建青等, 2008.汶川MS 8.0地震地表破裂带及其发震构造.地震地质, 30(3):597-629. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzdz200803003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 徐锡伟, 陈桂华, 于贵华等, 2013a.芦山地震发震构造及其与汶川地震关系讨论.地学前缘, 20(3):11-20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201303002.htm 徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 韩竹军等, 2013b.四川芦山7.0级强震:一次典型的盲逆断层型地震.科学通报, 58(20):1887-1893. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201320002.htm 许冲, 徐锡伟, 2014.2013年芦山地震滑坡空间分布样式对盲逆断层构造的反映.科学通报, 59(11):979-986. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201411005.htm 杨强, 党亚民, 2010.利用GPS速度场估算青藏高原地壳韧性层等效粘滞系数分布的研究.测绘学报, 39(5):497-502. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHXB201005012.htm 杨兴悦, 陈连旺, 杨立明, 李玉江, 谭佩, 2013.巴颜喀拉块体强震动力学过程数值模拟.地震学报, 35(3):304-314. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-85403-1013107357.htm 张培震, 徐锡伟, 闻学泽等, 2008.2008年汶川8.0级地震发震断裂的滑动速率、复发周期和构造成因.地球物理学报, 51(4):1066-1073. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200804017.htm 周光泉, 刘孝敏, 1996.粘弹性理论.合肥:中国科学技术大学出版社. Freed A. M., 2005. Earthquake triggering by static, dynamic, and postseismic stress transfer. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 33:335-367. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.33.092203.122505 Harris R. A., 1998. Introduction to special section:Stress triggers, stress shadows, and implications for seismic hazard. Journal of Geophysical Research, 103(B10):24347-24358. doi: 10.1029/98JB01576 Jia K., Zhou S. Y., Zhuang J. C., et al., 2014. Possibility of the independence between the 2013 Lushan earthquake and the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake on Longmen Shan fault, Sichuan, China. Seismological Research Letters, 85(1):60-67. doi: 10.1785/0220130115 Liu M., Luo G., Wang H., 2014. The 2013 Lushan earthquake in China tests hazard assessments. Seismological Research Letters, 85(1):40-43. doi: 10.1785/0220130117 Luo G., Liu M., 2010. Stress evolution and fault interactions before and after the 2008 Great Wenchuan earthquake. Tectonophysics, 491:127-140. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2009.12.019 Parsons T., Ji C., Kirby E., 2008. Stress changes from the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake and increased hazard in the Sichuan basin. Nature, 454(7203):509-510. doi: 10.1038/nature07177 Ran K. Y., Chen W. S., Xu X. W., et al., 2013. Paleoseismic events and recurrence interval along the Beichuan-Yingxiu fault of Longmenshan fault zone, Yingxiu, Sichuan, China. Tectonophysics, 584:81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.07.013 Toda S., Lin J., Meghraousi M., et al. 2008. 12 May 2008 M=7.9 Wenchuan, China, earthquake calculated to increase failure stress and seismicity rate on three major fault systems. Geophysical Research Letters, 35(17). https://darchive.mblwhoilibrary.org/bitstream/handle/1912/3372/2008GL034903.pdf;sequence=1 Wang Y. Z., Wang F., Wang M., et al., 2014. Coulomb stress change and evolution induced by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake and its delayed triggering of the 2013 MW6.6 Lushan earthquake. Seismological Research Letters, 85(1):52-59. doi: 10.1785/0220130111 Wells D. L., Coppersmith K. J., 1994. New empirical relationships among magnitude, rupture length, rupture width, rupture area, and surface displacement. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 84(4):974-1002. http://www.academia.edu/1151208/New_Empirical_Relationships_among_Magnitude_Rupture_Length_Rupture_Width_Rupture_Area_and_Surface_Displacement -



 下载:
下载: